The drainage basin system
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
fluvial hydrology and geomorphology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
what soil conditions lead to a shorter lag time (flash)
high antecedent soil moisture conditions
impermiable soil
what soil charecteristics lead to a subdued hydrograph
dry soil
permiable soil
what is the water table
the upper surface of the zone of saturation where soil are permenantly saturated with water
what drainage basin lead to a subdued hydrograph
low drainage density
shallow slopes
permiable rocks
high vegitation cover
deep soil
lakes
rural land
good agricultral practices
what precipitation types lead to a subdued hydrograph
low intesity rainfall
small amounts of rainfall
slow snow melt
high rates of evapotransperation
what climatic conditions lead to a shorter lag time (flash)
high intensity rainfall
large amounts of rainfall
fast snow melt
low rates of evapotransperation
what are the two types of storm hydrographs
flash and subdued
what are the two types of rock
sedmentry and ignious
what are the drainage charecteristics that lead to flash hydrographs
high drainage density
steep slopes
impermiable rocks
little vegiation cover
thin soil
urban development
poor agricultral prectices
waterfall
a place where a river decends vertically usually where hard rock overlies soft rock
v-shaped valley
a river valley with evenly sloped sides in the shape of a v cuased by erosion and weathering
urbanisation
the proportion of people living in towns and cities increases and so therefore does the size of towns and cities
transportation
the removal of weathered matitial and eroded matirial in rivers
river regime
expected seasonal pattern of discharge over the year at one particular point
ox bow lake
Cut off crecent shaped lake left after a meander neck has been cut through
Meander
A loop or bend in a river with a slip off slope on the inside bend and a river cliff on the outside
input/output
when something is either added or taken away from a system
Hydrograph
Graph showing variations in river discharge over a piriod of time
hydrocolic cycle
the circulatory system by which water is transfered between oceans atmosphere and land
human use
the way in which people make use of rivers to futher economic development and water supply
how does urbanised areas effect overland flow
increaced overland flow due to unpermiable surface preventing infiltraition
how does steep slopes effect overland flow
increase speed of overland flow reducing rate and time taken for interception to be able to take place
how does overgrazing effect overland flow
reduces vegitation and thus interception increacing overland flow
how does frozen of saturated soils effect overland flow
increaces over land flow as there is no unsaturated soil preventing infiltraition
how does deforestaiontion effect overland flow
reduces rate of interception increacing overland flow
how does bare rocky surfaces effect overland flow
increaces overland flow due to unpermiable surface preventing infiltaition
flood plain
flat low lying are of the valey floor which floods from time to time
flood
when a river channel recives more water than it can hold
Field capacity
The amount of water a drainage basin can hold
erosion
the wearing away of the beds and banks
drainage density
total length of all streams in the drainage baisen divided by total area of drainage basin
drainage basin
an area of land drained by a river and all of its tributrys
discharge
the volume of water in a river passing a mesuring point in a given time cubic meters per second
Delta
Landform produced by the deposition of sedement at the mouth of a river as it enters lake or sea
what is the hydrological cycle flows and stores
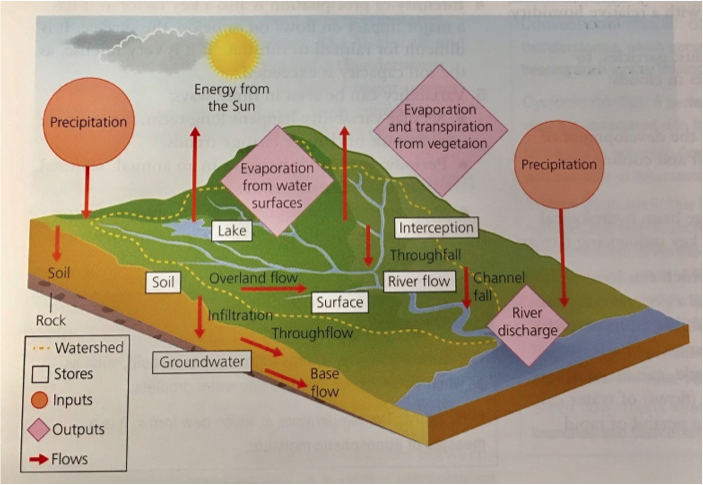
what is recharge
When precipitation exceeds evaporation causing soil moisture to increace
what are the 6 factors that increace overland flow
deforestation
steep gradient
Frozen + saturated soil
overgrazing
bare surfaces
urbanisation
What are the three types of river flow
Helicoidial
laminar
Turbulent
what are the three types of river channels
Straight
meandering
braided
what charicteristics can be atributed to braided channels
Braided channels
Trubulent flow
steep and complex system
eyots form
what are the charecteristics of a straight channel
straight channel
Laminar flow
middle and lower cource
symetrical
Rare in real life
what are the charecteristics of a meandering river
Meandering river
corkscrew motion
asemetrical
helicoidial flow
what are the four transportation process
Traction - large stones roll
suspension - small particals
soloution - disolved minerals
saltation - small stones skip
what factors effect transportation in a river
Competence - the diameter of the largest partials it can carry at a given velocity
Capacity - the total volume of load a river can carry
what are the four types of erosion
Hydraulic action - pressure of water
abrasion - scraping and rubbing of matirial
attrition - reduction in size of fragments in river
soloution - carbonates dissolved
what factors effect rate of erosion
Speed/velocity
Discharge
Climate
Geology
PH
Load
what is sineocity
curvyness of a river over time
what are the all the causes for a subdued hydrograph
Low intensity
High evapotransperation
Dry soil
permiable soil
low drainage density
gentle slopes
permiable rock
forest and vegitation
lakes
rural land
good agricultral practive
what are the all the causes for a flashy hydrograph
high intensity
fast snow melt
low evapotransperation
high antesedent conditions
impermiable soil
high drainage density
steep slopes
little vegitation
thin soil
no lakes
urban development
poor agricultral practices