Spinal Anatomy Exam 1
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
133 Terms
what are the 7 basic functions of the spine
1) Protect spinal cord & nerve roots
2) Passage of spinal nerve to/from spinal cord
3) Support/Stabilize body
4) Developmental origin of ribs
5) Shape/Position body
6) Movement of trunk and limbs (locomotion)
7) Provide horizontal orientation for eye (vision) and vestibular apparatus (balance)
Which somite gives rise to the vertebral column?
-paraxial mesoderm gives rise to somite which forms the sclerotome which forms the vertebral column
where is the intrasclerotomal fissure? what does it form
-between sclerotomites of a perichordal blastema is the intrasclerotomal fissure
-gives rise to perichordal disc (adult IVD)
during the 6th week of development, the ______________undergoes chondrification
-membranous vertebral blastema
--replacement of mesoderm by cartilage
how many chondrification centers are in a vertebra
6
-1 pair in the centrum
-1 par in the arches (right and left)
-1 pair in the TVP (right and left)
during the 7th week, cartilage is replaced by ___________. primary ossification occurs _______ secondary occurs _________
-bone
--primary: before brith
--secondary: between birth and late puberty (11-16 years) and fuse to the rest by age 25
how many primary centers of ossification and how many secondary?
-3 primary (1 centrum and 2 in the arch)
-5 secondary (2 in body and 3 in arch)
--epiphyseal plate, tip of TVP, tip of spinous process
primary centers of ossification grow _________, cartilage decreases until _____ form
-grow toward each other
-decrease until small synchondrosis join remains
synchondroses formed between each centrum and neural arch centers ossification on each side becomes _______
-neurocentral synchondrosis
synchondroses of secondary centers include:
-epiphyseal ring synchondrosis
-tip of TVP synchondrosis
-tip of spinous process synchondrosis
what is a primary curvature of the spine
-kyphotic (posterior, concave)
---thoracic, sarcococcygeal
-you are born with
what is the secondary curvature of the spine
-lordotic (anterior, convex)
--cervical (hold head up) and lumbar (walking)
-develop with milestones
the IVD has a greater _________ height than _______ height in cervical and lumber region which creates a ______ curve
-anterior
-posterior
-lordotic curve
a kyphotic curve is due to height difference of ___________. the ______ height is greater
-due to height difference of vertebral body
-greater posterior height
lateral curvatures of the spine are slight in ______ region. Tend to appear after ______ years of age. Deviations result from?
-slight in upper thoracic region
-appear after 6 years
-deviations from asymmetrical muscle use
lateral curvatures are originally thought to be only associated with?
-handedness
--we realized it my have some genetic factors and or environmental
where do we usually see lateral curvatures?
-usually in thoracic and lumbar regions
--convexity of curve is on the left in left handed people and o the right in right handed people
which part of the IVD attaches vertebral bodies and which part separates them?
-annulus fibrosis attaches
-nucleus pulposis separates
what are some other functions of the IVD (4)
-helps shape the spine
-acts as a powerful ligament
-forms part of the anterior border of vertebral canal and anterior border of IVF
-shock absorber
what makes up the annulus fibrosis of the IVD? nucleus pulposis?
annulus: type 1-2 collagen (restrict movement)
nucleus: water, collagen, proteoglycans (movement)
what are the 2 main things that make up IVD
-proteoglycan gel and collagen fibers
how do you lose water in IVD? how do you get it back?
-water loses volume during the day; 8 hour laying period returns water to IVD and restore height of the spine
*overall height diminished with age
nucleus pulposis becomes more _________ concentration of H2O and proteoglycans ________ with age
-more fibrous
-H2O and proteoglycans decrease
what is a small round projection or protuberance on a bone
tubercle
what is a project5ion or outgrowth of tissue from a larger body
process
what is a small flat surface on a bone
facet
what relates to the joints of the body
articular
what relates to the rib
costal
what does the superior epiphyseal rim do? what attaches here?
-keep IVD within the borders
-ligaments attach here
what does the pedicle do?
-aka superior and inferior vertebral notches
-connect body and arch
-form boundaries of intervertebral foramen!!!
what does the lamina do? what attaches here? what is the clinical significance
-flat, lack of blood supply, and thin (vulnerable)
-ligamentum flavia attaches here
-spondylosis can occur here
what are the veins within the spinal canal
-internal vertebral venous plexus
-anterior spinal vein
-posterior spinal vein
-basivertebral venous formamina
what does the internal vertebral venous plexus do?
-provides alternative route if IVC or jugular veins are comprimised
-surrounds whole vertebrae canal
-in epidural space
what are the arteries in the spinal canal
-segmental artery which goes to ....
-spinal branch which goes to .....
-mixed spinal n OR medullary (feeder) artery.....
-radicular A OR posterior spinal A OR anterior spinal A
which ligaments form the anterior and posterior boundary of the spinal cord
anterior boundary: posterior longitudinal ligament
posterior boundary: ligamentum flavum
the PLL does what? where does it attach?
-prevents hyperflexion and posterior spinal disc herniation
-attaches to body
the ligamentum flavum does what? where does it attach?
-preserve upright posture
-prevent hyperflexion
-straightens spinal column after flexion
-attaches at lamina: vertebral arch
spinal cord and meninges found in vertebral canal until what level?
L2
what is in the epidural, subdural and subarachnoid space?
epidural: external to dura; filled with fat
subdural: potential space between dura and arachnoid (BAD)
subarachnoid: between arachnoid and pia contains CSF
what is the filum terminale? what type of movement does it prevent
-extension of pia mater, anchors cord to sacrum and coccyx
-prevents vertical movement
what are denticulate ligaments? what type of movement does it prevent?
-extension of pia mater, anchors cord laterally to dura mater
-prevents side movement
the IVD develops from?
notochord and sclerotomes
what does the nucleus pulposis develop from?
-notochordal tissue
what is the composition of the cartilaginous end plates
-hyaline cartilage (attached at centrum
-fibrocartilage (attached at IVD)
what is the function of the cartilaginous end plates
-prevents centrum from undergoing atrophy and pressure
-keeps IVD within anatomical borders
-extremely porous
-diffusion of gases, nutrients, waste material
what is the joint classification of intervertebral discs
cartilaginous (amphiarthrosis) symphysis joint
--bones united by fibrocartilage
what is the innervation of anterior intervertebral discs
-afferent, sympathetic branches from sympathetic trunk
what is the innervation of posterior intervertebral discs
-receives input from sinu-vertebral nerve (recurrent meningeal)
-ventral ramus and gray ramus
-nociceptors (sensitive to annular tears)
what is the innervation of lateral intervertebral discs
-receives from gray ramus communicans
what are the boundaries of intervertebral foramina (superior, inferior, anterior, posterior)
superior: inferior vertebral notch of segment above
inferior: superior vertebral notch of segment below
anterior: IVD, vertebral bodies, PLL
posterior: prezygapophysis, postzygapophysis, capsular ligament, ligamentum flavum
what are the contents of intervertebral foramina
-spinal nerves and roots
-arteries, veins, lymphatics
-ligaments
neural tissue of IVF fills ____% what are the surrounding strucures?
8-50%
-ventral and dorsal nerve roots
-dorsal root ganglion
-mixed spinal nerve
spinal branch arteries arise from _______ in the IVF? what are branches that are given off before entering IVF
-segmental artery
-osseous branches
-anterior/posterior spinal plexus
What is the artery of Adamkiewicz? where does it enter? what does it supply
"anterior medullary feeder artery"
-enters T9/T19 IVF; 77% on left side
-principle supplies of lumbar enlargement L2-S3
the artery of AK (Adamkiewicz) is the only major arterial supply to ?
-anterior spinal artery inferior to entry
75% of thoracic IVD herniations occur below?
T8
-artery often compromised
-common signal of involuntary urination
Intervertebral veins are part of the IVF and are an anastomosis of
-various veins with epidural and subarachnoid space
intervertebral veins merge with??? and drain into???
-merge with external vertebral venous plexus and drain into segmental vein
lymphatic capillaries of the IVF arise in ______ space. vessels form near??
-arise in epidural space
-vessels form near IVF
transforaminal ligaments attach?
-vertebral bodies to articular process
superior transforaminal ligaments attach vertebral body to _______ of same verteba
-inferior articular process
middle transforaminal ligaments attaches IVD to _______ of segment above
-inferior articular process
inferior transforaminal ligaments attach vertebral body to _______ of same verteba
-superior articular process
corpotransverse ligaments attach?
attach vertebral bodies to TVP
superior corpotransverse attaches vertebral body and IVD to
-TVP of vertebra BELOW
inferior corpotransverse attaches vertebral body and IVD to
-TVP of vertebra ABOVE
what is a synarthrosis joint?
-no movement
-aka fibrous
-skull sutures
what is an amphiarthrosis joint
-slight movement
-aka cartilaginous
-IVD
what is a diarthrosis joint
-free movement
-synovial fluid filled cavity
-shoulder joint
what is a fibrous joints and movements allowed
-more than 2 bony surfaces connected by a thin layer of dense (fibrous) CT
what are some examples of fibrous joints
-sutures of skull
-syndesmosis
-gomphosis (roots of teeth with alveoli of mandible/maxilla)
-schindylesis
where are sutures located? can they move? what is the ligament called?
-only between skull bones
-NO movement in adults, slight movement in children
-sutural ligament
what are the 4 sutures of the skull and when do they ossify
-metopic= 1st year
-coronal= 24 years
-sagittal= 21-30 years
-lambdoid= 26 years
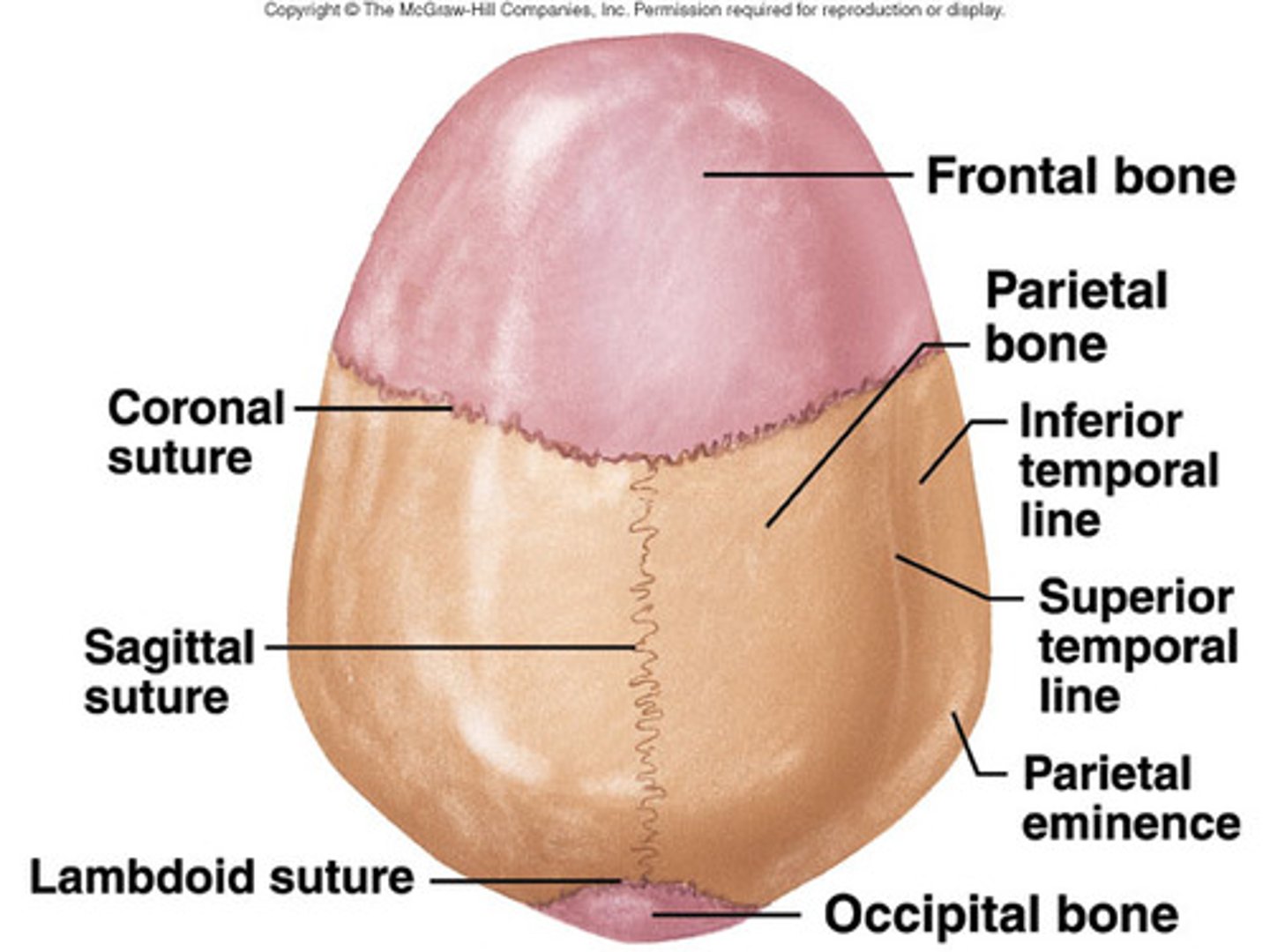
syndesmosis joints contain what 3 things?
-interosseous membrane
-collagen fibers- white fibrous CT (PLL and ALL)
-elastic fibers- ligamentum flavum
most ligamentous joints of the spine demonstrate measurable motion which is an example of ?
amphiarthrosis
gomphosis joint is a _________ process into a socket
conical
the only schindylesis example in the body is when what 2 parts articulate?
-rostrum of sphenoid and ala of vomer
what is a cartilaginous joint and what are some examples
-cartilage fills space between opposing bones
-symphysis (fibrocartilage)
-synchondrosis (hyaline)
what are 2 examples of a synchondrosis cartilaginous joint
-cartilaginous epiphyseal plate (temporary)
-costochondral joint
symphysis cartilaginous joints occur along ____ plane and is a _____ joint.
-median plane
-permanent joint
what are some examples of symphysis cartilaginous joints
-IVD
-pubic symphysis (provides shock absorption and stability to pelvis during birth; relaxin increases mobility at symphysis
what is a synovial joints and its 4 parts
-joint cavity filled with synovial fluid
-articular capsule
-articular cartilage
-synovial membrane
-synovial fluid
how are synovial joints classified (3 things)
-number of bones or articular surfaces
-types of movement allowed by joint
-morphological appearance
how do you distinguish between simple, complex, and compound in a synovial joint classification
simple: opposing bones (fingers and toes)
complex: joint cavity divided into 2 compartments (knee)
compound: more than 2 bones (tibia, fibula, femur)
what is a synovial plane joint, what movements are allowed and examples
-diarthrosis arthroidal
-flat plane or slightly concave-convex
-gliding and translation movement
-costovertebral/sygapophyseal/facet/zygapophysial
what is a synovial saddle joint, what movements are allowed and examples
-diarthrosis sellar
-flexion/extension/adduction/abduction/circumduction
-carpometacarpal joint
what is a synovial ellipsoidal joint, what movements are allowed and examples
-diarthrosis condyloid
-flexion/extension/lateral bending
-atlanto-occipital/metacarpophalangeal joint
what is a synovial pivot joint, what movements are allowed and examples
-diarthrosis trochoid
-proximal radioulnar/median atlanto-axial joint (limited flexion/extension)
-UNIAXIAL
what is a synovial ball and socket joint, what movements are allowed and examples
-spheroid
-all movments
-shoulder/hip joint
-MULTIAXIAL
what is a synovial hinge joint, what movements are allowed and examples
-ginglymoid
-flexion/extension
-IP joints hands and feet/humeroulnar
-UNIAXIAL
articular capsule location and function
-contains 4 types of mechanoreceptors located in superficial or deep layers of joint capsule and ligaments
type 1-3 mechanoreceptors in articular capsule are encapsulated or not??? what is their function?
-encapsulated
-proprioceptive function
type 1-3 mechanoreceptors are in charge of _______ movements and the maintenance of _____________ by monitoring?
-coordination and control of movements
-maintenance of upright posture
-monitor stationary position and movements of body parts
type 1-3 mechanoreceptors relay into to the? and provide information about?
CNS
-direction, velocity, and initiation of joint movements
type 1=
type 2=
type 3=
type 1= ruffini (mvmt at rest)
type 2= paciniann (normal mvmt)
type 3= golgi tendon organ (extreme mvmt)
type 4 mechanoreceptors in articular capsule are encapsulated or not??? what is their function?
-non-encapsulated
-unmyelinated free nerve endings (nocioceptors)
what do type 4 mechanoreceptors respond to
-potential mechanical injury or inflammation processes
articular surfaces are covered with _________
-hyaline cartilage
--avascular, lacks lymphatics and innervation; no potential for growth and repair
nutrition/waste elimination provided by _______
-synovial fluid
--BV in synovial membrane, and or sinuses of bone marrow
what is a major component of articular cartilage
proteoglycans and GAGs (water retention)