STRESS PSYC_002
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Stimulus-based stress
a demanding, challenging, or threatening event or situation
Response-based stress
physiological responses that occur when faced with demanding or threatening situations
Stimulus-based + Response-based =
process whereby an individual perceives and responds to events that the individual appraises (judges) as overwhelming or threatening to their well-being
Stress
a physical and mental response to a challenging or threatening situation
Stressor
A stressful stimulus or situation demanding adaptation
Appraisal
The way you evaluate events that happen to you
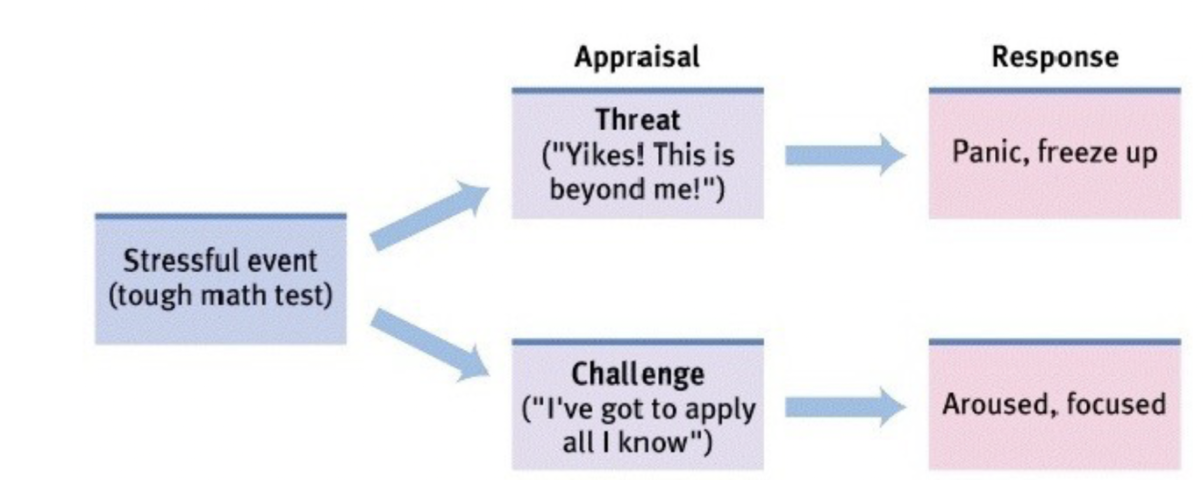
Cognitive Appraisals (primary/secondary)
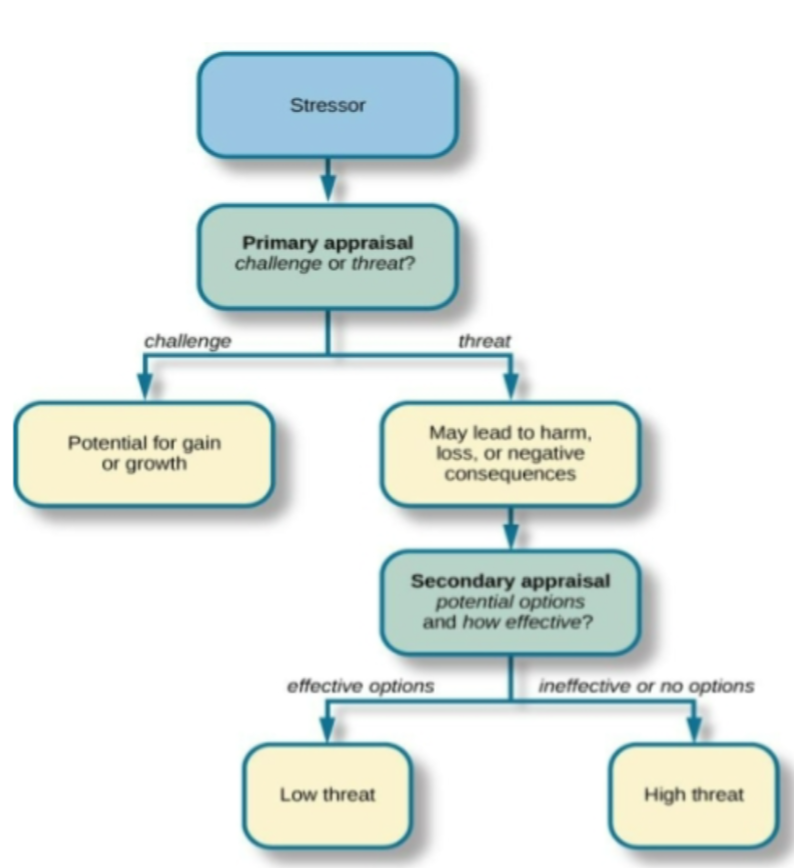
Primary appraisal: judgement about the degree of potential threat to well-being that a stressor might entail
Threat: stressor that could lead to harm/loss/negative consequences
Challenge: stressor that carries the potential for gain/personal growth
Secondary appraisal: judgement of the options available to cope with a stressor, and perceptions of how effective such options will be.
Health Psychology
studies psychological influences on health, illness, and how people respond when they become ill
Three Categories of Stress
Physiological: stress on the body
Psychological: stress from (interpretation of) life events
Sociocultural: stress from forces that affect social/cultural groups
Response to a Normal Stressor
physical response to a normal stressor is universal
initiation of arousal
protective behavioral reaction (fight or flight)
internal response of the autonomic nervous system
decrease in the effectiveness of the immune system
Nervous system
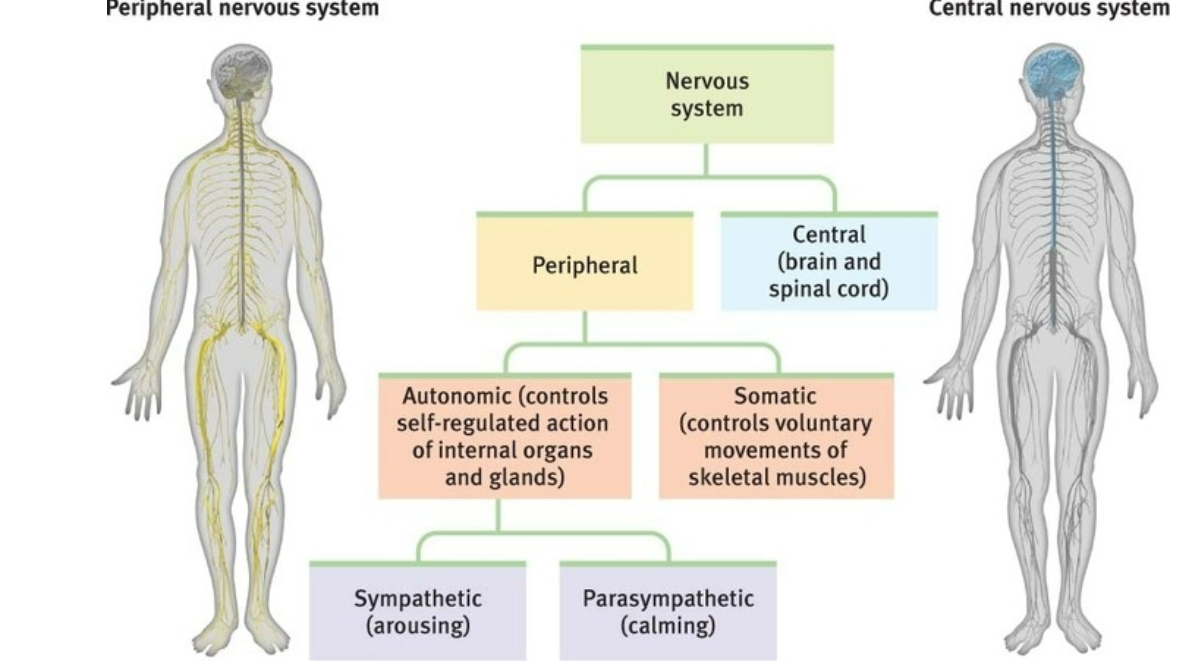
Autonomic Nervous System
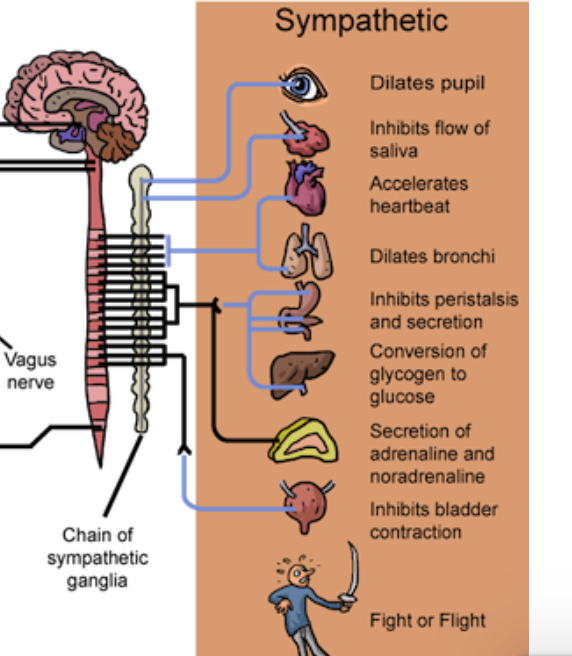
Sympathetic Division
control functions that accompany arousal and expenditure of energy
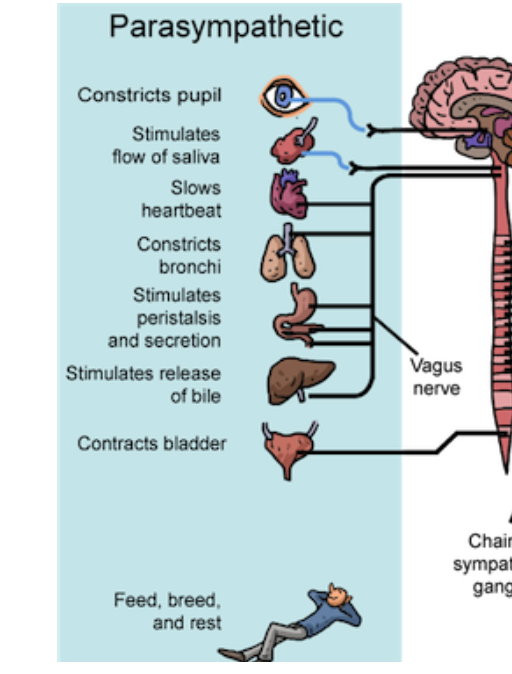
Parasympathetic Division
controls functions that occur during a relaxed state (digest)
Automatic Nervous System : controls self regulated actions of internal organs and glands
Somatic : controls voluntary movements of skeletal muscles
Arousal
The more rapid pulse, the deeper breathing, the increase of sugar in the blood, the secretion from the adrenal glands, were very diverse and seemed unrelated
Walter Cannon
Walter Cannon
Flight or Fight response
psychological reaction that occurs when an individual encounters a perceived threat
activation of the sympathetic nervous system and endocrine system
adaptive response in preparation for effort/energy expenditure
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Sympathetic Nervous System
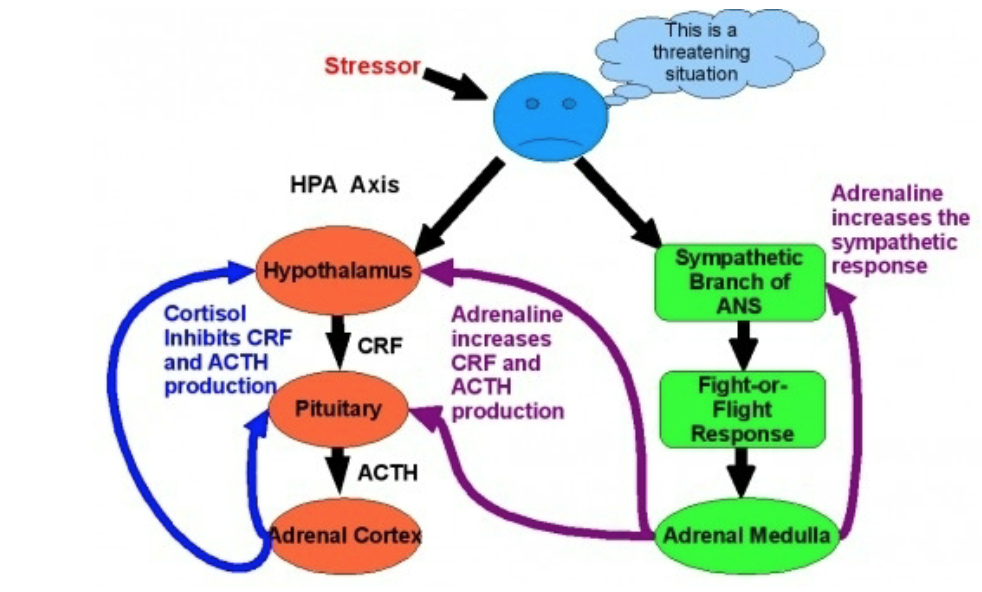
The HPA Axis
H : Hypothalamus
P : Pituitary Gland
A : Adrenal Cortex
Sympathetic and HPA Interaction
Types of Stress
Acute Stress
temporary pattern of stressor-activated arousal with a distinct onset, and limited duration (SHORT TERM STRESS)
Chronic Stress
continues state of stressful arousal, persisting over time (LONG TERM STRESS)
Effects of Stress
Physiological
accelerated heat rate, headaches, gastrointestinal problems
Cognitive
difficulty concentrating or making decisions
Behavior
drinking alcohol, smoking, taking actions directed at eliminating the cause of stress
General Adaptation Syndrome
pattern of physical responses to any serious chronic stressor
Alarm Reactions
body mobilizes its resources to cope with a stressor
Resistance
body seems to adapt to the presence of the stressor
Exhaustion
body depletes its resources
Physiological Effects of Stress
Cortisol
helps body respond to brief stress
chronically high level damage the body
Stress as a Sudden Emergency
temp immune system repression makes sense
immune responses consume energy
stress results in a rapid mobilization of energy
infection doesn’t matter if you don’t escape
adrenal steroids also suppress inflammation
Prolonged Stress Response
produces symptoms similar to depression
weakens the immune system
harms hippocampus
^toxins or overstimulation damage or kills neurons
Stress = increase risk of disease
Stress and Health
Psychoneuroimmunology - interaction of immune system with CNS and Behavior
stressful exams reduce the immune system
dental study = stress reduces body ability to heal
Stress & Immune Function (Cohen, 1998)
Interviews 276 healthy volunteers about recent stressful experiences
given nasal drops w/ cold virus
participants who reported experiencing chronic stressors more than one month were more likely to develop colds than those who reported no chronic stressors
Stress & Aging
stress can shorten telomeres (protect ends of chromosomes)
may inhibit cell division/growth and proliferation of new cells, causing rapid again
shorter in adults who experienced more trauma as childrenN
Negative Affectivity
tendency to experience distressed emotional states involving anger, contempt, disgust, guilt, fear, and nervousness
Hypertension
High blood pressure.
caused by stressors (job strains, marital conflict, natural disasters, and negative affectivity)
forces heart to pump harder increasing physical strain
Heart Attack Symptoms
Males:
lightheadedness
perspiration
chest pain and pressure
stomach pain
shortness of breath
Females:
dizziness
anxiety
back and neck pain
shortness of breath
nausea and vomiting
Type A and Type B personalities
Type A: extremely competitive, intensely driven, impatient, rushed, and hostile toward others
Type B: tend to be relaxed and laid back
one of the most important factors in the development of heart disease is the hostility dimension of Type A
Asthma
chronic disease of inflamed and narrowed airways
stressful experiences linked to developing asthma
expecting symptoms may lead to symptoms
often occur during periods of high or negative emotions
Perceived Control
beliefs about our personal capacity to exert influence over and shape outcomes.
has major implications for health and happiness
lower reactivity to stressors in daily life
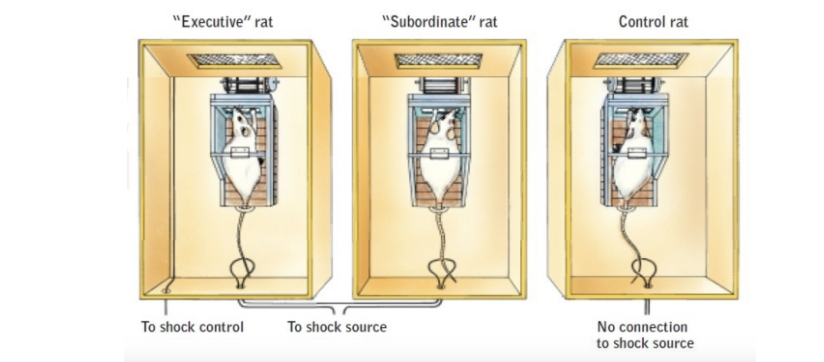
Perceived Level of Control Experiment
executive and subordinate rats received shocks which the executive was able to turn off for both
subordinate did not have control over the shock which created more stress and health issues
Learned Helplessness
acquired belief that one is powerless to do anything about a situation
MARTIN SELIGMAN (1967) : dogs placed in a chamber where they received electric shocks from which they could not escape. When given the opportunity to escape shock, most did not try.
Catastrophic Events
situation that threatens yours or others physical safety and promotes a feeling of helplessness.
certain events go beyond a “normal” stressor
Response to Catastrophic Situations
Five stages:
Psychic Numbness
shock, confusion, lack of understanding
Automatic Action
little awareness of the experience, poor memory/recall
Communal Effort
people work together, but with little planning
Letdown
setting in of the magnitude and impact of situation
Recovery
survivor adapt to changes caused by the disaster.
Epigenetics, Stress & Violence
change in the expression of a gene (turning on or off)
early abuse or severe trauma may reduce the ability to handle stress and increase emotional reactivity
Post Traumatic Stress Disorder
prolonged pattern of stress symptoms following trauma which are commonly associated with but not limited to : combat, assault, torture
Post Traumatic Stress Disorder
Behaviors
agitation, irritability, hostility, hyper-vigilance, self-destructive behavior, social isolation
Psychological
flashback, fear, severe anxiety, mistrust
Mood
inability to feel pleasure, guilt, loneliness
Sleep
insomnia/nightmares
Also common
emotional detachment or unwanted thoughts
Resilience
ability to tolerate and thrive in stressful circumstances
protective factors are resources that help people cope more effectively
Resilience
responses to stress may vary
early life stress can increase or decrease resilience to later stress
genes
social support
physical health
previous stressful experiences