Theories of Personality: Introduction to Theories of Personality
Introduction to Theories of Personality
Personality is…
Relatively stable
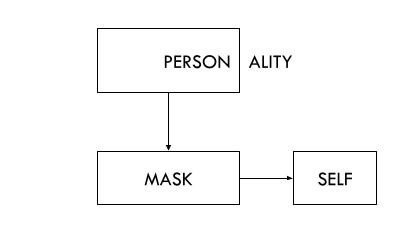
Persona
an archetype usually used in the arts
your public personality
Ex. hero archetype = Superman; villain archetype = Joker
“Mask”
Identity
The capacity to be aware of ourselves as separate entity
from Erich Fromm; humanistic psychoanalysis
Traits
basic units of personality (Gordon Allport)
Trait researchers attempt to define personality in terms of stable and enduring behavior patterns
Big 5 (OCEAN)
openness to experience, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness, neuroticism
Portrayal of self
Center of psyche
Represents our striving for unity of opposing forces
Considered congruent with potentialities
Innate Factors that Influence Personality
Genetics
Although we do inherit our genes, we do not inherit personality in any fixed sense
Temperament
they can be influenced by an individual's family, culture or their experiences
Biological make up
biological factors include genetic, hereditary factors, physical appearance and physique and rate of maturation
Nature
nature vs nurture
One's personality is shaped by a combination of nature (genetic) and nurture (environmental) influences
External Factors Influencing Personality
Experiences (childhood), relationship, culture, religion, race, environment, nationality
Type vs Trait
Type:
Categorizing
Dominant
Preferences
Can change over time
Trait:
Might lessen/grow but will not change
More enduring
More consistent
Ideographic vs Nomothetic
Idiographic
individual/unique characteristics
Center core of the person
“idios”: Greek word meaning own or private
Nomothetic
Commonalities
Bigger picture
“nomos”: Greek word meaning law
compares individuals in a bigger scale (in terms of traits or dimensions common to everyone)
Assessment
Techniques to know what a person is like
Clinical Interview
Interviews, conversations, can be structured/unstructured (demographics, childhood history, diagnosis, life experiences, hobbies, lifestyle, difficulties)
Standardized questionnaires (mostly Western)
Behavioral Observations
Naturalistic
Checklist, forms
Specific behavioral manifestations
Surveys
Personality Tests
Self-report inventory/rating scale
Ex. MBTI
Objective:
More reliability
Paper and pen test
Ex. MMPI, NEO PI
Subjective:
Unstructured test
Stimulus but response is open-minded
Ex. Sentence completion test, Rorschach inkblots, Thematic Apperception Test
Dimensions
Framework for looking at different theories
Free Choice vs Determinism
revolves around the extent to which our behavior is the result of forces over which we have no control or whether people are able to decide for themselves whether to act or behave in a certain way
Free Choice
Free will
Ex. Maslow (self-actualization)
Determinism
Pre-determined
Learned behavior
Pessimism vs Optimism
Pessimism
negative view in life
Ex. Freud
Optimism
positive view in life
Possibility for change
Causality vs Teleology
Causality
Past experiences affect who you are
Ex. Freud, Skinner
Teleology
What they can do in the future
Ex. Rogers (humanistic)
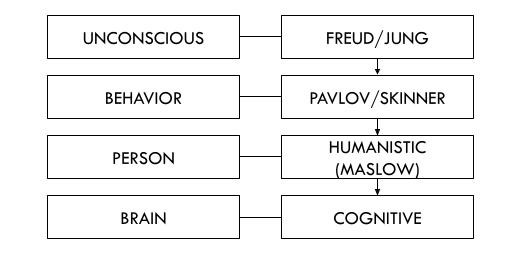
Conscious vs Unconscious
can be defined as two distinct but overlapping systems of learning and memory
Conscious
we are fully aware of what is going on in the conscious mind
Unconscious
a reservoir of feelings, thoughts, urges, and memories that are outside of our conscious awareness
Ex. Freud, Jung
Determinants of behavior
Biological vs Social Influences
Biological
Genetics (nature)
Social Influences
Environment (nurture)
Uniqueness of a Person vs Similarities to Others
Personality Theories
Psychodynamics
an approach to psychology that emphasizes systematic study of the psychological forces underlying human behavior, feelings, and emotions and how they might relate to early experience
Ex. unconscious motivation, childhood experiences
Humanistic
a perspective that emphasizes looking at the the whole person, and the uniqueness of each individual
Ex. self-actualization, self-worth
Cognitive Social
personality is shaped by interacting social factors, cognitive factors, and behavior
Ex. learned behavior, traits, personality
Trait
people are different from one another based on the strength and intensity of basic trait dimensions
Ex. characteristics, types