Meiosis and Errors in Meiosis Quiz
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/22
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
1
New cards
Label a chromosome
\
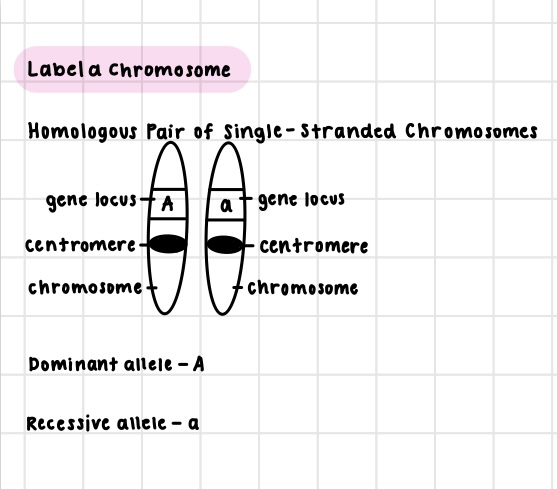
2
New cards
How does meiosis result in daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell?
This process results in half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell because the chromosomes are copied once, but are divided twice (meiosis I separate homologous chromosomes and meiosis II separate sister chromatids)
3
New cards
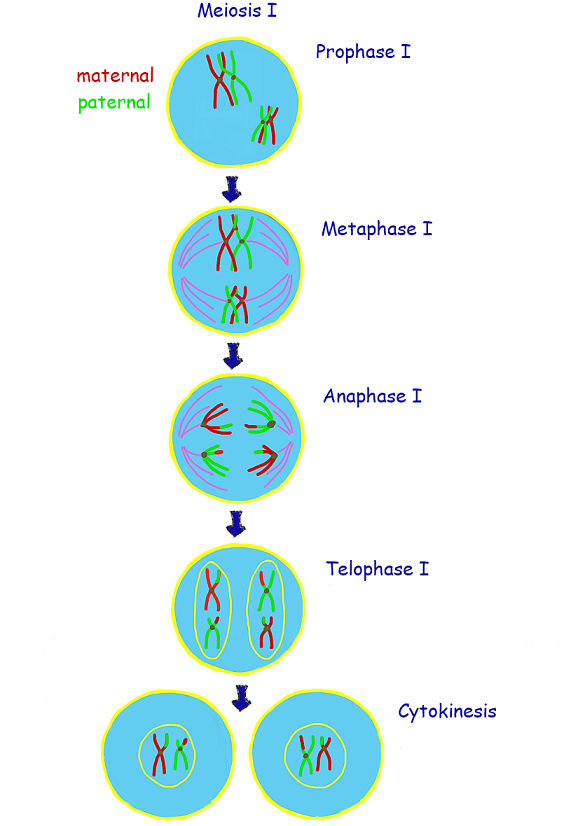
Explain the process of meiosis I
**Interphase**: Chromosomes are ***replicated*** to form ***sister*** ***chromatids***, which are ***genetically*** ***identical*** and join at the ***centromere***. The ***single*** ***centriole*** is also ***replicated***.
\
__**PMAT**__:
**Prophase 1**: During ***synapsis***, chromosomes ***condense*** and homologous chromosomes ***form pairs*** to create ***tetrads***. This is also when ***crossing over*** can occur in the chromatids of homologous chromosomes. A ***spindle*** forms from each ***centromere*** and ***spindle fibres*** move the ***tetrads*** around.
\
**Metaphase 1**: The ***tetrads*** are all arranged at the ***metaphase plate.***
\
**Anaphase 1**: The ***homologous chromosomes*** are ***separated*** and are pulled to ***opposite ends*** of the cell.
\
**Telophase 1**: Movement of the ***homologous chromosomes*** continues until a ***haploid set*** is at ***each pole.***
\
**Cytokinesis 1**: Two **haploid daughter cells** form. **Chromosomes** are still **double-stranded.**
\
__**PMAT**__:
**Prophase 1**: During ***synapsis***, chromosomes ***condense*** and homologous chromosomes ***form pairs*** to create ***tetrads***. This is also when ***crossing over*** can occur in the chromatids of homologous chromosomes. A ***spindle*** forms from each ***centromere*** and ***spindle fibres*** move the ***tetrads*** around.
\
**Metaphase 1**: The ***tetrads*** are all arranged at the ***metaphase plate.***
\
**Anaphase 1**: The ***homologous chromosomes*** are ***separated*** and are pulled to ***opposite ends*** of the cell.
\
**Telophase 1**: Movement of the ***homologous chromosomes*** continues until a ***haploid set*** is at ***each pole.***
\
**Cytokinesis 1**: Two **haploid daughter cells** form. **Chromosomes** are still **double-stranded.**
4
New cards
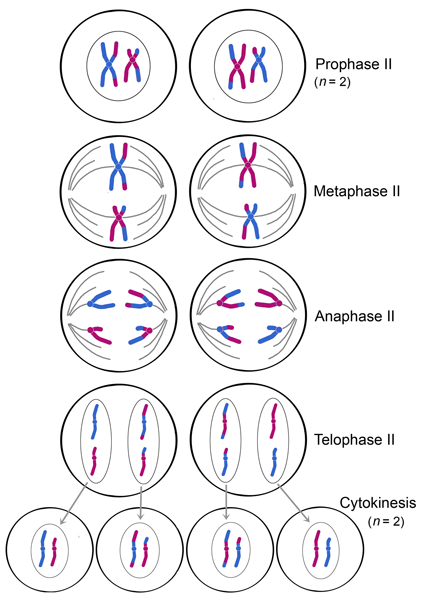
Explain the process of meiosis II
\*Note: Meiosis II is **very similar** to mitosis, but **not identical**
__**PMAT:**__
**Prophase 2:** ***Spindle fibres*** form, attaching to ***each sister chromatid*** and ***moving*** them around.
\
**Metaphase 2:** ***Sister chromatids*** are arranged at the ***metaphase plate*** and the ***sister chromatids*** face ***opposite ends.***
\
**Anaphase 2:** The ***centromeres*** of ***sister chromatids*** ***separate*** and the now separated sisters ***travel toward*** ***opposite ends*** of the ***cell***.
\
**Telophase 2:** The ***separated sister chromatids*** arrive at the ***opposite ends*** and ***nuclei*** form around the ***chromatids***.
\
**Cytokinesis 2:** ***Cytokinesis*** separates the ***cytoplasm*** and ***4 haploid daughter cells*** are produced.
__**PMAT:**__
**Prophase 2:** ***Spindle fibres*** form, attaching to ***each sister chromatid*** and ***moving*** them around.
\
**Metaphase 2:** ***Sister chromatids*** are arranged at the ***metaphase plate*** and the ***sister chromatids*** face ***opposite ends.***
\
**Anaphase 2:** The ***centromeres*** of ***sister chromatids*** ***separate*** and the now separated sisters ***travel toward*** ***opposite ends*** of the ***cell***.
\
**Telophase 2:** The ***separated sister chromatids*** arrive at the ***opposite ends*** and ***nuclei*** form around the ***chromatids***.
\
**Cytokinesis 2:** ***Cytokinesis*** separates the ***cytoplasm*** and ***4 haploid daughter cells*** are produced.
5
New cards
How are mitosis and meiosis similar in the way chromosomes segregate but differ in the number of cells produced and the genetic content of daughter cells?
Both of these processes are similar in the way that the chromosomes separate at opposite ends of the cell.
\
However, they also differ in the number of cells produced as mitosis produces 2 diploid, identical daughter cells, whereas, meiosis produces 4 haploid, non-identical daughter cells.
\
However, they also differ in the number of cells produced as mitosis produces 2 diploid, identical daughter cells, whereas, meiosis produces 4 haploid, non-identical daughter cells.
6
New cards
What is nondisjunction?
It is when there are problems with the meiotic spindle causing errors in daughter cells, resulting in too many or too few chromosomes.
7
New cards
What is crossing over?
It is when the non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes exchange segments of their DNA. This occurs during synapsis in prophase 1 of meiosis.
8
New cards
What is independent assortment?
It is when homologous pairs line up on the equator of the cell independently of each other. This occurs during metaphase 1 of meiosis.
9
New cards
How do processes like crossing over and independent assortment increase genetic variation?
10
New cards
What is a gene?
A gene is a section of DNA that encodes for a certain trait e.g. eye colour
A part of a chromosome that controls the expression of a trait and is passed on to offspring; it has a specific DNA sequence
A part of a chromosome that controls the expression of a trait and is passed on to offspring; it has a specific DNA sequence
11
New cards
What is a chromosome?
It is a structure in the nucleus that contains DNA
12
New cards
What are homologous chromosomes?
It is a pair of chromosomes that contain the genetic code for the same traits. One chromosome comes from each parent. e.g. chromosomes contain information about hair colour
13
New cards
What is an allele?
An allele is a variant form of a gene e.g. blue eyes
14
New cards
What is the difference between a gene and an allele?
Genes encode for a certain trait, whereas, alleles are variant forms of a gene
e.g. a gene for hair colour, an allele for brown hair
e.g. a gene for hair colour, an allele for brown hair
15
New cards
How do DNA, genes, chromosomes and alleles account for the transmission of hereditary characteristics?
16
New cards
What is nondisjunction?
It is when a gamete with the incorrect number of chromosomes is fertilized, causing errors in daughter cells
e.g.
homologous chromosomes not separating properly during meiosis I
sister chromatids failing to separate during meiosis II
too many or too few chromosomes
e.g.
homologous chromosomes not separating properly during meiosis I
sister chromatids failing to separate during meiosis II
too many or too few chromosomes
17
New cards
How does nondisjunction result in the wrong number of chromosomes in a gamete?
18
New cards
What are some examples of human genetic disorders that can result from a gamete with the wrong number of chromosomes combining with a gamete with the correct number of chromosomes?
Down syndrome (trisomy 21), Turner syndrome (monosomy X or XO), Klinefelter’s syndrome (XXY male), Jacob’s syndrome (XYY male), trisomy X (XXX - doesn’t actually cause any health problems, just a female with an extra X chromosome)
19
New cards
What is down syndrome (trisomy 21)?
3 copies of chromosome 21 are made instead of 2
1 in 700 children born in the U.S. have trisomy 21
Chromosome 21 is the smallest human chromosome, but still has severe effects
Correlates to the age of the parents, as the mother and father grow older, the likelihood of trisomy 21 in a baby increases
1 in 700 children born in the U.S. have trisomy 21
Chromosome 21 is the smallest human chromosome, but still has severe effects
Correlates to the age of the parents, as the mother and father grow older, the likelihood of trisomy 21 in a baby increases
20
New cards
What is Turner syndrome (monosomy X or XO)?
It is a female-only genetic disorder that occurs when an individual only has one X chromosome instead of 2
1 in every 5000 births
Degree of effects are varied: webbed neck, short stature, sterile
1 in every 5000 births
Degree of effects are varied: webbed neck, short stature, sterile
21
New cards
What is Klinefelter’s syndrome (XXY male)?
It is when a male is born with an extra X chromosome
1 in every 2000 births
Have male sex organs, but are sterile
Feminine characteristics: some breast development and lack of facial hair
Tall
Normal intelligence
1 in every 2000 births
Have male sex organs, but are sterile
Feminine characteristics: some breast development and lack of facial hair
Tall
Normal intelligence
22
New cards
What is Jacob’s syndrome (XYY male)?
It is when a male receives an extra Y chromosome from his father
1 in 1000 births
Slightly taller than average
More active
Normal intelligence or slight learning disabilities
Delayed emotional immaturity
Normal sexual development
1 in 1000 births
Slightly taller than average
More active
Normal intelligence or slight learning disabilities
Delayed emotional immaturity
Normal sexual development
23
New cards
What is trisomy X (XXX)?
It is when a female is born with an extra chromosome
1 in every 2000 births
Doesn’t have any negative effects and produces healthy females
1 in every 2000 births
Doesn’t have any negative effects and produces healthy females