APMB: Salmonella
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Salmonella coliform status? (Coliform/Non-coliform)
Non-coliform
- Do not convert lactose or sucorse to acid
Salmonella growth environments
Resistant to/can grow in:
Low pH
High concentrations of detergents: Bile salts & Brilliant Green compared to faecal coliforms
Tetrathionate (S₄O₆²⁻)
Typical Salmonella vs Atypical Salmonella
Typical Salmonella:
Produce H2S from Thiosulfate (S2O3⁻)
Atypical Salmonella:
Do NOT produce H2S from Thiosulfate (S2O3⁻)
Sources of Salmonella
1) Contaminated hands
2) Reptiles
3) Raw Poultry (more frequently in Chicken)
4) Contaminated soil and water (from faecal matter)
5) X-contamination in the kitchen/from utensils
What is the most common strain of Salmonella and what are the symptoms?
Salmonella enteriditis — Foodborne, common cause for intestinal diseases
Symptoms:
1) Vomitting
2) Diarrhea
3) Nausea
4) Fever
5) Andominal Cramp
6) Headache
Why do Food & Pharmaceutical samples require resuscitationa and enirochment while Clinical samples can undergo direct isolation/enumeration on selective media?
Cells damaged after undergoing processing → Low number of damaged bacteria
The low nnmber of damaged bactera can still be resusicitated in a suitable environment and medium
Low numbers of salmonella is NOT negligible, and may still cause disease in people
Resuscitiation media for Salmonella
1) Lactose Broth
2) Brilliant Green water
3) Nutrient Broth
4) Buffered Peptone water
[Resuscitation Media] Why is Lactose Broth used?
Salmonella does not use lactose (non-coliform)
Can still grow in the medium due to other coliforms → acid produced → Lower pH
[Resuscitation Media] Why is Brilliant Green Water used?
Does not inhibit enteric bacteria (Enteric bacteria resistant to detergents)
Resuscitates salmonella from samples with higher fat content
Enrichment media for Salmonella
1) Selenite broth
2) Tetrathionate broths
[Enrichment Media] Why is Selentie broth used?
Selenite is inhibitory to many G+ and G- bacteria, including coliforms, and select for Salmonella
[Enrichment Media] Why is Tetrathionate Broth used?
Contains:
Caesin & Meat peptones
Bile salts (and Brilliant Green) bacteria → inhibit G+ and non-enteric bacteria
CaCO3 → neutralising agent
Sodium Thiosulfate
Iodine solution
Thiosulfate + Iodine → Tetrathionate
inhibits coliforms and Shigella
alternative O2 source during anaerobic respiration
Differential Agars for Salmonella
1) Brilliant Green Agar
2) Xylose, Lysine, Desoxycholate (XLD) Agar
3) Bismuth Sulphite Agar
[Differential Agar] Brilliant Green Agar
Brilliant Green Agar | ||
Differential agents | Selective agents | Appearance |
|
| Pink colonies
|
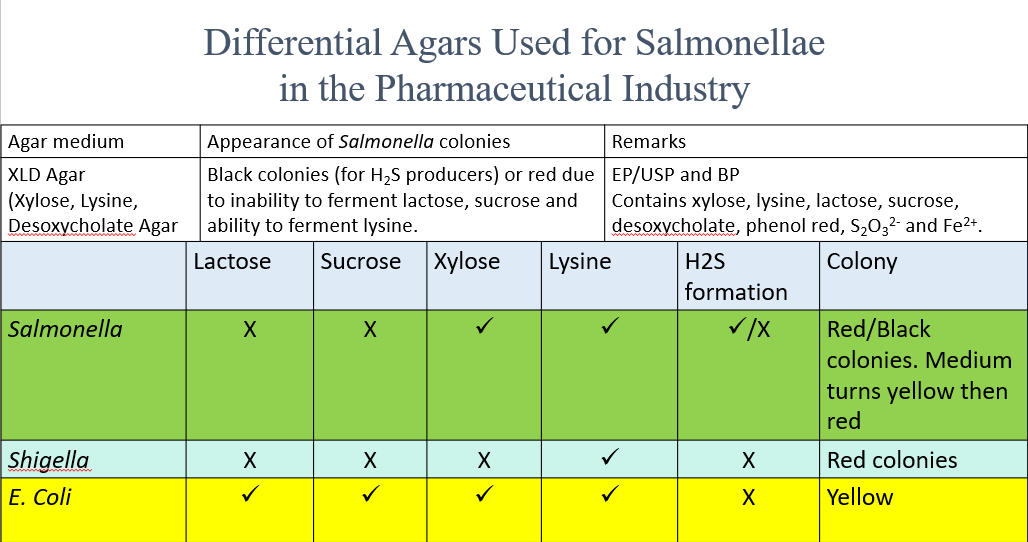
[Differential Agar] XLD Agar
XLD Agar | ||
Differential agents | Selective agents | Appearance |
|
| (Typical) Black colonies
(Atypical) Red colonies
Don’t ferment: Lactose and Sucrose Ferment: Xylose and Lysine |
Fermentation of Lactose, Sucrose, Xylose, Lysine in Shigella and E. coli
[Differential Agar] Bismuth Sulphite Agar
Bismuth Sulphite Agar | ||
Differential agents | Selective agents | Appearance |
|
| Black colonies with a metallic sheen (for typical colonies) |
[Differential Media] Salmonella Shigella Agar
Salmonella Shigella Agar | ||
Differential agents | Selective agents | Appearance |
|
| (Typical) Black colonies (Atypical) Yellow-brown colonies |
What does Triple Sugar Iron Agar test for?
1) H2S formation → (+) Black agar
2) Ability to use Lactose and Sucrose
3) Gas production
[TSI Agar] Atypical Salmonella result
Buttt - Yellow (due to glucose fermentation)
Slant - Red (no fermentation of lactose/sucrose)

[TSI Agar] Atypical Salmonella result
Buttt - Black (H2S formation)
Slant - Red (no fermentation of lactose/sucrose)
