Chapter 19 Lecture Anatomy 2
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
What is the function of the cardiovascular system?
Transports blood throughout the body through the heart and blood vessels. It involves the delivery of O2 & nutrients and removal of CO2 & wastes.
Function of the blood vessels
Arteries carry blood away from the heart (some may carry oxygenated blood)
Veins carry blood toward the heart (some may carry deoxygenated blood)
Capillaries are sites of exchange (e.g., of gases)
Between blood and air in lungs
Between blood and body cells
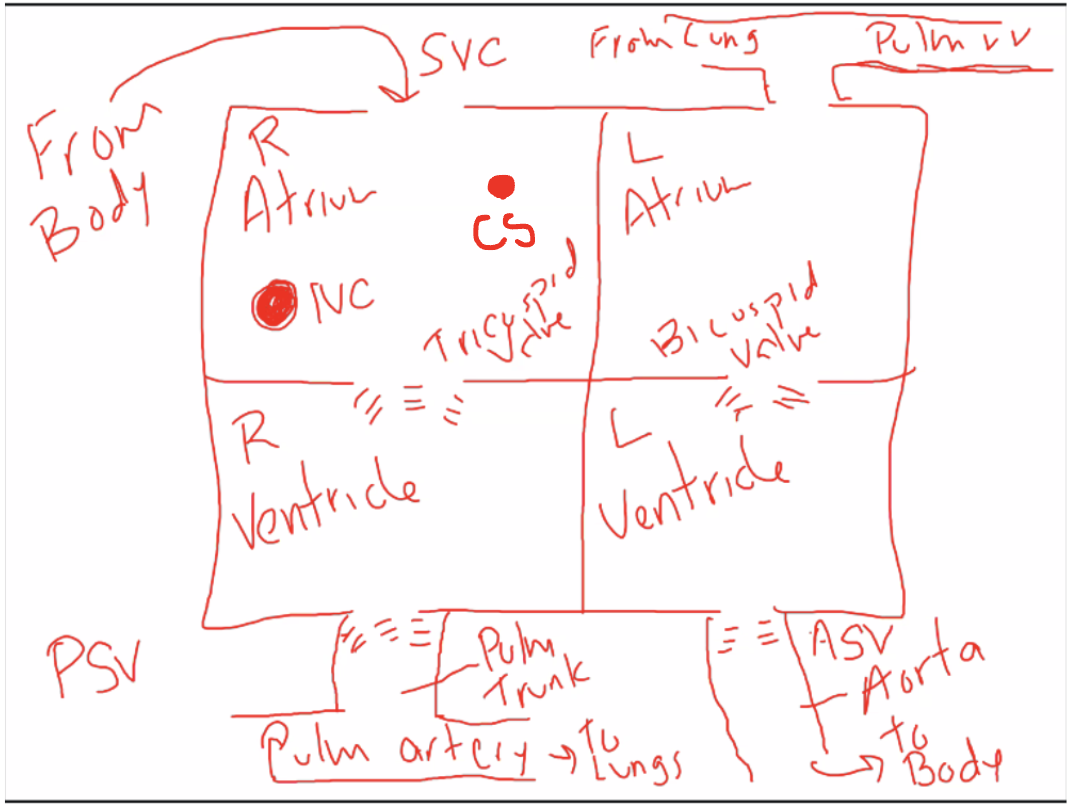
What are the main functions of the heart? What are the hearts four main chambers?
Pump deoxygenated blood to the lungs
Pump oxygenated blood to the body
Four main chambers:
- 2 Atriums (right & left) & 2 ventricles (right & left)
Atria are superior chambers that receive blood and send it to ventricles below
Ventricles are inferior chambers that pump blood away
What are great vessels of the heart? Function?
Function of the great vessels is to transport blood to and from heart’s chambers'
2 Arteries (carry blood away from heart)
Pulmonary trunk
Transports blood from right ventricle
Splits into pulmonary arteries
Aorta
Transports blood from left ventricle
2 Veins (carry blood toward the heart)
Superior vena cava and inferior vena cava
Drain deoxygenated blood into right atrium
Pulmonary veins
Drain oxygenated blood into left atrium
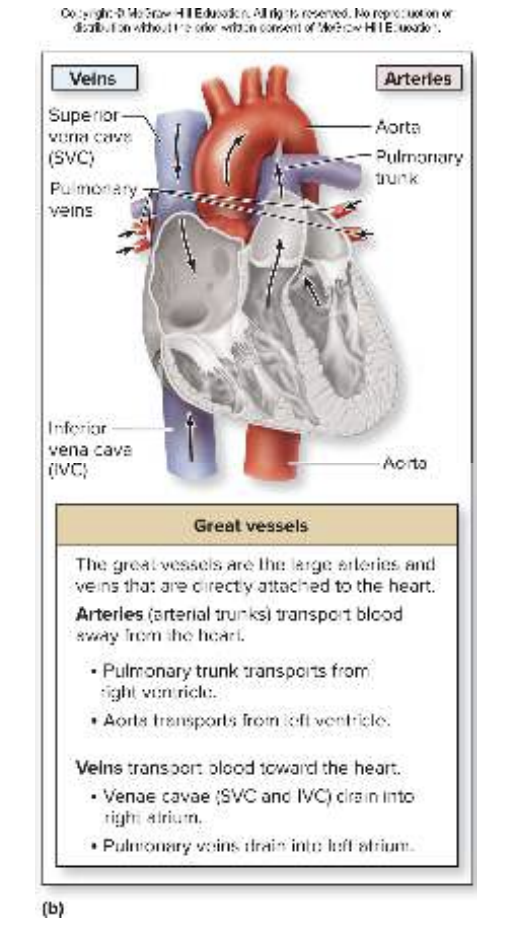
What is the difference between the function of the superior vena cava and inferior vena cava?
Superior vena cava returns deoxygenated blood from above the heart such as head, neck, and upper arms
Inferior vena cava returns blood from below the heart such as abdomen, lower limbs, etc
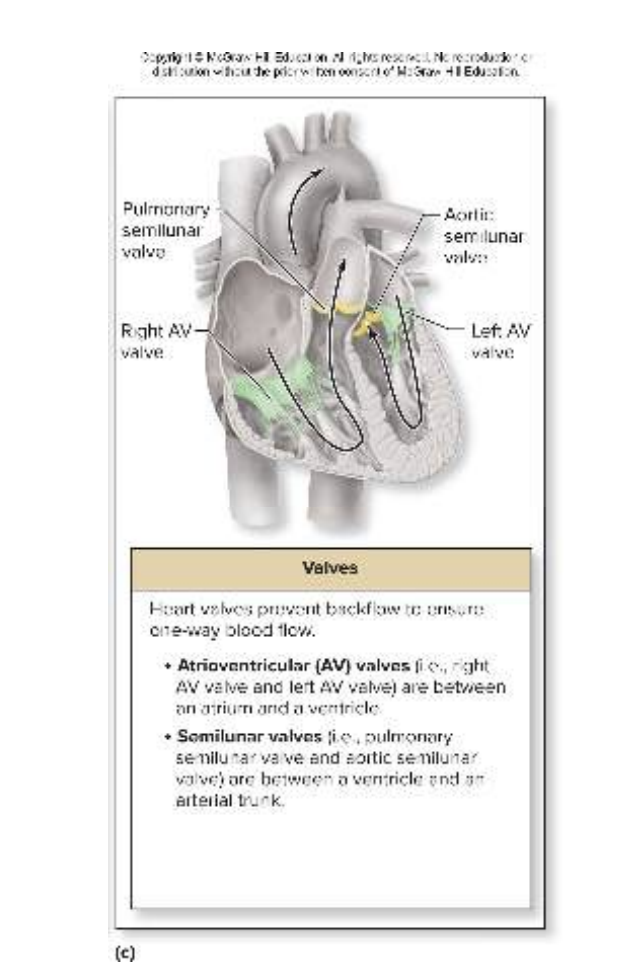
The heart has how many valves? What are the function?
The heart has two sets of valves. These valves ensure one-way flow of blood through heart.
Atrioventricular (AV) valves
Sit between atrium and ventricle of each side
Right AV valve (tricuspid bc it has 3 tissue flaps)
Left AV valve (bicuspid bc it has 2 tissue flaps)
Semilunar valves
Sit at boundary of ventricle and arterial trunk
Pulmonary semilunar valve: located between right ventricle and pulmonary trunk (3 tissue flaps)
Prevents backflow of blood from the pulmonary trunk
Aortic semilunar valve: located between left ventricle and the aorta (2 tissue flaps)
Prevents backflow of blood from the aorta
Explain the process of heart pumping blood throughout the body
Right side of the heart
Right Atrium receives nasty used blood, from the body (either from the superior vena cava or inferior vena cava).
Right Atrium can also receive deoxygenated blood from the coronary sinus (which is blood from the heart)
Blood passes by the tricuspid valve (called this bc it has 3 tissue flaps) into the right ventricle below it.
From the right ventricle, the blood passes through the pulmonary semilunar valve. (The blood will be very dark bc the oxygen is poor)
From there it goes to the pulmonary trunk, to the pulmonary artery, which carries the blood to the lungs.
Left side of the heart
The blood from the lungs comes back via the pulmonary veins and into the left atrium.
The left atrium receives the blood, which then passes through the bicuspid valve (has 2 tissue flaps) into the left ventricle below it.
From the left ventricle, the blood passes through the Aortic semilunar valve, then through the aorta, and then to the body.
Cycle repeats over nd over when the blood from the body goes back to the right side of the heart.