Principles of Economics Final Exam Review
1/31
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
How did the Employment Act of 1946 change the responsibility of the federal government?
Prior to this law, the govt. didn’t attempt to fix an unhealthy economy, the government didn’t take any responsibility for the economy.
What are the 5 factors that affect GDP Growth Rate?
Population growth
Labor force participation rate
Output per worker
Capital per worker
Technology and innovation
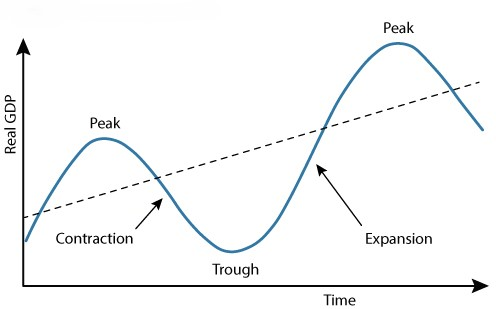
What does this graph represent?
The business cycle
What are the 4 types of unemployment?
Frictional
Structural
Seasonal
Cyclical
What is frictional unemployment?
People in between jobs which include recent college grads
What is structural unemployment?
People who lack skills that firms seek
What is seasonal unemployment?
People whose jobs depends on the time of the year
What is cyclical unemployment?
People who lose their job due to a recession
What are the 5 flaws with how inflation is measured?
It is a weighted average
It is only updated every 10 years
There are no regional items
No adjustment for quality improvement
Ignores substitutional effect
What is the difference between expansionary and contractionary fiscal policy?
Expansionary policy is used during a recession to encourage economic growth (ex. Increase in govt. spending and decrease in taxes) while contractionary policy is when inflation is high to slow economic growth (ex. decrease in govt. spending and increase in taxes)
What are the 5 potential problems from using fiscal policy?
Timing problem to estimate a peak or trough
Congress takes 9 months to pass a law on average.
After policy change, it takes 18-24 months to affect the whole economy
Must estimate the size of change needed
Politicians bias for always using expansionary policy.
How do automatic stabilizers smooth-out the business cycle?
Include all social programs; If people qualify, then they get the benefit.
During a recession, more people qualify, so then govt. spending increases without a new law.
During a recovery, less people qualify, so govt. spending decreases without a new law they avoid all the problems with fiscal policy.
What are the 3 measures of the fiscal balance?
Actual budget balance is govt. revenue minus govt. expenditures
Structural balance removes automatic stabilizers from actual balance
Primary structural balance subtracts national debt from structural balance
What are the 3 types of inflation?
Demand, cost, and built-in.
What is demand inflation?
When an increase in money supply and easy credit raises demand faster than production capacity.
What is cost inflation?
Is when a cost of production increases or a negative supply shock.
What is built-in inflation?
When people expect current rate to continue and they demand a higher pay raise.
What are 5 reasons that inflation is bad for the economy?
Erodes purchasing power
Causes more inflation
Can cause stagflation
Weakens US dollar
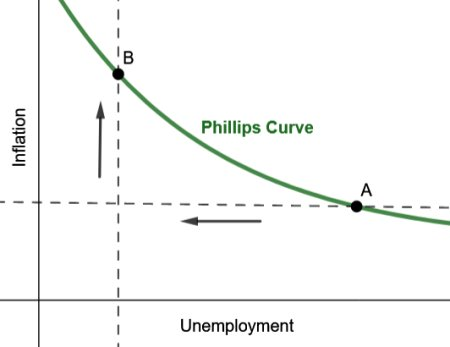
What does this other graph represent?
The original Phillips curve
What is the difference between hyperinflation and deflation?
Hyperinflation is when inflation is out of control; Some say 50%/month or more and others say $1,000/yr or more while deflation is when the inflation is negative which also causes issues regarding recession, slow growth, and high unemployment.
Business cycle
A pattern of irregular but repeated expansion and contraction of aggregate economic activity.
Inflation rate
A sustained increase in the average level of prices of all goods and services.
Unemployment rate
A percentage of the labor force that is unemployed.
Gross domestic product
A measure of the value of total output of goods and services produced within a country.
The value at current market prices of all final goods and services produced annually in a given country.
Cost of Living Adjustment (COLA)
When inflation is low, wages here are low, vice versa. This is supposed to help with purchasing power; All employees get the same percentage.
Fiscal policy
Policy that is concerned with government purchases, taxes, and transfer payments.
Continuing resolution
A temporary spending bill in case the government gets shut down due to no budget being presented.
Mandatory spending
Social security, Medicaid, unemployment compensation, free school lunch, welfare, food stamps, section 8 housing; This makes 60% of the federal budget.
Structural balance
Actual budget balance (automatic stabilizers)
PAYGO
No new spending in federal budget without an equal cut in spending somewhere else in the budget.
Discretionary spending
Can be changed from year to year; Makes up 40% of the federal budget.
Primary structural balance
The structural budget balance adjusted to remove government net interest payments.