Mycology lab final exam
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
Types of tinea infections
Tinea barbae: beard
Tinea capitis: scalp
Tinea corporis: body
Tinea cruris: jock itch
Tinea pedis: foot
Tinea onychomycosis: nail
Tinea versicolor: skin, M. furfur
"Tinea" (worm) + location of infection
Dermatophyte morphology (most)
cottony (fluffy)
Granular, powdery
*white front, yellow reverse
Sab-Dextrose
non-selective fungal agar
Inhibitory mold agar (IMA)
chloramphenicol: inhibits many bacteria
Mycosel agar
Chloramphenicol and cycloheximide
Inhibits: zygomycetes, aspergillus, Cryptococcus, some Candida
Dermatophyte test medium (DTM)
chloramphenicol and cycloheximide
also a differential media
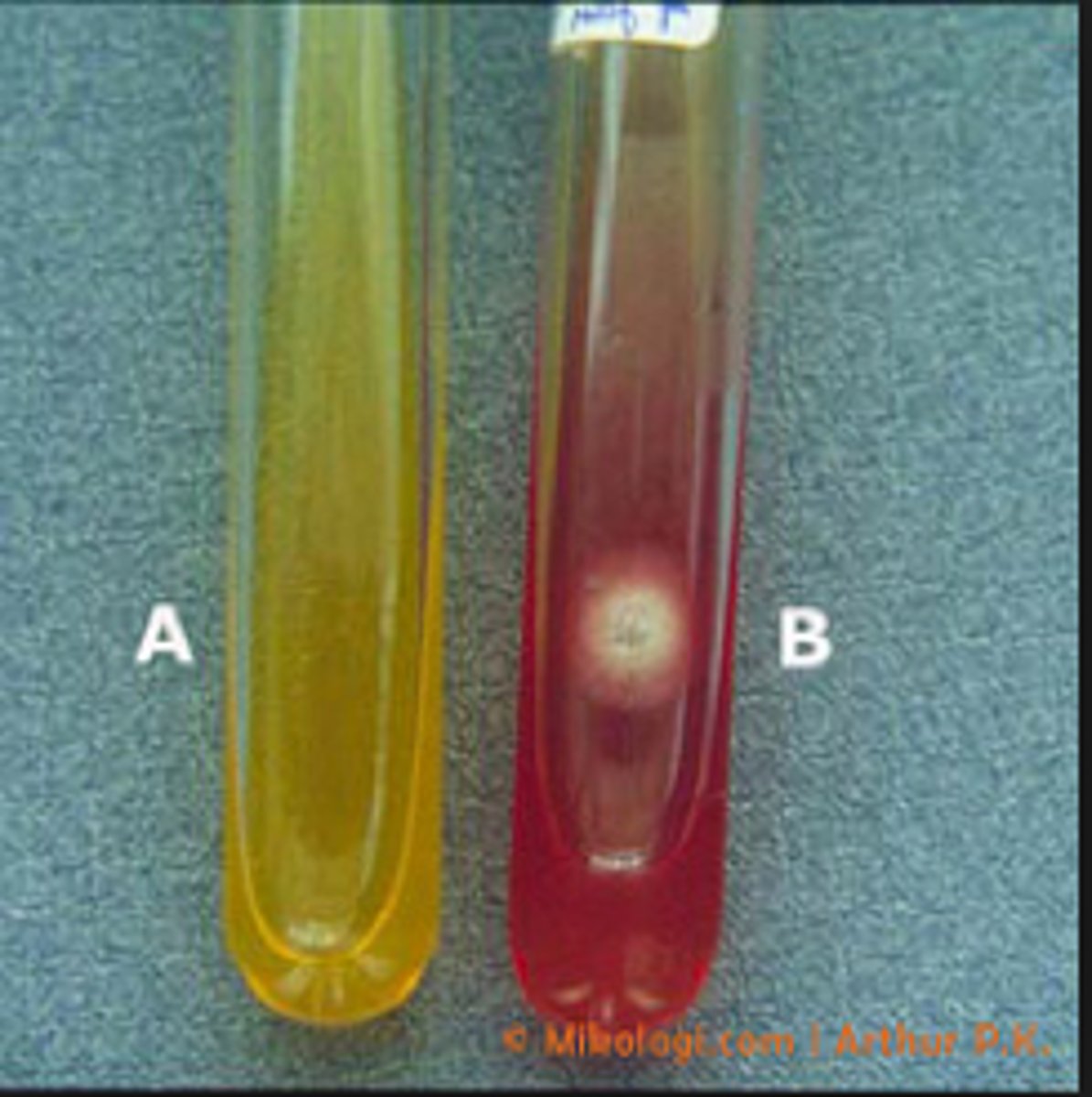
Dermatophyte test medium coloration
Phenol red: red color appears in presence of alkaline metabolites
--chloramphenicol and cycloheximide inhibit other organisms
Ectothrix
spores and hyphae form sheath around hair
Spp: Microsporum spp, Trichophyton mentagrphytes
Endotrhix
spores and hyphae inside hair shaft
Spp: Trichophyton tonsurans and Trichophyton violaceum
Wood's UV lamp
for detection of ectothrix hair infection
KOH preps of skin/nails
degrade keratinized tissue to free fungal elements
--may add calcofluor white or LPCB to help visualize
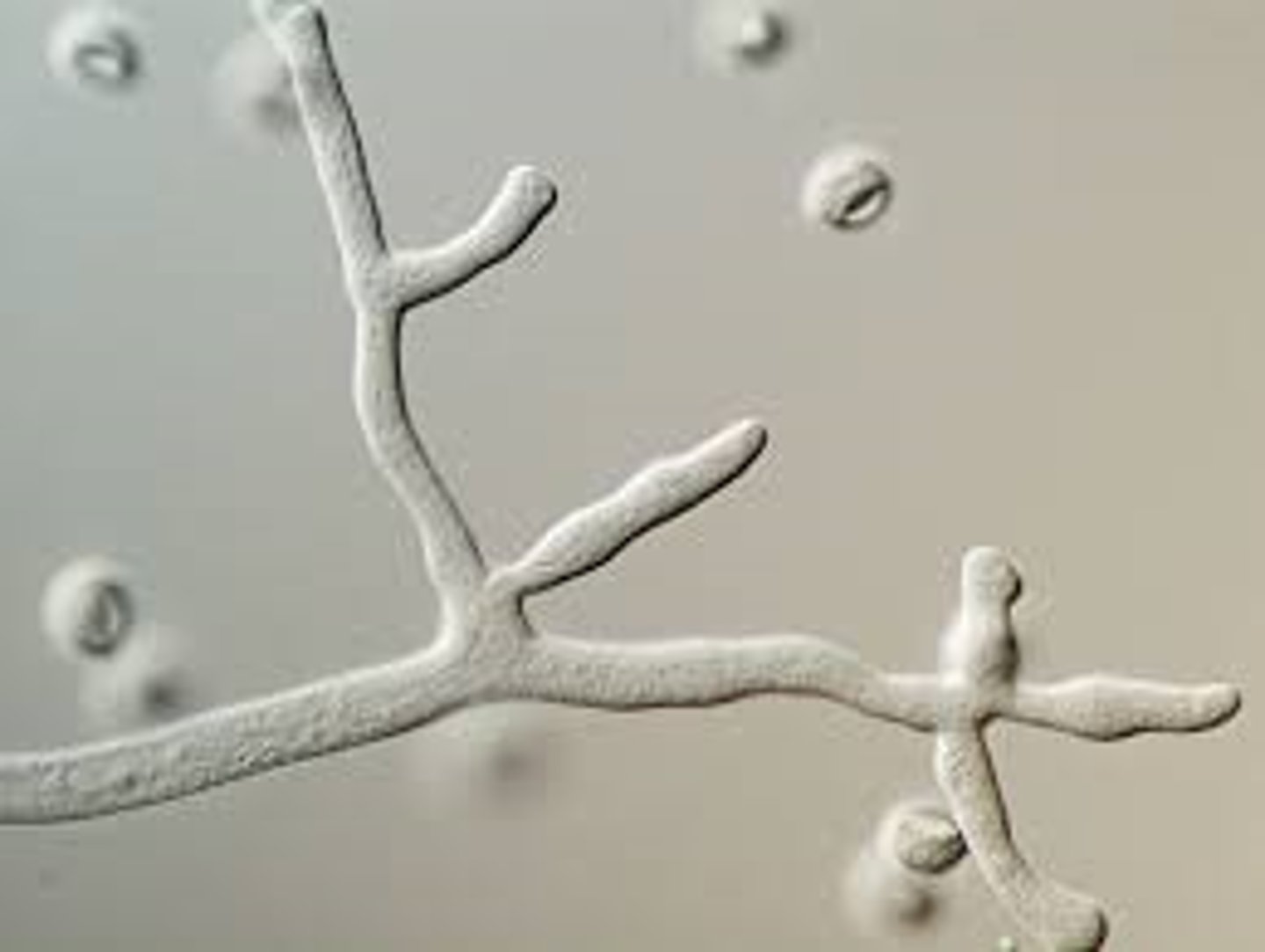
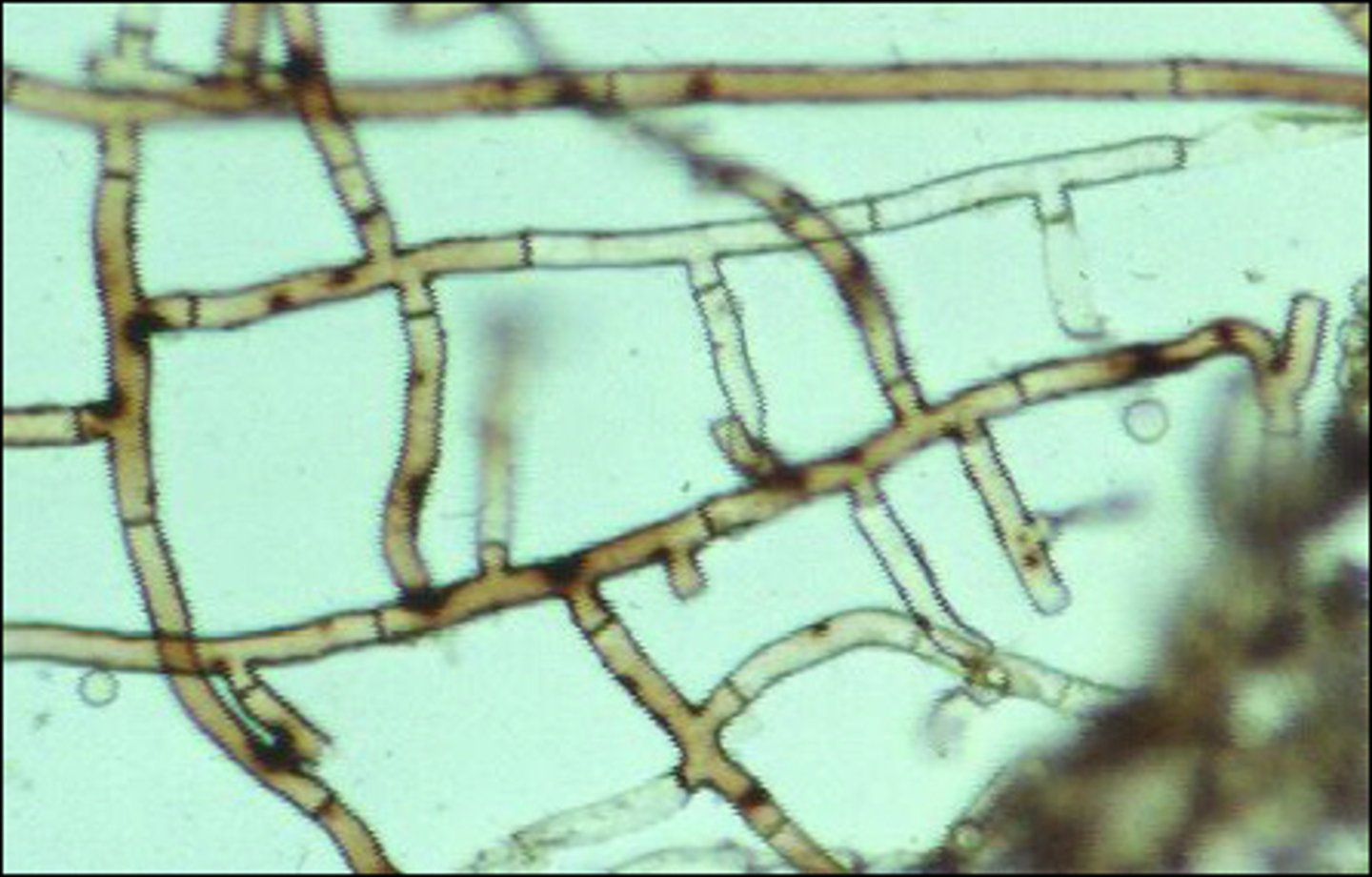
Conidia
asexual spore structures formed from septate hyphae
MACROconidia: hyphal elements convert to multi-cellular structure
aseptate hyphae
septate hyphae

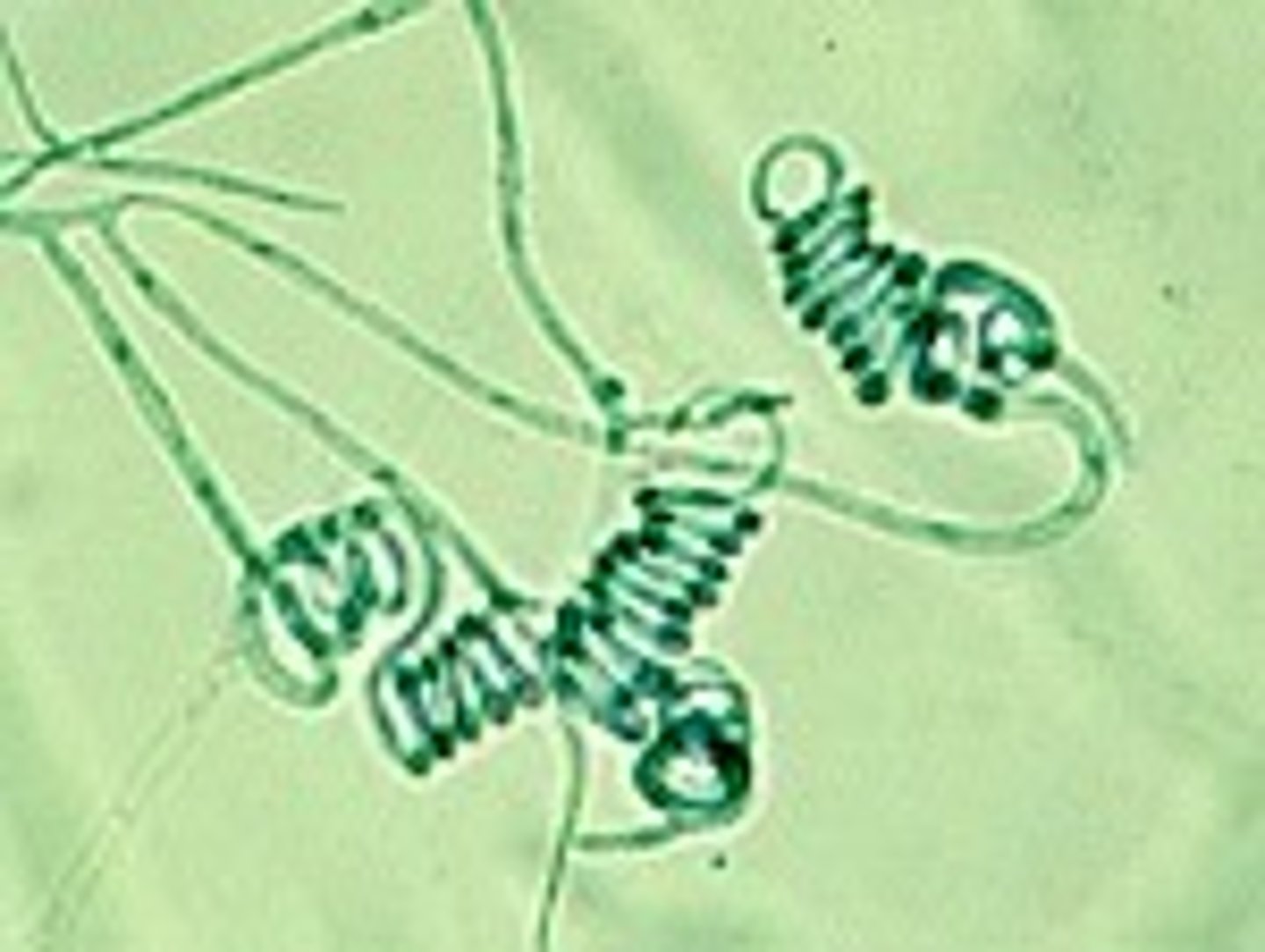
spiral hyphae
nodular organ
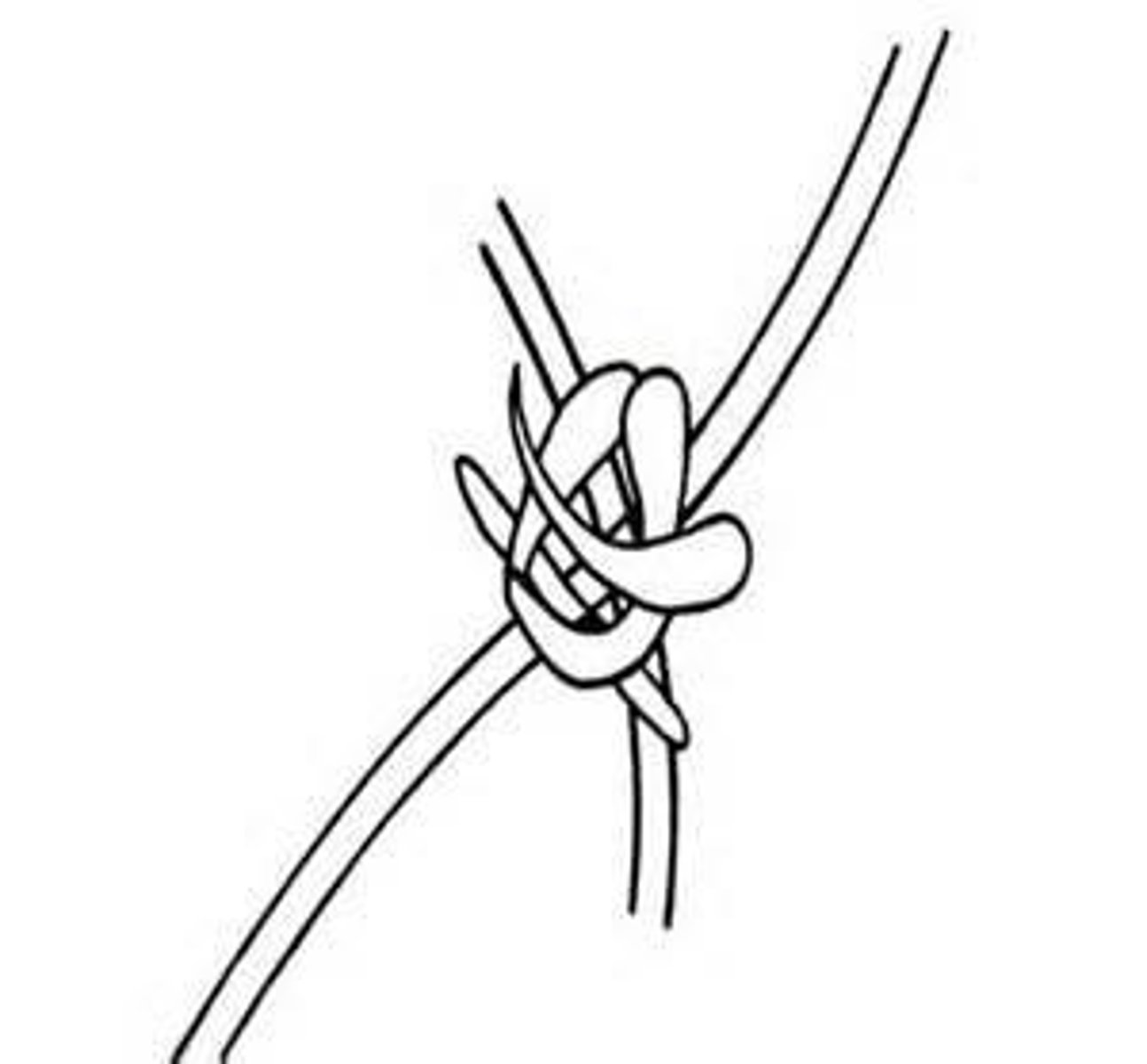
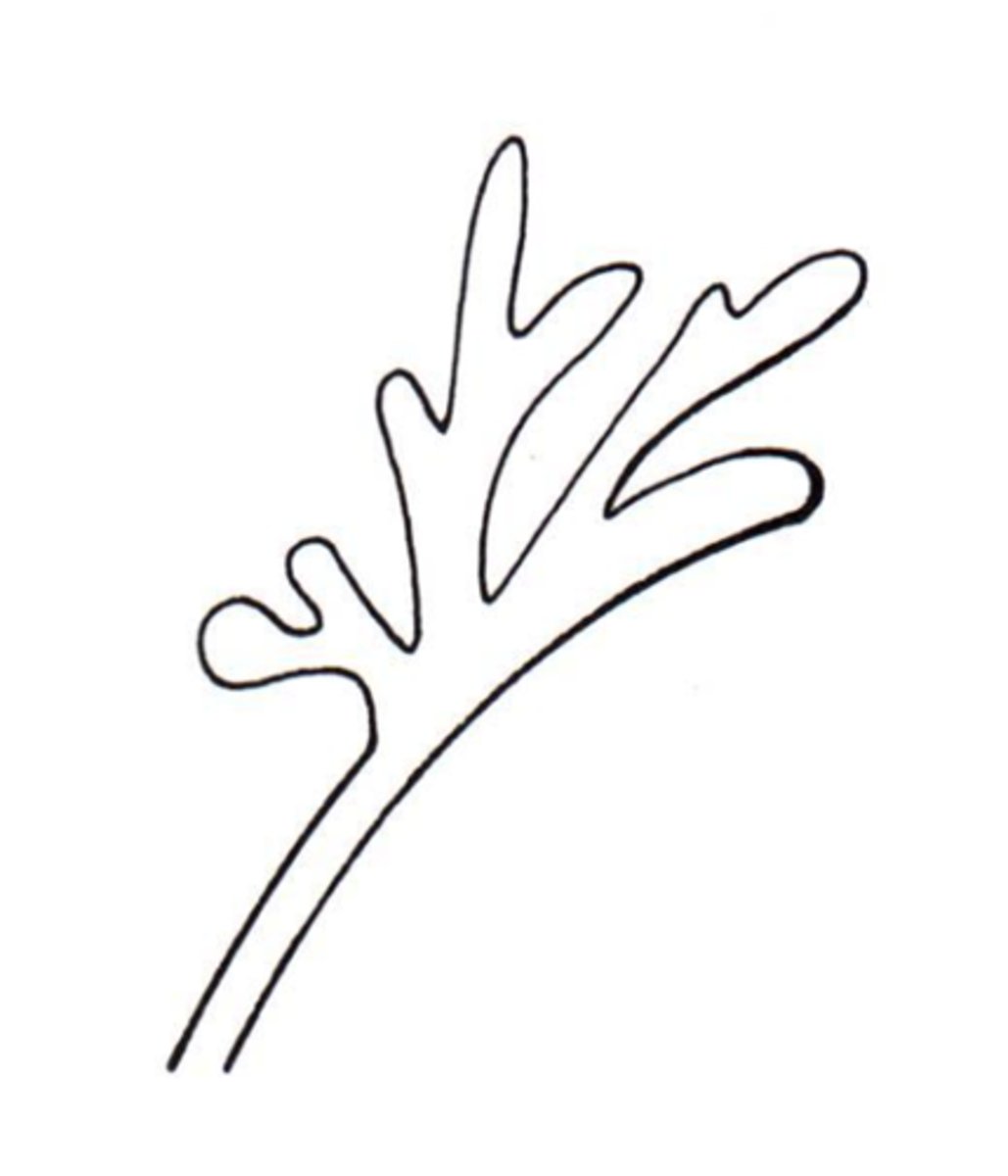
favic chandeliers/antler hyphae

Malassezia furfur
tinea VERSICOLOR
--lipophilic: needs lipid overlay to grow
Conidia and hyphae: spaghetti and meatballs
--normal flora in 90% of adults
*yeast-like fungus
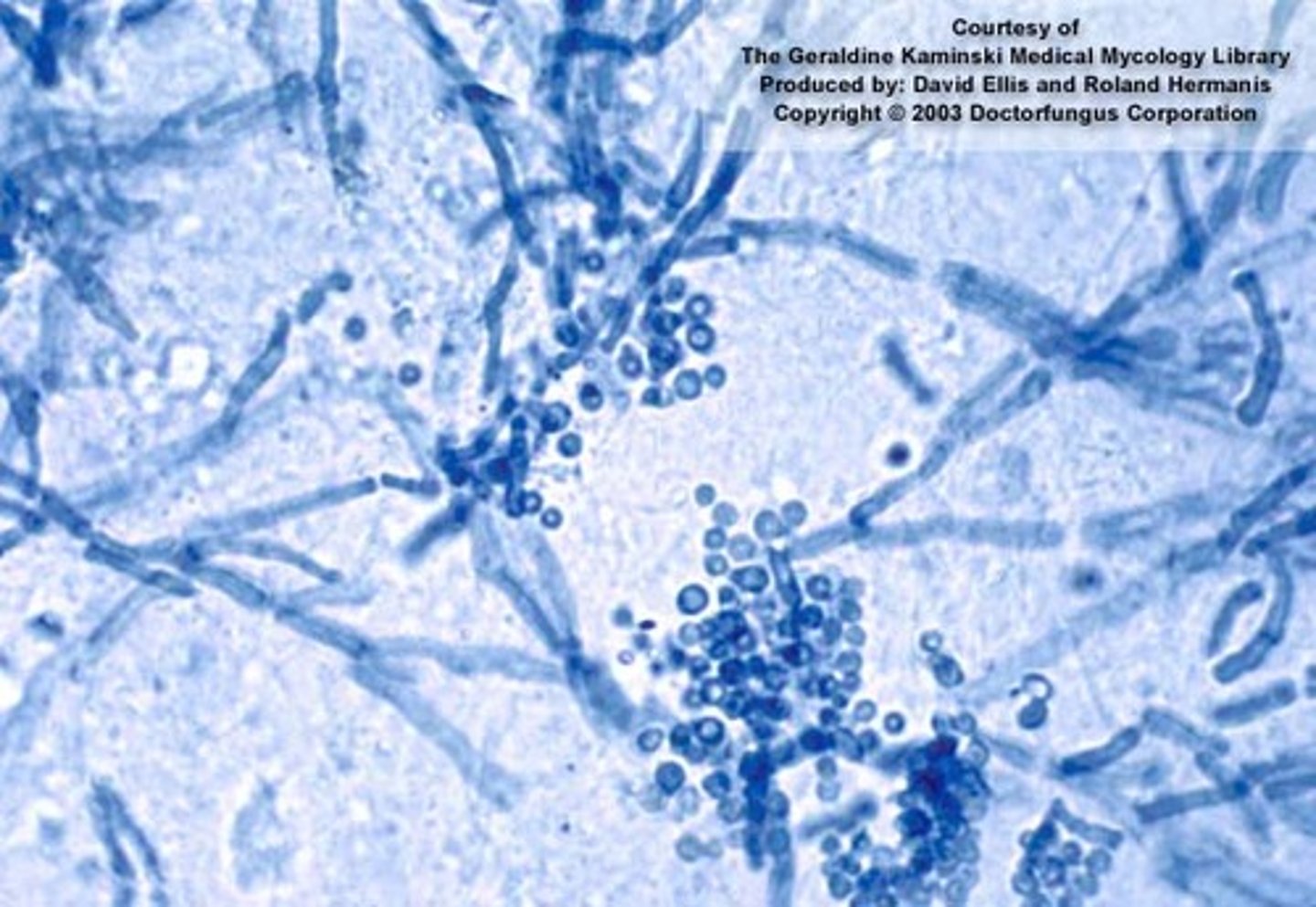
Exophiala dermatitidis
colony: mucoid changing to velvet
--dark brown-black
--reverse (same)
Young culture: yeast-like cells
Mature colonies: pointed annelides branch from hyphae
--conidia cluster at tipe (cylindrical-oval)
septate hyphae
Disease:
Cutaneous: phaehyphomycosis granular cysts (immunocompetent)
Systemic: affinity for CNS, eyes (immmunocompromised)
*yeast-like fungus
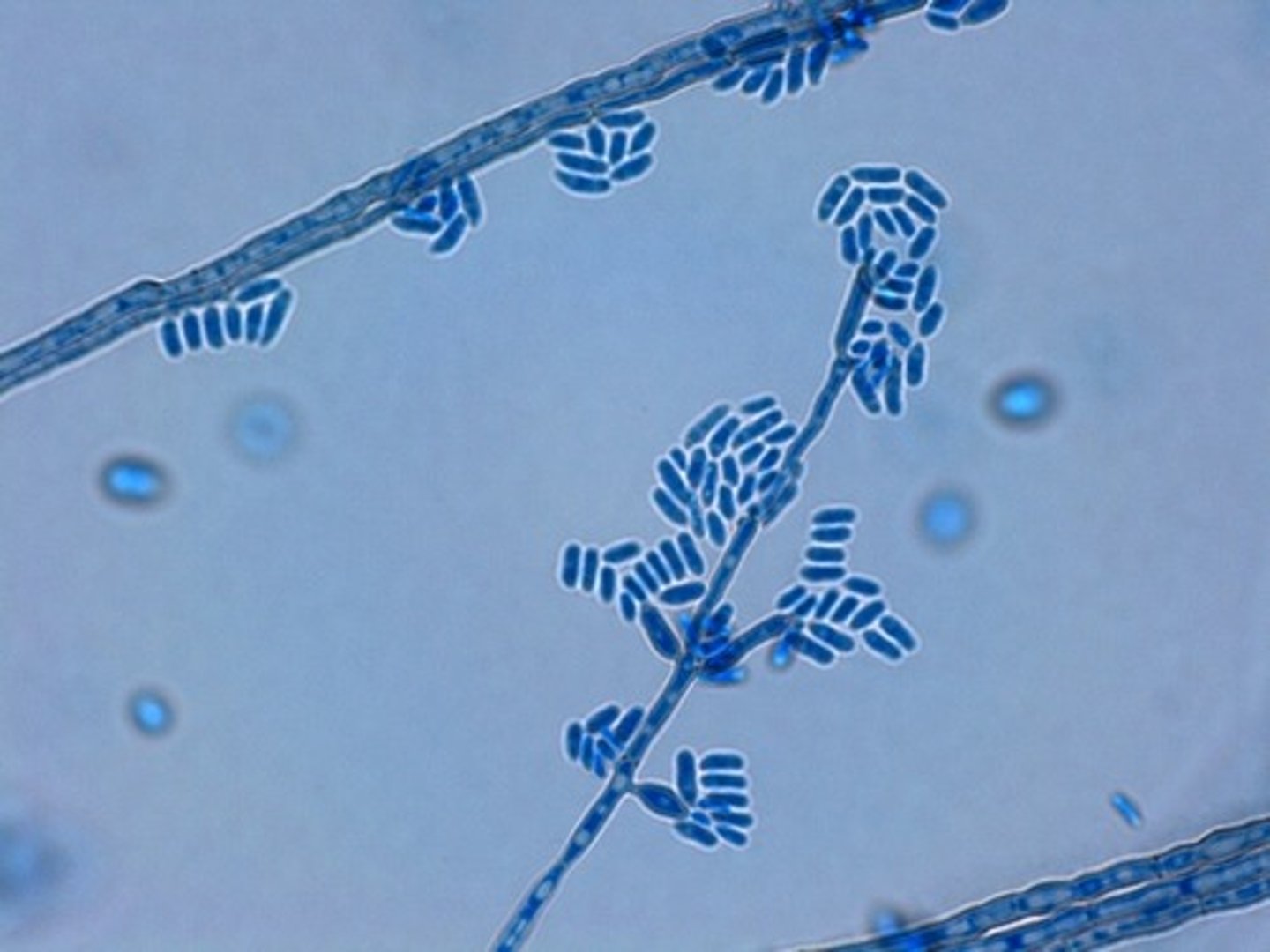
Epidermophyton floccosum
Colony morph:
--felty, cottony tufts in older colony, white-yellow-khaki
--Reverse: light to medium brown
Microconidia: NO
Macroconidia: 'beaver tail', one end broader, smooth cell wall (2-5 perpendicular division, clustered at tapered end)
septate hyphae
Conditions: Tinea corporis and cruris, onchomycosis, DOES NOT INFECT HAIR
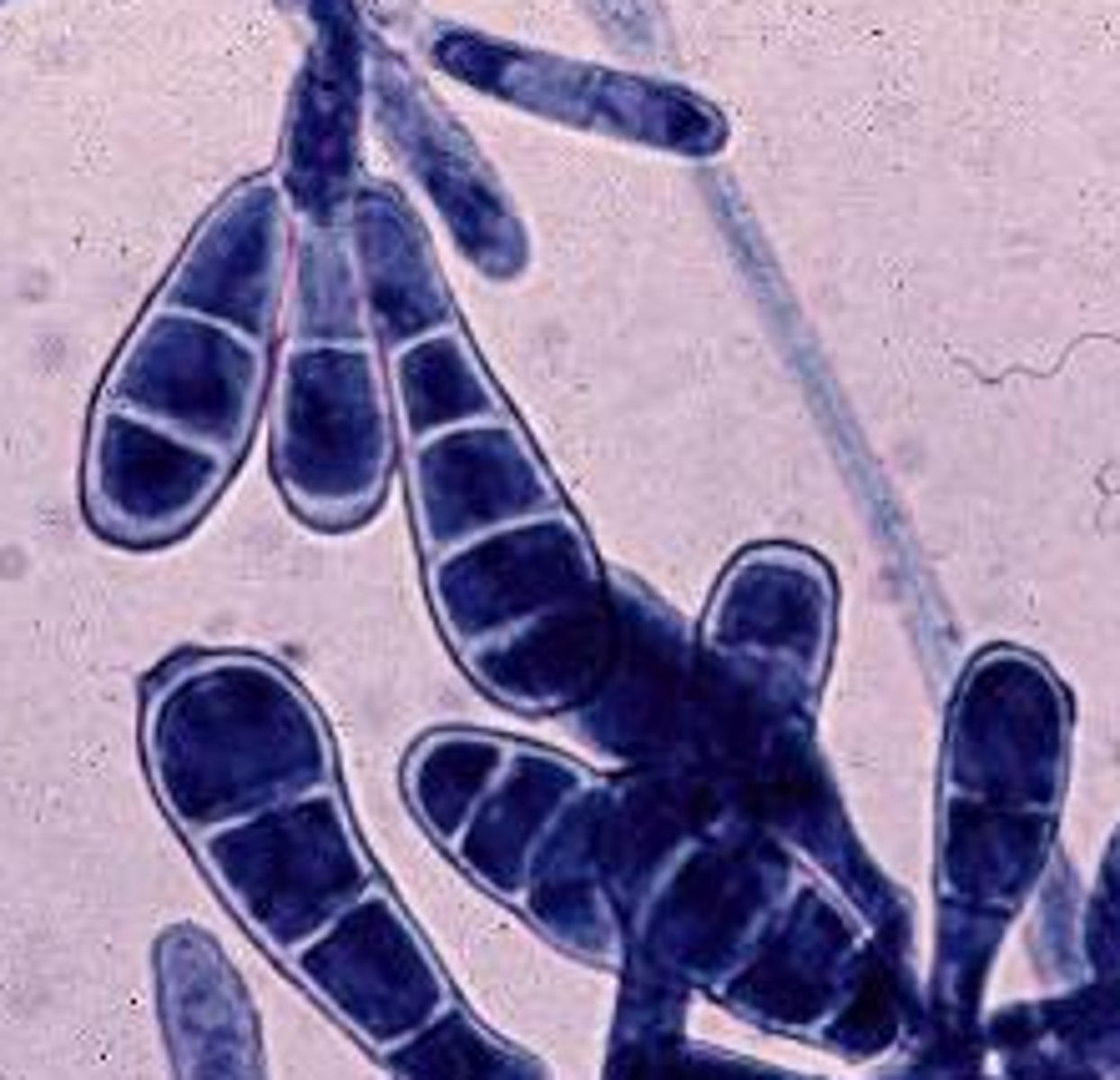
Microsporum canis
Colony: downy, white-yellow
Reverse: orange-yellow
Microconidia: rare
Macroconidia: fusiform spindle, septate macroconidia, thick cell wall, echinulate, 3-15 cells
septate hyphae
Conditions: scalp and skin;
--dogs, cats, farm animals
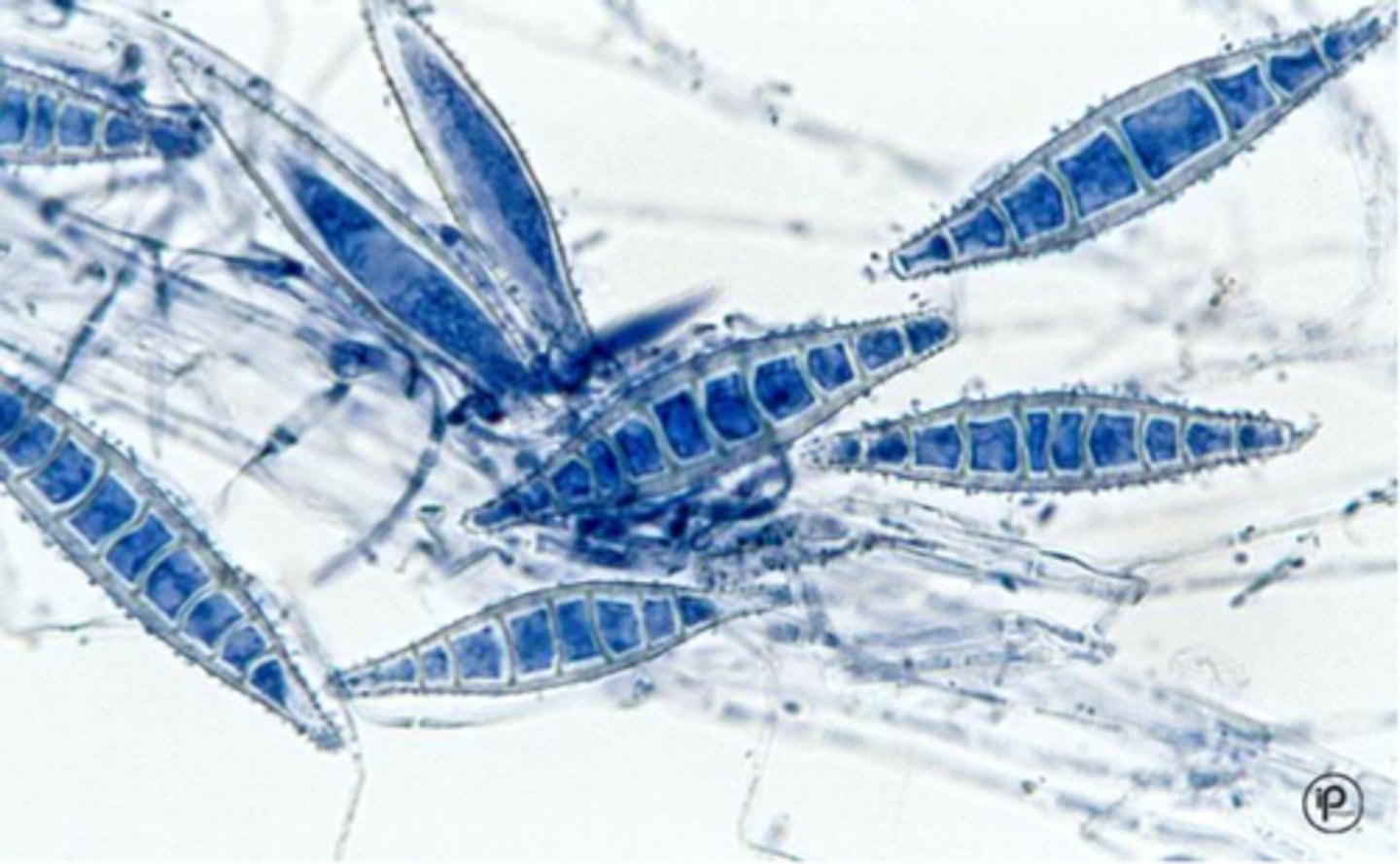
Nannizzia gypsea (Microsporum gypseum)
Colony: powdery, granular, yellow-beige
Reverse: same or red-brown
Microconidia: claviform (club-shaped)
Macroconidia: fusiform spindle, septate, thin-moderate cell wall, < 6 cells in spindle, spindle ends rounded
septate hyphae
Conditions: scalp and skin
animal cases more common
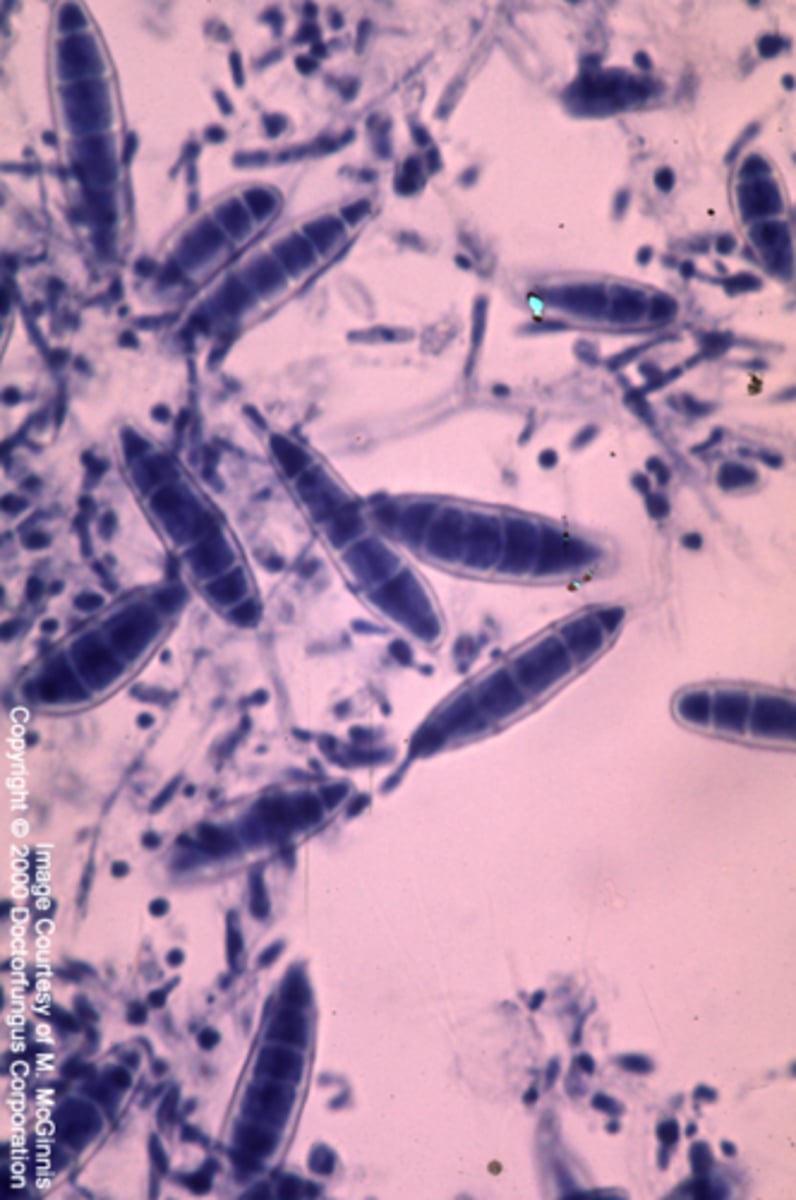
Trichophyton mentagrophytes (interdigitale) complex
Colony: velvety-white cream
Reverse: yellow or red-brown
Microconidia: pyriform to round
Macroconidia: claviform (club-shaped), may be absent; septate
septate hyphae
Disease: skin, hair, nails all common
--zoophilic
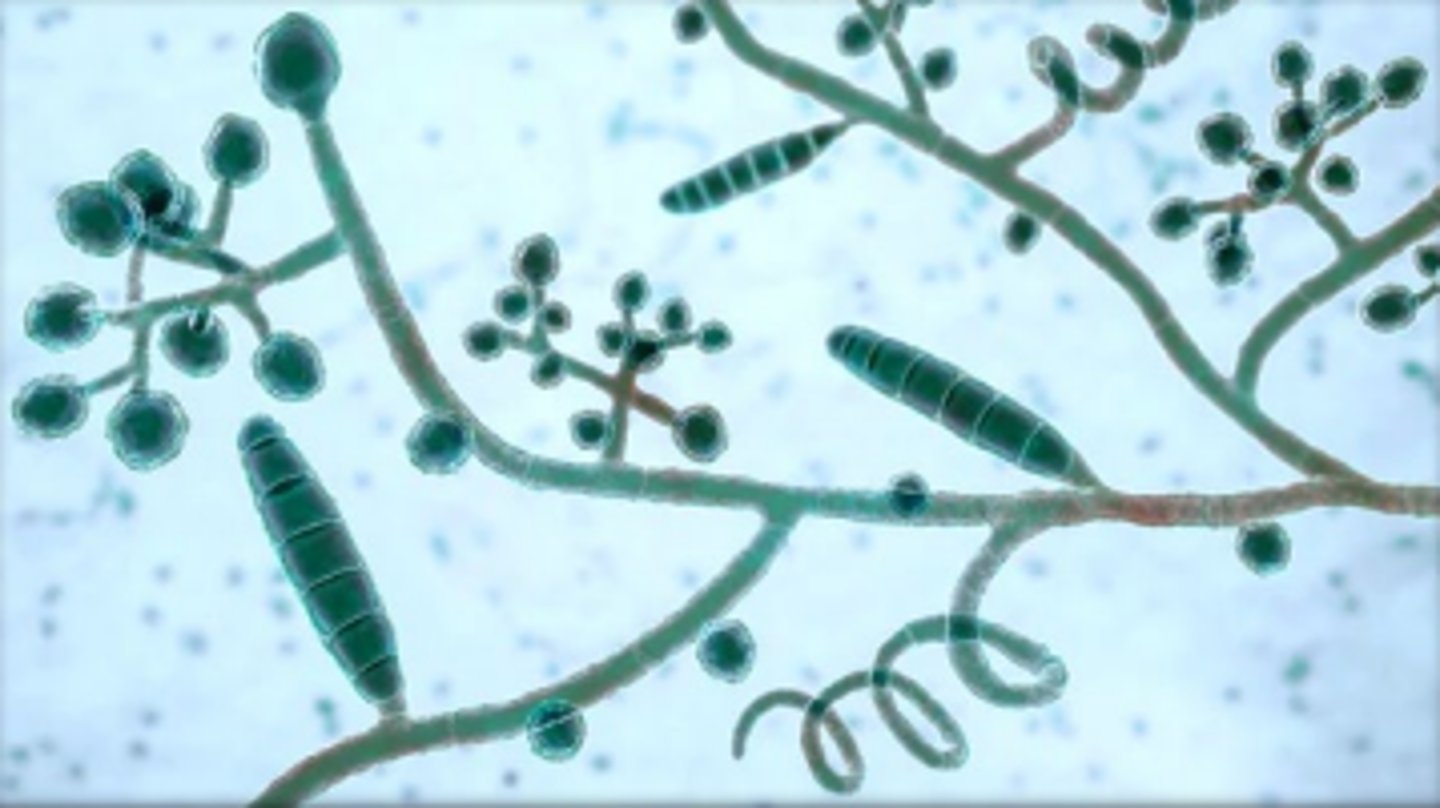
Trichophyton rubrum
Colony: powdery-downy, granular, white-pink
Reverse: red or yellow-brown
Microconidia: claviform or pyriform "birds on a wire"
Macroconidia: cigar shaped, often absent; septate and may be at end of hyphae
septate hyphae
Conditions: skin and nails common
Rare: beard/hair/scalp
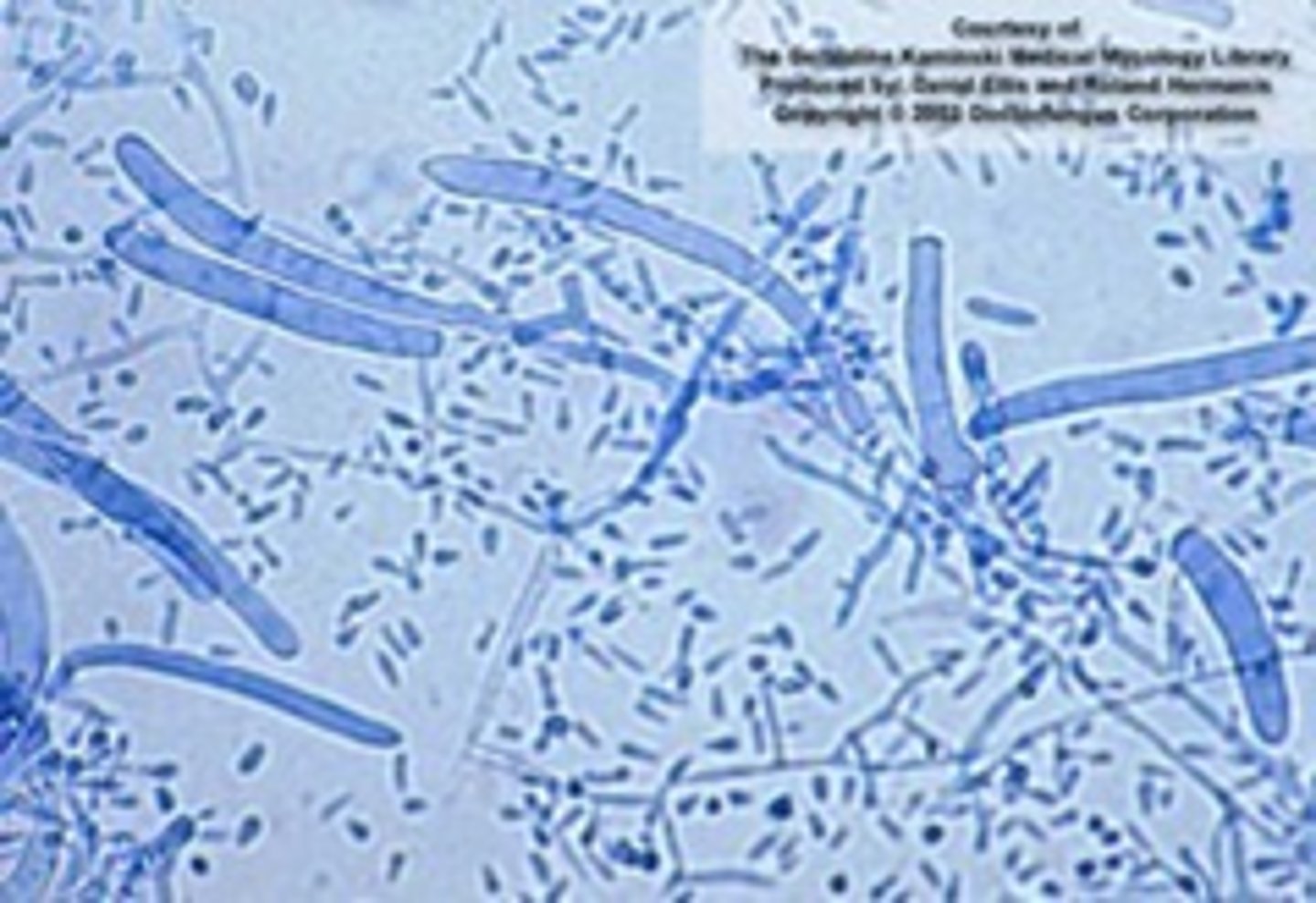
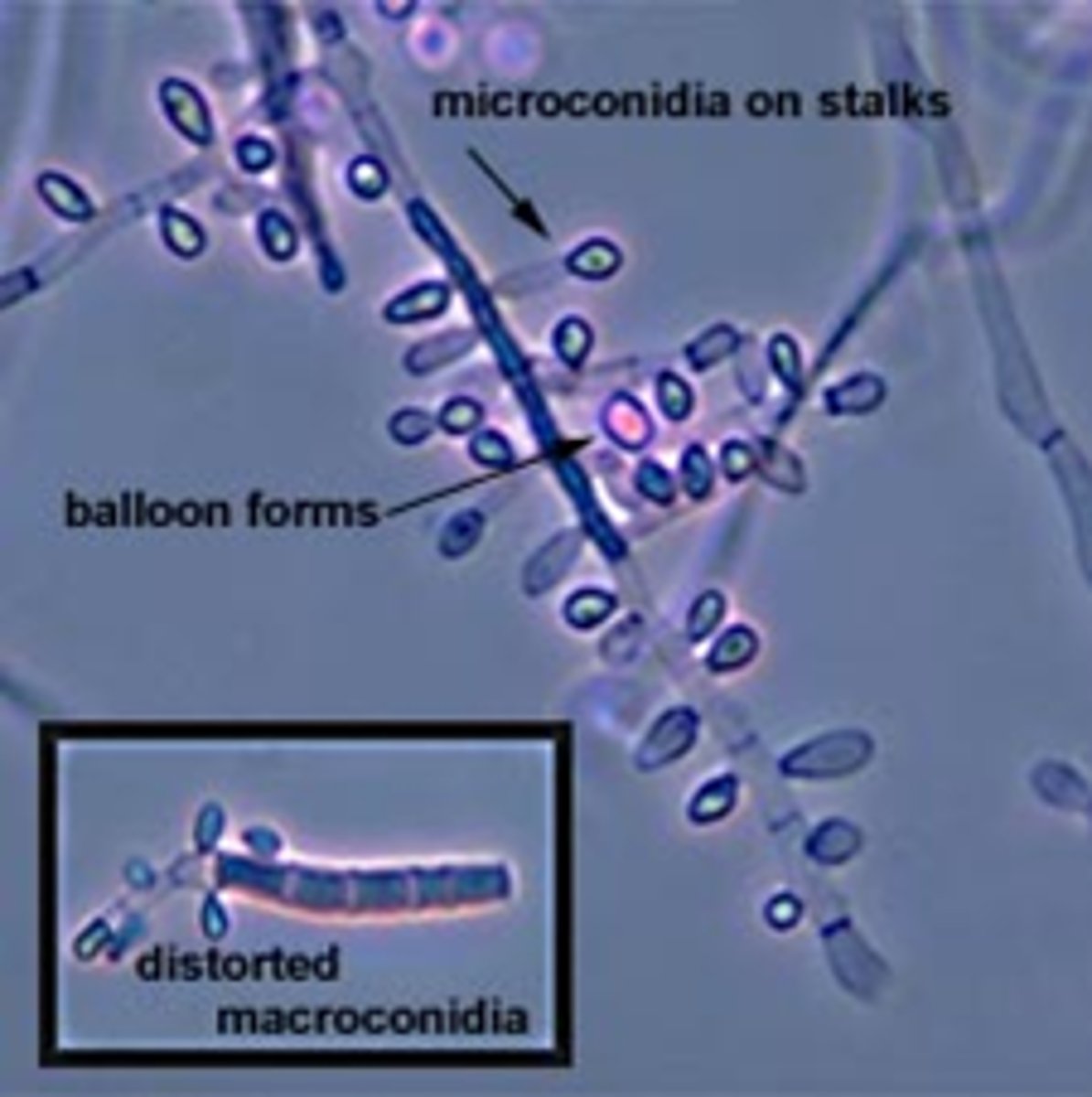
Trichophyton tonsurans
Colony: powdery-downy, white-yellow-beige
Reverse: brown or red-brown
Microconidia: teardrop, club, balloon shaped, numerous
Macroconidia: club-shaped/curved, may be absent; septate
septate hyphae
Disease: tinea capitis (#1 cause in US)
--Skin, nails also possible
--anthropophilic
Trichophyton violaceum
Colony: glabrous, red violet brown or cream
Reverse: same, diffuses
Microconidia: usually absent
Macroconidia: typically absent
Hyphae: septate, irregular width
--may form chlamydospores
Disease: tinea capitis (#1 in Africa, Asia)
--skin, nails
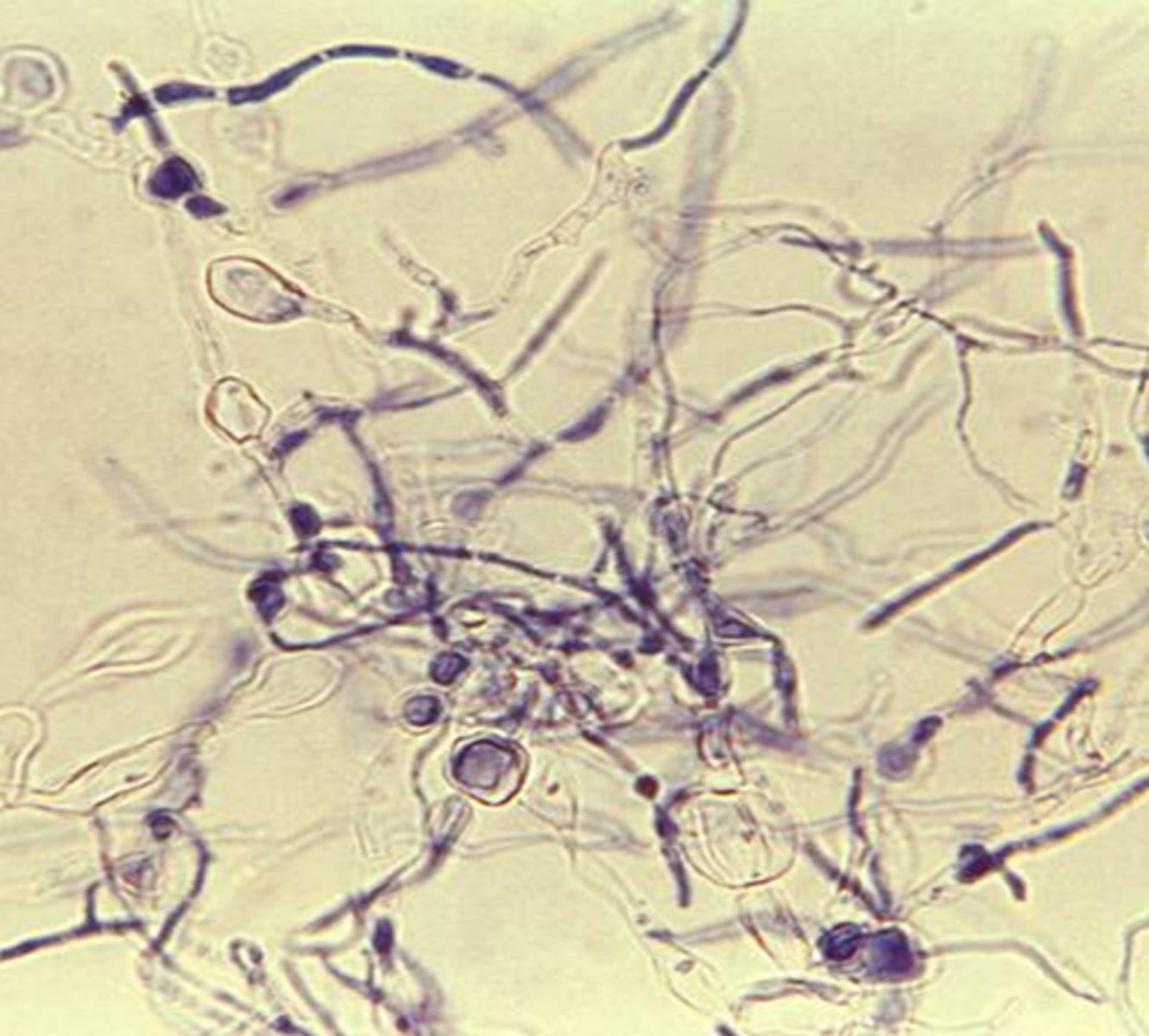
Actinomycetoma
caused by actinomycetes (fungus-like bacteria)
--slow-growing, will grow on fungal media
Eumycotic mycetoma
true fungal infection
What do eumycotic mycetoma and actinomycetoma cause?
tumerous masses in subq tissue
--painless
--weeping sinuses
--granular discharge
--feet most commonly infected
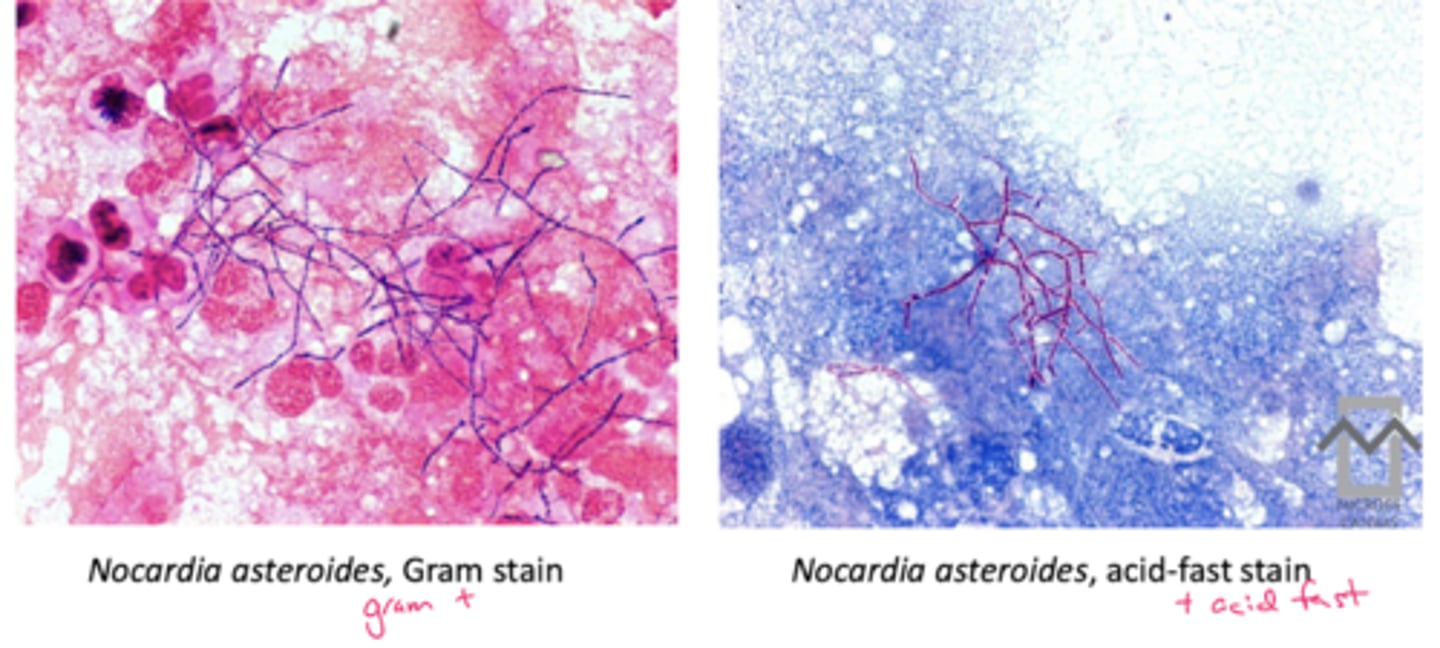
Nocardia spp characteristics
Branching, filamentous AEROBES, grow on many media types
--Beaded GPB
--partially acid fast (some mycolic acid in cell wall)
--colony and micro morpho can resemble fungus
--slower growing
Soil organisms:
--Immunocompro: at higher risk for pulmonary--> brain lesion
--immunocompet: cutaneous, feet
Nocardia spp gram stain
beaded GPB
Acid fast: partially
Streptomyces spp
branching, filamentous aerobes
--common cause of actinomycetomas
--rare systemic infections
--used for antimicrobials
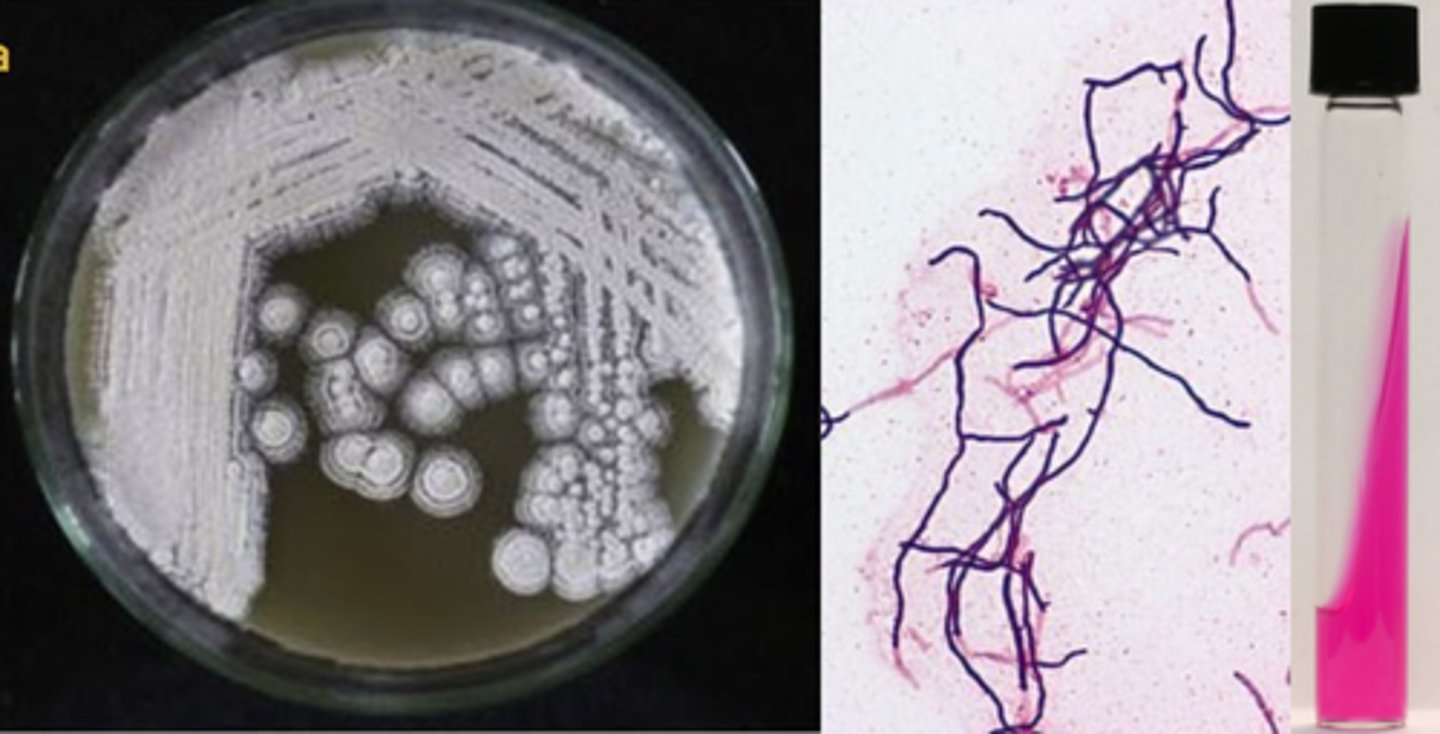
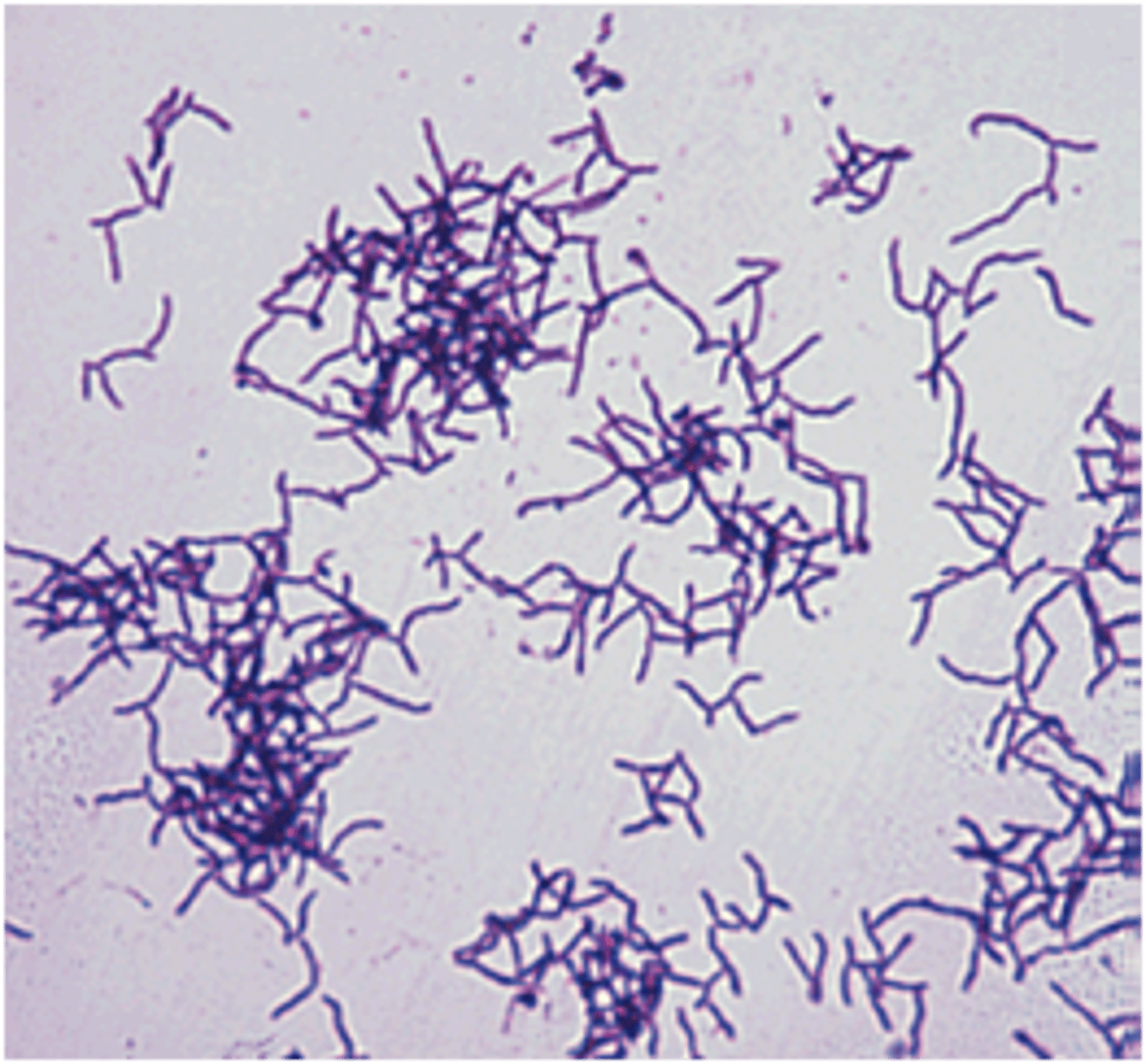
Actinomyces spp
Branching, filamentous ANAEROBES (many NOT obligate), fastidious
Colonies may be pigmented
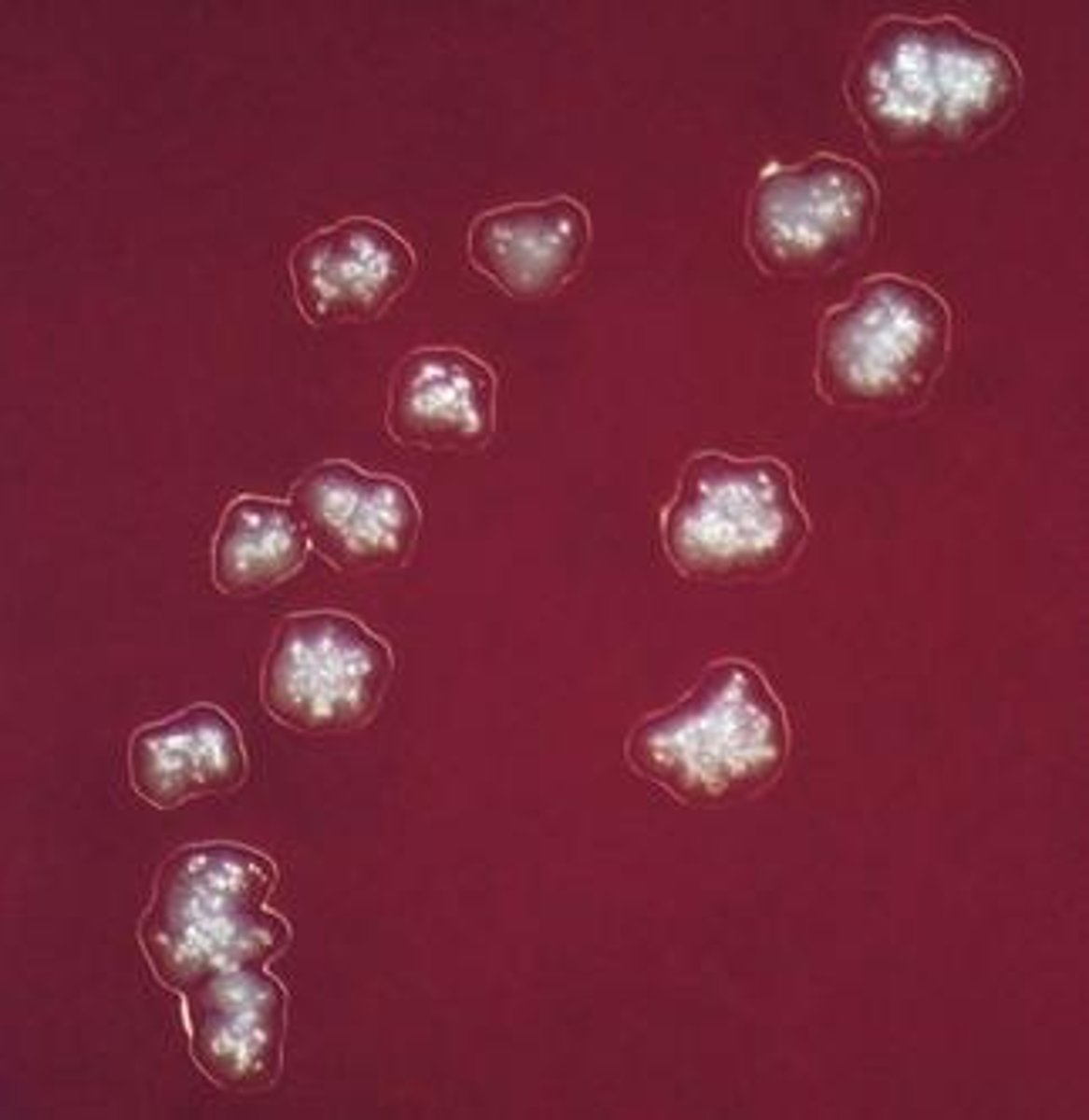
A. israelii: molar tooth colonies
Actinomyces israelii molar tooth colonies
Actinomyces spp disease locations
mouth, pharynx, GU tract, distal esophagus
Mycobacterium spp
Acid fast: large amounts of mycolic acid in cell wall; AFB +
Skin infections: M. marinum, M. ulcerans, M. leprae
Pulmonary infections: M. tuberculosis, M. avium-intracellulare complex "MAC"
Mycobacterium spp in the lab
Acid fast:
--Kinyoun and Ziehl-Neelson stain
OR
Auramine rhodamine stain (fluorescent)
Growth media: Middlebrook 7H10, 7H11
Lowenstein-Jensen
Urea test
Nocardia spp POSITIVE
pinK: Klebsiella
P: Proteus
U: Ureaplasma
N: Nocardia
C: Cryptococcus
H: Helicobacter
Temperature tolerance testing
some actinomycetes can tolerate high temp
-score growth as 0 to 4+
--incubate at various temps (ex: 25, 37, 42 C)
Dimorphic fungi
yeast phase: body temp
Mold phase: room temp
Risk factors for dimorphic fungal infection
immunocompromised and immunocompetent
--certain geographic locations
Prepping dimorphic mold for microscopy
BSL3
--Coccoides spp has the highest risk for aerosolization and lab-acquired infection
Blastomyces dermatitidis
Blastomycosis: all ages vulnerable, immunocompromised more severe infection
Infection: inhalation of conidia, expore to lake/stream soil or disturbed soil
Infection types: skin lesions or pneumonia
Blastomyces dermatitidis mold form
B. dermatitidis
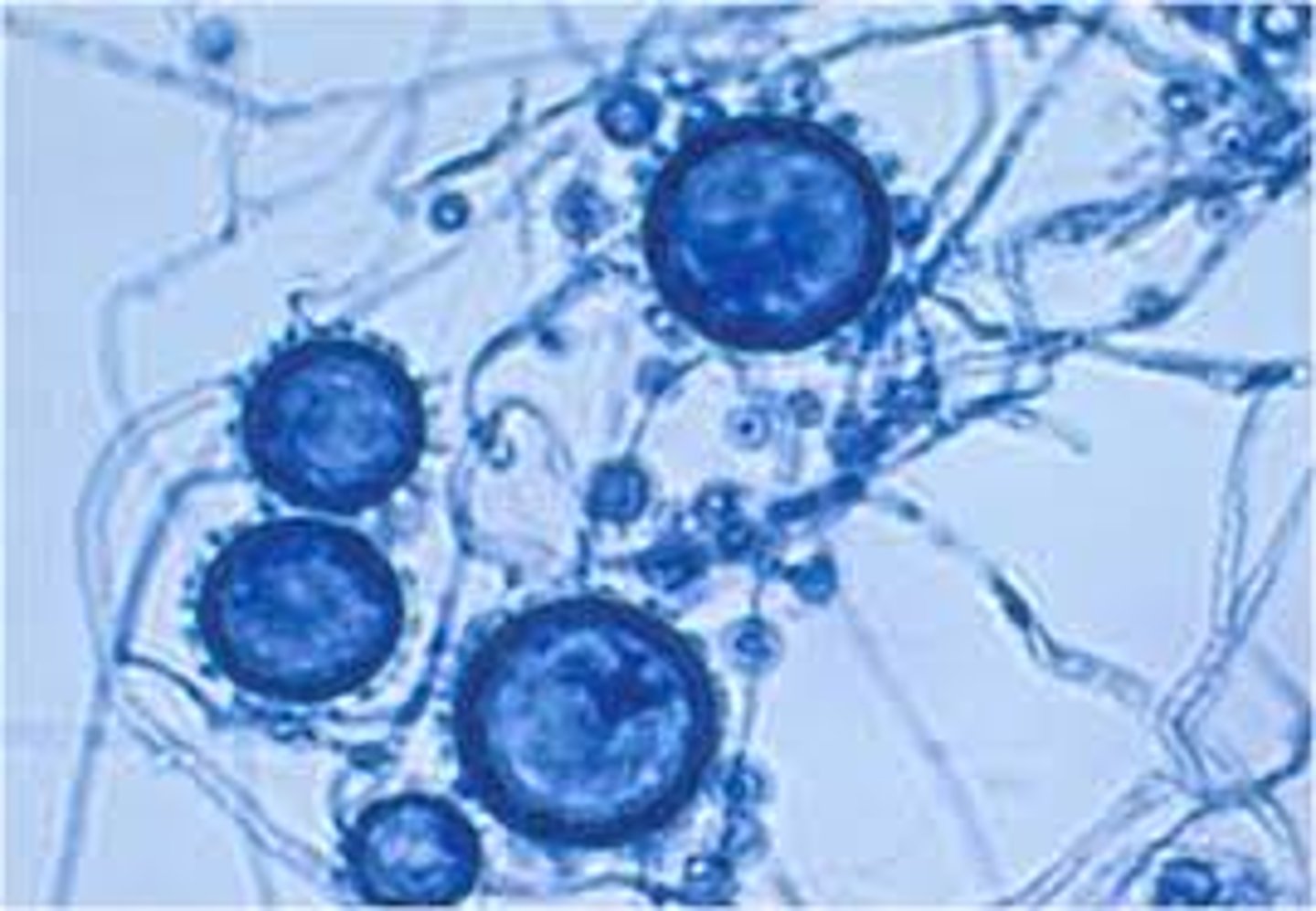
Coccioides imnitis
Coccoidiodomycosis/ Valley fever
--hot and dry conditions increase incidence
--inhalation of conidia
--all at risk, esp elderly/immunocompromised
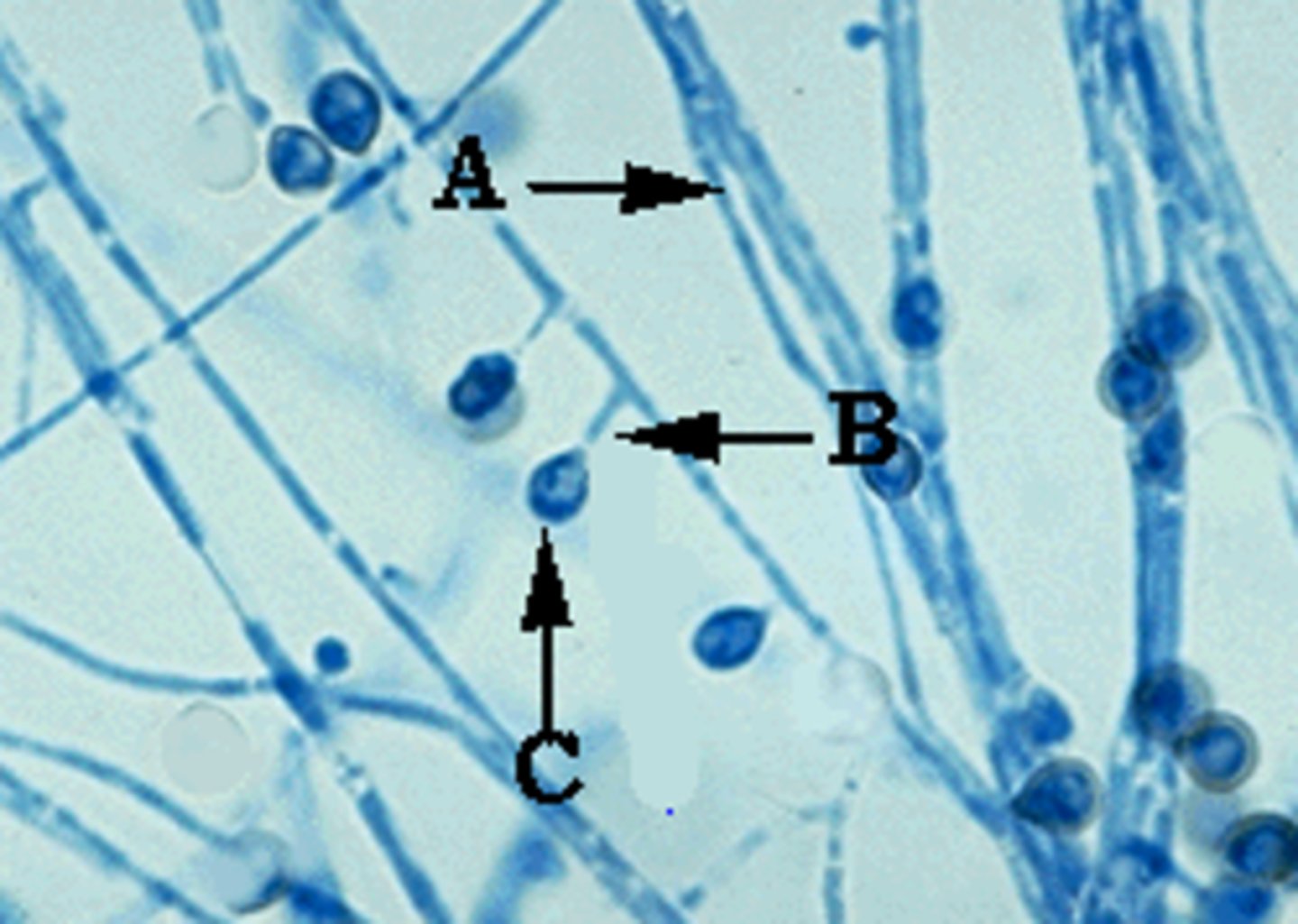
Histoplasma capsulatum
Histoplasmosis
--inhaled microconidia
Risk factors: disturbed soil, bird bat dropping exposure, immunocompromised
Target tissue: pulmonary
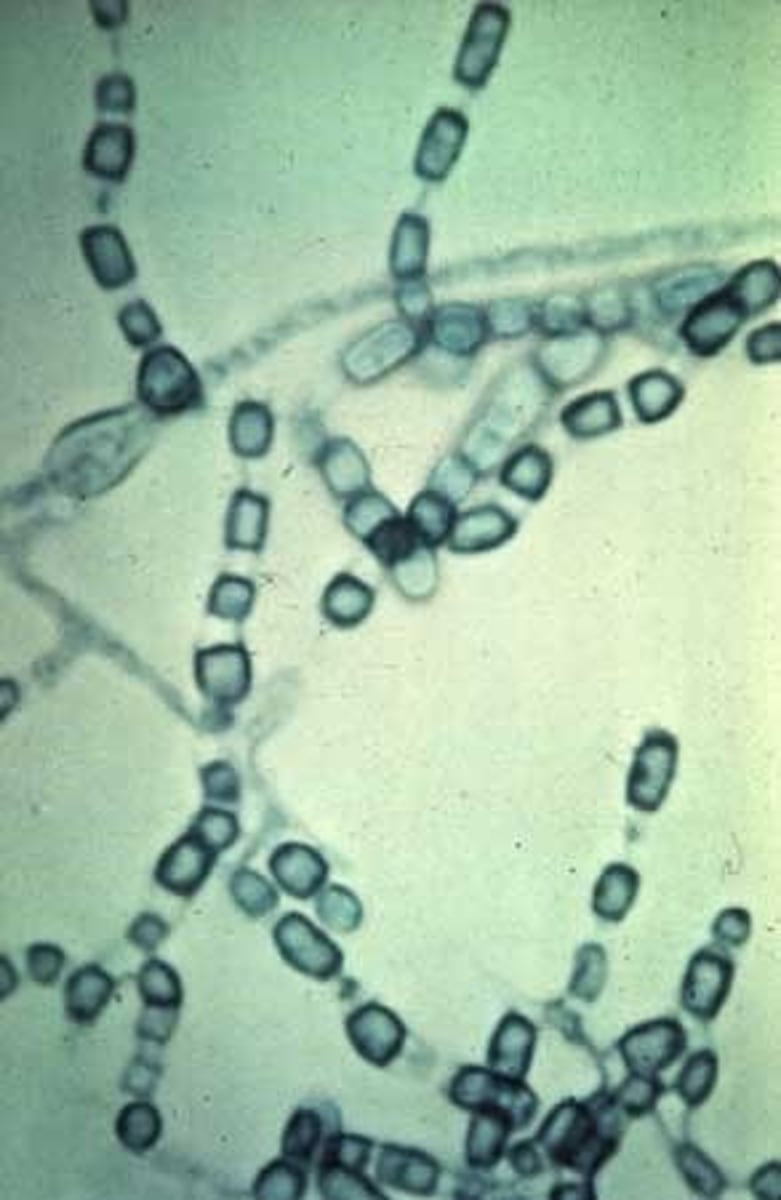
Paracoccidioides brasiliensis
Paracoccidioidomycosis
Infection: inhalation of conidia (disturbed soil)
--direct handling of plants
Sites of infection: pulmonary, lymphatics, mucous membranes
Estrogen protects against infection
"mariner's wheel"
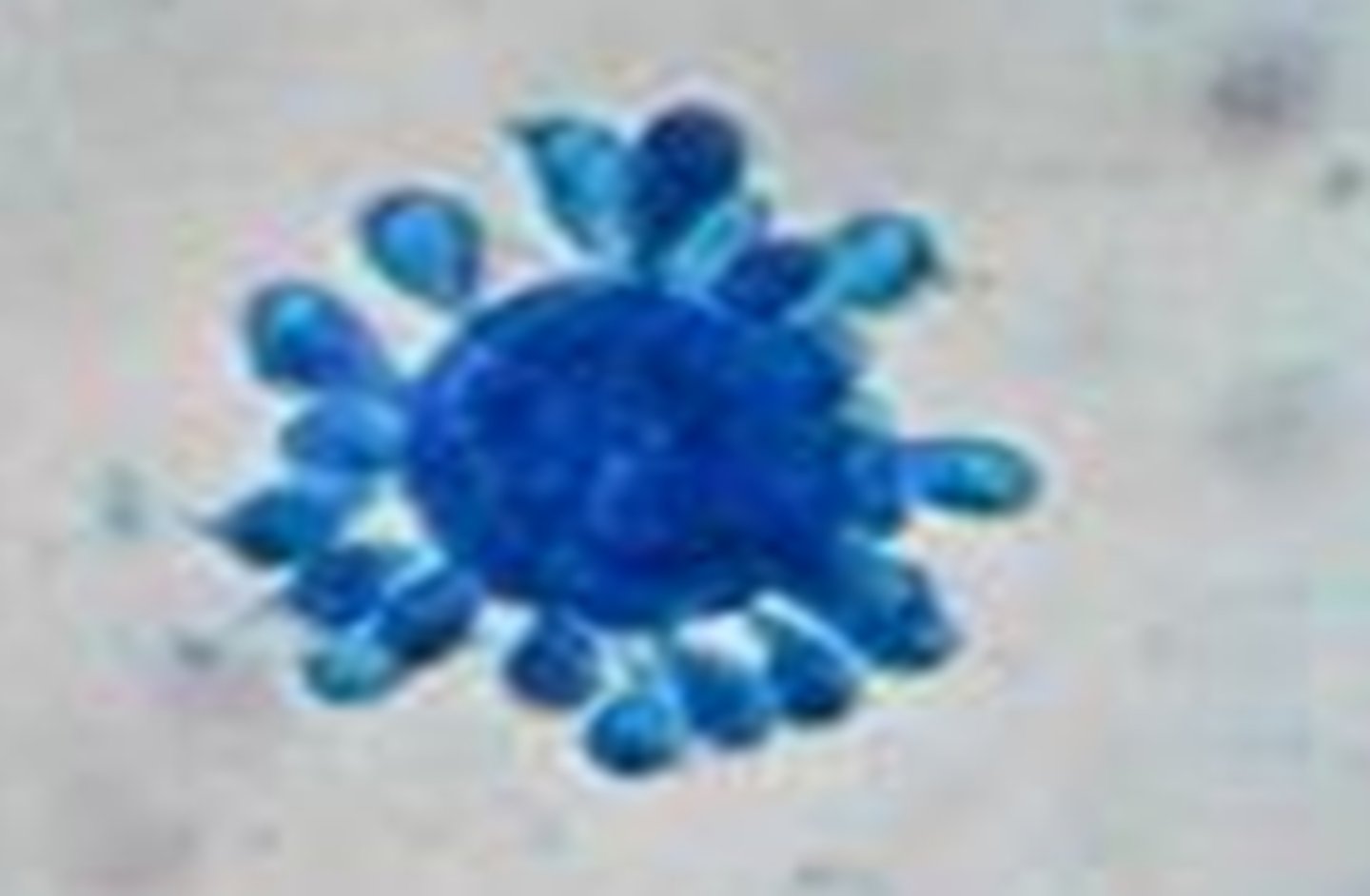

Sporothrix schenckii
"rose gardener's disease"
--cutaneous lesions on people that work with plants
--pulmonary or disseminated disease (joints) in the immunocompromised
Opportunists
very common in the environment, but can cause infections in certain scenarios (ex: pt is immunocompromised or in sterile sites)
--common culture contaminants
Opportunistic mold characteristics
fast growers; 2-3 days to mature
Not a contaminant when: isolated repeatedly from same patient/different sites, predominant organism in culture or pt is immunocompromised
Aspergillus spp prevalence
(in order)
1. Aspergillus fumigatus
2. Aspergillus flavus
3. Aspergillus niger
4. Aspergillus terreus
Media to Grow and ID the Opportunists
SAB-DEX
IMA (+ chloramphenicol)
Mycosel (+ chloramphenicol and cycloheximide; MANY Aspergillus spp inhibited)
Mucormycosis
a serious, acute fungal infection of the nasal sinuses+ eyes (rhino-orbital); leads to meningitis and can be rapidly fatal
Associated with: lymphoma, diabetes, AIDS, post-transplant
Suspect if: wooly, gray-white rapid grower; "lid-lifter"
Most common cause: Rhizopus spp
Mucormycete hyphae
broad and ribbon-like; ASEPTATE (sparse septa possible, but rare, unlike SEPTATE)
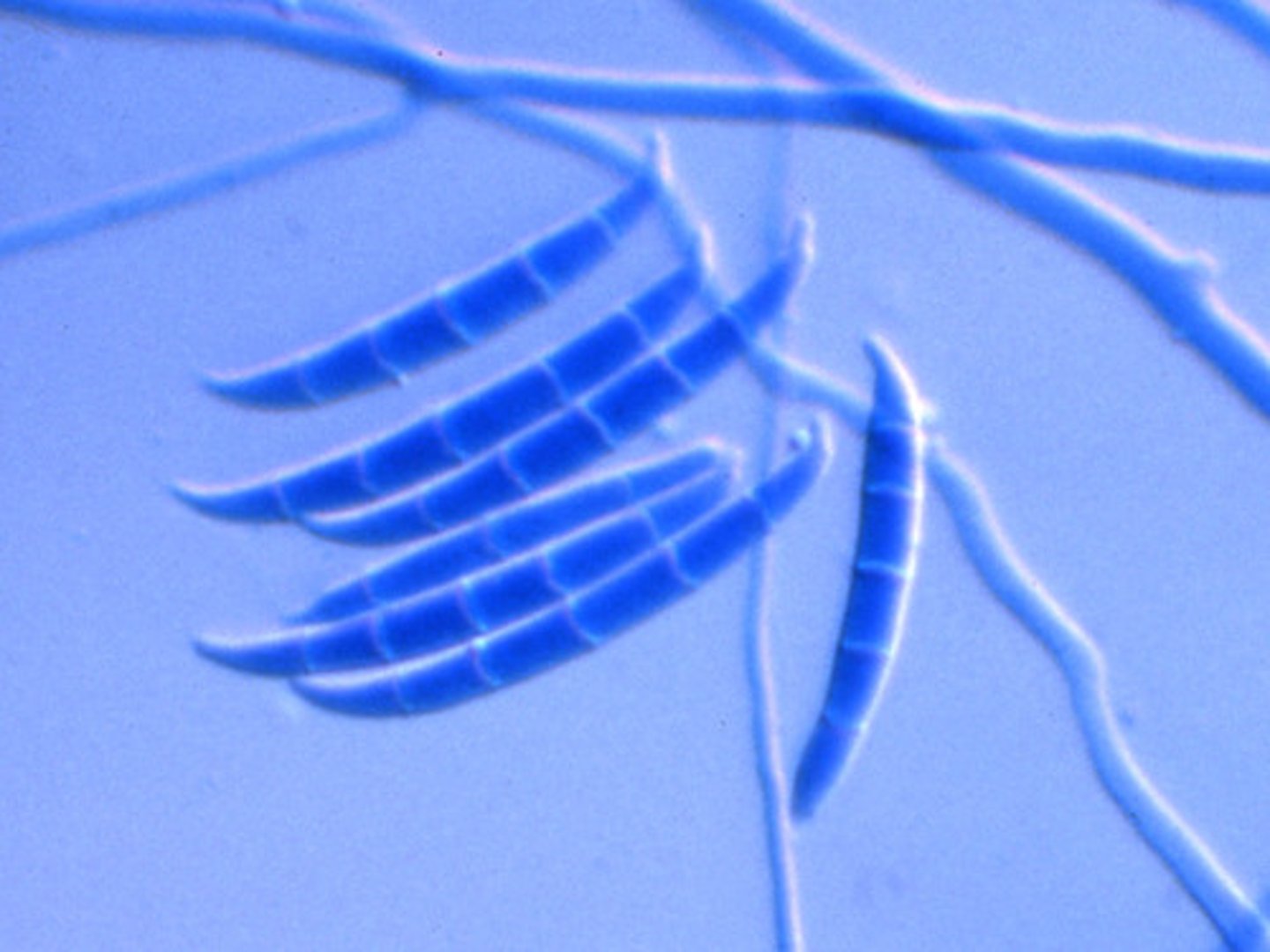
Alternaria spp
2-3 days
Light gray, wooly
Reverse: black
Microscopic: dark hyphae, chained, club-shaped poroconidia with tapered ends
Conditions: keratomycosis, skin, osteomyelitis, pulmonary disease, nasal septum
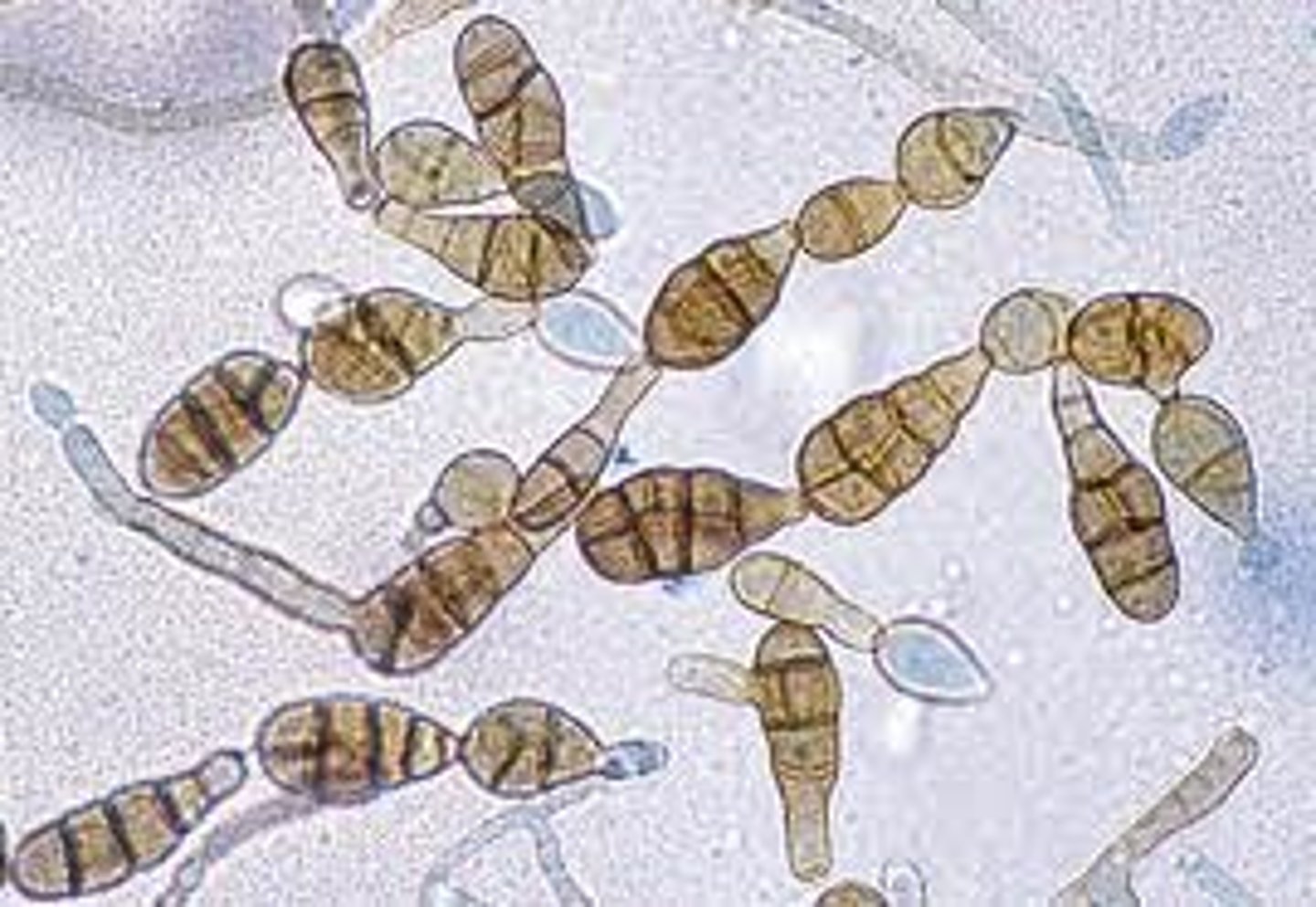

Bipolaris spp
2-3 days
Velety, wooly, gary-brown
Reverse: black
Microscopic: septate, dark hyphae
--cylindrical-shaped poroconidia with 4-5 cells inside
Conditions: keratomycosis and fungal sinusitis
Cladophialophora/ Cladosporium spp
Moderately slow; 7 days to mature
Powdery, velvet, dark gray, green; heaped and folded
Reverse: black
Microscopic: septate hyphae, short chains of dark blastoconidia
Conditions: keratomycosis/allergies
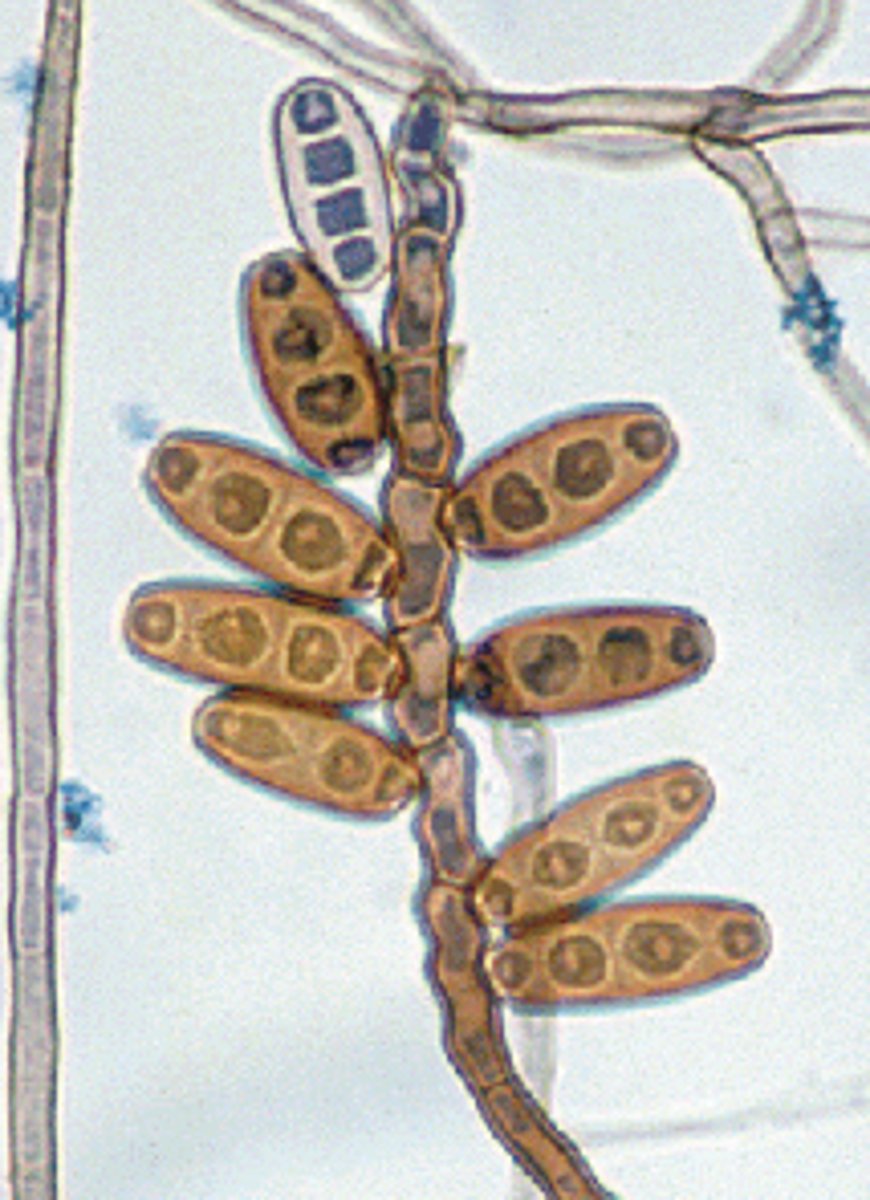
Curvularia spp
Rapid; 2-3 days
Cottony, white, light pink, orange or green
Reverse: brown
Microscopic: septate hyphae with dark poroconidia with 4-5 cells inside; boomerang shape
Conditions: keratomycosis, mycetoma, endocarditis, pulmonary, allergies, nasal septum
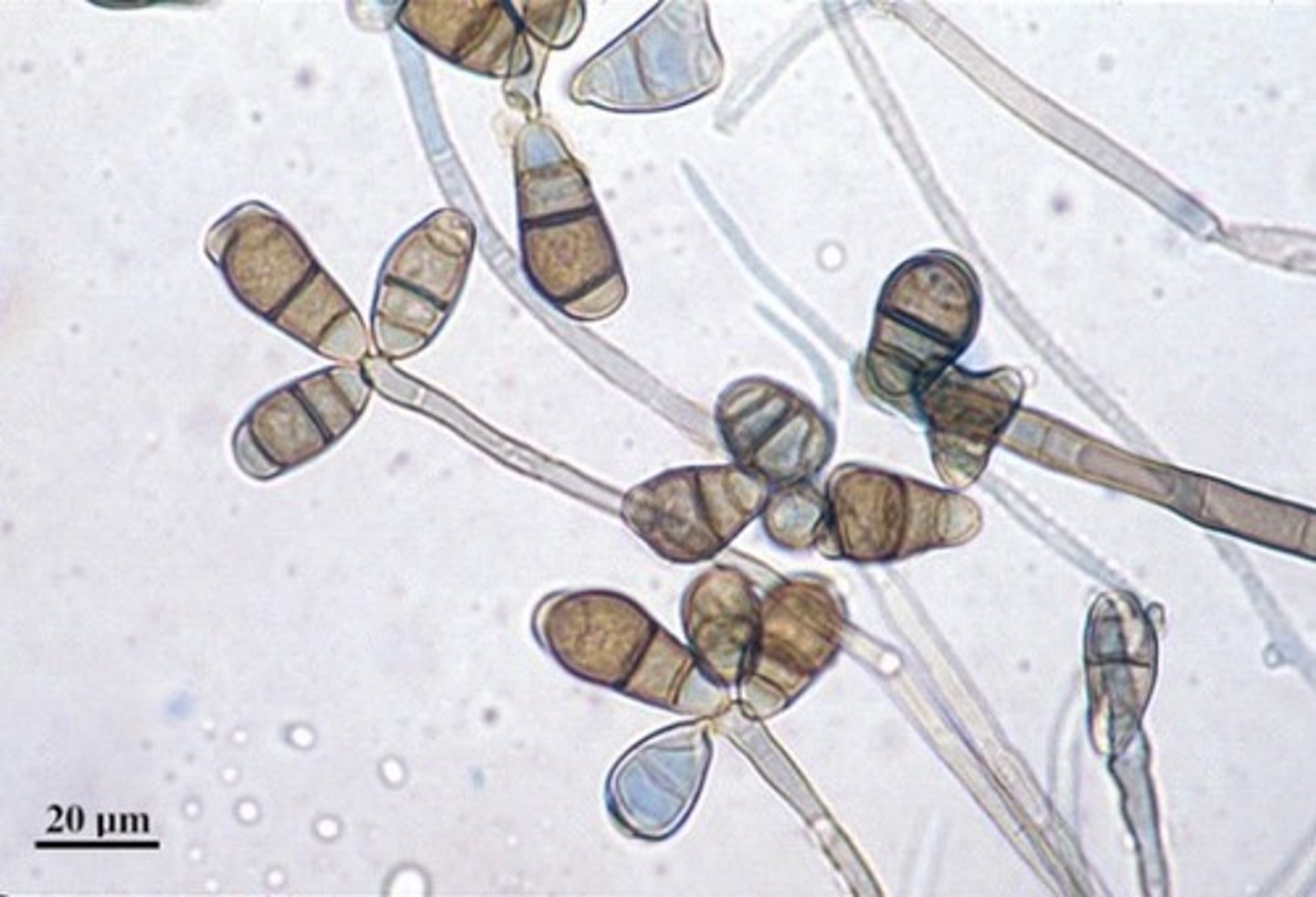

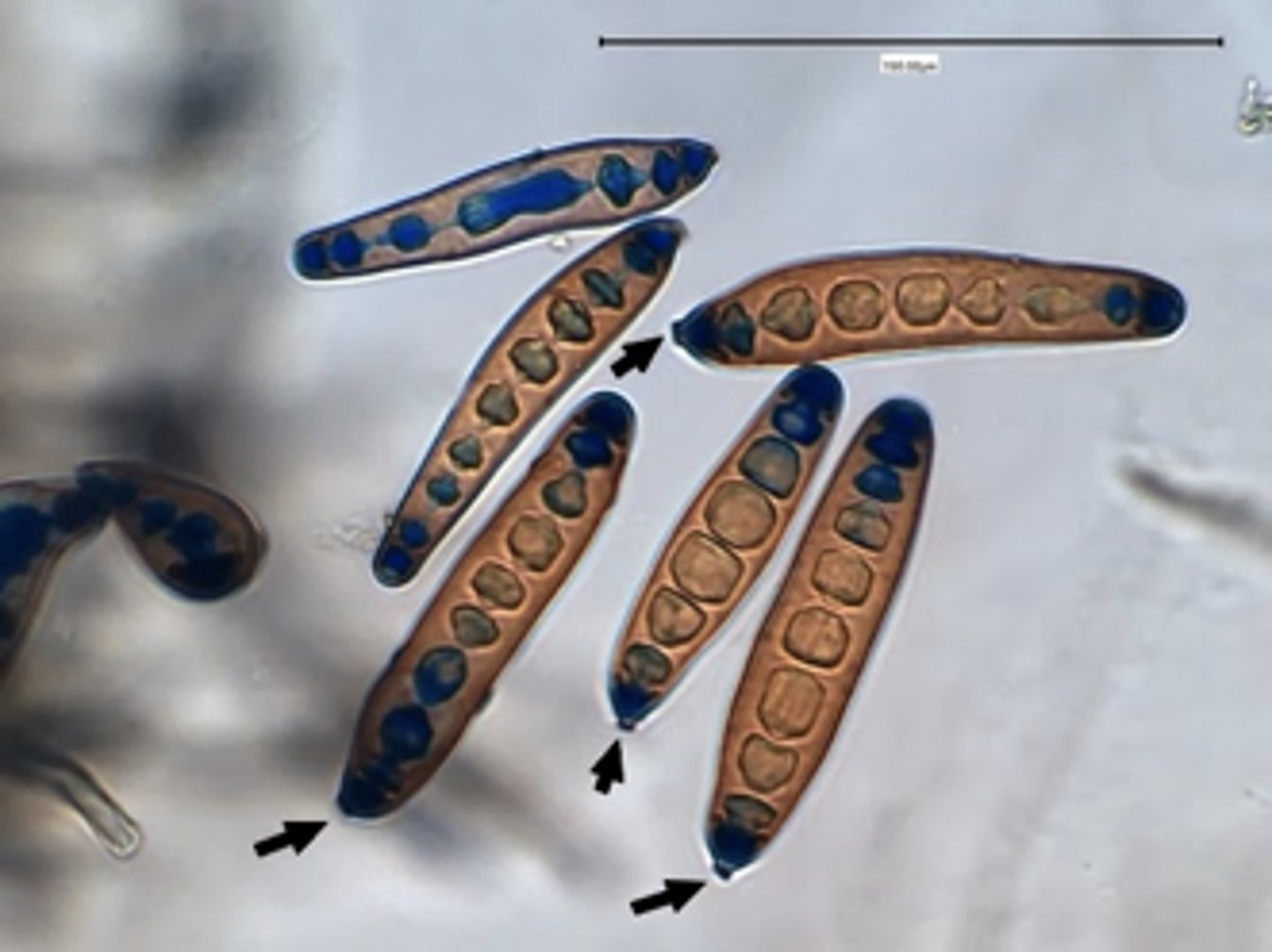
Exserohilum spp
2-3 days; rapid
Light gray, wooly, becomes gray-black
Reverse: black
Microscopic: septate hyphae with long cylindrical poroconidia with 6-14 cells. has a scar on the conidium
Conditions: Fungal sinusitis
Epicoccum spp
2-3 days; rapid
Rings of yellow, orange, brown pigment that diffuses into agar
Reverse: black
Microscopic: thick clusters of poroconidia
Conditions: allergies

Nigrospora spp
rapid; 2-3 days
White, wooly
Reverse: black
Microscopic: short, fat conidiophores; black conidia at tips
Conditions: keratomycosis
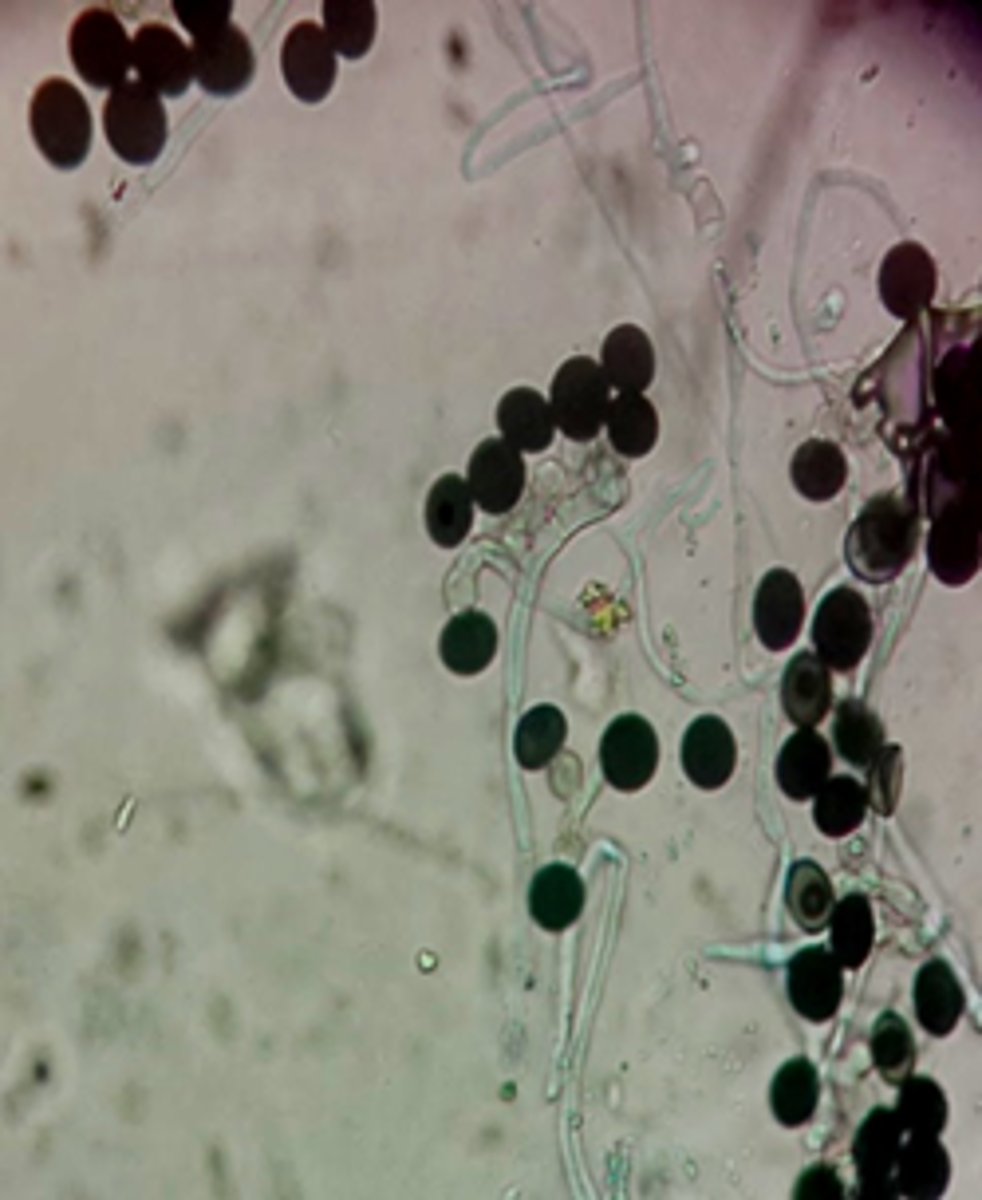
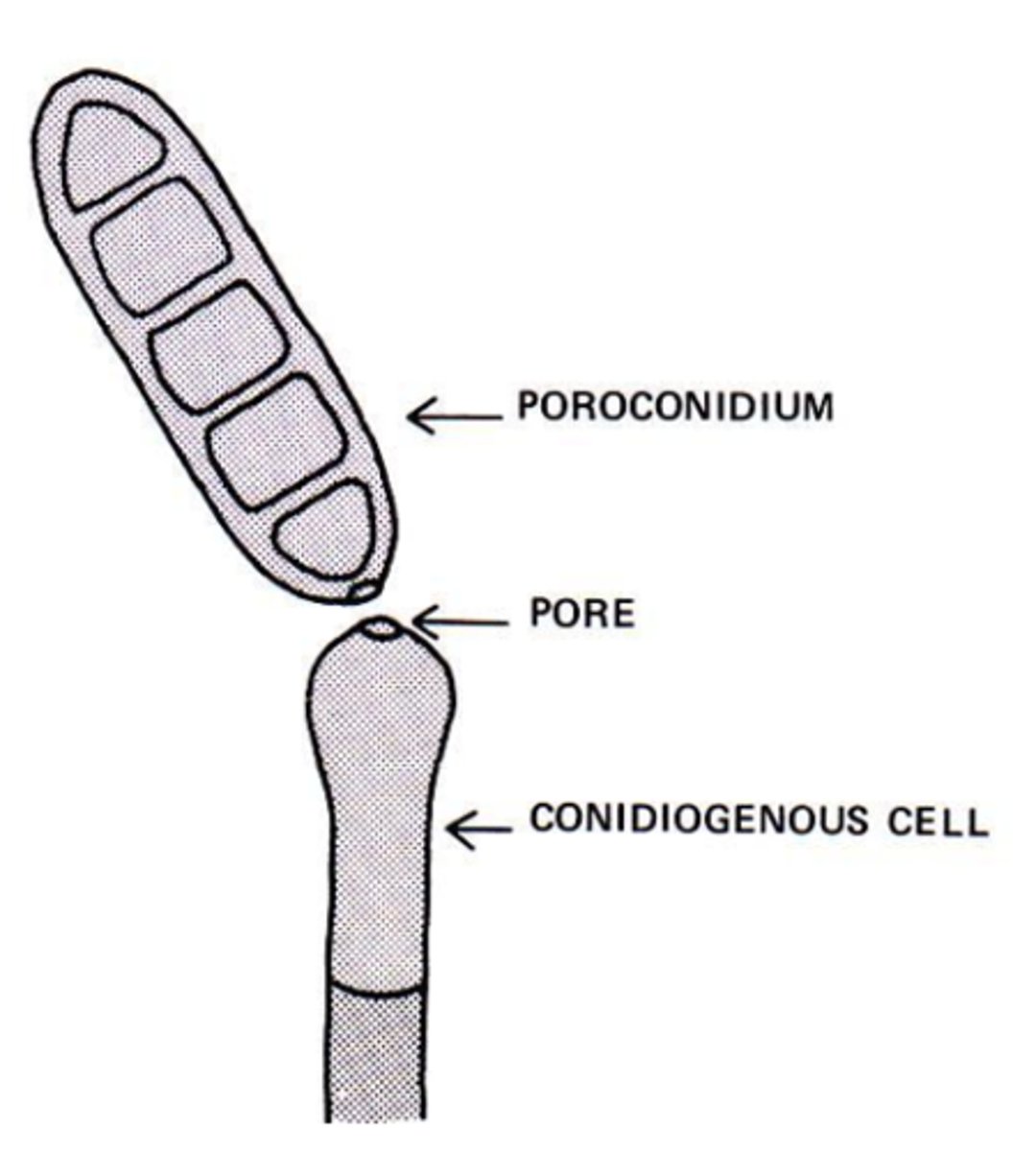
Poroconidium
a conidium developed through a channel or pore in hyphae
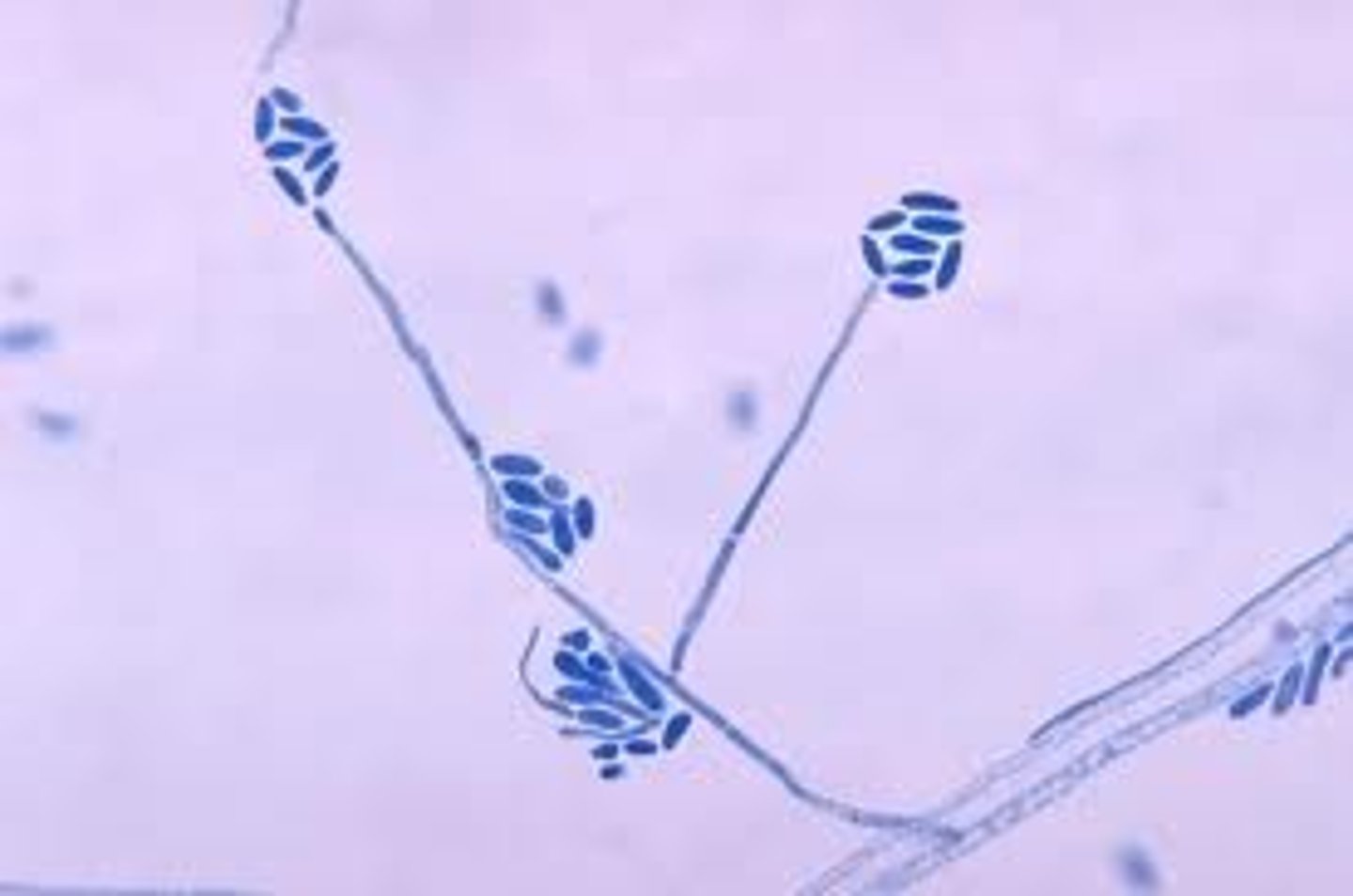
Acremonium spp
rapid; 2-3 days
Wrinkled, white, gray or rose
Reverse: colorless, pale yellow, pink
Microscopic: septate hyphae; tapering conidiophores that support balls of of conidia; can be confused with Sporothrix
Conditions: keratomycosis
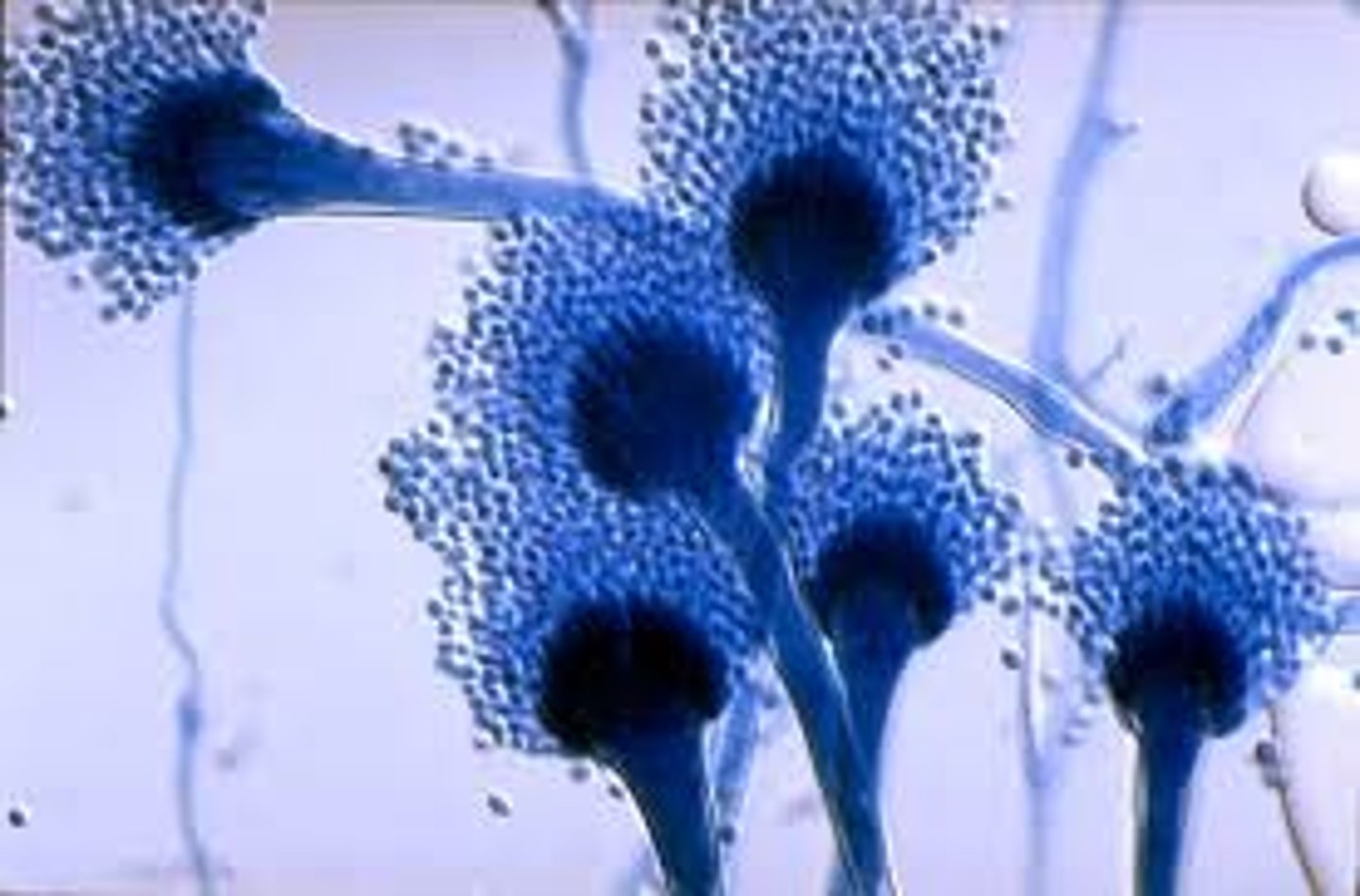
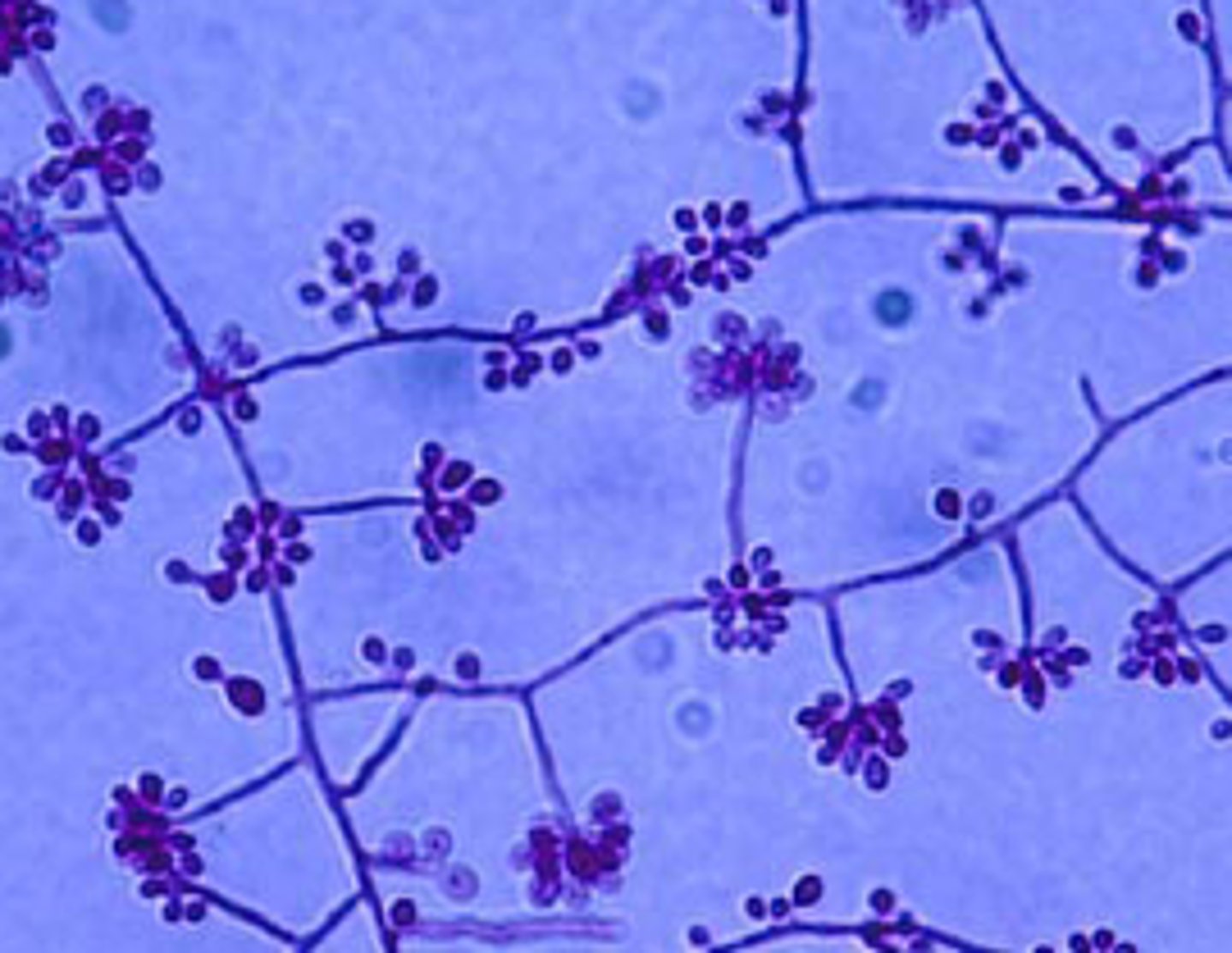
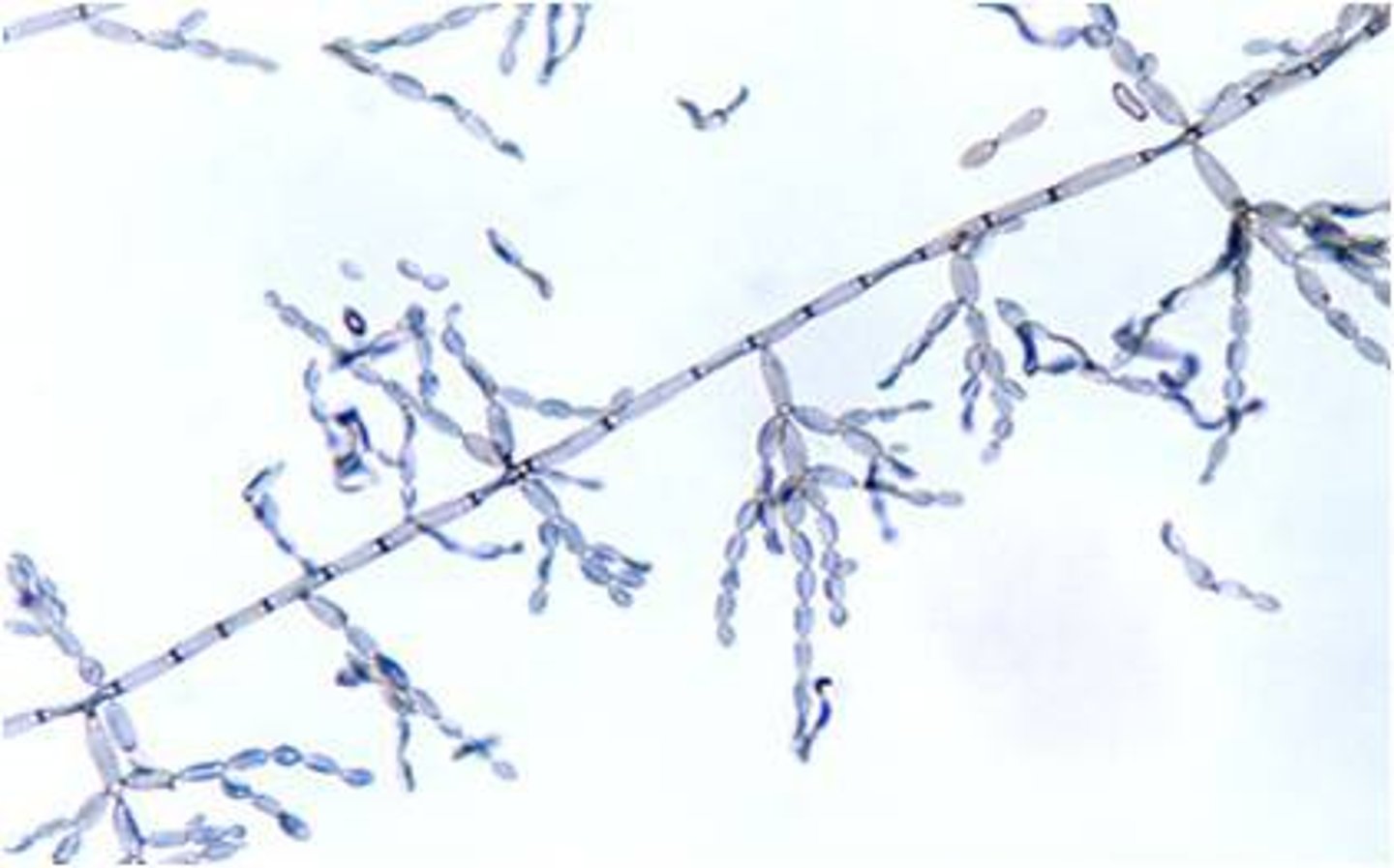
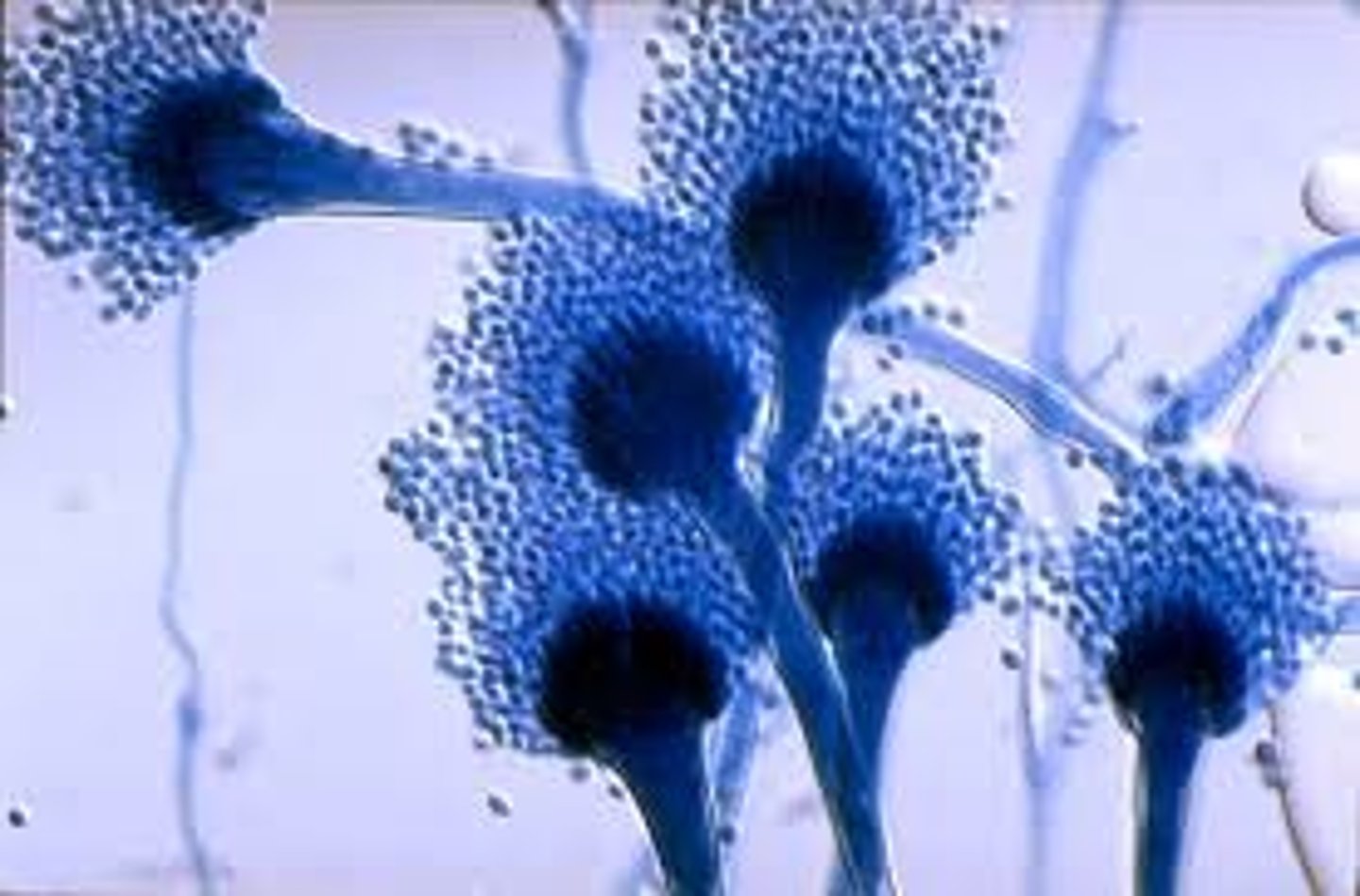
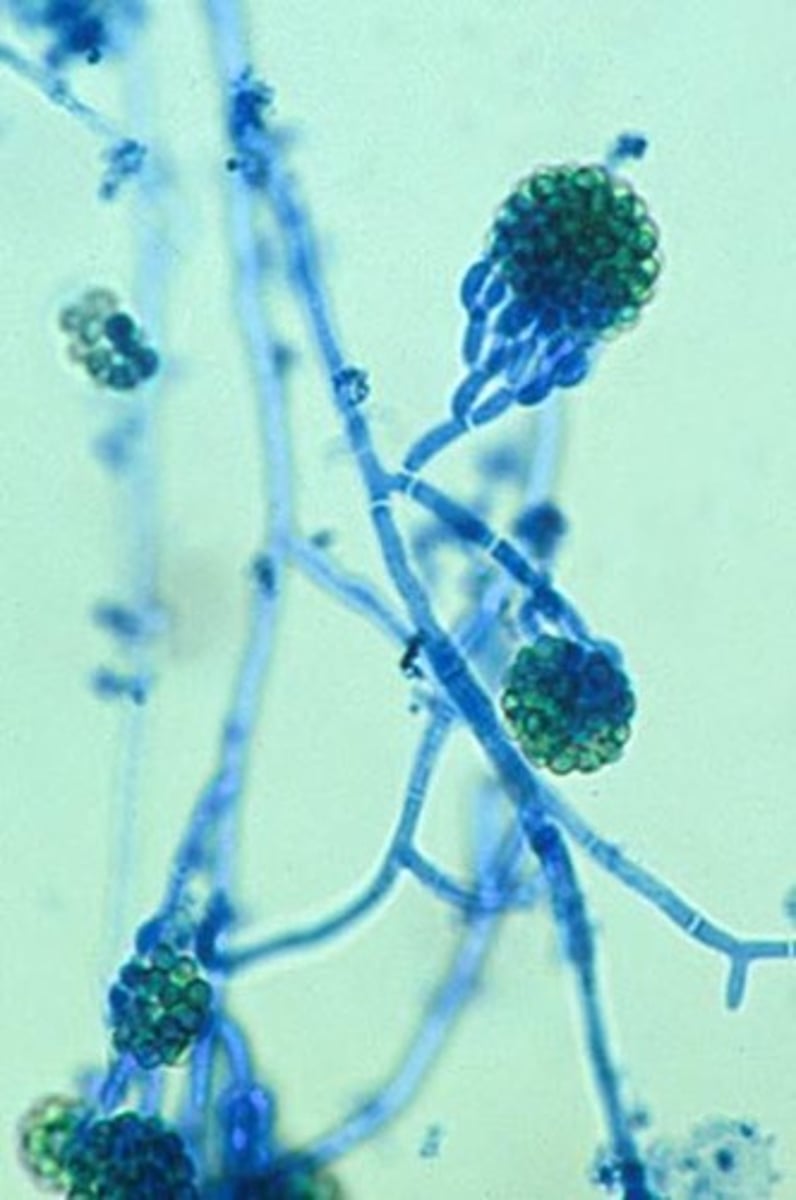
Aspergillus spp
Rapid; 2-3 days
Rugose, velvety, blue, green, yellow, black or white
Reverse: colorless
Microscopic: septate, unbranched conidiophores with a foot cell and large vesicle at tip. phialides will form a single or double row. around vesicle
A. fumigatus will grow at 45 C
Conditions: disseminated aspergillosis, pulmonary, allergies, keratomycosis, otomycosis, nasal sinusitis
**most common opportunist pathogen
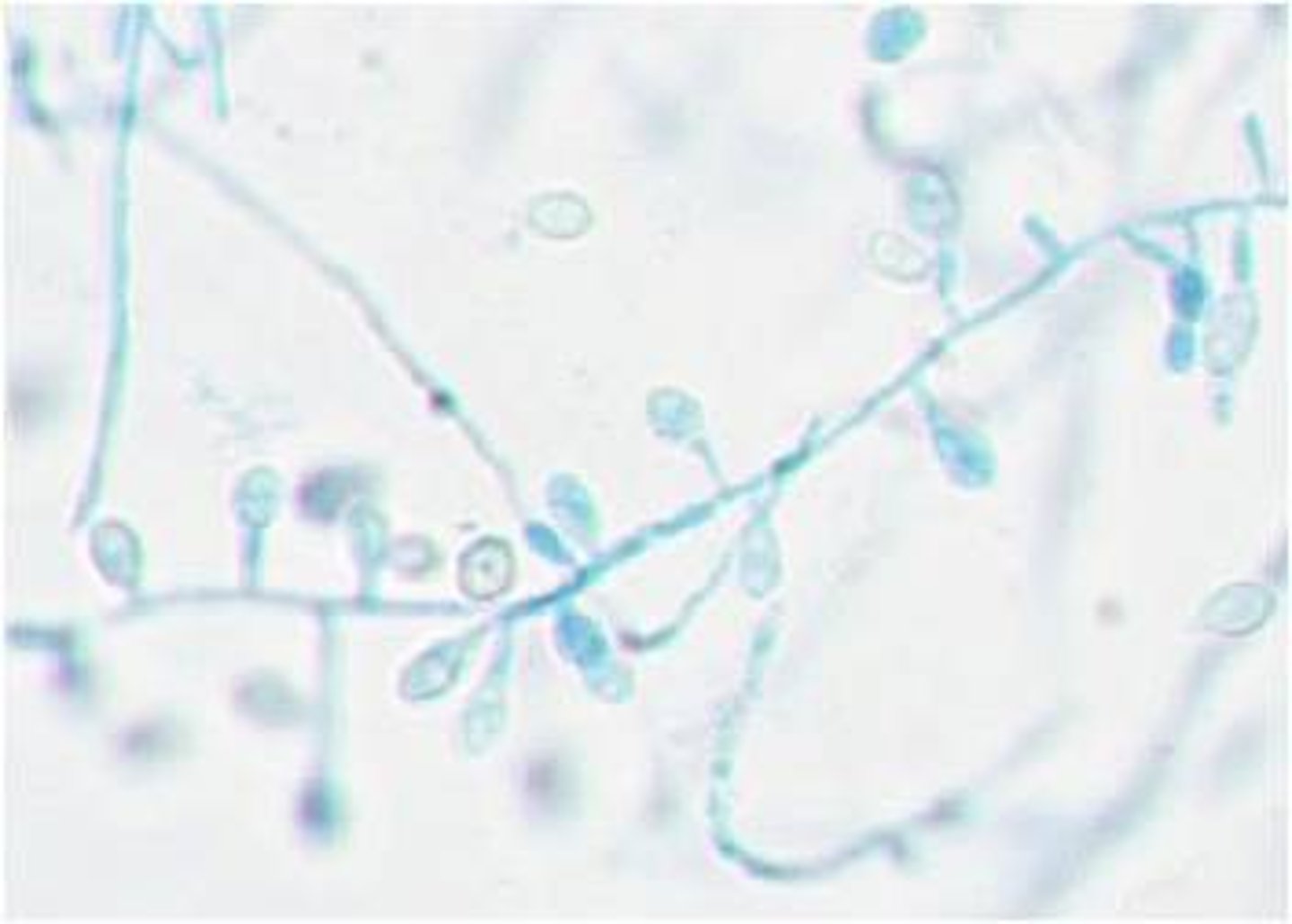
Chrysosporium spp
rapid; 2-3 days
Heaped, velvety, buff color
Reverse: white, yellow or brown
Microscopic: single, clubbed conidia: may be confused with blasto or histo
Conditions: n/a usually a contaminant
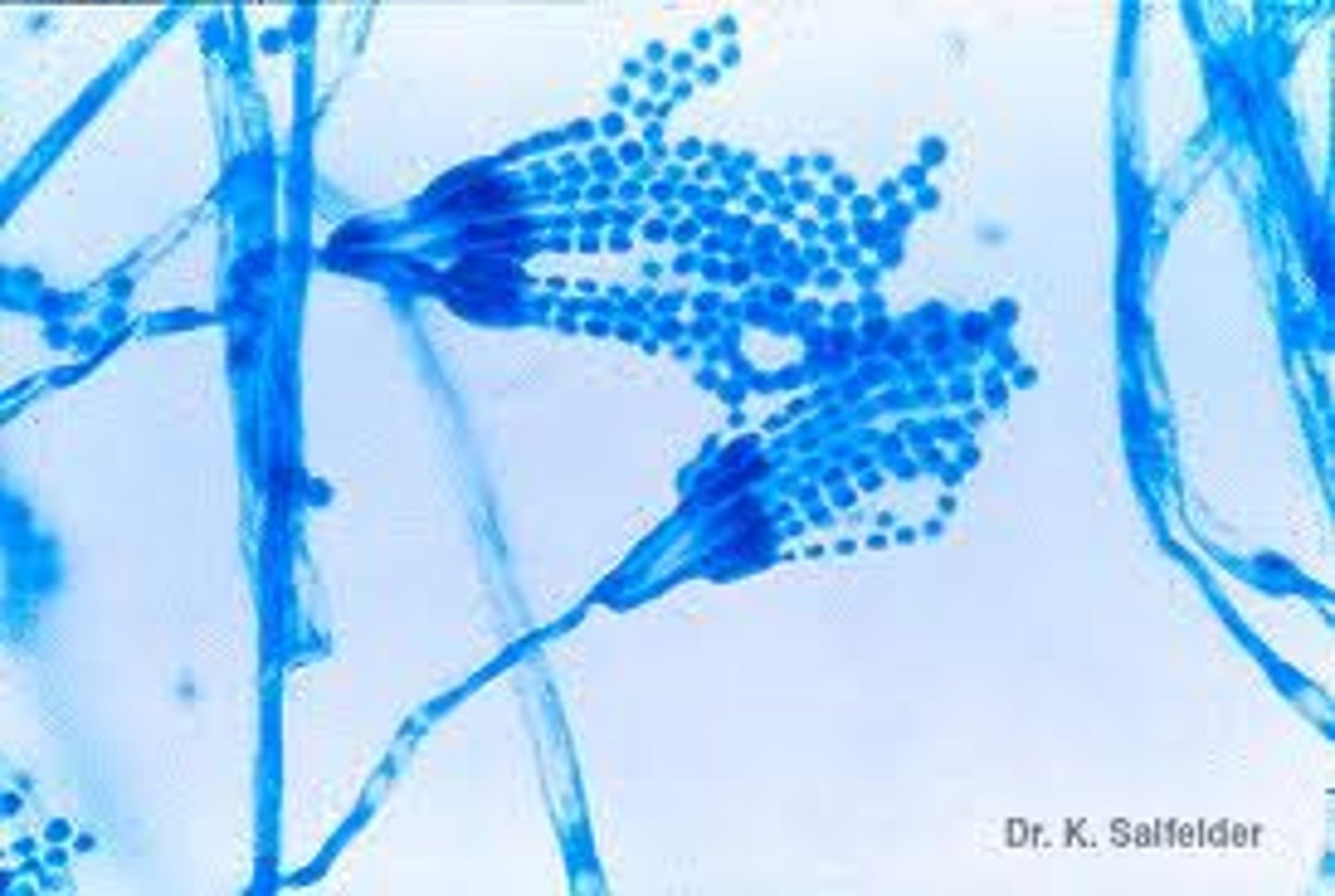
Fusarium spp
Rapid
White, wooly, turns lavender with age
Reverse: colorless
Microscopic: macrophialoconidia banana shaped
Conditions: keratomycosis (most common cause)
Gliocladium spp
Rapid
White, fluffy, turns green
Reverse: white
Microscopic: phialoconidia held in a ball
Conditions: contaminant; n/a
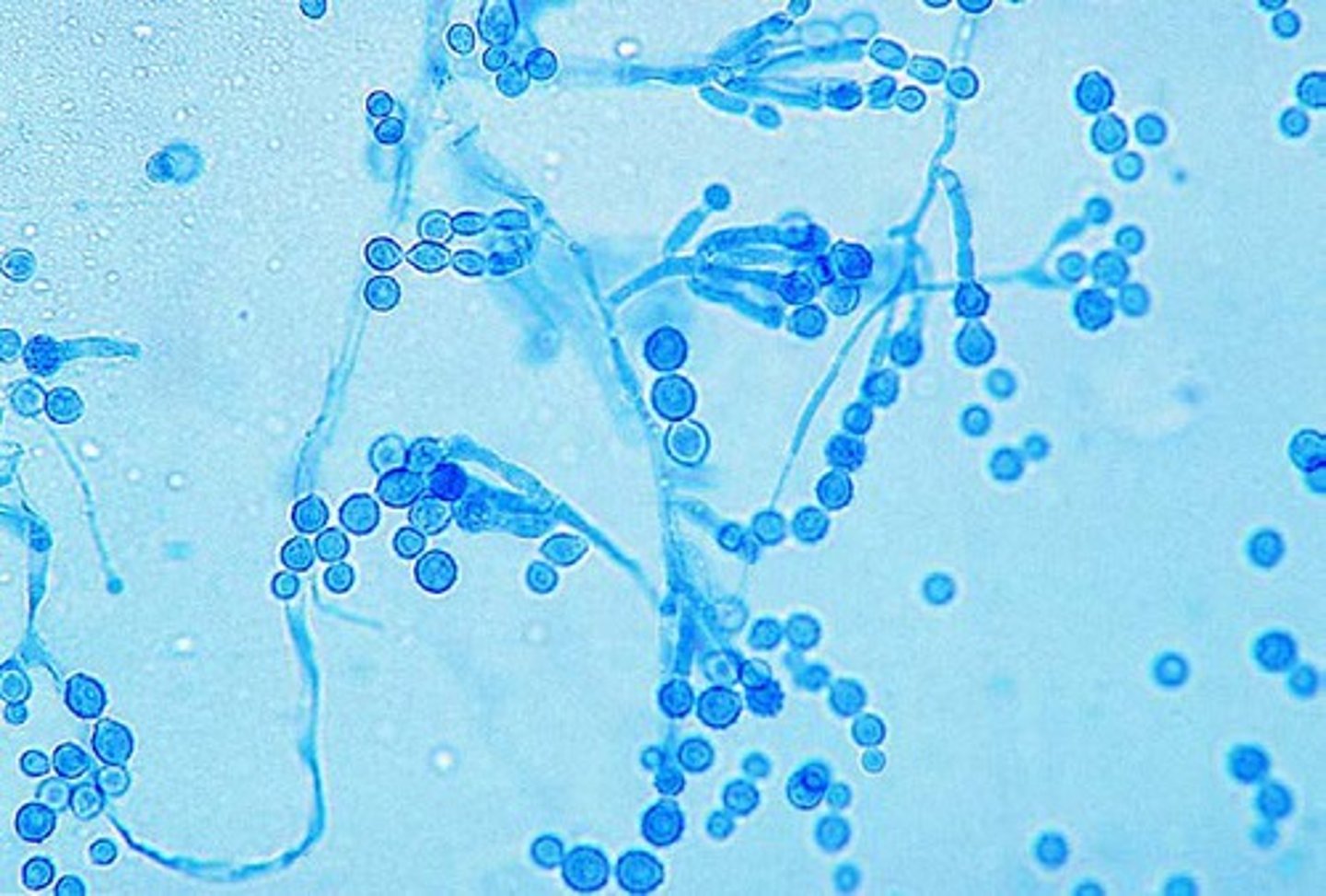
Paecilomyces spp
rapid
Powdery, velvety-white, becomes olive tan or pink
Reverse: colorless
Microscopic: elongated phialides have chains of oval conidia
Conditions: skin lesions and endocarditis
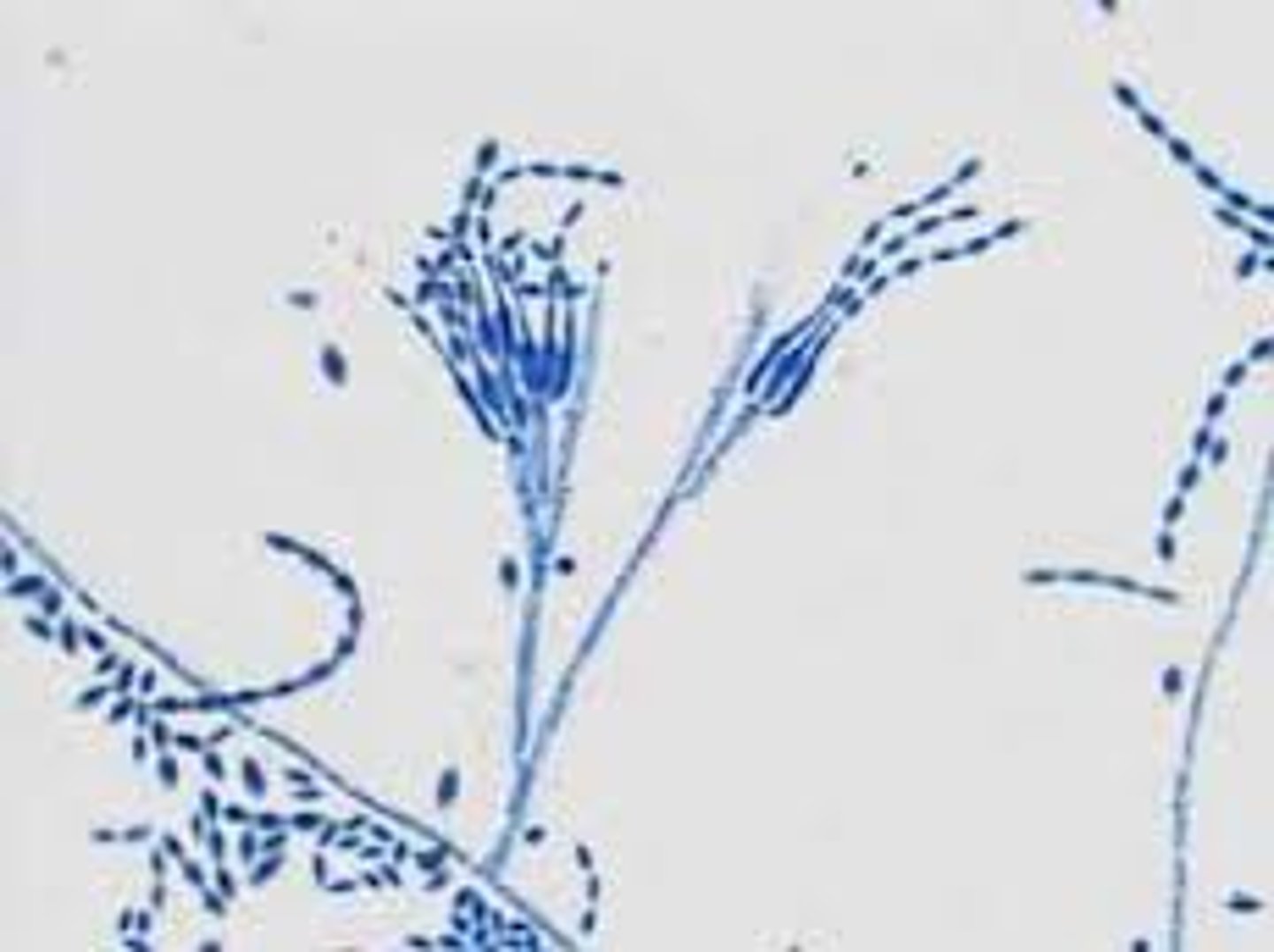

Penicillium spp
Rapid; 2-3 days
Velvety-white, becomes powdery, blue green
Reverse: colorless
Microscopic: chains of phialoconidia--paint brush
Conditions: contaminant; also causes keratomycosis, penicillinosis, otomycosis, onychomycosis
Scopulariopsis spp
Rapid; 2-3 days
Velvety, rugose, white then tan-brown
Reverse: brown
Microscopic: penicillium-like anelides support large, lemon-shaped anelloconidia that have spines (with age)
Conditions: keratomycosis
Sepedomium spp
Rapid; 2-3 days
Waxy, white, velvety lemon color with age
Reverse: white
Microscopic: thick walled, round macroconidia; differentiate from Histoplasma by lack of yeast phase (37 C)
Conditions: n/s, contaminant
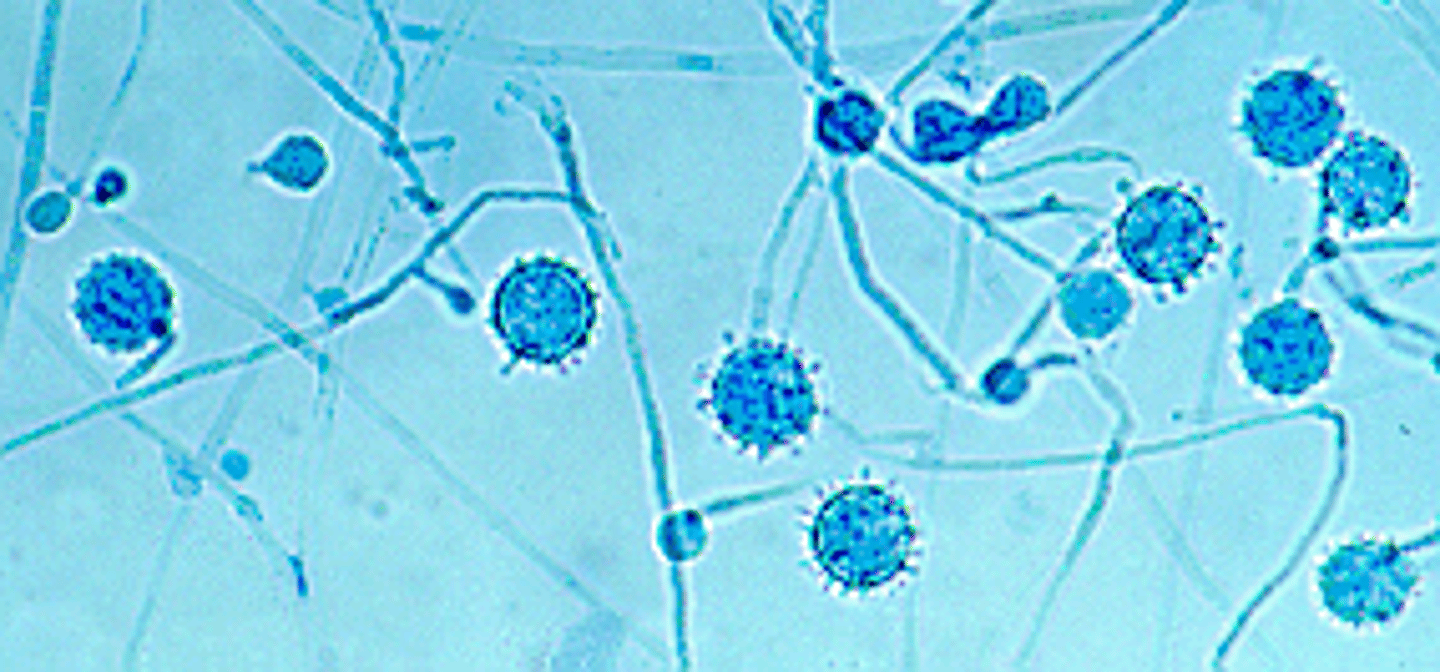
Uniserate phialides
1 level of phialides and then conidia
biserate phialides
two levels of phialides, then conidia
Rhizopus spp
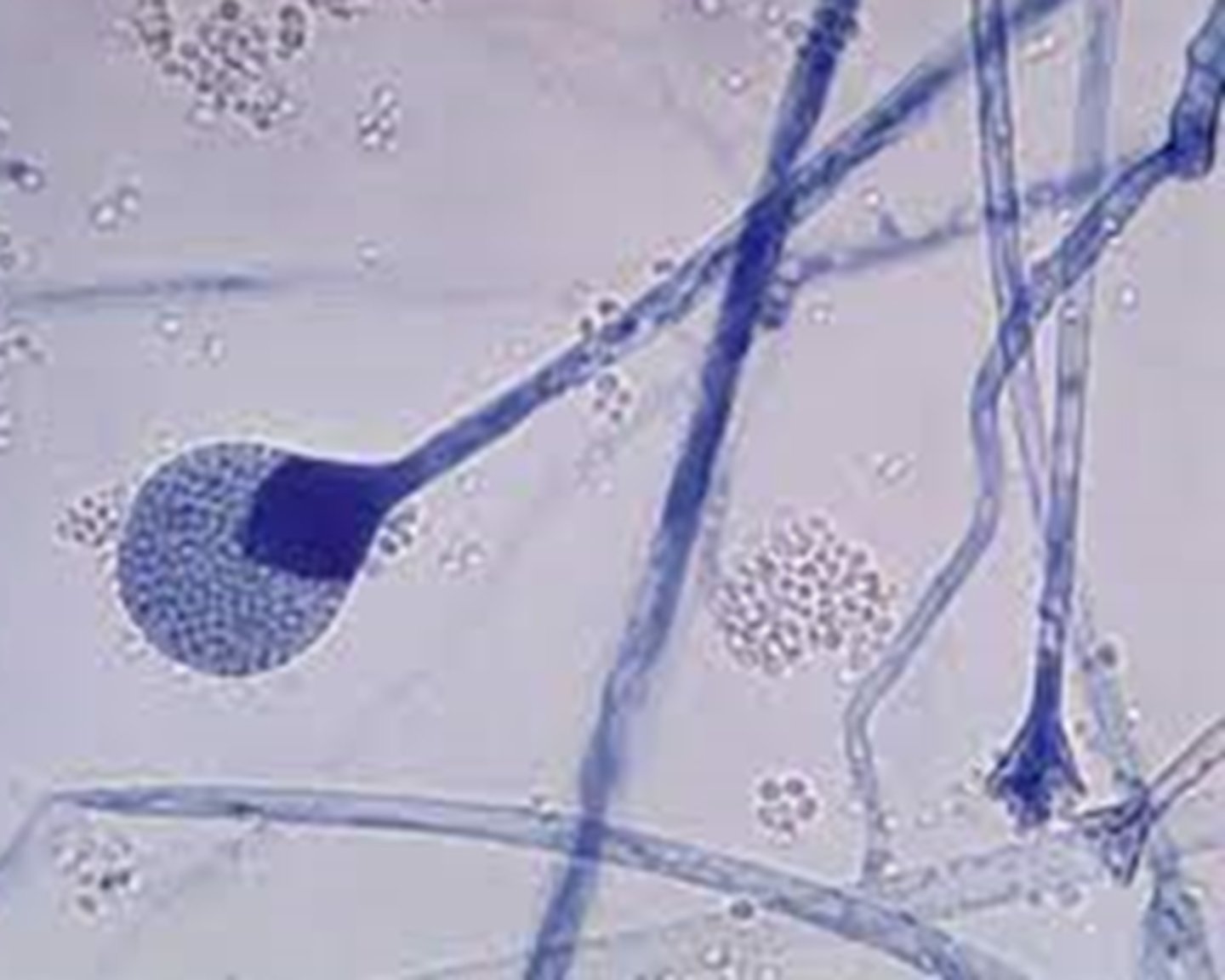
Mucor spp
Cunninghamella spp
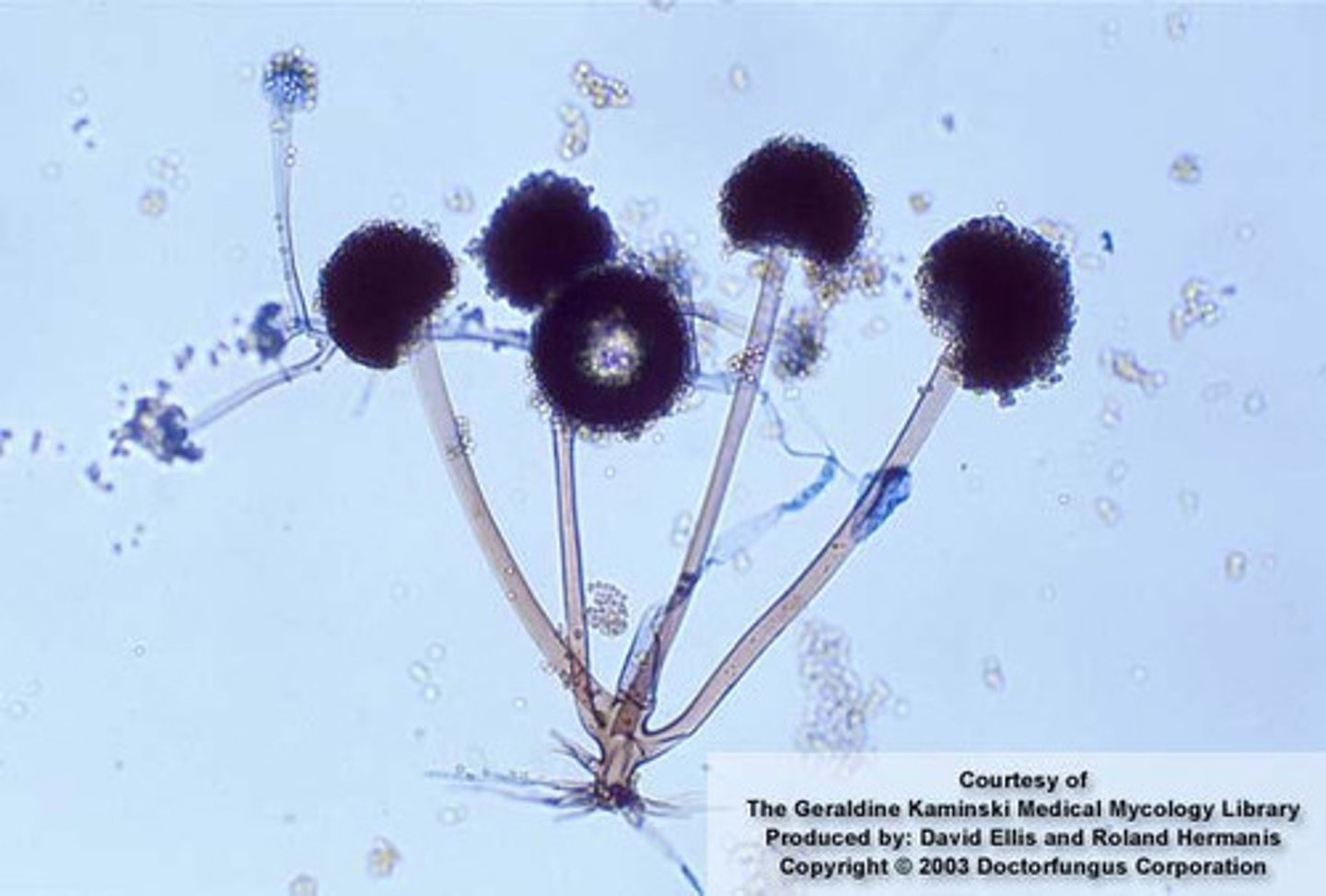
Aspergillus niger
Aspergillus niger microscopic
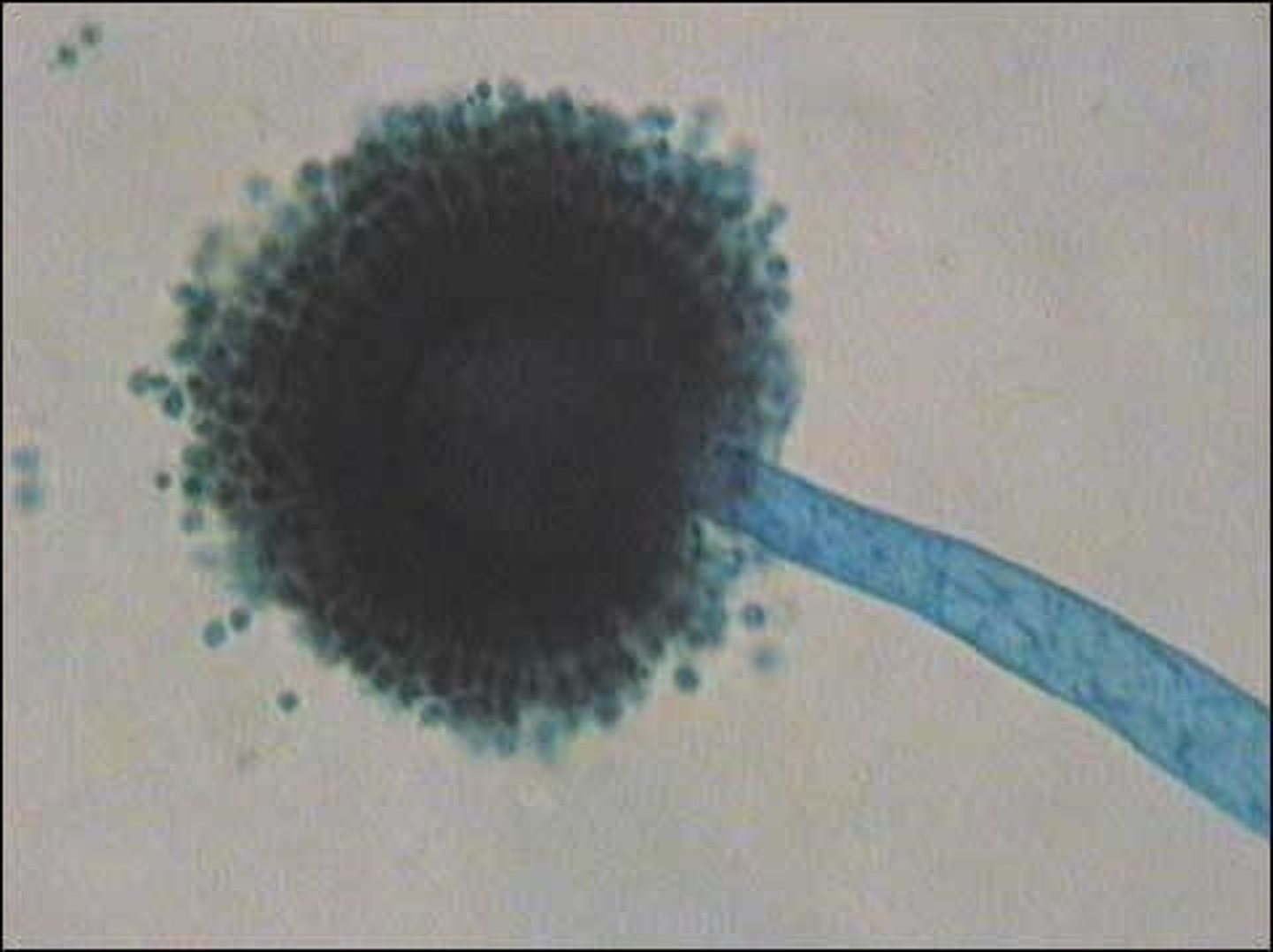
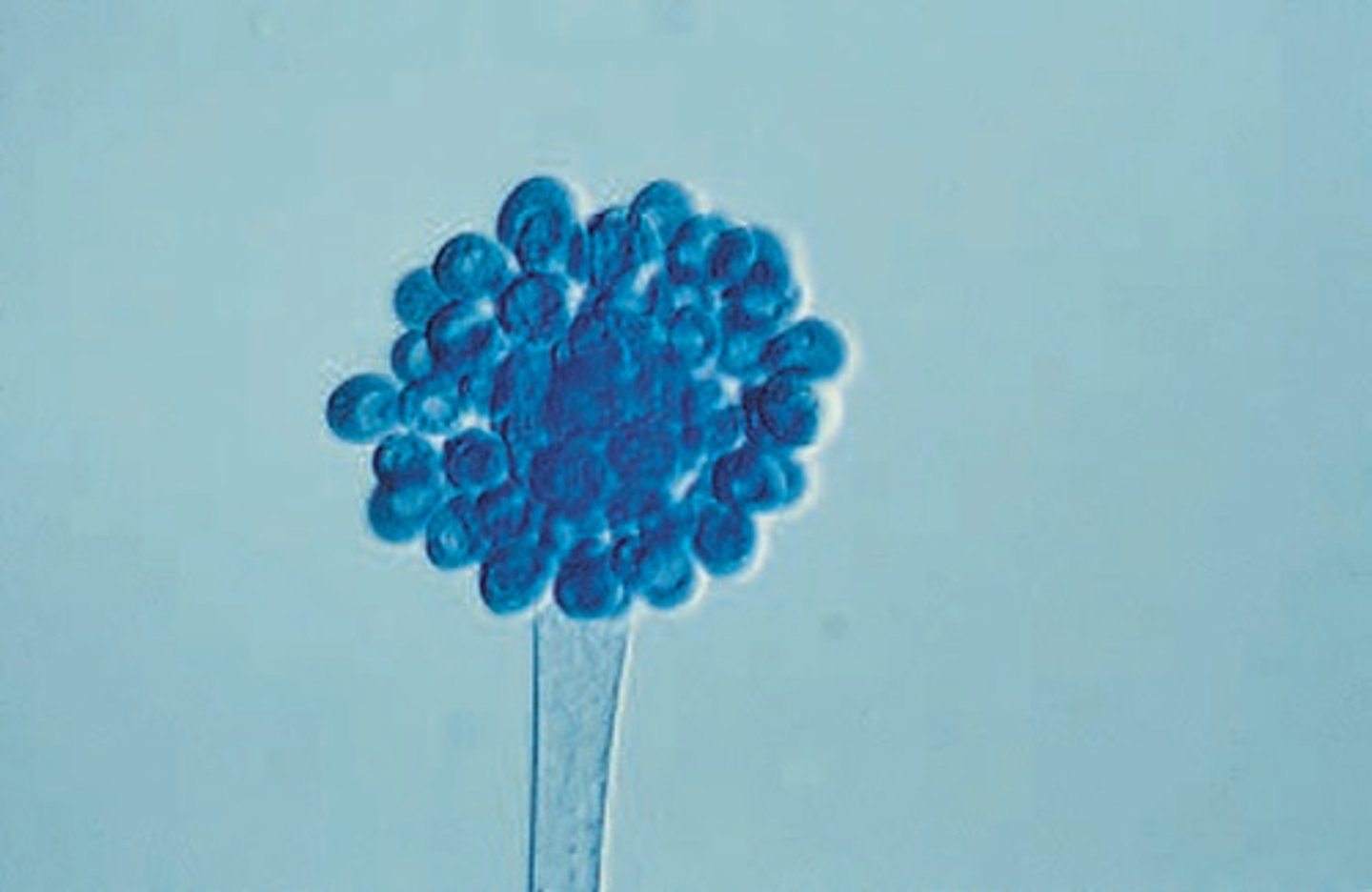
Aspergillus flavus
Aspergillus flavus microscopic
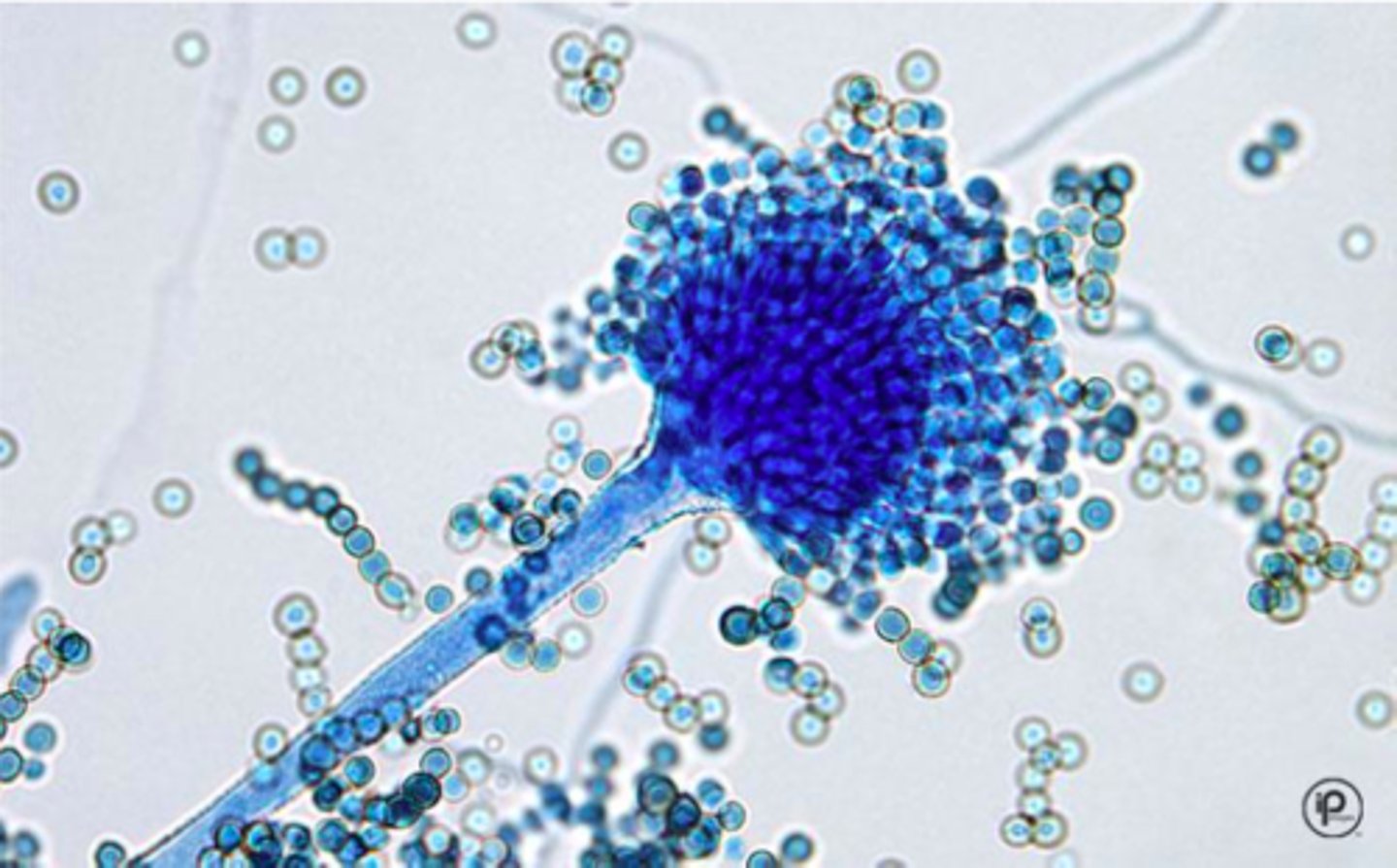
Aspergillus fumigatus
Aspergillus fumigatus microscopic