Biology- B1.1: Carbohydrates and Lipids
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
carbon
building blocks of life
forms 4 covalent bonds
can form numerous stable compounds
carbon-carbon bond
strong and stable
longer the c-c chain, the stronger the molecule
found in chain form, ring form, branch form
macromolecules
large molecules made up of smaller molecules called monomers
condensation reaction
specific monomers join together to form a macromolecule
polymerisation reaction
two monomers join together
one releases the hydroxyl group (OH)
the other releases the hydrogen atom (H)
giving water and a disaccharide
condensation of glucose molecules
2 glucose molecules join together to form maltose
OH group of Carbon-1 and H atom of carbon-4 are released
resulting bond that links glucose molecules together is called a 1-4 glycosidic bond
hydrolysis reaction
process of breaking down macromolecules into monomers (reverse of condensation)
OH group of water joins to one of the monosaccharides and the H atom joins to the other to break them into individual monomers
monosaccharides
simplest form of a carb and can’t be broken down into simpler means by hydrolysis
fundamental biological molecules that:
serve as a source of energy for cells
are involved in various cellular processes
types of monosaccharides
classified by number of carbon atoms
pentose: 5 C atoms-ribose
hexose: 6 C atoms- glucose, fructose, galactose
properties of glucose
most common monosaccharide found in nature
soluble (polar)
stable
can be oxidised
2 isomers (alpha-glucose and beta-glucose)
OH group below in alpha and above in beta
different isomers form different polysaccharides
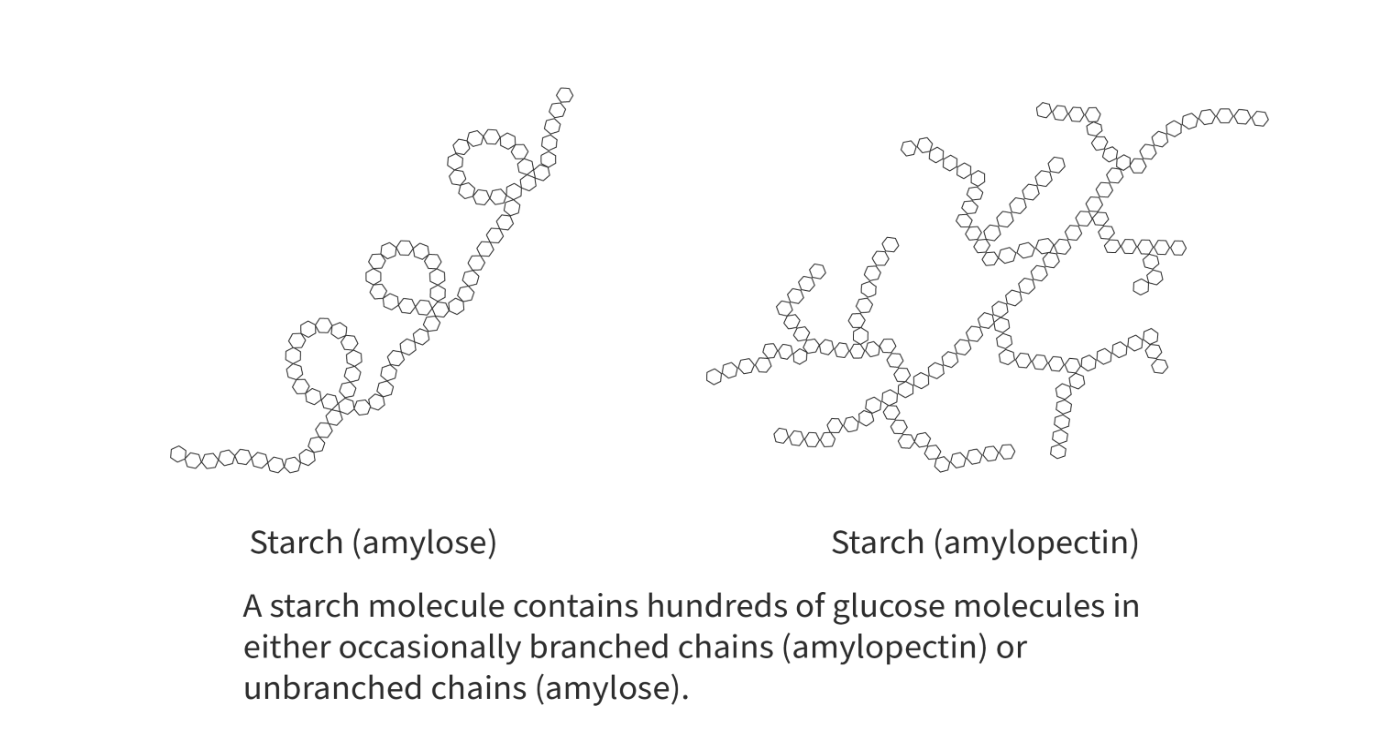
starch
composed of alpha-glucose molecules
serves as storage for glucose in plants
2 types: amylose and amylopectin
amylose: linear, 1-4 glycosidic bonds, coiled
amylopectin: highly branched, 1-4 glycosidic bonds with occasional 1-6 glycosidic bonds that create branches, major component (80%-85%)
glycogen
composed of alpha-glucose molecules
serves as storage for glucose in animals
stored mainly in the liver and muscle cells
branched, highly compact, coiled
1-4 glycosidic bonds, occasional 1-6 glycosidic bonds every 8-12 glucose molecules
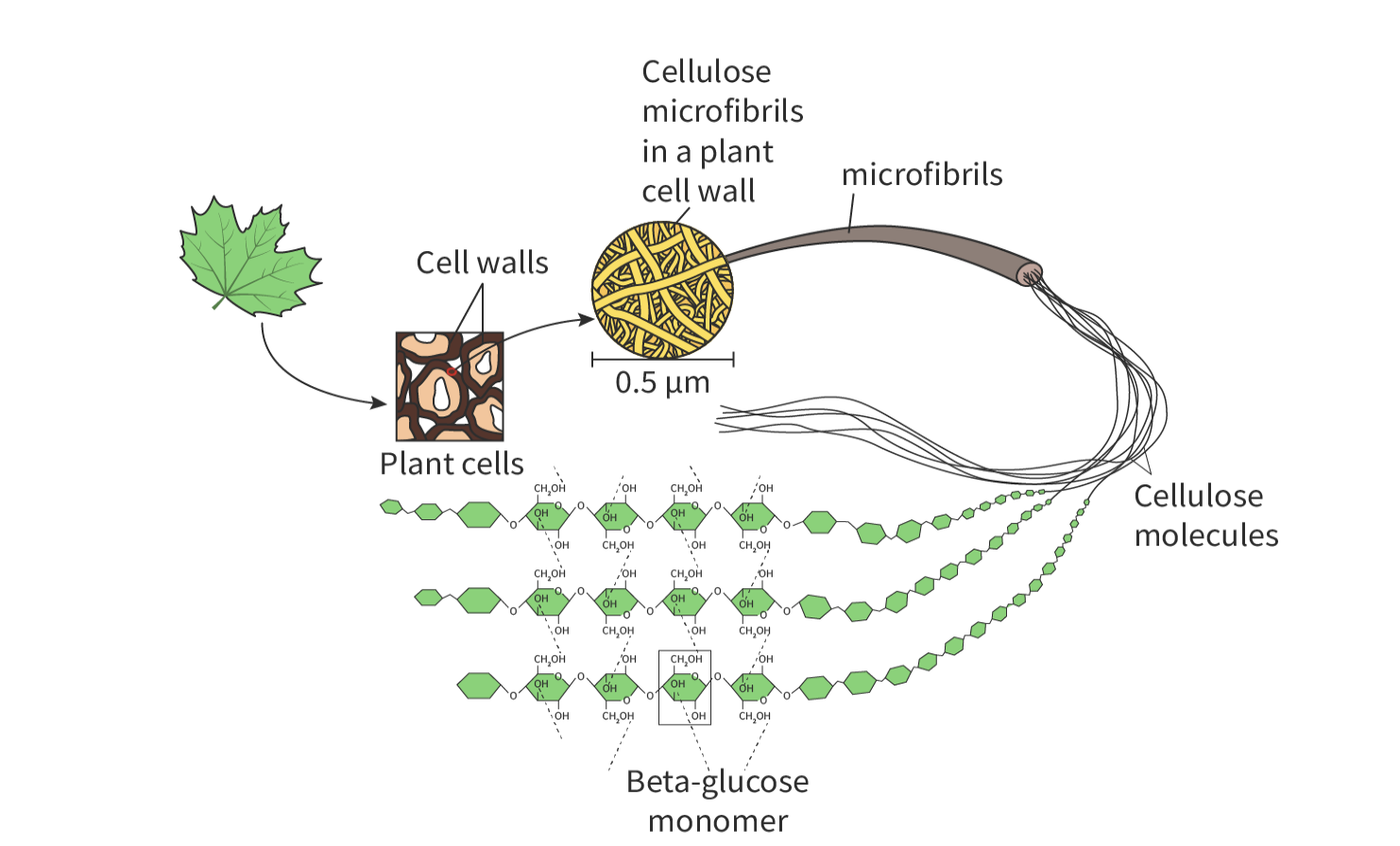
cellulose
composed of beta-glucose molecules
essential components of plants cell walls
forms a straight chain
long chains grouped into bundles called microfibrils
strong structure due to how chains are cross-linked
hydrogen bonds make the cellulose rigid due to forming a strong and stable lattice
glycoproteins
proteins that have one or more carbohydrates attached to them
found in many cellular structures, including the extracellular matrix, cell membranes and secreted proteins.
roles of glycoproteins
cell-cell recognition
receptors
ligands
structural support
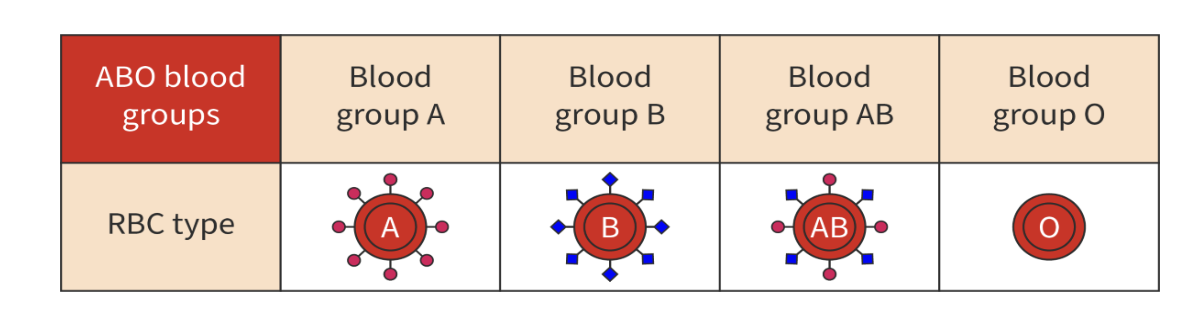
ABO blood groups
based on the presence of specific glycoproteins on the surface of red blood cells
called A and B antigens
presence or absence of antigens determines an individuals blood type
hydrophobic properties of lipids
non-polar molecules
low solubility in water
insoluble in aqueous solutions (hydrophobic nature causes them to repel)
lipids dissolve in non-polar solvents
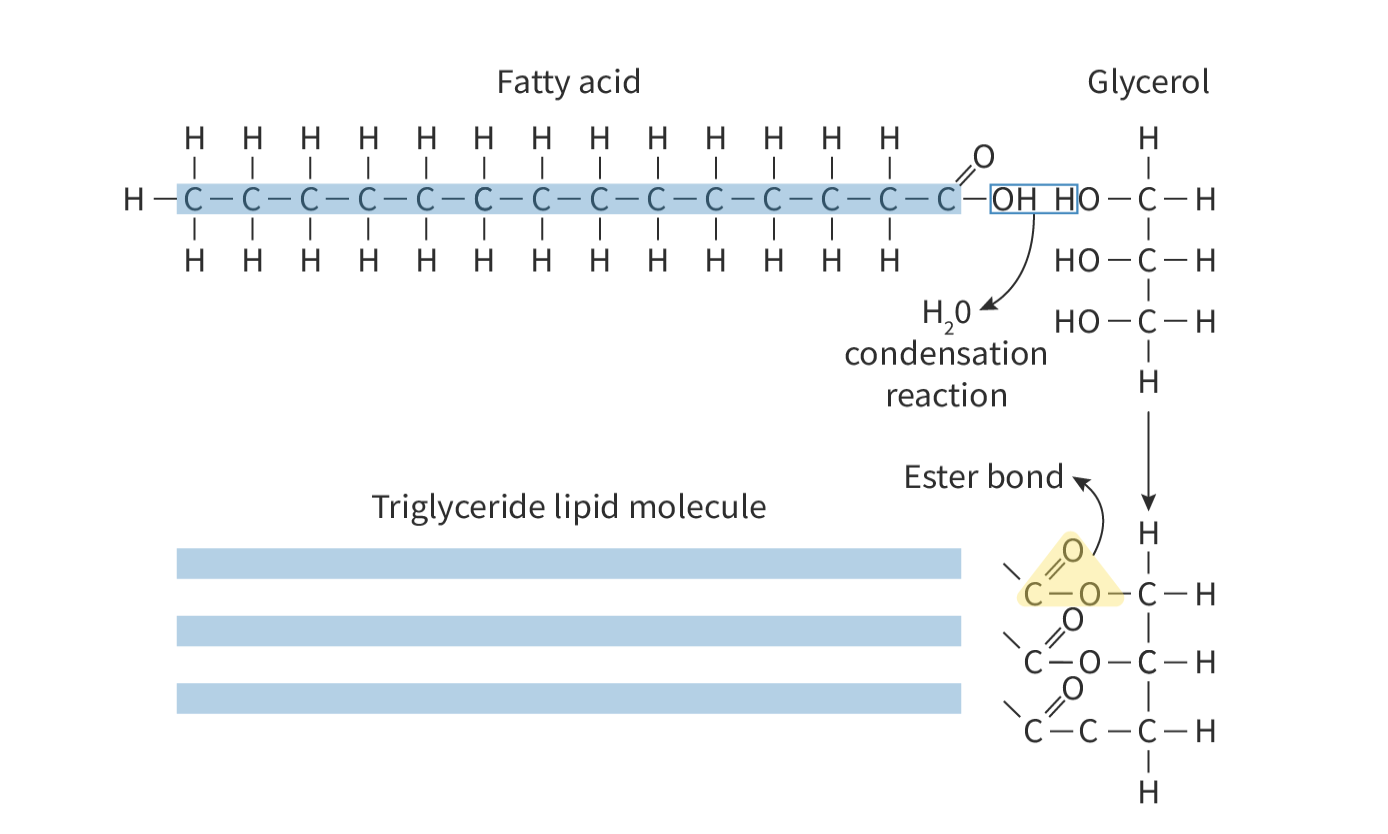
triglycerides
composed of 3 fatty acid chains and a glycerol molecule
can be found in food and synthesised by the liver
solid at room temperature
used for thermal insulation inside animals
formation of triglycerides
formed by condensation of 1 glycerol molecule and 3 fatty acid molecules
each time fatty acid joins to glycerol, a water molecule is released
called an ester bond
phospholipids
formed by condensation of a modified glycerol molecule with a phosphate group and 2 fatty acids
a water molecule is released and is called an ester bond
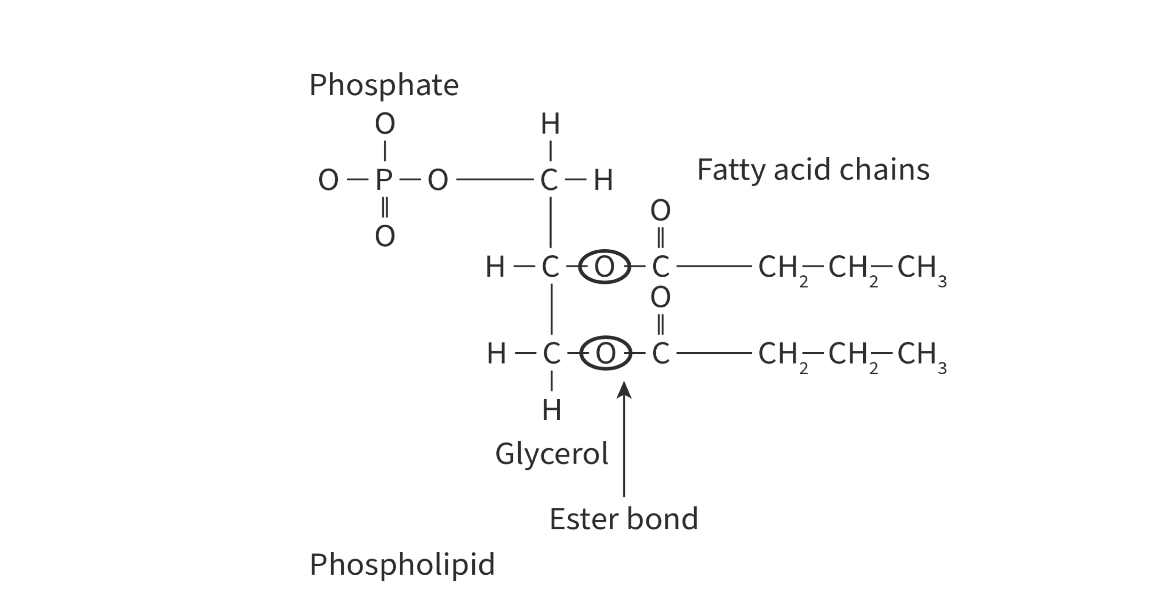
saturated fatty acids
straight, linear shape because there are no double bonds between carbon atoms
solid at room temperature as the straight shape allows atoms to be tightly packed
unsaturated fatty acids
have one or more double bonds, causing them to have a bend/kink
bends prevent fatty acid atoms from being packed tightly, therefore is a liquid at room temperature
monounsaturated or polyunsaturated
monounsaturated fats
1 double bond in their chain so only 1 bend
examples: oleic acid found in olive oil, palmitoleic acid found in macadamia nuts
polyunsaturated fats
2 or more double bonds in their chains so multiple bends
examples: linoleic acid found in vegetable oils and alpha-linolenic acid found in fatty fish
degree of unsaturation of fatty acids
more double bonds, lower melting point
double bonds disrupt the regular packing, making it easier to break bonds
CIS unsaturated fatty acids
hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon atoms around the double bond are located on the same side of the molecule
creates a bend or a kink in the molecule, which causes the molecule to have a less linear structure
TRANS unsaturated fatty acids
the hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon atoms around the double bond are located on opposite sides of the molecule
creates a more linear structure and results in a molecule that is less flexible and more rigid
made industrially and are unhealthy
lipid storage in plants
Plants store fats or oils as a source of energy in many of their seeds, primarily as unsaturated fatty acids
energy from the stored fat is used by the germinating seedling to grow
endotherms
animals that rely on metabolic reactions to generate heat to maintain a constant internal body temperature
lipid usage in endotherms
important source for energy
stored in adipocytes as liquid droplets and can be broken down into ATP- used to power cellular processes
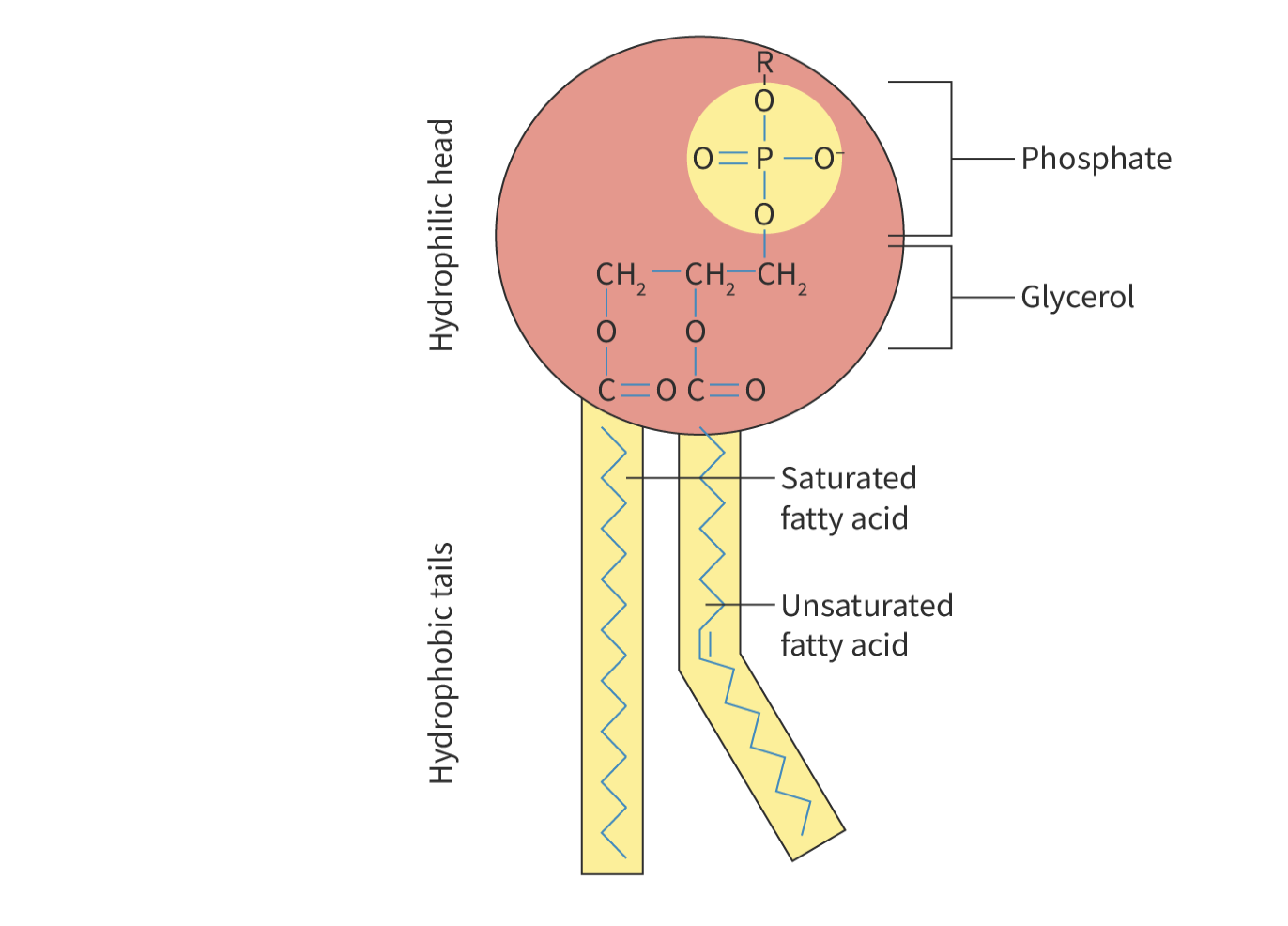
structure of phospholipids
hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail (amphipathic molecules)
head: phosphate and glycerol molecule (polar)
tail: 1 unsaturated and 1 saturated fatty acid (non-polar)
phospholipid bilayer
phospholipids oriented in a special way
when placed in water, head faces the aqueous solution, tail faces away from the solution
orient themselves this way
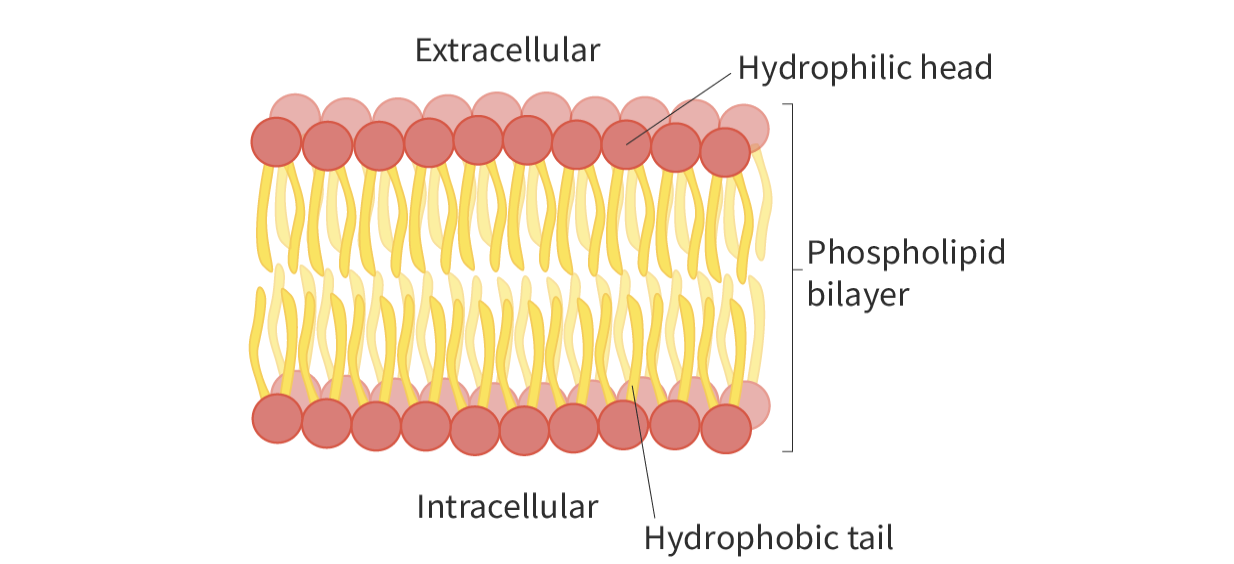
steroids and the phospholipid bilayer
steroids are naturally occuring hormones
they are hydrophobic
steroids can pass through the bilayer and are an important component of it:
cholesterol provides it with stability and flexibility
some play a role in signalling