Anatomy ch. 7 test
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/77
Last updated 2:39 PM on 3/23/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
1
New cards
Describe a lifestyle that may prevent the development of osteoporosis (GENETIC ENDOWMENT)
Dark skinned people are less apt to get osteoporosis; men are also less likely to get it- it’s just genetics
2
New cards
Describe a lifestyle that may prevent the development of osteoporosis (NUTRITION)
High intake of calcium and vitamin D with dietary supplements starting at an early age helps offset bone loss
3
New cards
Describe a lifestyle that may prevent the development of osteoporosis (ACTIVITY)
Regular stress on bone can produce mild hypertrophy. This will also help offset bone loss
4
New cards
Describe a lifestyle that may prevent the development of osteoporosis (DRUG TREATMENT)
Estrogen replacement in women helps to reduce bone loss
5
New cards
Turning the palms of hands upward
Supination
6
New cards
Shrugging the shoulders
Elevation
7
New cards
Bending the arm at the elbow
Flexion
8
New cards
Reaching for an object that is just beyond ones reach
Protraction
9
New cards
Turning the hands down so the palms face the floor
Pronation
10
New cards
Moving the legs apart in an “at ease” position
Abduction
11
New cards
Moving the legs together in an “attention” position
Adduction
12
New cards
Swiveling the head
Rotation or circumduction
13
New cards
Drawing a large circle on the blackboard
Circumduction
14
New cards
Pointing the toes together with the heels apart
Inversion
15
New cards
What is osteoporosis
Loss of bone mass, primarily occurs in light skinned women; drop of estrogen, easy to fracture due to loss of Ca
16
New cards
How is calcium released from bone so that it is available for physiologic processes
OsteoClasts release Ca+2
17
New cards
What are the major inorganic salts stored in bone?
Calcium (Ca+2) and phosphate (PO4-3)
18
New cards
What is the difference between red marrow and yellow marrow?
Red- blood
Yellow- store fat
Yellow- store fat
19
New cards
What bones function primarily to provide support?
The feet, legs, and spine
20
New cards
Whats high stress
Hypertrophy
21
New cards
Whats low stress
Atrophy
22
New cards
What do osteoBLASTS do
Make bone
23
New cards
What do osteoCLASTS do
Break down bone
24
New cards
When is ossification complete?
When the disks harden- late 20’s
25
New cards
What bones are endochondral bones
Long bones
26
New cards
What bones are intramembranous bones
Flat bones (skull)
27
New cards
Moving the parts at a joint so that the angle between them is increased is called
Extension
28
New cards
The type of joint that permits the widest range of motion is
Ball and socket
29
New cards
The function of bursae is to
facilitate movement of tendons over bones
30
New cards
Synovial membrane is found in
Freely moveable joints
31
New cards
Fibrous joints are
immovable; Ex. Sutures of skull, teeth
32
New cards
Cartilaginous joints are
Disks of Fibrocartilage, slightly moveable; Ex. Vertebra
33
New cards
Synovial joints are
Very moveable; ex. The knee, arms, legs
34
New cards
Ball and socket joint example
Hip and shoulder joint
35
New cards
Condyloma joint example
Joint between a metacarpal and a phalange
36
New cards
Gliding joint example
Joint of wrist or ankle
37
New cards
Pivot joint example
Axis and atlas; proximal ends of radius and ulna
38
New cards
Saddle joint example
Joint between trapezium and the metacarpal of the thumb
39
New cards
What part of the vertebral column acts as a shock absorber
Intervertebral disks
40
New cards
The upper jaw is formed by the
Maxillae
41
New cards
The only moveable bone of the skull is the
Mandible
42
New cards
The hormone associated with the development of osteoporosis is
Estrogen
43
New cards
Which of the following salts is normally stored in bone
Calcium
44
New cards
The bones most often affected by osteoporosis
Hips and vertebrae
45
New cards
To accomplish movement, bones and muscles function together to act as
Levers
46
New cards
The gap between broken ends of fractured bone is filled by a
Cartilaginous callous (bones callous)
47
New cards
When a bone is fractured, a hematoma is formed from blood escaping from the
Periosteum and blood vessels within the bones
48
New cards
The band of cartilage between the primary and secondary ossification centers in long bones is called the
Epiphyseal disk
49
New cards
Bones that develop masses of hyaline cartilage are called
Endochondral boens
50
New cards
Bones that develop from layers of membranous connective tissue are called
Intramembranous bone
51
New cards
Bone that consists of numerous branching bony plates separated by irregular spaces is called
Spongy bone
52
New cards
Bone that consists of mainly tightly packed tissue is called
Compact bone
53
New cards
To what part of the bone do tendons and ligaments attach
Periosteum
54
New cards
The shaft of the long bone is the
Diaphysis
55
New cards
The hardest most enduring human tissue is
Bone
56
New cards
The major limitation of cartilage in the knee is it cant
Regenerate
57
New cards
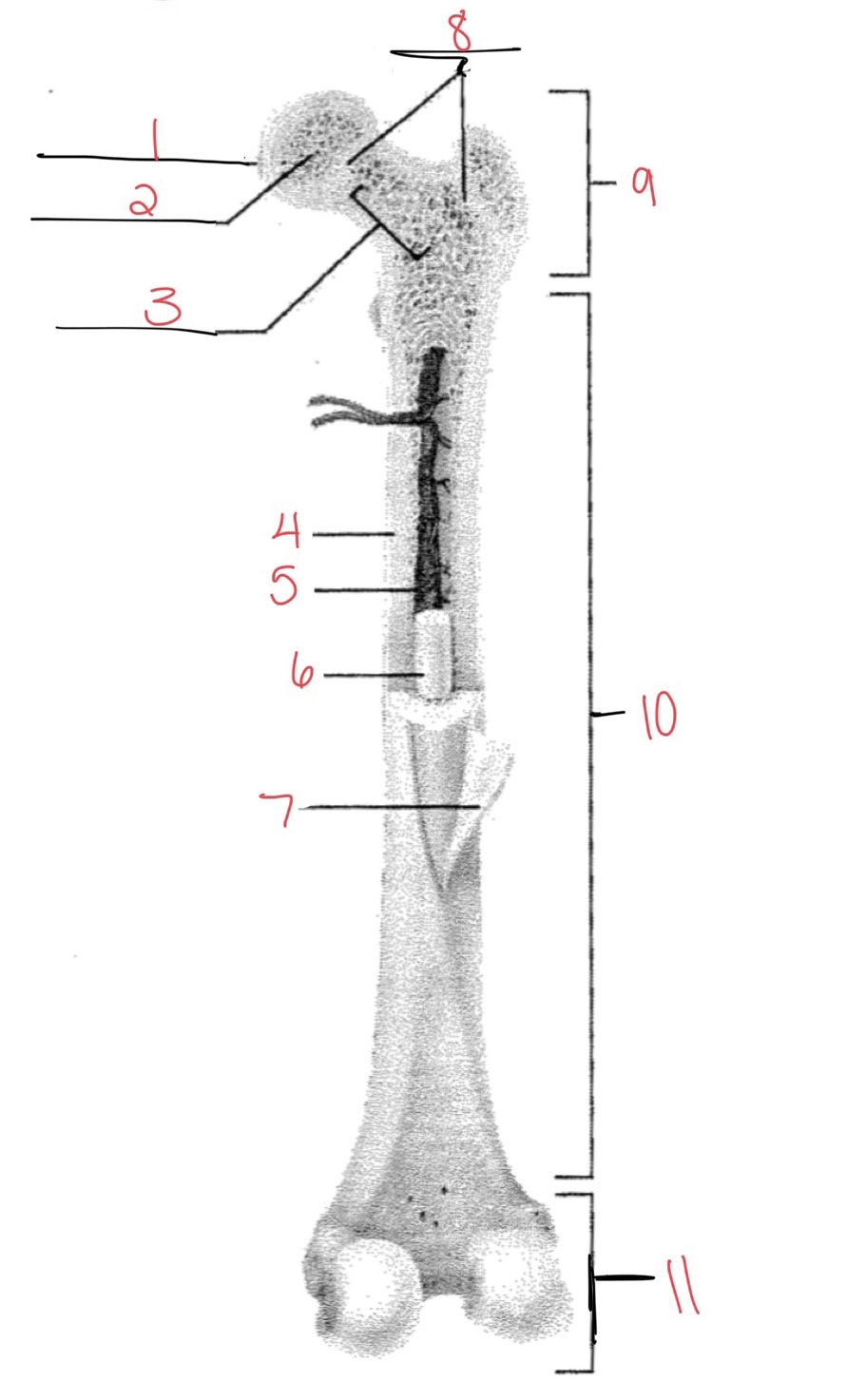
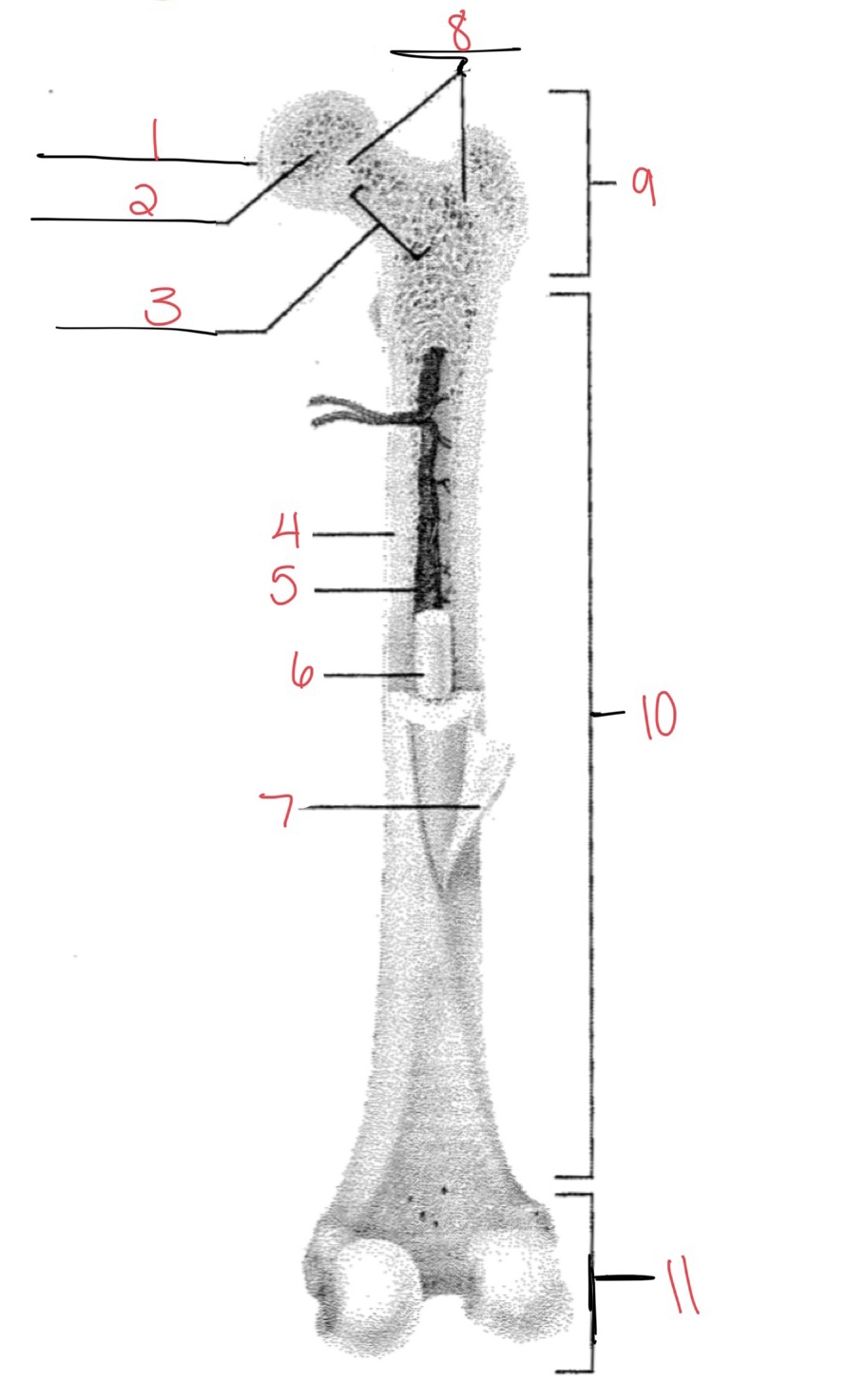
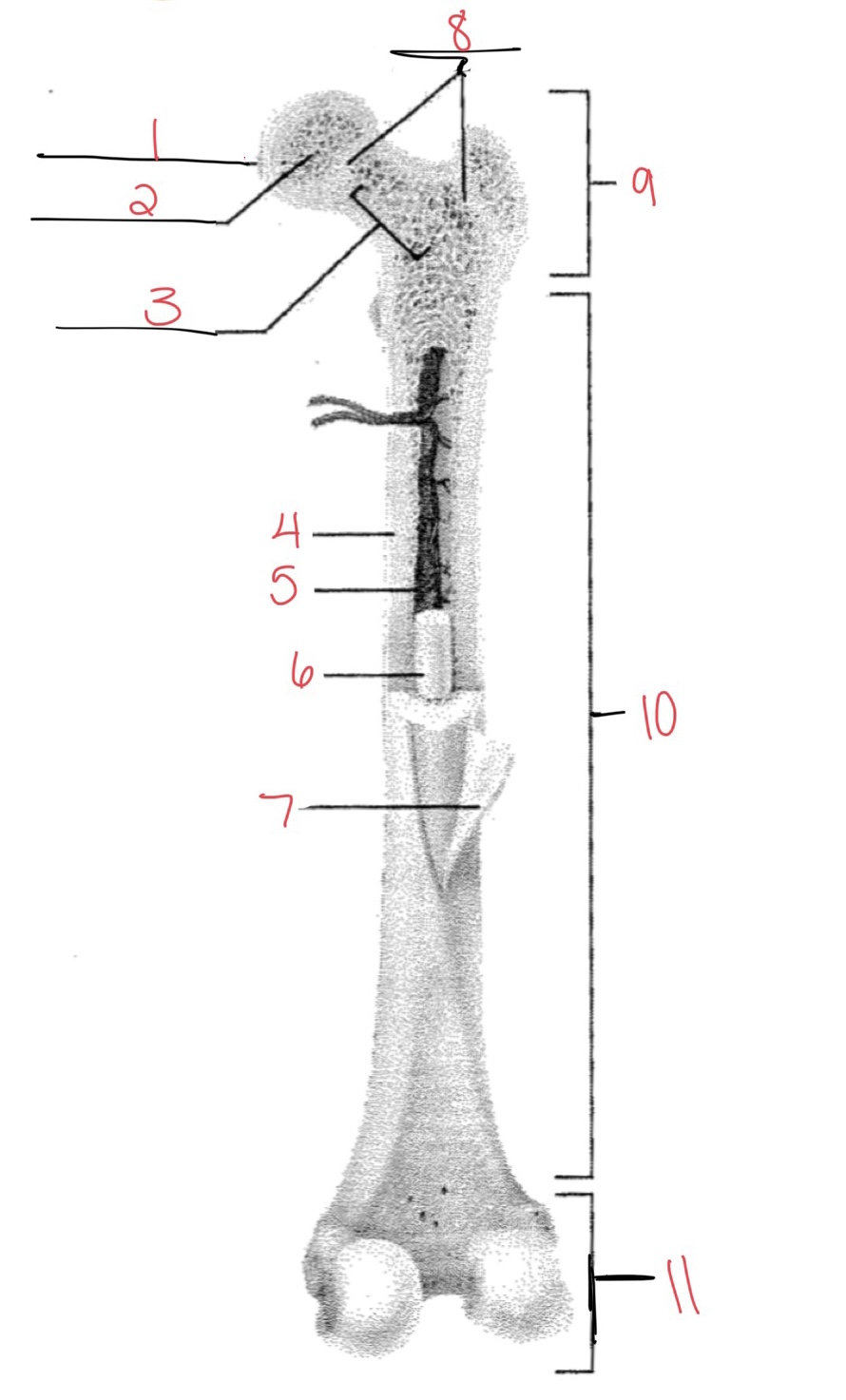
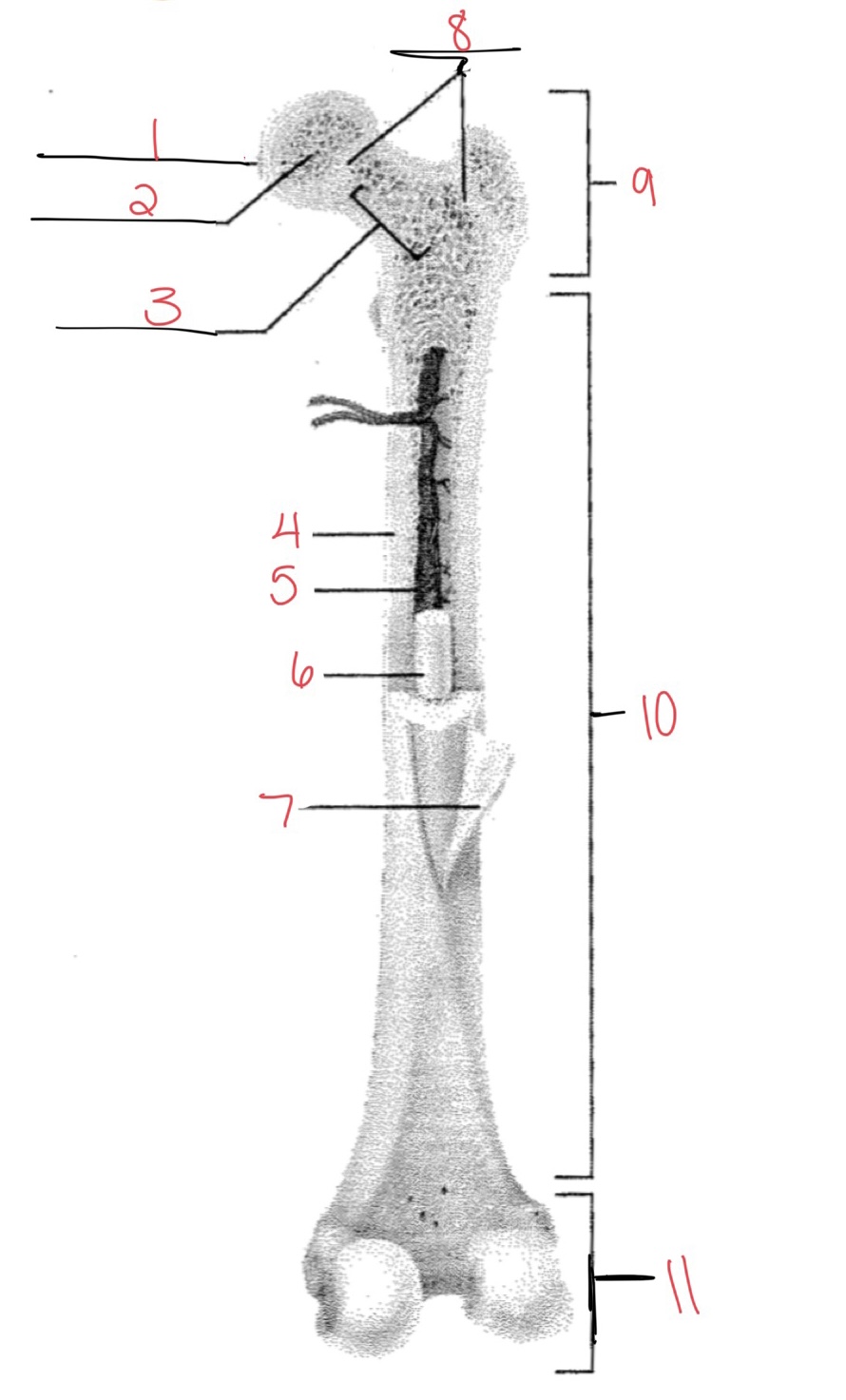
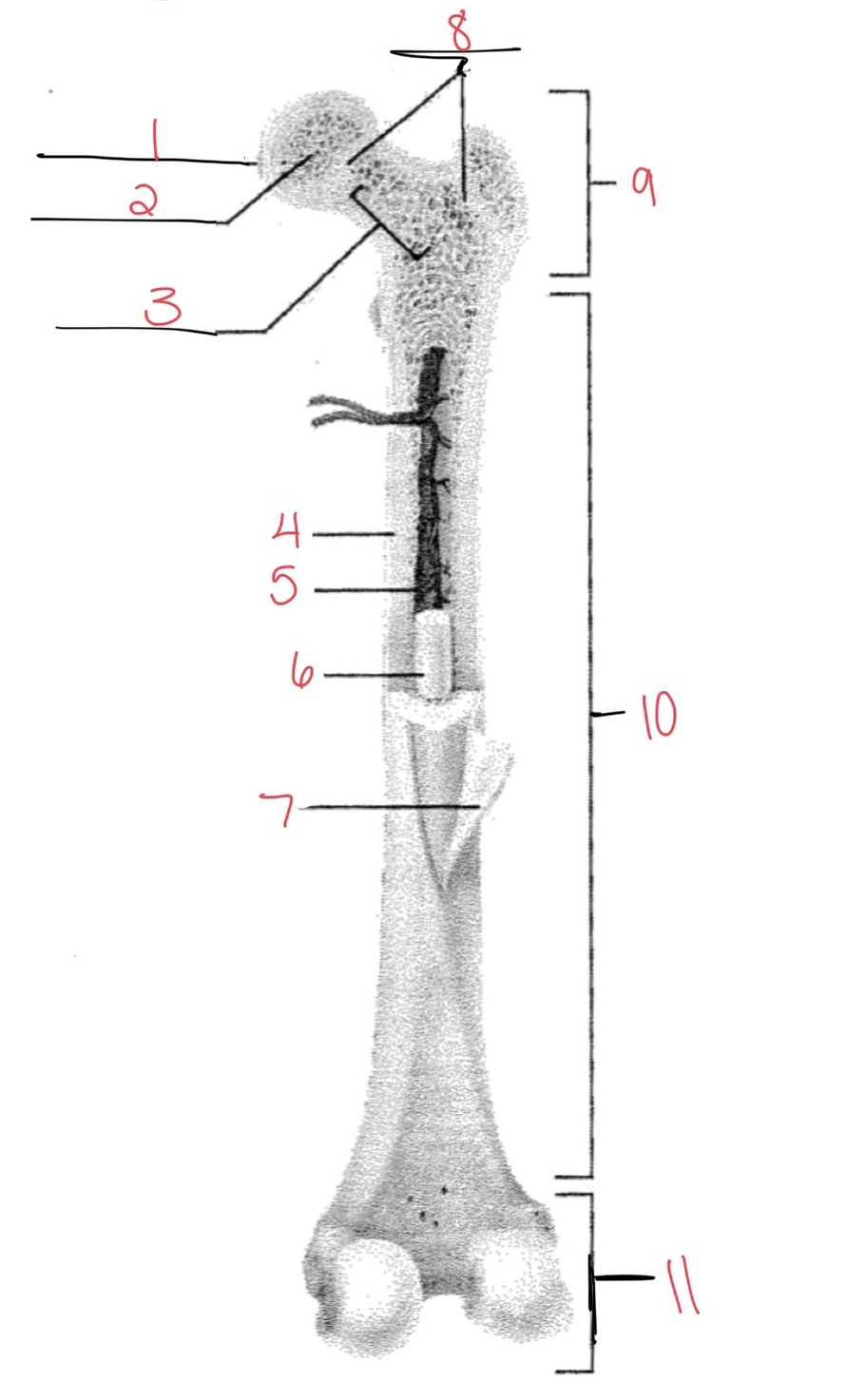
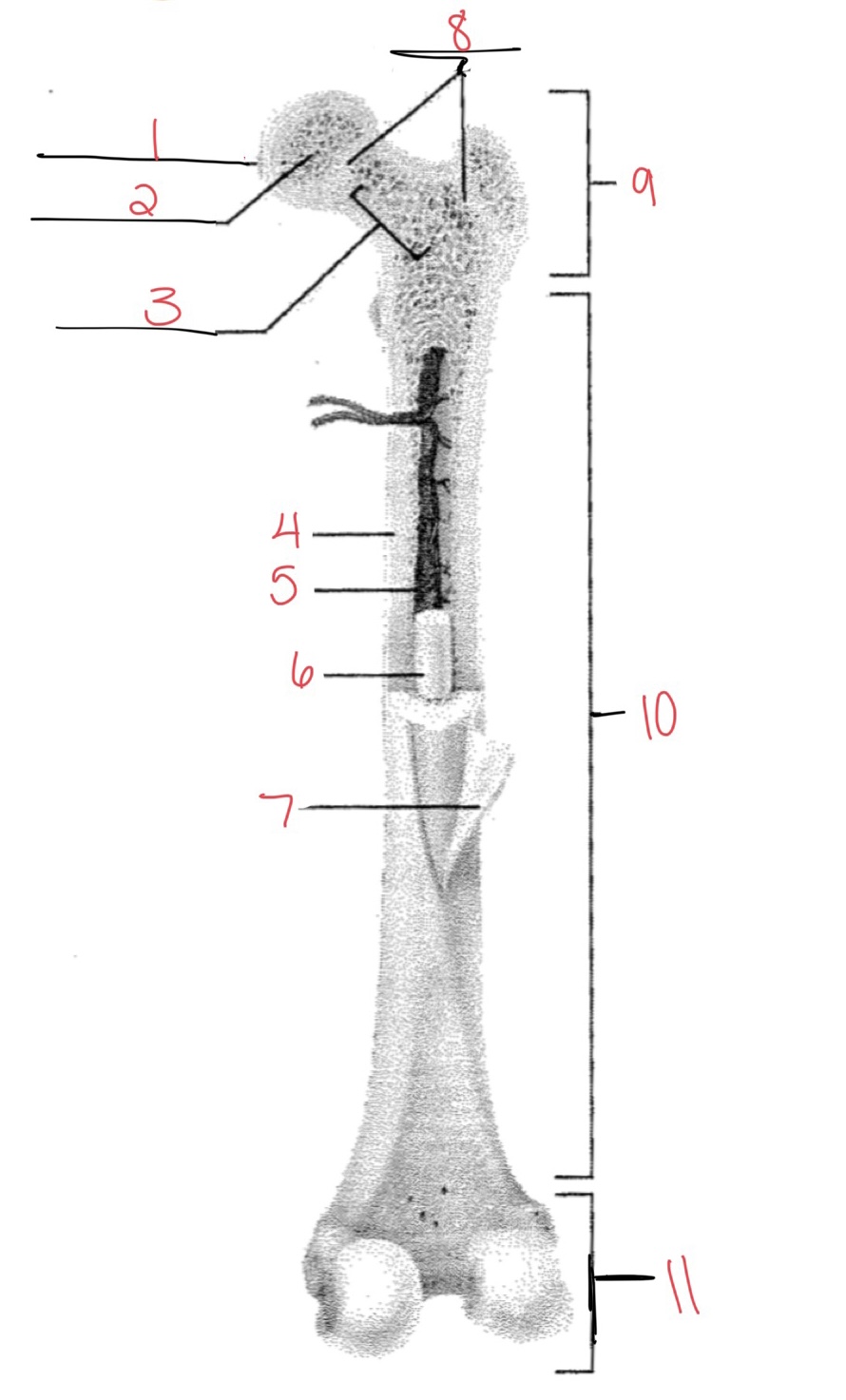
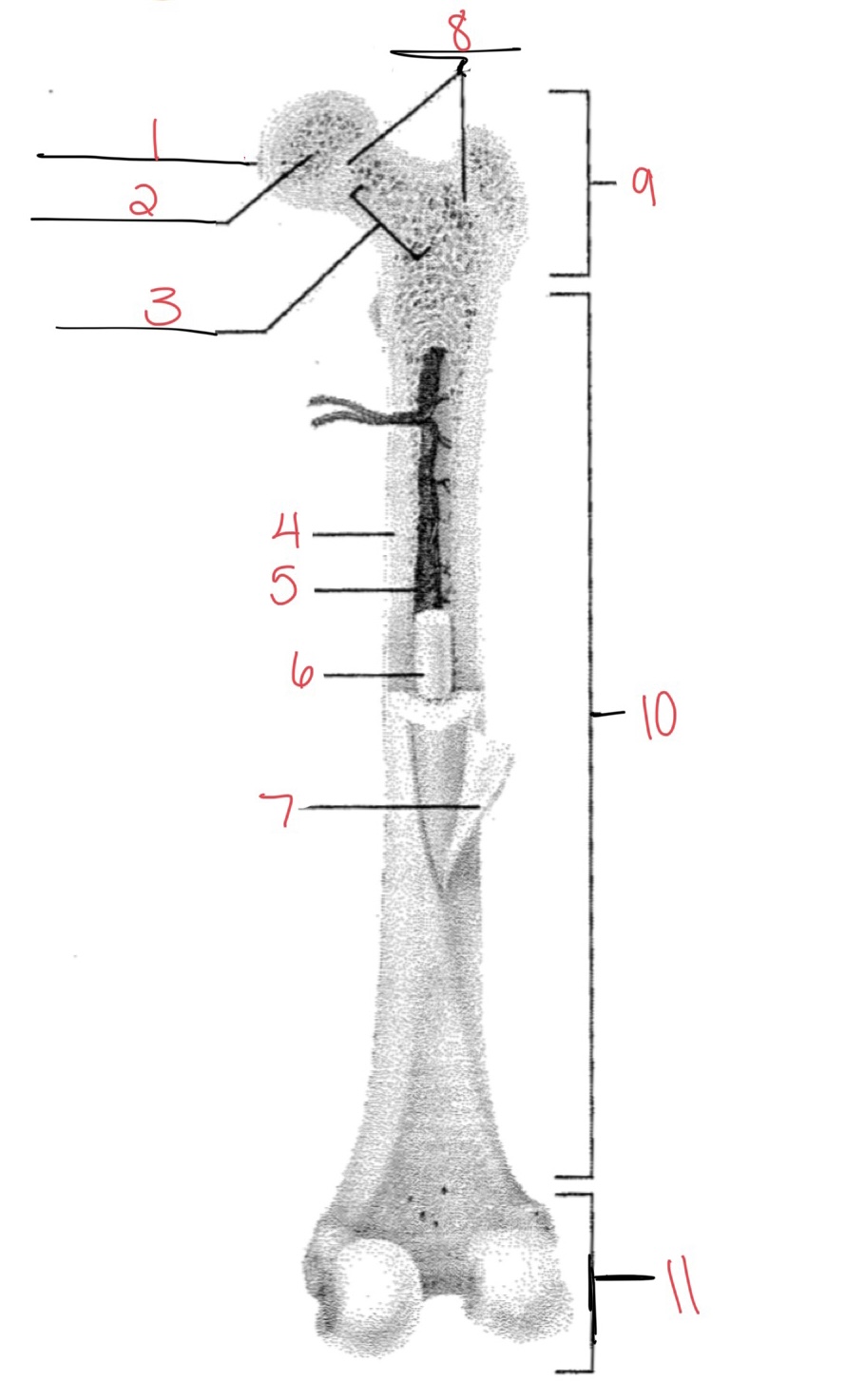
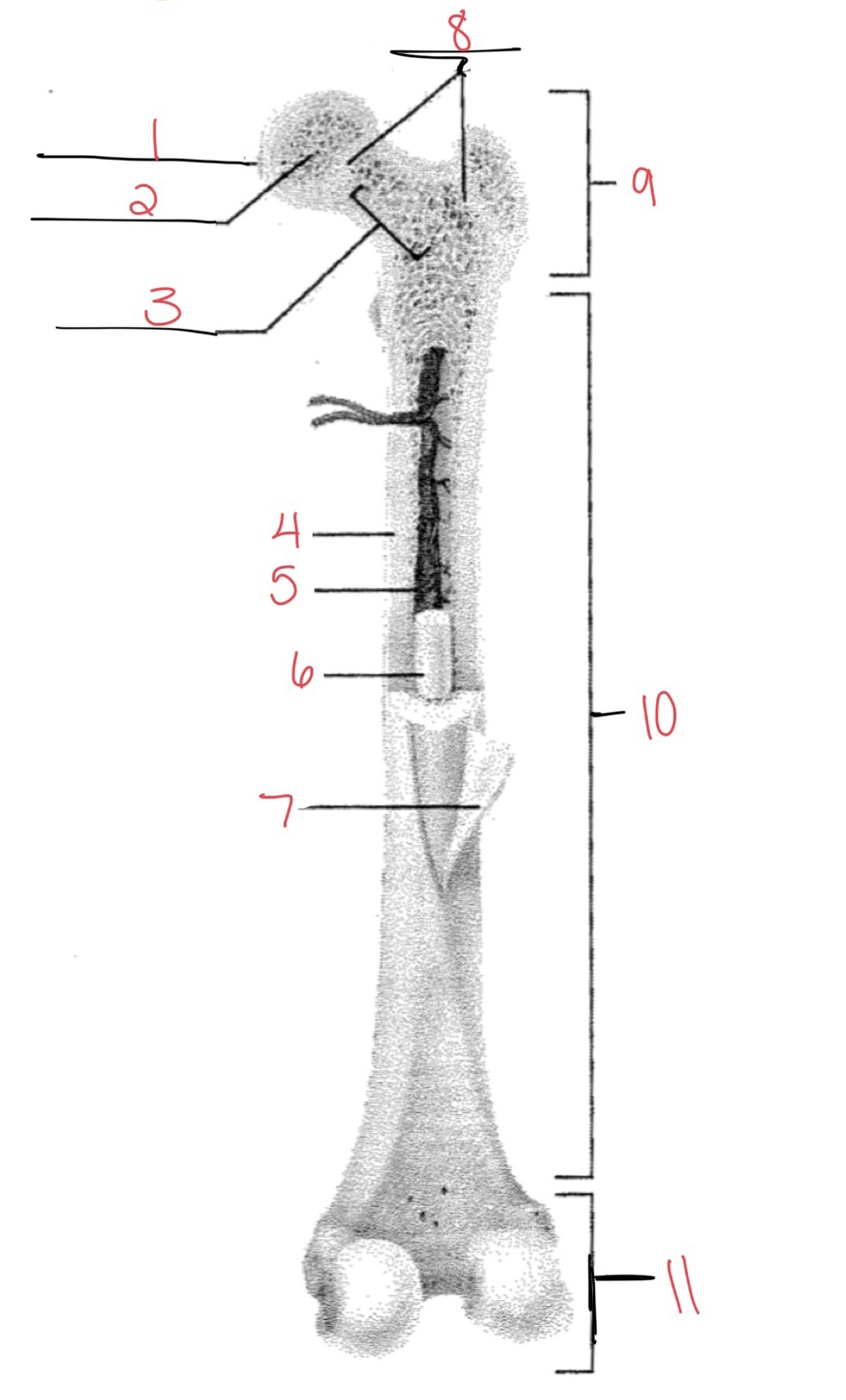
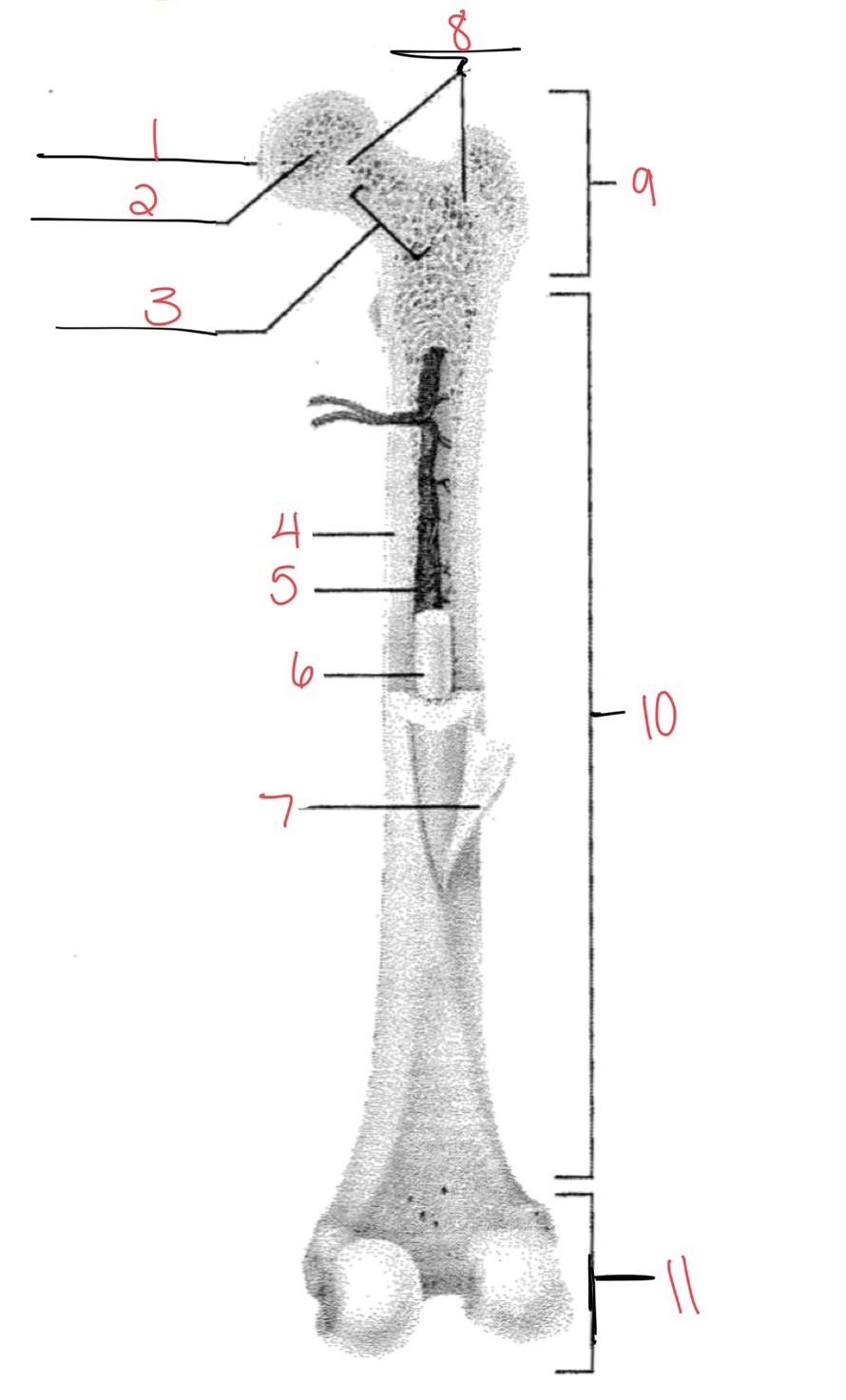
Whats at 1?
Articular cartilage
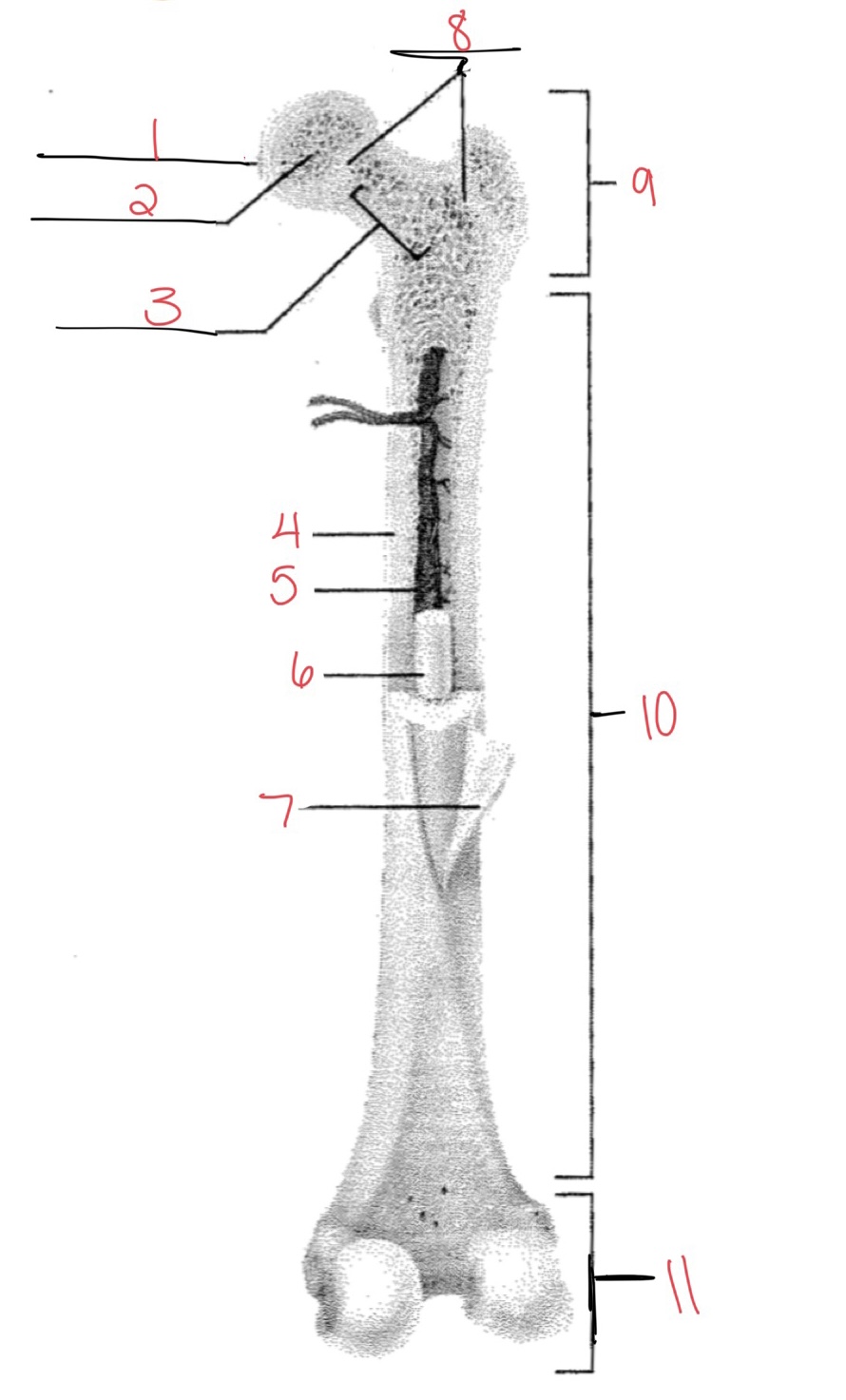
58
New cards
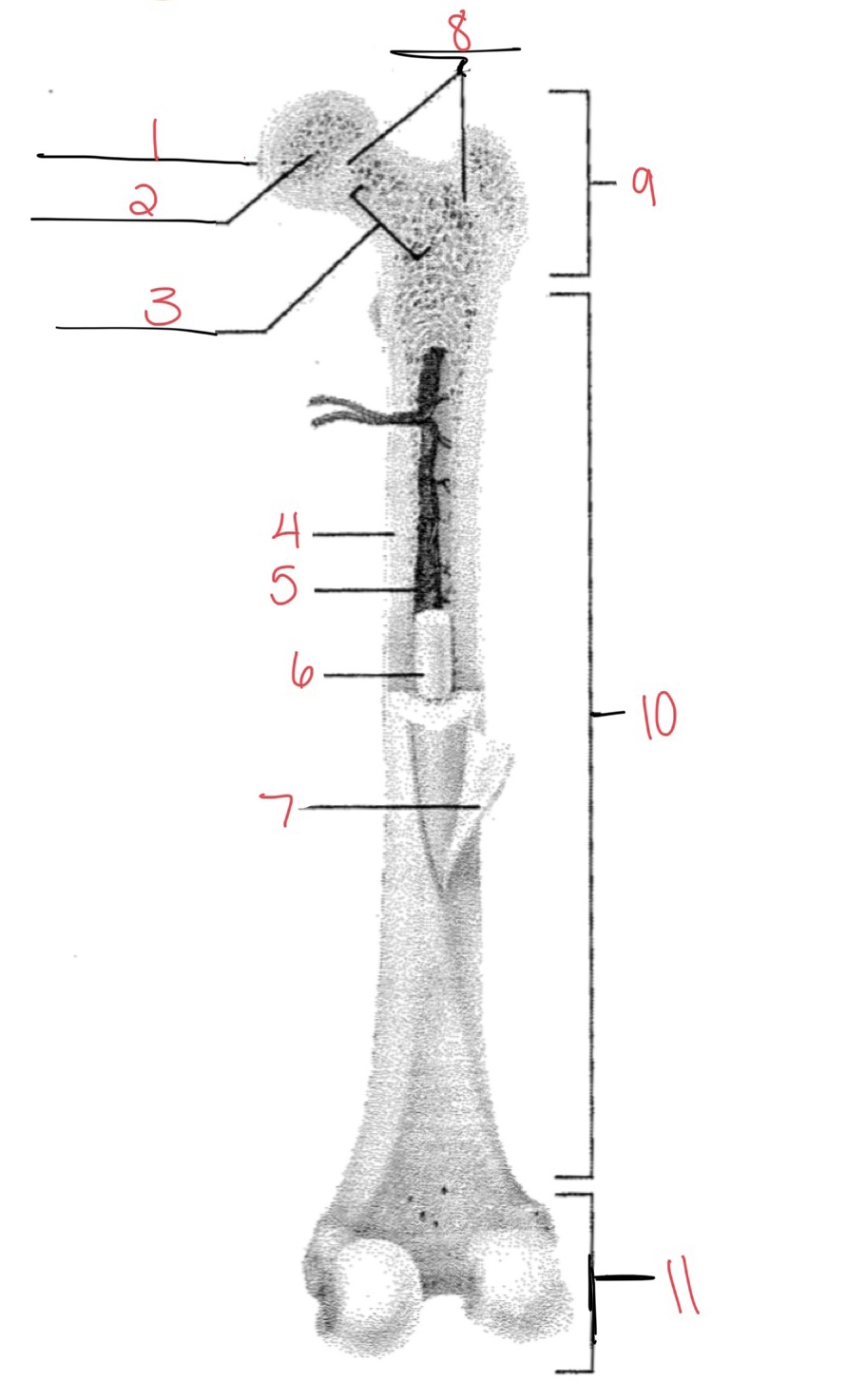
Whats at 2?
Spongy bone
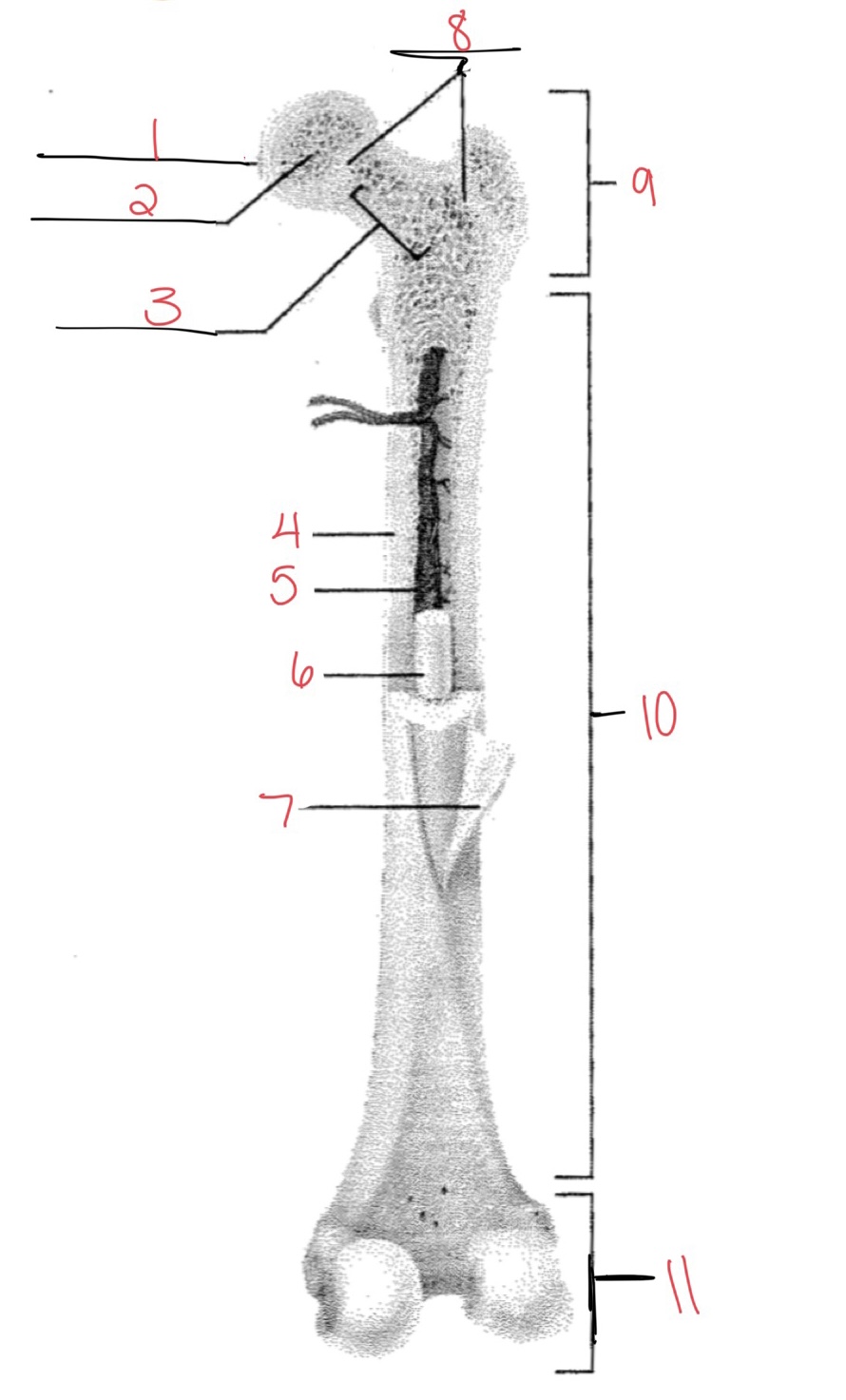
59
New cards
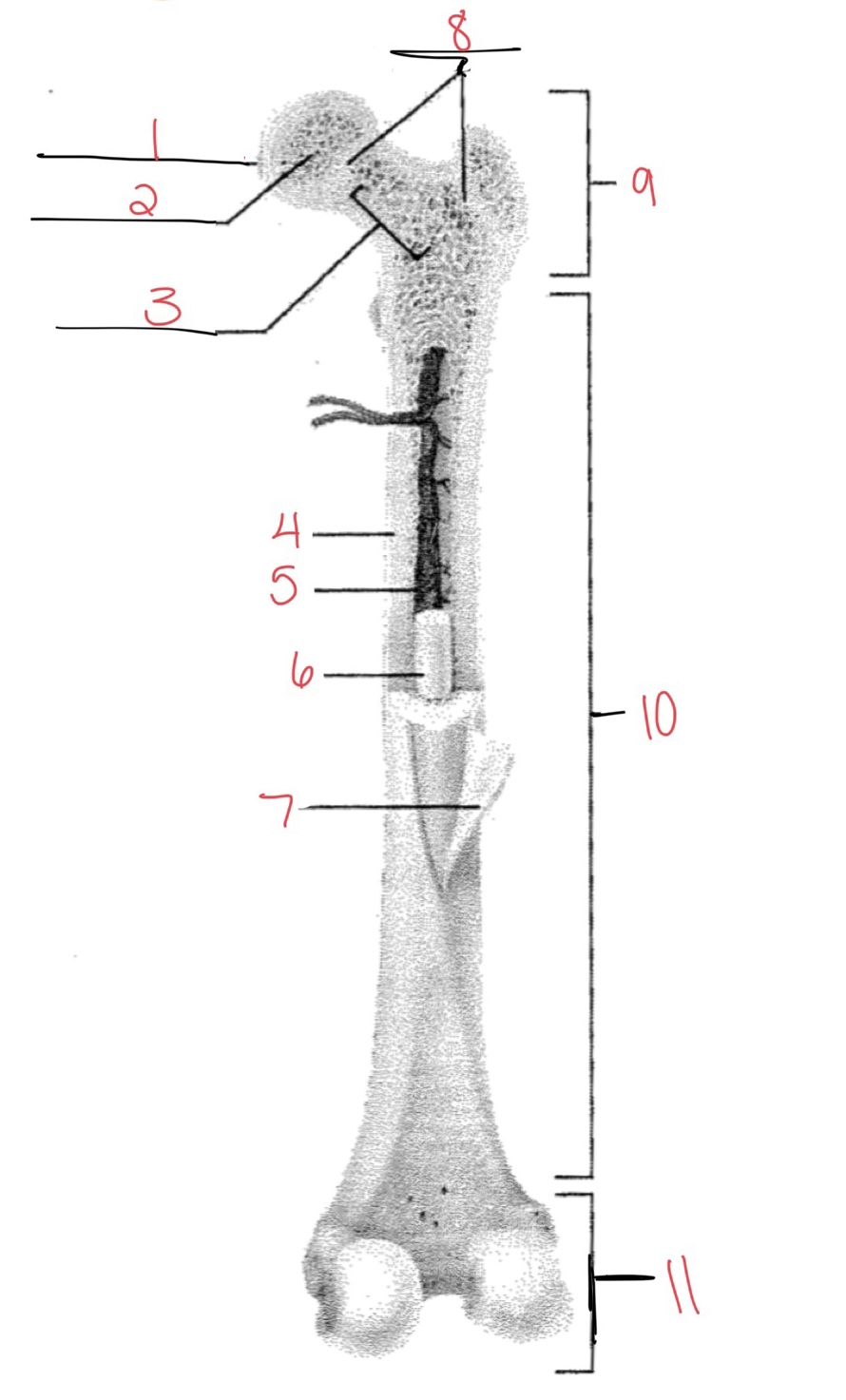
Whats at 3
Space with red marrow
60
New cards
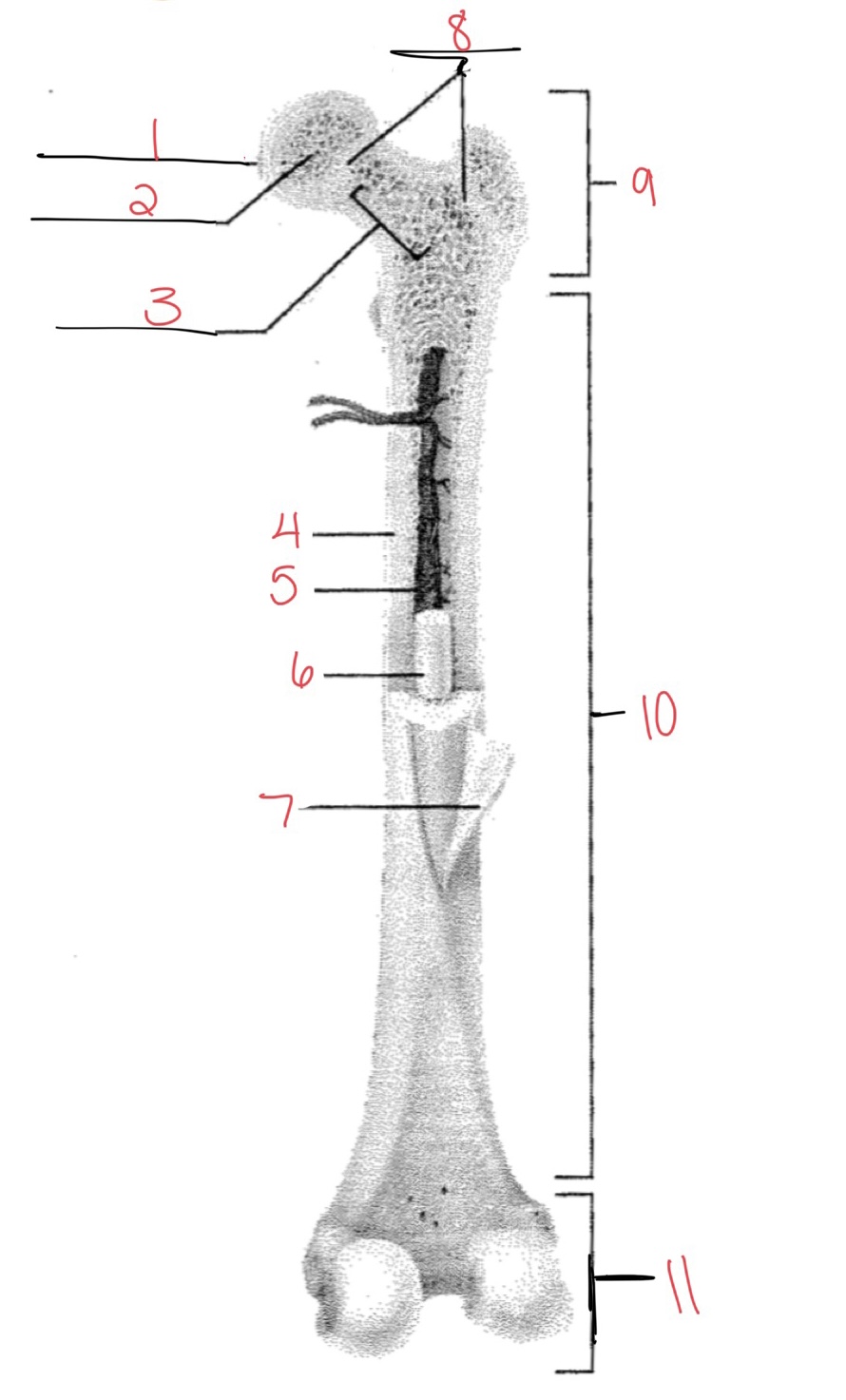
Whats at 4
Compact bone
61
New cards
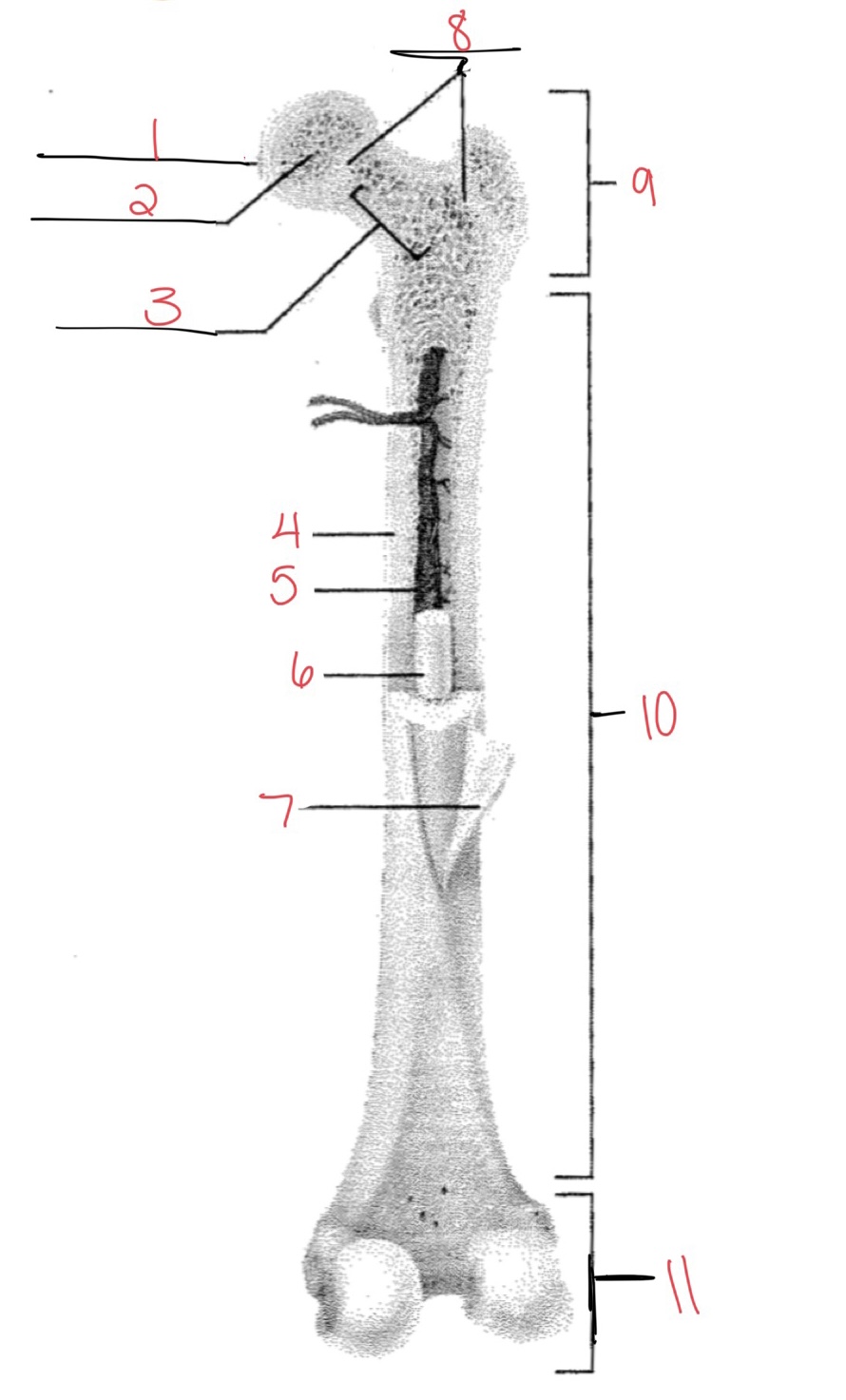
Whats at 5
Medullary cavity
62
New cards
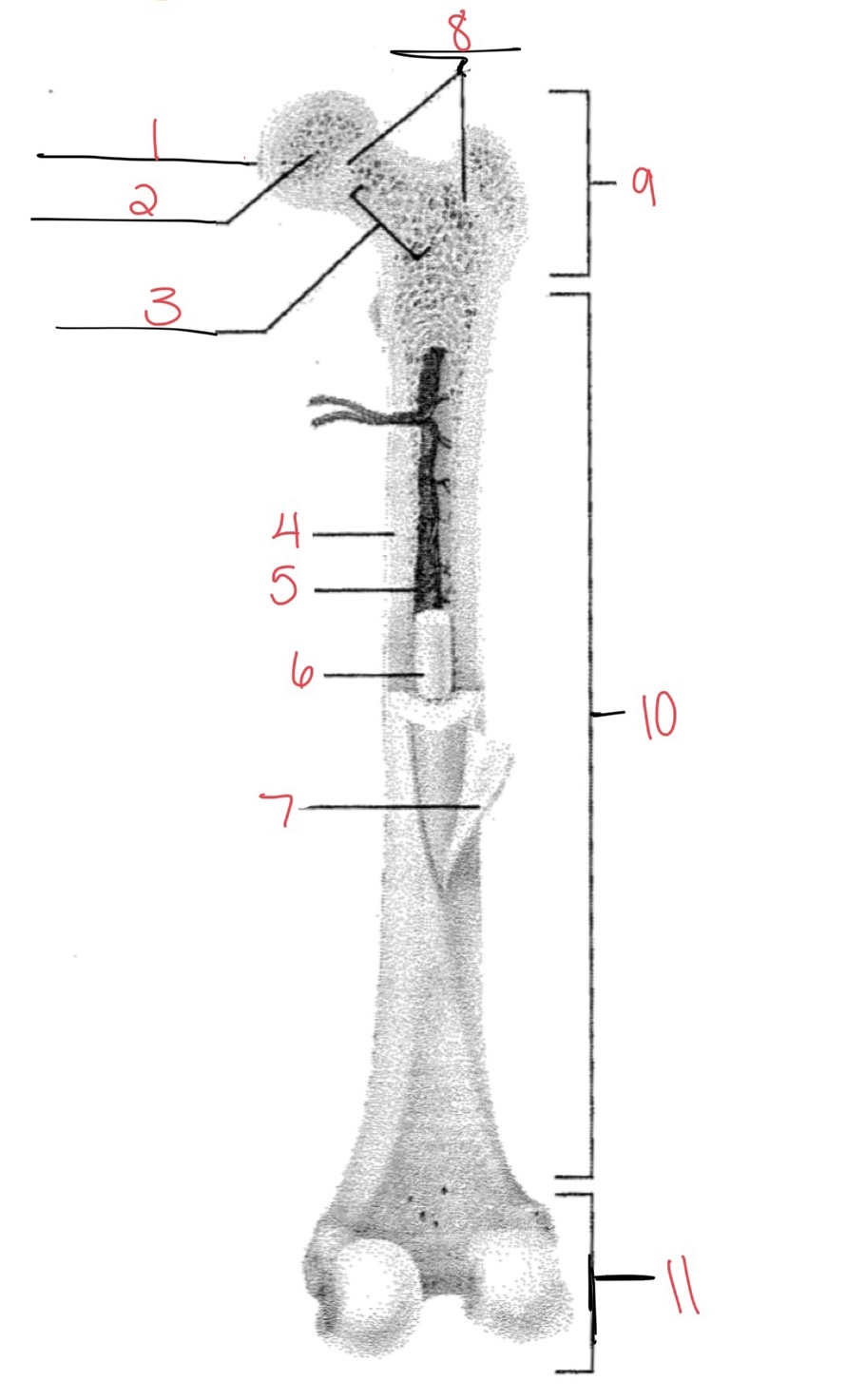
Whats at 6
Yellow marrow
63
New cards
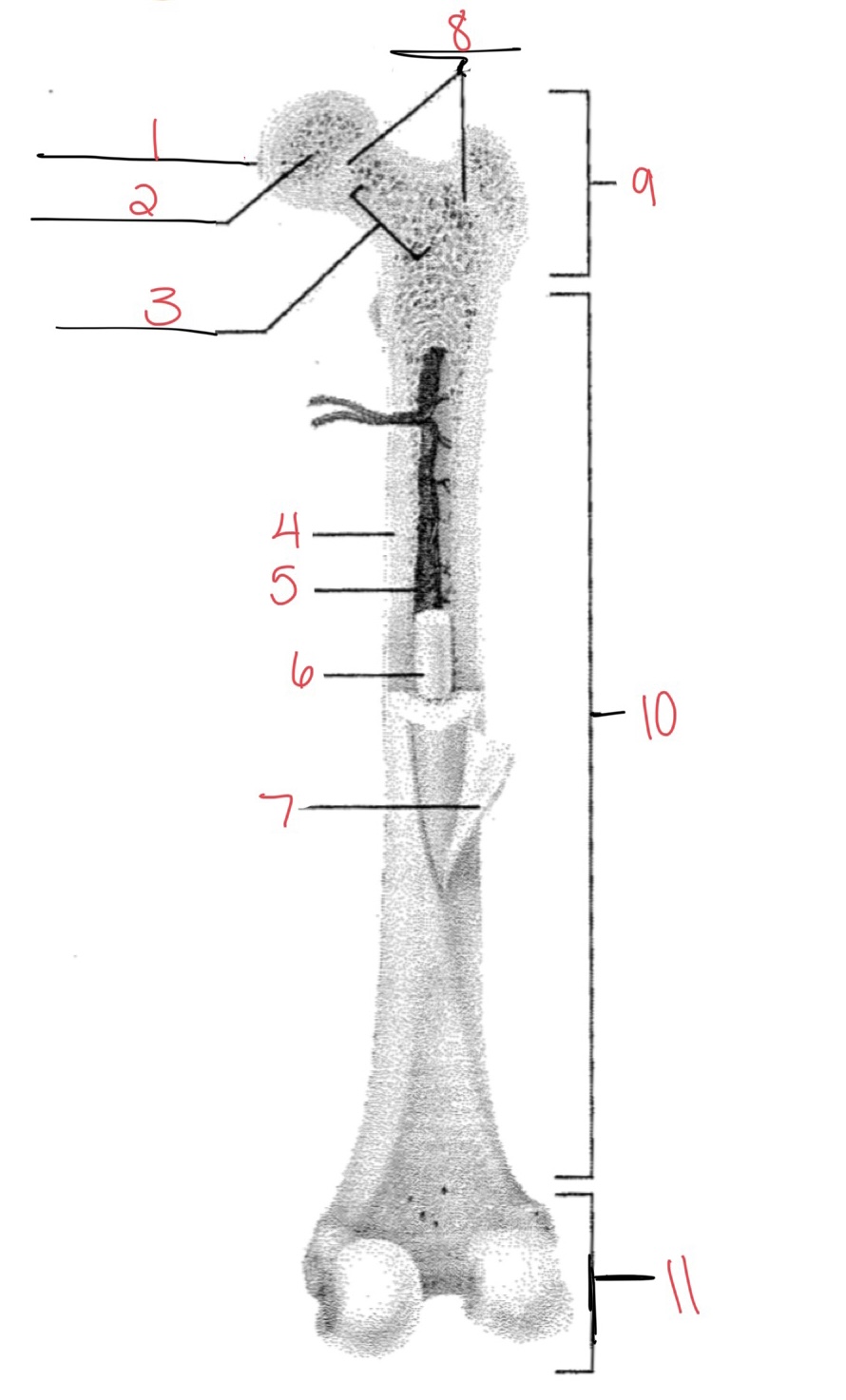
Whats at 7
Periosteum
64
New cards
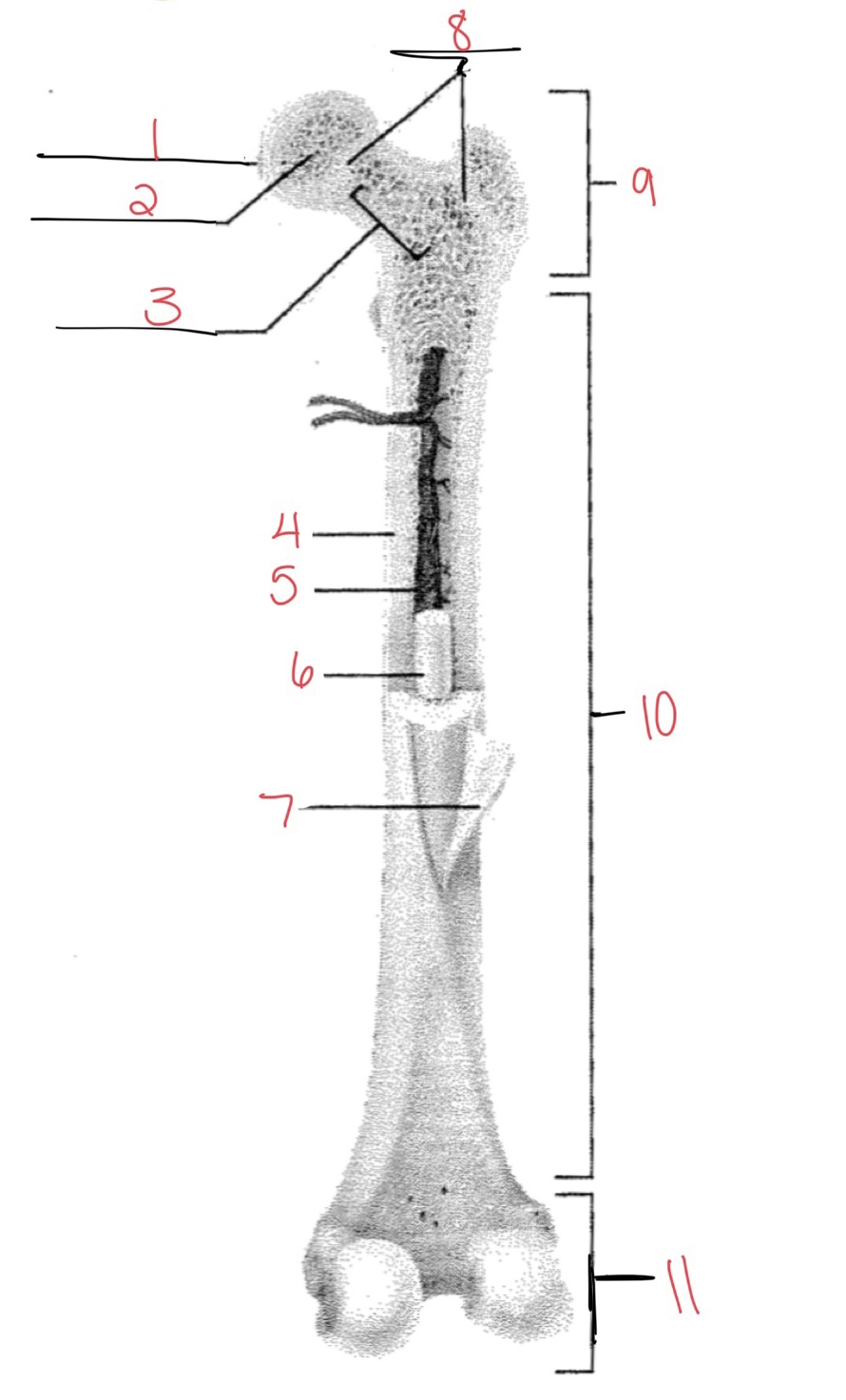
Whats at 8
Epiphyseal disk
65
New cards
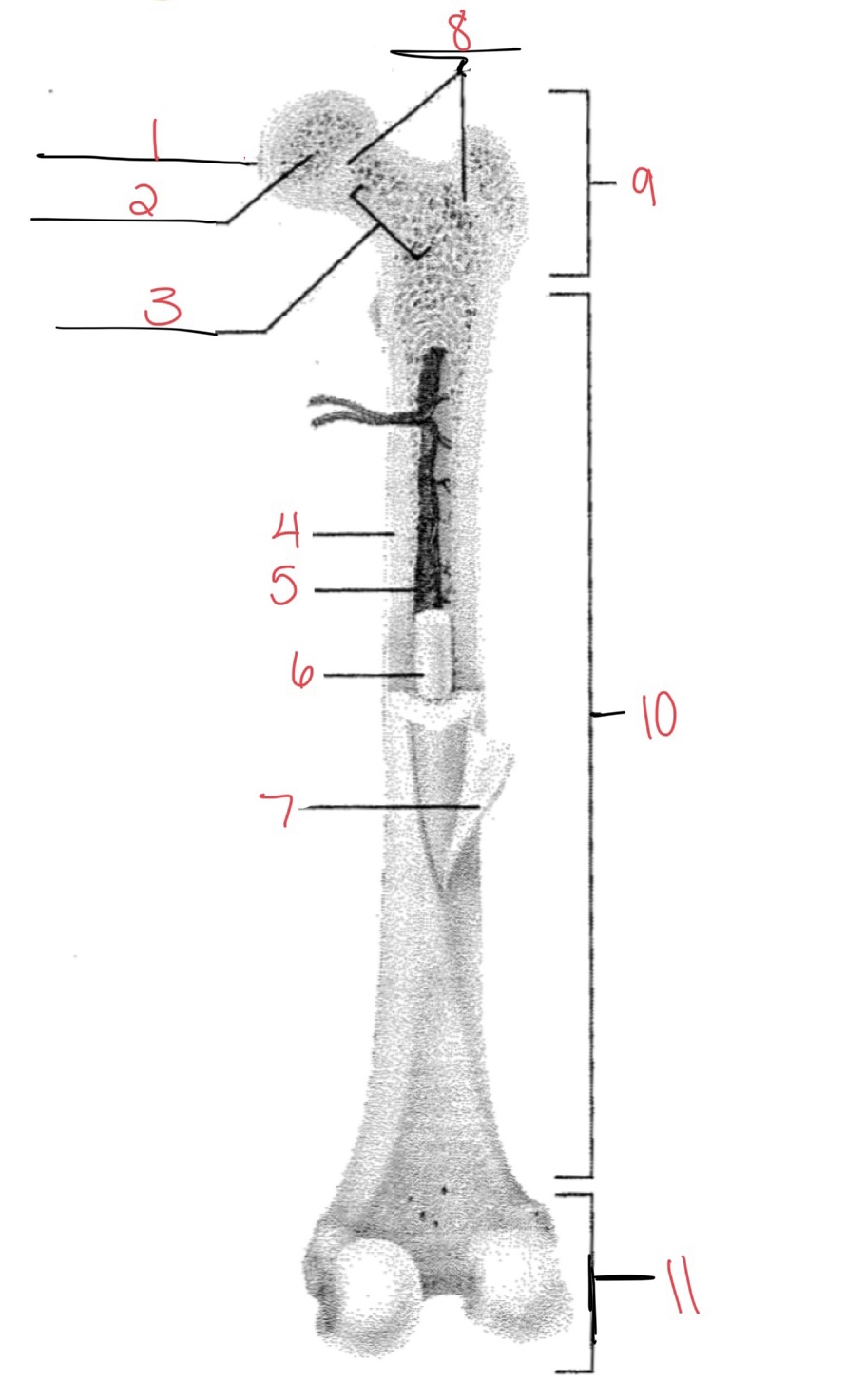
Whats at 9
Proximal diaphysis
66
New cards
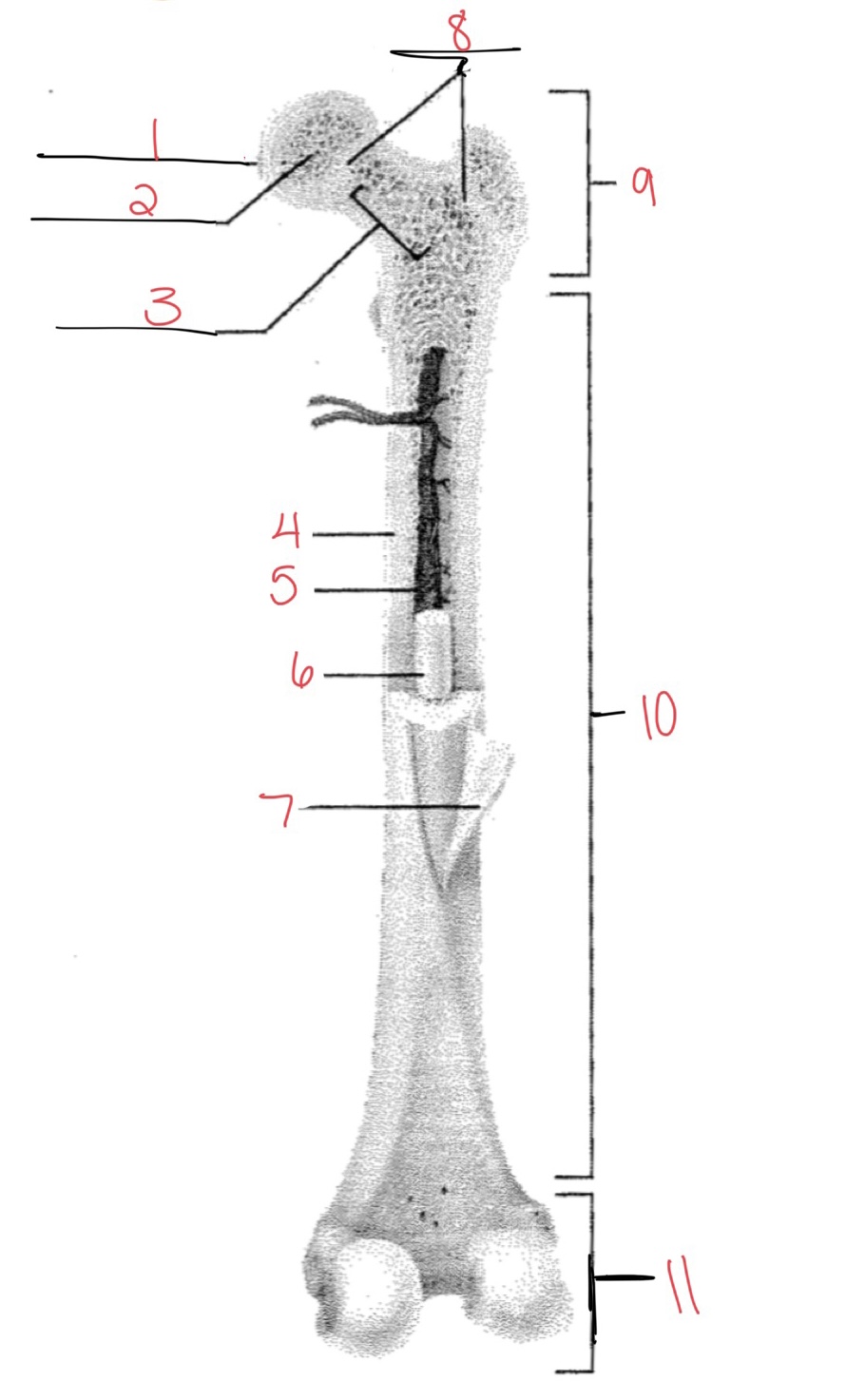
Whats at 10
Diaphysis
67
New cards
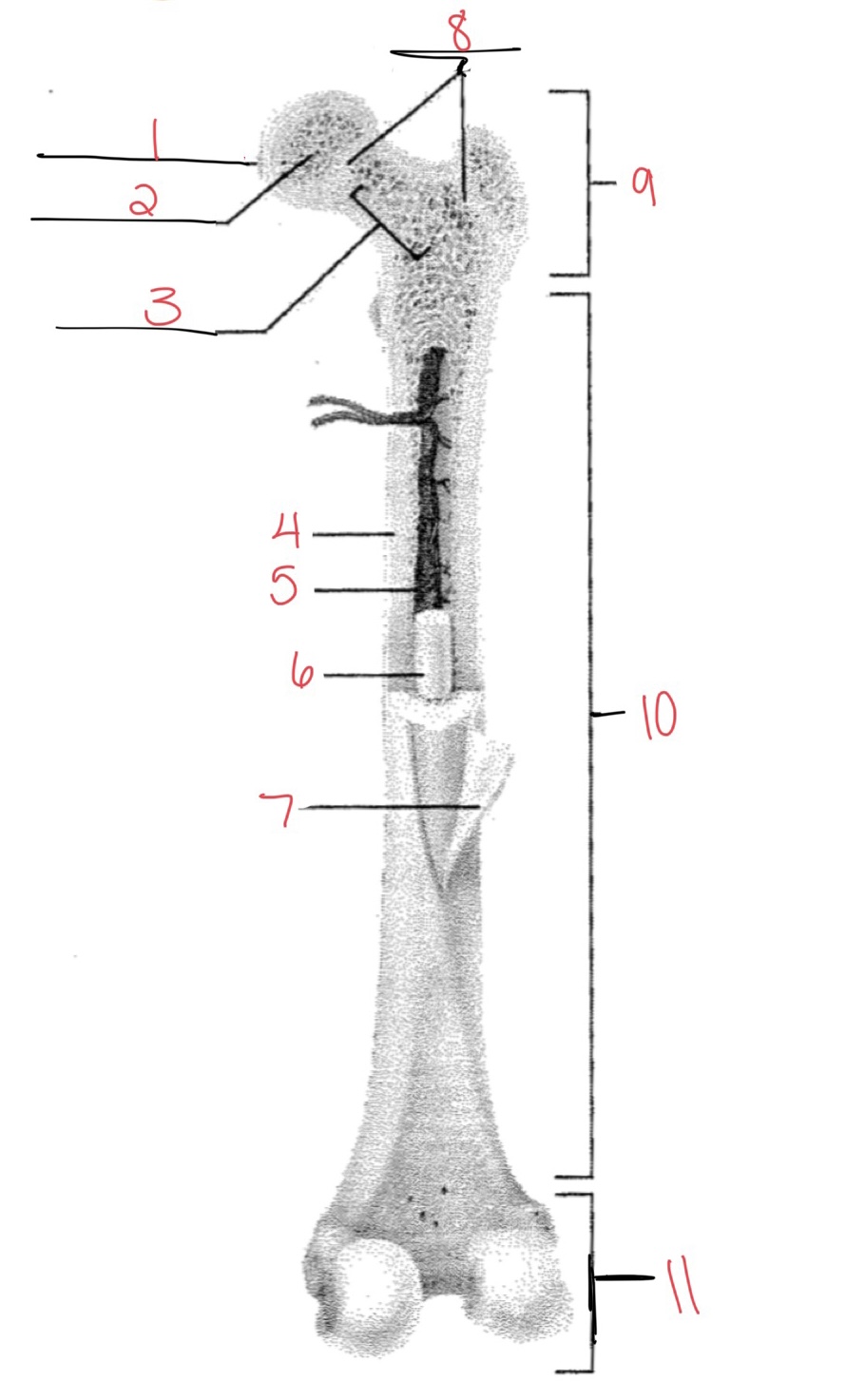
What’s at 11
Distal epiphysis
68
New cards
Scoliosis
Spine curves left or right
69
New cards
Kyphosis
Hunchback (too much curve in upper back)
70
New cards
Lordosis
Swayback (too much curve in lower back)
71
New cards
Spina bifida
Missing backbone, spinal chord is exposed
72
New cards
Incomplete fracture (green stick)
Not all the way through
73
New cards
Transverse fracture
Across the bone (straight through)
74
New cards
Oblique fracture
Angled fracture with sharp edge
75
New cards
Spiral fracture
Sharp point, spirals
76
New cards
Longitudinal fracture
Length of the bone (vertically), starts off small
77
New cards
Comminuted fracture
Breaks into pieces
78
New cards
Compound fracture
Bone outside of body (gangrene, shock)