MIC 205 Exam #4: Chapter 17. Immunization and Vaccinations
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
What are the 4 types of acquired immunity
1.) Natural Acquired Active Immunity
2.) Natural Acquired Passive Immunity
3.) Artificial Acquired Active Immunity
4.) Artificial Acquired Passive Immunity
Naturally Acquired Active Immunity (basic definition)
Antigens enter the body naturally: body produces antibodies and specialized lymphocytes
Naturally Acquired Passive Immunity (basic definition)
Antibodies pass from mother to fetus via placenta or to infant in the mother’s milk
Artificially Acquired Active Immunity (basic definition)
Antigens are introduced in vaccines; body produces antibodies and specialized lymphocytes
Artificially Acquired Passive Immunity ( basic definition)
Preformed antibodies in immune serum introduced into body by injection
How is Naturally Acquired Active Immunity developed?
This immunity develops after antigens ( e.g. microbial pathogens) enter the body by natural process such as infection and, in resposne, the body’s immune system forms antibodies and memory cells
Length of Naturally Acquired Immunity varies
Lifetime ( e.g: smallpox, measles, chickenpox, yellow fever)
A few years ( dipheria, tetanus)
A less period ( influenza, penumonia)
How does Naturally Acquired Passive Immunity occur?
When antibodies are produced in the body of an individual (mother) are naturally transferred into the body of other individuals ( child)
The child develops immunity by receiving the antibodies
What class antibodies are transferred from mother to child in naturally acquired passive immunity?
IgA is transferrred from mother to infant via breast milk during nursing
Another name of IgA is maternal antibodies, are they short lived in Naturally Acquired Passive Immunity?
Yes, IgA is short lived, and they will reamin in the child for about three to six months
How does Artifically Acquired Active Immunity work?
When a carefully chosen antigen ( e.g., vaccine, chemically altered or inactivated toxins called toxid) is intentonally introduced into a body to be immunized
Why is Artificially Acquired Active Immunity dubbed “artifical” and “active”
The antigens are intentionally or purposely introduced and it is active becaue the recipient’s immune system synthesizes antibodies.
Vaccines are now avilable against many infectious agents, what are some of these infectious agents
Cholera, Tuberculosis
Plague, pneumonia
rocky mountain spotted fever
smallpox
polio
tetanus
influenza
measles
rabies
Toxoids are currently available for protection against these infectious agents
Diptheria
Tetanus
Boosters help an individul reach what?
Active Immunity
How does Artifically Acquired Passive Immunity Work?
Known as antibody therapy, by the introduction of antibody-rich serum( blood plasma devoid of clotting factors) taken from diseased individual who has recovered and given to a susceptible individual currently with the disease
Today, artifically acquired passive immunity is referred to as these two names?
Monoclonal Therapy
Convalescent Therapy
Some examples of Artifically Acquired Passive Immunity/ antibody therapy
COVID-19
Bamlanivimab
Casirivimab
Sotrovimab
Neutralizing antibodies in artifically acquired passive immunity allow for __
an imediate response from the individual with the disease.
However, antibodies start showing up only after 2-3 weeks
Examples of viral diseases that Artificially Acquired Passive Immunity protects from
Hepatitis B
Chicken Pox
COVID-19
Examples of Bacterial diseases that Artificially Acquired Passive Immunity protects from
Botulism
Dipheria
Tetanus
Staphylococcal Posioning, where toxins are involved in disease caustion
Anti-Serum or Anti-venom is delivered in the form of?
Artificially Acquired Passive Immunity
How does Anti-venom work using snake example ( Artifically Acquired Passive Immunity)
Researcher collects venom from a snake —> Venom of snake is injected into a horse —> Horse neutralizes the antibodies —> Person that got poisoned with snake takes the anti-venom and feels an inmmediate response
Downside: the presence of antibodies appear 2-3 after infection
Very expensive ( thousands of dollars per dose)
Common in Arizona
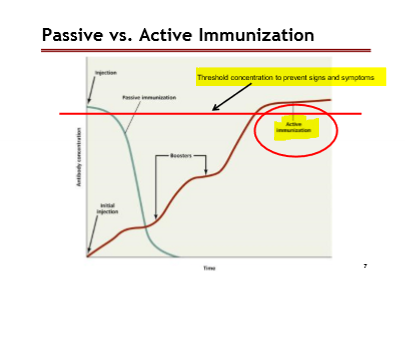
Passive vs. Active Immunization graph: Important Points
Red line: Threshhold concentration to prevent signs and symptoms
Active Immmunization: Starts from the bottom of the graph and goes up
Passive: Dramatically goes down
What are the 4 types of vaccines?
Attenuated (live, weakened)
Killed (inactivated)
Subunity/Toxoid
Vector Based Recombinant
History of Smallpox Vaccine: 1500 AD to Today: Outbreaks have been documented throughout the world
1694: Queen Mary II and Ben Franklin’s son passed away from small pox
1751: London recorded 3,538 deaths from small pox
1776: 50% of Continental Army fell ill due to small pox
1977: Last natural out-break was in Somala
1980: WHO organization declared smallpox eradicated
History of Smallpox Vaccine: 17th century saw the first treaatment regimens for Small Pox, what did this look like
1.) Use of Variolation techniques on Army, royalty, and slaves ( individuals with economic value)
2.) Edward Jenner (1798) documents his uses of variolation and challenges with smallpox
History of Smallpox Vaccine: The U.S Vaccine Agency was established in 1813, its establishment caused what?
Congress required the U.S Post office to carry the smallpox vaccine for free
History of Smallpox Vaccine: What year did many governments require their citizens to get vaccinated against Smallpox?
1874
In 1898, what became the standard method of vaccination for smallpox in the U.K?
Calf Lymph
Is the Small Pox vaccine adminsitered in the U.S?
No, the last time it was adminstered in the U.S was in 1972.
Additioanlly, there is an adverse risk of the small pox virus, and these is no need to distrubute it in the United states ( Choosing between Risk or Safety)
What population is usually infected by HIV?
Sex workers because HIV usually happens in populations that are sexually active ( Nevada or Eastern countries)
HIV vaccines are currently in development and research studies use sex workers for their vaccine development/ research, what happens?
One group receives placebo and other group gets vaccines
Usually a longitudinal study because scientists follow both groups over a long period of time.
Considerations of A Vaccines
Virus Subtypes due to “H” and “N” antigen on the surface of the virus ( find the causiative agent and the epitope that is strongly antigenic)
How many variations of “H” antigens are there?
15
How many variations of “N” antigens are there?
9
“ H” and “N” antigen have parts that vary from strain to strain, what is happening to their epitopes?
Each flu season, the epitopes will be different, and therefore the antibodies from the previous year’s vaccine will not bind
“ H” and “N” antigen have parts that conserved from strain-to-strain, what happening to their epitopes?
Each flu season, these epitopes are similar to the previous year virus, and the antibodies from the previous year’s vaccine should bind
BUT this region does not prevent the binding of the virus to the host cell
Attenuated (Live, Weakneed) Vaccines ( Definition)
Microbes that has been cultivated under ocnditions that disable their VIRULENT properties
What are the 3 methods to design Attentuated vaccines?
1.) Remove virulence genes from vaccine ( this changes the microbe signficantly)'
2.) Use closely-related but less dangerous organsims to produce a broad immune response ( Cowpox will ofer immunity for smallpox)
3.) Microbe has been cultivated under different conditions
More aboout “ Microbe has been cultured under different conditions”
Culturing the microbe in alternative cell lines with closely related receptors
Microbe will “ learn to grow better” nonhuman cell lines
When exposed to humans’ cells, the microbe will slowly replicate, and the immune system will able to build a strong response
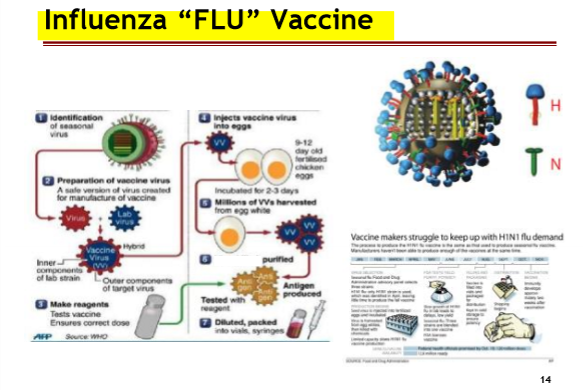
What is an example of Attenuated Vaccine?
The Influenza “Flu” Virus
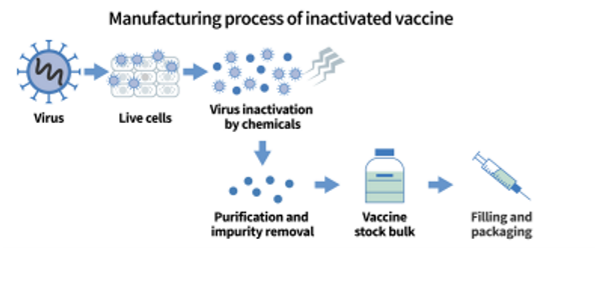
Killed/ Inactivated Vaccines ( Definition)
Contains killed, but previously virulent, microorganisms that has been inactivated by chemicals or heat
In relation to killed vaccines, it it important to not heat the microbe to extreme levels, why is that?
Heat can cause proteins of the microbe to misfold and change shape
In inactivated vaccines, the humoral response will create to a response to multiple epitopes of the microbe, what does that look like?
Humoral response stimules a TH response that promotes antibody-mediated immunity
Are Killed Vaccines safer?
Yes, they are safer because the organism cannot replicate or mutate
Are Killed Vaccines less effective or more effective?
Less effective because the immune response will create only one humoral response unless boosters are given.
Must give multiple does (“boosters”) to acheive “ active immunity”
When receiving a killed vaccine, is one dose sufficient?
No, because the immune system will only produce one humoral response, so booster/ multiple doses are necessary to achieve “active” immunity
Are attenuated vaccines used today?
No, because the risk is greater ( Remember, risk vs safety)
Subunit Vaccines (definition)
Antigenic fragments (protein) of microbe can create an immune response
( usually a small piece of the microbe/ glycoprotein spike)
Subunit vaccines must be able to do what?
Elicit an immune response to protect the individual from signs and symtpoms
Protein subunit of ‘Subunit Vaccines’:
Hepatitis B: composed of the viral envelope protein
Human Papillomavirus ( HPV): composed of the capsid protein
Modified toxins of ‘Subunit Vaccines’
Tetanus, Diphteria, Rattlesnake toxoid (dogs)
Subunit vaccines stimulate what type of immunnity?
Antibody-mediated immunity
Are subunit vaccines safer?
Yes, there is a no-risk of replication
Are subunit vaccines less effective or more effective?
Less effective because they require multiple doses/ boosters
Examples of Subunit Vaccines?
COVID-19 Moderna and Pfizer Vaccines
Vector Based Recombinant Vaccines ( definition)
Genes for antigens of pathogens are inserted into non-pathogen
Non-pathogens are injected into an individual and will express the genes from the pathogen to elicit an immune response
What is an example of a Vector Based Recombinant Vaccines?
Covid-19 Johnson & Johnson Vaccine ( specifically, adenovirus vector vaccine)
For Subunit vaccines, genes for antigens of pathogens are inserted into non pathgen. what is the effect on us?
Our cells do transcription and translation of the genes glycoprotein cell, and our cells produce it over and over again
Con for Subunit vaccines
Only one piece of the protein is used, so a strong antigen must be used for protection
Vaccinia Virus ( cowpox) infection protects a person against lethal smallpox infection. Today, researchers are attempting to clone multiple genes from different pathogens into Vaccinia virus to offer immuntiy to what infectionous agents?
Smallpox
Bacillus Anthracis ( anthrax)
Human papillomavirus (HPV)
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
Herpes Simplex
Vaccinia virus has a uniquely large DNA genome for a virus which makes this genome required to express its genes, why?
Required for encoding various enzymes and proteins
Involved in viral DNA replication and gene transcription
Express Attachment proteins
Researchers need to clone the genes of Vaccinia Virus from other organisms to become antigens for immunity, what is involved in this process?
Molecular Techniques such as PCR, DNA isolation, and using restriction enzymes
Boosters are only effective for the loss of ___
memory cells
What are the two types of Cancer vaccines?
1.) Vaccines that protect an individual from a viral infection that can result in cancer such as HPV or Hepatitis B
2.) Vaccines that treat existing cancer, called treatment vaccines or therapeutic vaccines ( these work to boost the body’s immune system, eleicit a cell mediated response known cancer aantigens)
MUC-1 protein causes
Breast Cancer
HER-2/neu protein cuases
breast, ovarian, bladder, pancreatic, stomach cancer
IGF1R protein causes
Prostate, Breast, Colon Cancer
PDL-1 protein causes
Lung cancer
Sp17 protein causes
Ovarian and Sperm Cancer
Cancer Vaccines ( simplied)
Certain cancers produce unique cancer antigens —> isolate antigens from cancer cell and inject it into person —> creates robust memory response —> if cancer enters body, it has memory cells to deal with the cancer
Methods of Vaccine Administration
1.) Direct Injection
2.) Inhalation or Nasal Spray
3.) Oral
4.0 Subcutaneous
Direct Injection ( Method of Administration)
Direct to the blood stream or intermuscular but will not induce secretory antibodies in mucous membranes ( antigens pass the mucous membranes)
Stimulate immune response in the lymph nodes
Inhalation or Nasal Spray ( Method of Administration)
Fast method, Easy, but tends not to make it to the bloodstream, very little response to lymph nodes
May induce secretory antibodies (IgA) in them ucus membranes
Low penetration of anitgens comapred to direct injection
Oral ( Method of Administration)
must not be deactivated by the low pH of stomach acids and be able to diffuse from the intestines/stomach
may induce secretory antibodies (igA) in the mucus membranes
diffuse through mucus membranes
problem: relies on antigens to penetrate through the mucus membrans
Subcutaneous
Induced just under the skin ( Epidermis)
allows for the microorganism to replicate locally and NOT THROUGHOUT THE BODY
can induce a systemic immune response
Direct Injection of a vaccine will place the antigens in the tissues and elicit an immune response in the lymphatic system, but there is a drawback
Drawback to this method is that it will alow the microbe into the body, and the immune system will start its protection in the lymphatic system
Inhalation and Oral vaccines will place antigens in the mucus membrane, the following things happen
elicit a localized response by M-cell and the Peyer’s patch
Activate B-cells to produce IgA antibodies in the mucus membranes, therefore, prevention of the microbe crossing the mucus membranes
Drawback to this method is mucocilitary clearance of the vaccine, thus, low level response
Vaccine Safety & Problems
General SIde Effects
Residual Virulence
Vaccine Recalls
Contamination
Public Conceptions'
Stability
Allergic Reactions
Research Cost/Government
General Side Effects
Interferon Response
Residual Virulence ( part of Vaccine Safety & Problems)
Attenuated Vaccine
Vaccine Recalls
Gardasil (HPV) and COVID-19 J&J Vaccine
Contamination
2004 flu vaccine contamination, Thimerisoal as a bacteriostatic agent
Public Misconceptions
Jenny McCarthy announced that her son was diagnosed with autism due to preservation agent in MMR.
Based on her belief on a paper from Andrew Wakefield, a doctor, who claimed MMR vaccine cases autism
Stability
Pfizer requires ~80° for storage and lasts at 4°C for 30 days
Moderna requires ~20° for sotrage and lasts at 4° for 30 days
J&J requires 4° for storage
Allergic Reactions
Gelatin/MMR/ Eggs/ Influenza
Research Cost/Government
-FDA,CDC, WHO
1 attempt cost about 1.1 billion per drug; 1/250 will make it to the market
requires lots of research for different ethnic groups
price gouging
Herd Immunity
A type of immunity that occurs when the vaccination of a paortion of the population ( or herd) provides protection to unproteced individual
more difficult to maintain a chain of infection when large numbers of a population are immune
The higher the propoertion of individuals who are immune, the lower the likelihood that a susceptible person will contact an infectious individual