AP Environmental Science Midterm Study Guide
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study this study set and you will slay your APES midterm!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
strategies used to reduce or eliminate pests through biological, cultural, or chemical practices.
Urbanization
an increase in the number of people living in cities and towns.
Charles Darwin
English researcher responsible for cementing the idea of evolution in the science field. Wrote the book “On the Origin of Species”.
Clear Cutting
a method of logging in which one area is rapidly and thoroughly cleared of all its trees at once.
Organic Farming
farming where the use of synthetic pesticides, GMO’s, and synthetic fertilizers are prohibited (NO,NO,NO).
Continental Plates
A type of tectonic plate; includes North America as well as the oceanic crust between it and a portion of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge.
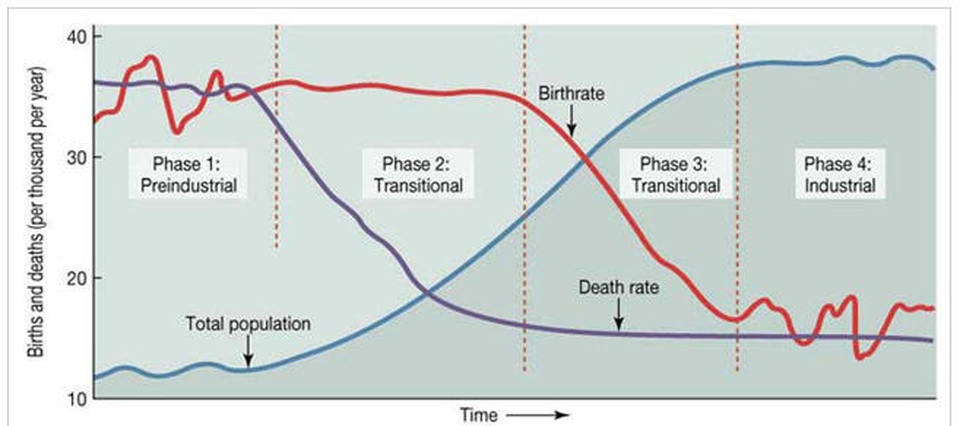
Demographic Transition Model
a model used to show the transition from high to lower birth a death rates in a country or region as development occurs and that country moves from a pre-industrial to an industrialized economic system.
Thomas Malthus
believed human population can outgrow food supply; result will be war, famine, disease.
Density Independent
any force that affects the size of a population of living things regardless of the density of the population; ex. wildfires or floods.
Developed Nations Characteristics
Countries that exhibit characteristics such as having a lower fertility rate, being industrialized, and having a high GDP.
Natality
Birth Rate
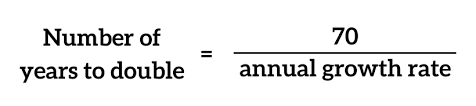
Rule of 70
used to determine the number of years it takes for a variable to double by dividing the number 70 by the variable's growth rate.
Ecology
The study of home.
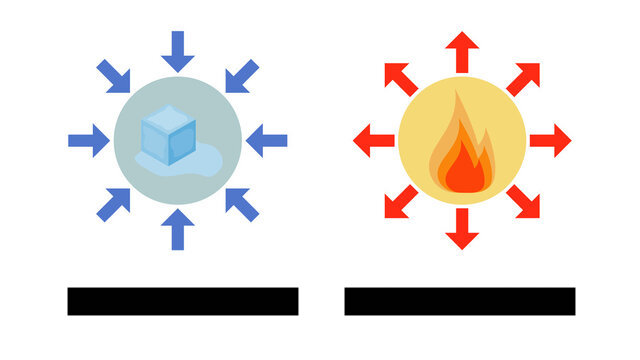
Ectothermic (Exothermic)
A chemical reaction that releases energy, usually in the form of heat.
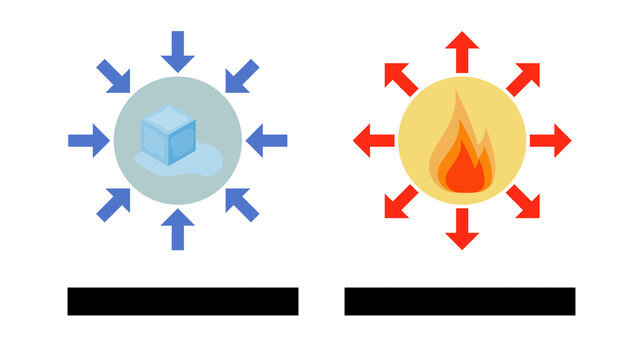
Endothermic
A chemical reaction in which energy is absorbed.
Environmental Science
The study of human impacts on the environment.
Mutualism
an interaction between individuals where both parties benefit.
Commensalism
an interaction between individuals where one party benefits and the other one is unaffected.
C.A.F.O.
places where animals are reared in a small space where the food is brought to them rather than allowing them to graze.
Exponential Growth
when populations grow at their intrinsic rate of increase (r) and are limited by resource increase by a fixed rate each year.
Wolves in Yellowstone
The reintroduction of a keystone species in Yellowstone National Park. Rebalanced elk and deer populations, allowing the willows and aspen to return to the landscape.
The Haber Process
A process that combines N2 (nitrogen) gas from the air with H2 (hydrogen) gas derived mainly from natural gas (methane) into ammonia.
(Cellular) Respiration
The process by which cells convert glucose and oxygen into energy, carbon dioxide, and water.
Formula : C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O (glucose + oxygen -> carbon dioxide + water).
Industrial Revolution
Transformed economies that had been based on agriculture into economies based on large-scale industry. As a result, there was an increase of fossil fuels.
Garret Hardin
Known for “The Tragedy of the Commons”
Infant Mortality Rate
the number of children that die before the age of one.
Spray Irrigation
A type of irrigation that disperses mist and water which results in a lot less water being lost to evaporation or runoff
Flood Irrigation
A type of irrigation that simply dumps water on the field of crops and allows it to disperse accordingly.
Furrow Irrigation
This Is a type of surface that uses trenches that are dug underground between rows of crops.
Drip Irrigation
This system is localized and uses an underground hose full of holes which dispenses water closest to the plant root.
ISLE ROYALE
Case study showing the relationship between the Moose and the Wolf.
Lamprey
Parasitic fish usually found in the Great Lakes.
Limiting Factors in a Population
Food, water, living space, disease, predation, and natural disasters are all examples of…
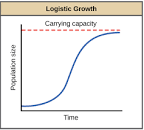
Logistic Growth
Population’s growth rate increases until it reaches a “Carrying Capacity” and levels out.
R.I.F.A. (Red Imported Fire Ant)
ant species originally native to South America, and has now spread throughout the whole world.
Developing Nations Characteristics
Countries that exhibit characteristics such as having a high fertility rate, having low access to contraceptives, and having a low GDP.
Density Dependent
Those where the size/density of the population will influence an individual's probability of survival, these tend to be biotic factors. Examples, are disease and competition.
Paris Green
A man-made poison developed in 1867 that controlled the potato beetle.
Oceanic Plates
Plates that are located beneath the ocean.
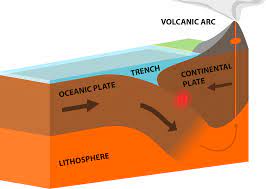
Convergent Boundaries
Two tectonic plates are moving towards each other. The Pacific Ring of Fire is an example of this type of boundary.
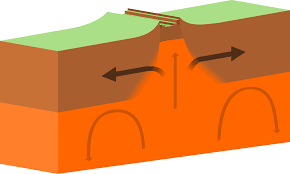
Divergent Boundaries
Two tectonic plates are moving apart from each other.The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is an example of this type of boundary.
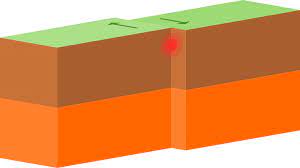
Transform Boundaries
Two tectonic plates slide past each other. The San Andreas Fault and Queen Charlotte Fault are examples of this type of boundary.
Aldo Leopold
He was an American writer, philosopher, naturalist, scientist, ecologist, forester, conservationist, and environmentalist. Known as the father of wildlife ecology and a true Wisconsin hero.
Morbidity
refers to the condition of suffering from a disease or medical condition.
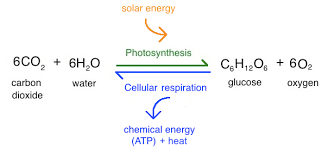
Photosynthesis
The process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy to chemical energy in the form of sugars.
Population Pyramid
A graphical illustration of the distribution of a population by age groups and sex.
Rachel Carson
Wrote the book “Silent Spring” which influenced major environmental movements and lead to tighter control of pesticides, including DDT.
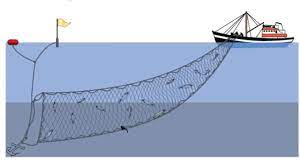
Drift Net
A large net for herring and similar fish, kept upright by weights at the bottom and floats at the top and allowed to drift with the tide.
Overgrazing
excessive grazing which causes damage to grassland.
Long Line
Thousands of hooks are attached to a main line that is stretched for as much as 50 miles in length.
Trawling
this destroys the natural seafloor habitat by essentially rototilling the seabed.
Pure siene
net that catches surface-dwelling species that tend to be in large schools like a purse.
Primary Succession
Succession that starts with an essentially lifeless area where there is no soil or bottom sediment in an aquatic area.