Pharmacology of Hyperlipidemia
1/169
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
170 Terms
What is the main process that occurs when dietary fat and cholesterol are absorbed in the intestines?
They form chylomicrons.
What protein mediates the absorption of fats/cholesterol from food in the intestines to form chylomicrons?
Niemann-Pick C1-like 1 protein (NPC1L1).
How are chylomicrons broken down; and what are the resulting components?
This is broken down by LPL (Lipoprotein Lipase) to the chylomicron remnant and free fatty acids (FFA).
What substance does the liver produce endogenously in lipid metabolism?
VLDL (Very Low-Density Lipoprotein).
Describe the breakdown pathway of VLDL via LPL activity?
VLDL breaks down to IDL (Intermediate-Density Lipoprotein); which breaks down to LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein).
Where does LDL bind in the body?
LDL binds to receptors in the liver and target tissues in the periphery.
Where is nascent HDL generated?
The intestines and liver.
What is the role of nascent HDL in reverse cholesterol transport?
Free cholesterol is collected by nascent HDL from macrophages and peripheral cells.
What enzyme is responsible for esterifying cholesterol collected by nascent HDL?
Lecithin:cholesterolacyltransferase (LCAT).
What protein mediates the exchange of cholesterol esters for triglyceride from other lipoproteins?
Cholesterol ester transfer protein (CETP).
What happens to cholesterol esters carried by mature HDL?
HDL carries cholesterol esters back to the liver for excretion as bile in the intestines.
What is the hallmark of lipid-lowering therapy? What is their primary therapeutic effect ?
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (aka Statins). Reduce LDL levels.
When is it most beneficial to take statins and why?
Oral administration. Most beneficial when taken in the evening because the majority of hepatic cholesterol synthesis occurs between 12-2 am.
What is the half life of most statin? Which statins have longer half-lives and can be taken at any time?
Most have a half life of less than four hours.
Atorvastatin; pitavastin; and rosuvastatin.
high intensity statins
What percent effectiveness classifies a statin as high-intensity?
lowering LDL >50%
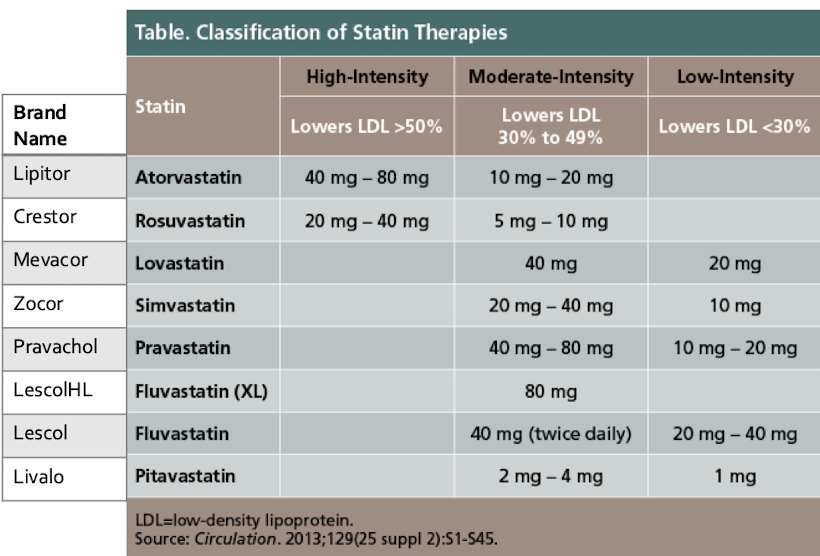
What percent effectiveness classifies a statin as moderate-intensity?
lowering LDL 30% to 49%

What percent effectiveness classifies a statin as low-intensity?
lowering LDL <30%

What is the primary mechanism of action of statins?
Complete inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase.
In cholesterol synthesis; what rate-limiting step do statins prevent?
The conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonate.
Thus, shutting down endogenous creation of cholesterol
What effect does HMG-CoA reductase inhibition have on LDL receptors?
Leads to increased LDL receptor gene expression and enhanced LDL uptake out of the blood.
Greatest effect
What is HMG-CoA and what is Mevalonate in the context of statin MOA?
HMG-CoA is β-hydroxy β-methylglutaryl coenzyme A; Mevalonate is a compound required for the production of sterols.
What are the minor therapeutic effects of statins besides LDL reduction?
Smaller effect on VLDL and IDL reduction; reduce triglyceride levels at higher intensity doses.
What is the absorption rate of statin drugs in the intestine?
30-85% of drug is absorbed in the intestine.
Describe the bioavailability and protein binding characteristics of statins?
Bioavailability is 5-30% of administered dose; 95% of statins are protein-bound in the plasma.
Undergo extensive first pass uptake by liver
Which statins are metabolized by CYP 3A4/3A5?
Atorvastatin; lovastatin; simvastatin.
Which statins show minimal metabolism by CYP2C9 or are mostly unchanged?
Rosuvastatin (minimal CYP2C9); and Pravastatin (mostly unchanged).
Mostly excreted in original form.
How are statin metabolites primarily eliminated?
Excreted by the liver and eliminated via feces (70%).
Which statin is excreted primarily in the urine?
Pravastatin.
What are the typical peak concentrations and half-lives (T1/2) for most statins?
Peak concentrations are 1-4 hours; T1/2 is most 1-6 hours.
Which statins have a longer half-life of approximately 20 hours?
Atorvastatin and rosuvastatin.
How much LDL reduction is achieved for each doubling of the statin dose?
6% reduction.
When does the maximal effect on plasma lipid levels occur for statins?
In 7-10 days.
What is the approximate reduction in triglyceride levels and increase in HDL levels achieved by statins?
Triglyceride reduction is similar to LDL reduction; HDL increases by 5-10% (not that many studies out).
How does gemfibrozil interact with statins?
Decereases statin catabolism
It inhibits uptake of statin by hepatocytes and inhibits enzymatic breakdown; doubling the plasma concentration of statin (38%).
How does Niacin interact with statins?
Enhanced inhibition of skeletal muscle cholesterol synthesis.
Name drugs metabolized by CYP3A4 that increase the plasma concentration of statins?
Cyclosporin; Digoxin; Warfarin; Macrolide antibiotics; and Antifungals (specifically -azoles).
Which two statins are less likely to have drug interactions because they are not metabolized by CYP3A4?
Pravastatin and rosuvastatin.
Which statin dose should not be used with diltiazem or verapamil?
Simvastatin (>10 mg).
What are the absolute contraindications to statin use?
Active liver disease; Pregnancy (& other cholesterol lowering drugs) discontinue prior to conception; and Breastfeeding.
What statin can be used in renal disease without requiring renal dosing?
Atorvastatin.
What is the main adverse effect (AE) associated with statins; and what is the spectrum of complaints?
Myopathy; spectrum ranges from mild weakness/soreness to severe rhabdomyolysis (<1%).
What factors increase the risk for statin-associated myopathy?
Increased doses, advanced age; Hepatic/renal dysfunction; Perioperative period; Small body habitus; and Untreated hypothyroidism.
What parameters should be monitored for efficacy and toxicity when a patient is on a statin?
LDL levels; ALT/AST (baseline); monitoring for toxicity including rhabdomyolysis and rare hepatotoxicity.
Which two statins are generally tolerated best?
Rosuvastatin and pravastatin.
Which statin is better absorbed when taken with food?
Lovastatin.
What is the risk of cognitive impairment associated with statin use?
There is NO evidence for cognitive impairment.
Describe the clinical significance of the small increased risk for diabetes associated with statins?
It is outweighed by ASCVD benefit.
Which statins are indicated for children with Familial Hypercholesterolemia (FH)?
Atorvastatin; lovastatin; and simvastatin (>11 yrs); pravastatin (>8 yrs).
What is the brand name of the cholesterol absorption inhibitor Ezetimibe?
Zetia.
What is the standard dose and administration method for Ezetimibe?
Oral 10 mg tablet for daily use; can be taken with or without food; can be added to statins.
What is the mechanism of action of Ezetimibe?
It inhibits cholesterol uptake in the intestinal lumen by inhibiting the transport protein (NPC1L1) in jejunal enterocytes.
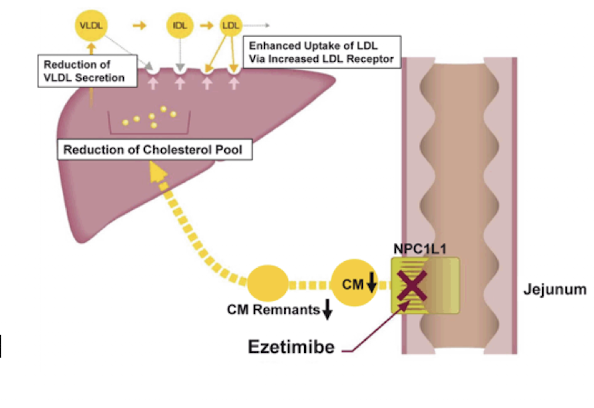
What happens when cholesterol isn’t incorporated into chylomicrons
Decreased delivery to the liver
Stimulates LDL receptor gene expression and cholesterol synthesis
Increases LDL clearance from plasma
By what percentage does Ezetimibe decrease intestinal cholesterol absorption?
By 54%.
What physiological reaction occurs in the liver when Ezetimibe decreases cholesterol delivery?
A compensatory increase in cholesterol synthesis occurs.
How is Ezetimibe absorbed and distributed?
Very water soluble, absorbed in intestinal epithelium
• 90% protein bound
How is Ezetimibe metabolized; leading to multiple plasma concentration peaks?
Through enterohepatic recirculation.
How is Ezetimibe primarily excreted?
70% fecal; 10% urine.
What is the half-life (T1/2) of Ezetimibe?
22 hours. Hence its once a day dosing
What is the typical LDL reduction achieved by Ezetimibe monotherapy?
Reduction in LDL by approximately 15-20%.
When is Ezetimibe monotherapy indicated?
Limited to patients who do not tolerate statins.
What is the benefit of using Ezetimibe as adjunctive therapy with statins ( and bempedoic acid)?
Additive reduction in LDL; leading to greater LDL reduction than with a statin alone; similar to high-intensity statins.
Which drugs inhibit the absorption of Ezetimibe?
Bile acid sequestrants.
What are the contraindications to Ezetimibe use?
Allergic to drug/components; Pregnancy; and breastfeeding.
What are the adverse effects associated with Ezetimibe?
Rarely severe allergic reactions; otherwise; no adverse effects.
EZ to tolerate
What should be monitored for efficacy and toxicity when a patient is on Ezetimibe?
Lipid panel; ALT/AST (baseline); and monitoring for rare hepatotoxicity.
Name the two main fibric acid derivatives?
Fenofibrate; gemfibrozil.
When are fibric acid derivatives the drug of choice?
For severe hypertriglyceridemia (>1000 mg/dL) and patients at risk for pancreatitis.
Is co-administration of fibric acid derivatives with statins recommended?
No; they do NOT have additive effect with statins and their use is not recommended.
When are fibric acid derivatives taken and what is the MOA?
Taken orally before meals and mechanism of action remains unknown.
What receptors do fibric acid derivatives interact with to regulate gene transcription?
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs).
What are the main effects of PPARs on lipid metabolism?
Regulate gene transcription
Increase fatty acid oxidation
Increase lipoprotein lipase synthesis → clears triglyceride-rich lipoproteins
Reduce apo C-III expression → enhances VLDL clearance
Increase apo A-I & apo A-II expression → raises HDL levels
How do fibrates affect apo C-III and VLDL clearance?
They reduce expression of apo C-III; enhancing clearance of VLDL.
How do fibrates affect HDL levels?
They increase apo A-I and apo A-II expression; increasing HDL levels.
What non-lipid modifying effects do fibric acid derivatives possess?
Antithrombotic effects; inhibiting coagulation and enhancing fibrinolysis.
When are fibric acid derivatives absorbed rapidly? When do they reach peak concentrations?
When taken with a meal. Reach peak within 1-2 hours
How are fibric acid derivatives distributed?
Wide: Hepatic, renal, intestinal
>95% protein bound (albumin)
How are Gemfibrozil and Fenofibrate primarily metabolized?
Gemfibrozil undergoes hepatic metabolism and inhibits cytochrome P450 2C8
Fenofibrate undergoes glucuronidation.
How are fibric acid derivatives primarily excreted?
Up to 90% via urine.
What are the half-lives (T1/2) for gemfibrozil and fenofibrate?
Gemfibrozil T1/2 is 1.5 hours; Fenofibrate T1/2 is 20 hours.
By what percentage do fibric acid derivatives lower triglycerides and increase HDL?
Lower triglycerides by 30-50%; Increase HDL by 5-15%.
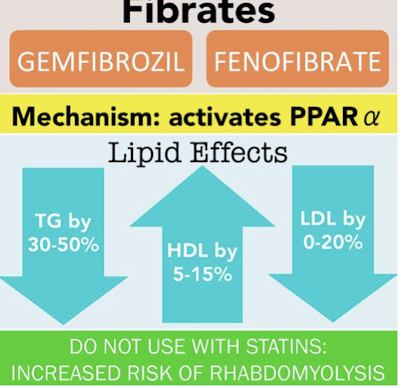
What is the typical range of LDL reduction observed with fibric acid derivatives?
LDL effect varies; up to 20% reduction (0-20%).
How do fibric acid derivatives interact with warfarin; and what monitoring is required?
Increased warfarin activity; monitor prothrombin time; consider dose reduction of warfarin as appropriate.
When is the risk of rhabdomyolysis greatest regarding statin and fibrate co-use?
Risk is greatest with gemfibrozil plus higher intensity or higher dose statins.
What monitoring is required if statins and fibrates must be used together?
Close monitoring of creatinine kinase levels.
What are bile acid sequestrants interaction with gemfibrozil
Bile acid sequestrants decrease absorption of gemfibrozil
This can reduce gemfibrozil’s effectiveness in lowering triglycerides
What are the contraindications to fibric acid derivatives?
Concurrent statin use; Renal failure; Gallstone disease; Children; and Pregnant women.
What are the main adverse events of fibric acid derivatives? What are the infrequent side effects?
Myopathy; and GI side effects.
Infrequent:
Rash, urticaria, hair loss
Myalgias, fatigue, headache
Impotence
Anemia
What should be monitored for efficacy and toxicity when a patient is on a fibric acid derivative?
LDL levels; ALT/AST (baseline); and monitoring for renal & hepatotoxicity.
What class of medication is Bempedoic Acid and when was it FDA approved?
ATP-citrate lyase (ACL) inhibitor; class FDA approved in 2020.
For which patient populations is Bempedoic Acid (Nexletol) indicated as an adjunct to diet and maximally tolerated statin?
Patients with familial hypercholesterolemia or ASCVD; and statin-intolerant patients.
What combination medication containing Bempedoic Acid is available?
A combination med with ezetimibe.
Nexlizet
How does Bempedoic Acid inhibit cholesterol synthesis?
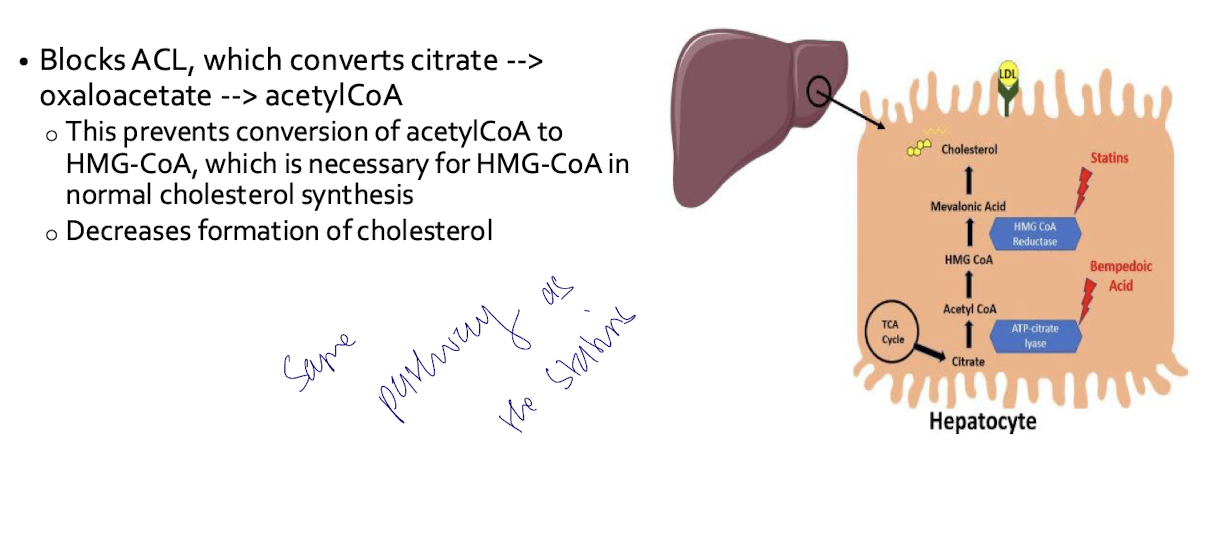
It blocks ACL; which prevents conversion of acetylCoA to HMG-CoA; decreasing formation of cholesterol.
What are the absorption and peak concentration characteristics of Bempedoic Acid?
Absorption occurs in the small intestine; unaffected by food; peak plasma concentration in 3.5 hrs.
How is Bempedoic Acid distributed and metabolized?
99.3% proten bound
It is a prodrug metabolized by the liver via CYP2C9 -> bempedoyl coenzyme A.
What is the half-life (T1/2) and primary excretion route of Bempedoic Acid?
T1/2 is 21 hrs; Excretion is via urine.
What are the therapeutic effects of Bempedoic Acid?
Decreases LDL up to 28%; Decreases apolipoprotein B; and Decreases total cholesterol.
What doses of Simvastatin and Pravastatin are notable drug interactions with Bempedoic Acid?
Simvastatin >20 mg; and Pravastatin >40 mg.
What are other bempedoic acid drug interactions?
Cyclosporine
Bile acid sequestrants (block absorption of ezetimibe combinations)
What are the main contraindications for Bempedoic Acid?
Gout (can increase uric acid levels), pregnancy, breastfeeding
What severe adverse effect (0.5%) is associated with Bempedoic Acid when used with high-dose statins?
Tendon rupture.