Cellular Respiration: Glycolysis to Electron Transport Chain
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
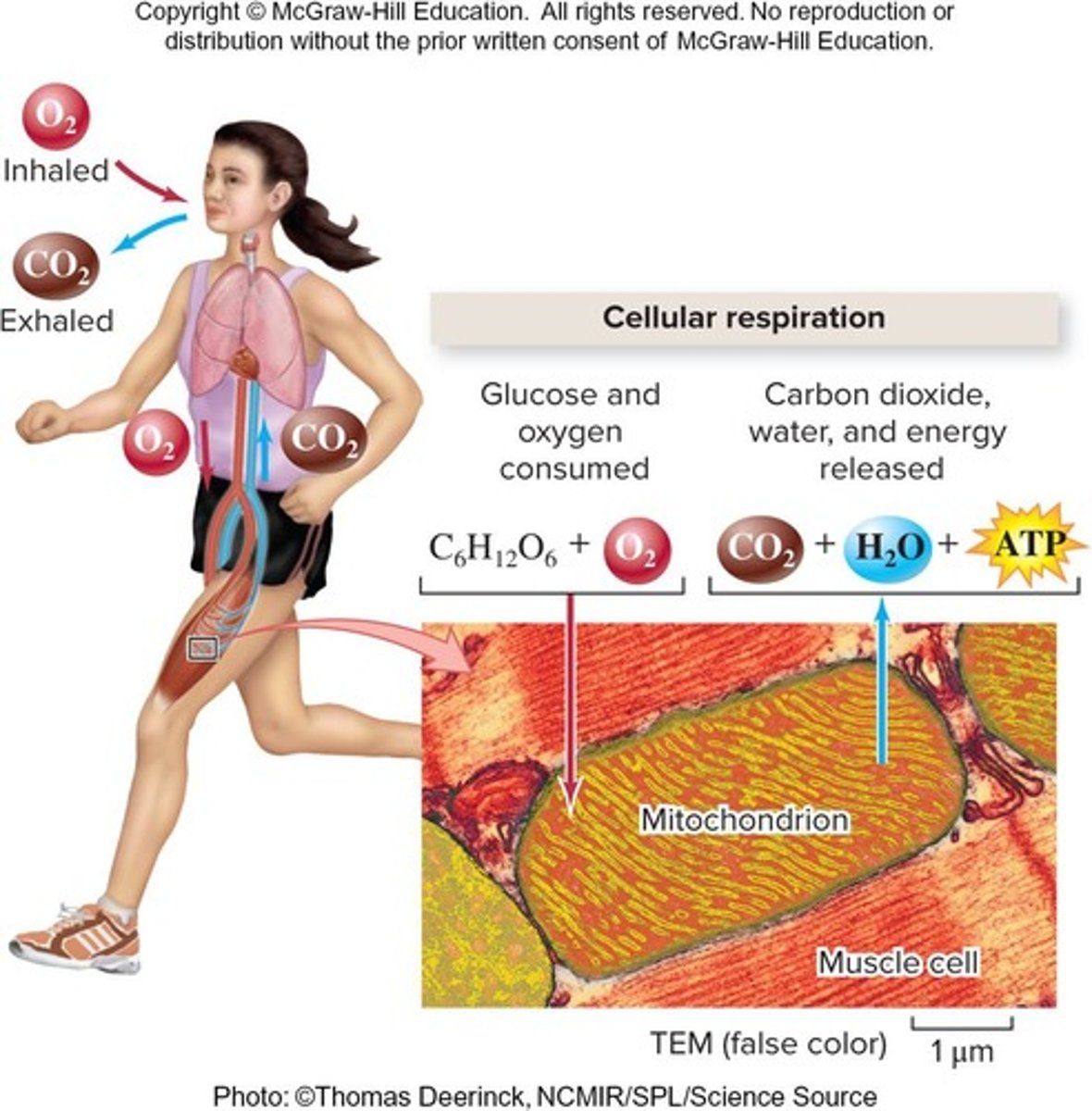
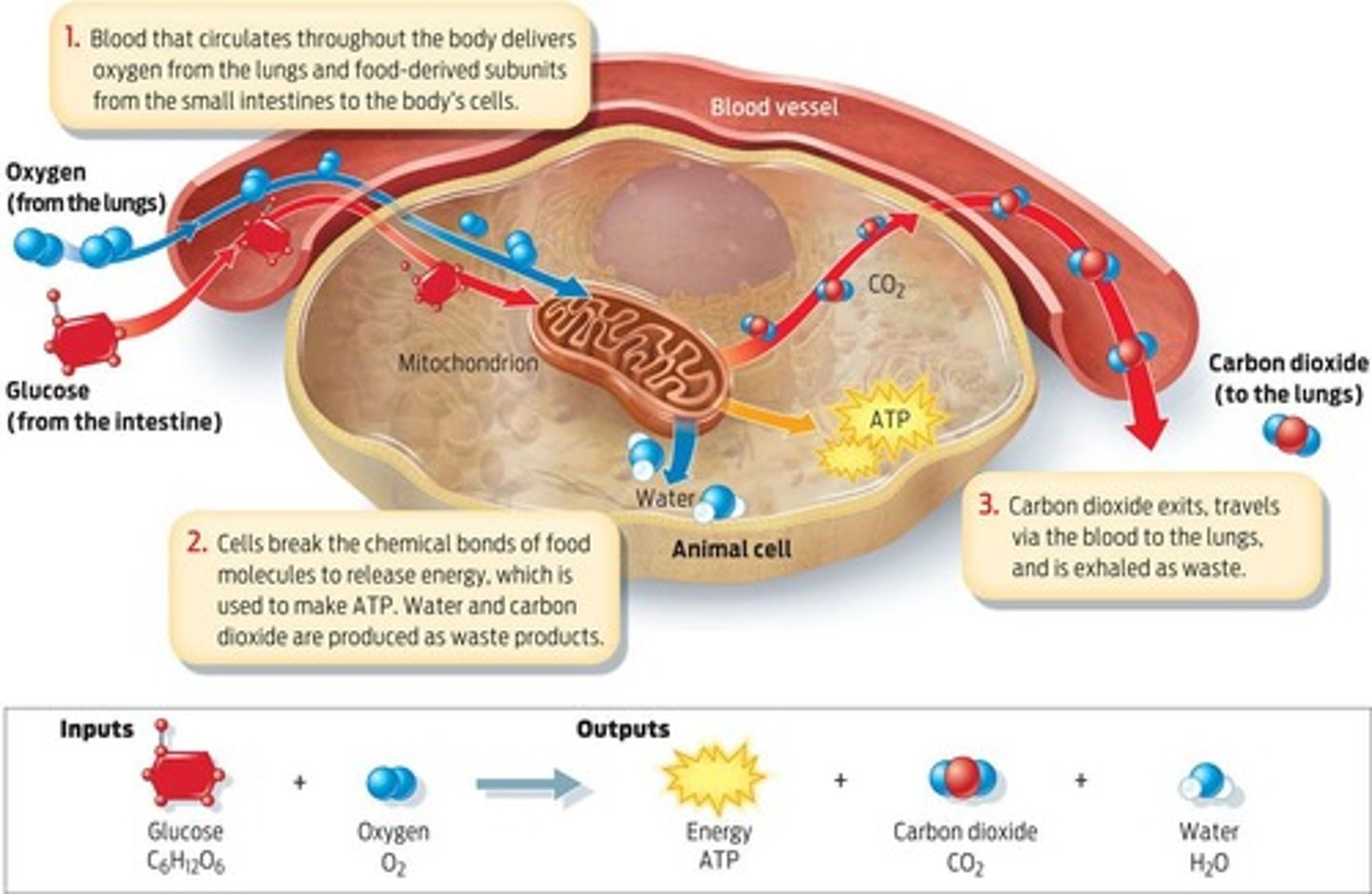
Cellular respiration
Catabolizes macromolecules to produce ATP.
ATP
Adenosine triphosphate, energy currency of cells.
ADP
Adenosine diphosphate, formed from ATP hydrolysis.
Catabolism
Breakdown of molecules to release energy.
Anabolism
Building larger molecules from smaller ones.
Aerobic respiration
Uses oxygen to convert food into ATP.
Anaerobic respiration
Occurs without oxygen, less efficient ATP production.
Calorie
Amount of heat to raise 1 liter of water by 1°C.
Proton gradient
Difference in proton concentration across a membrane.
Mitochondria
Cell organelles where aerobic respiration occurs.
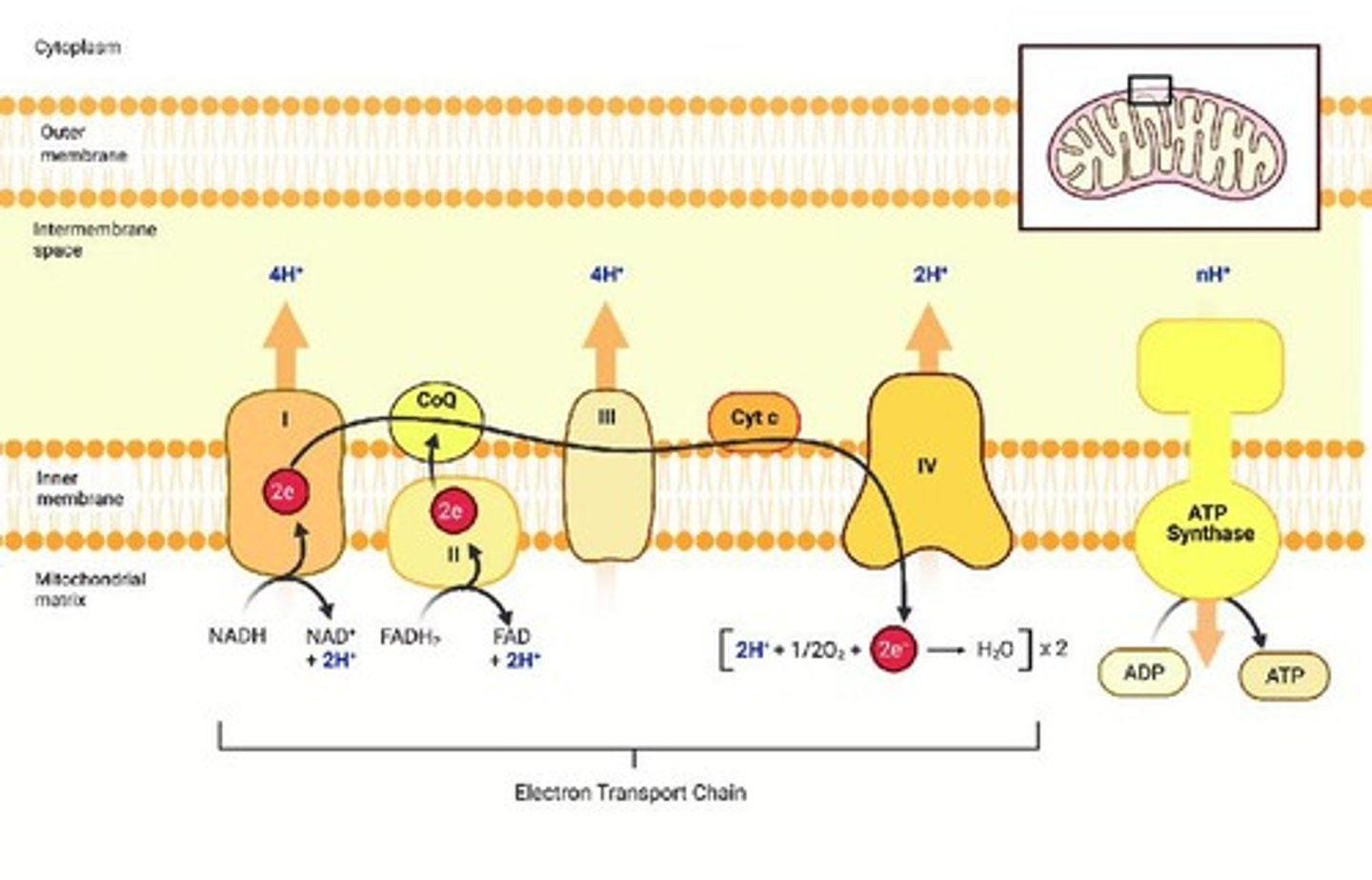
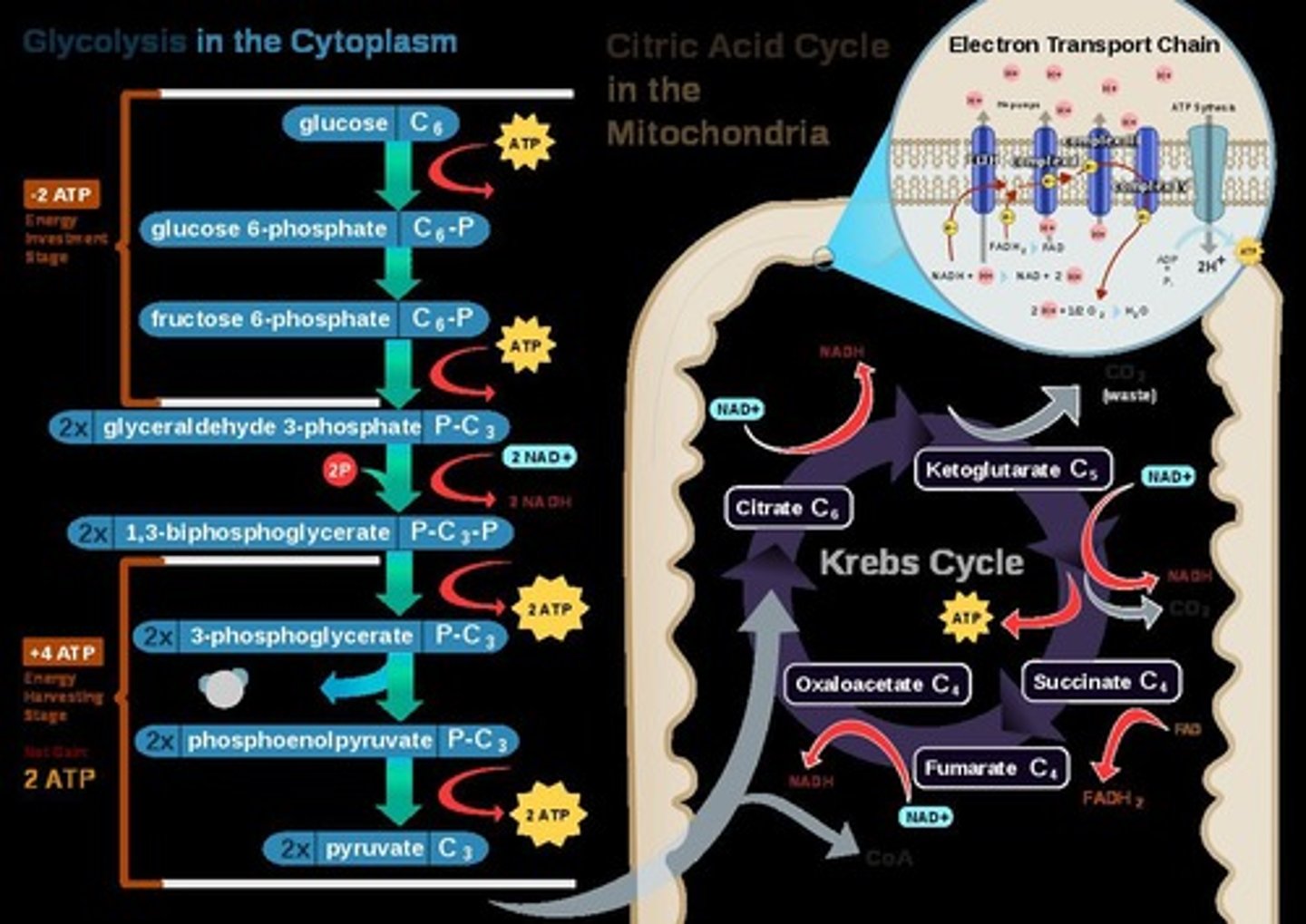
Electron transport chain (ETC)
Series of proteins transferring electrons to produce ATP.
NAD+/NADH
Electron carrier, cycles between oxidized and reduced forms.
FAD/FADH2
Another electron carrier, involved in energy metabolism.
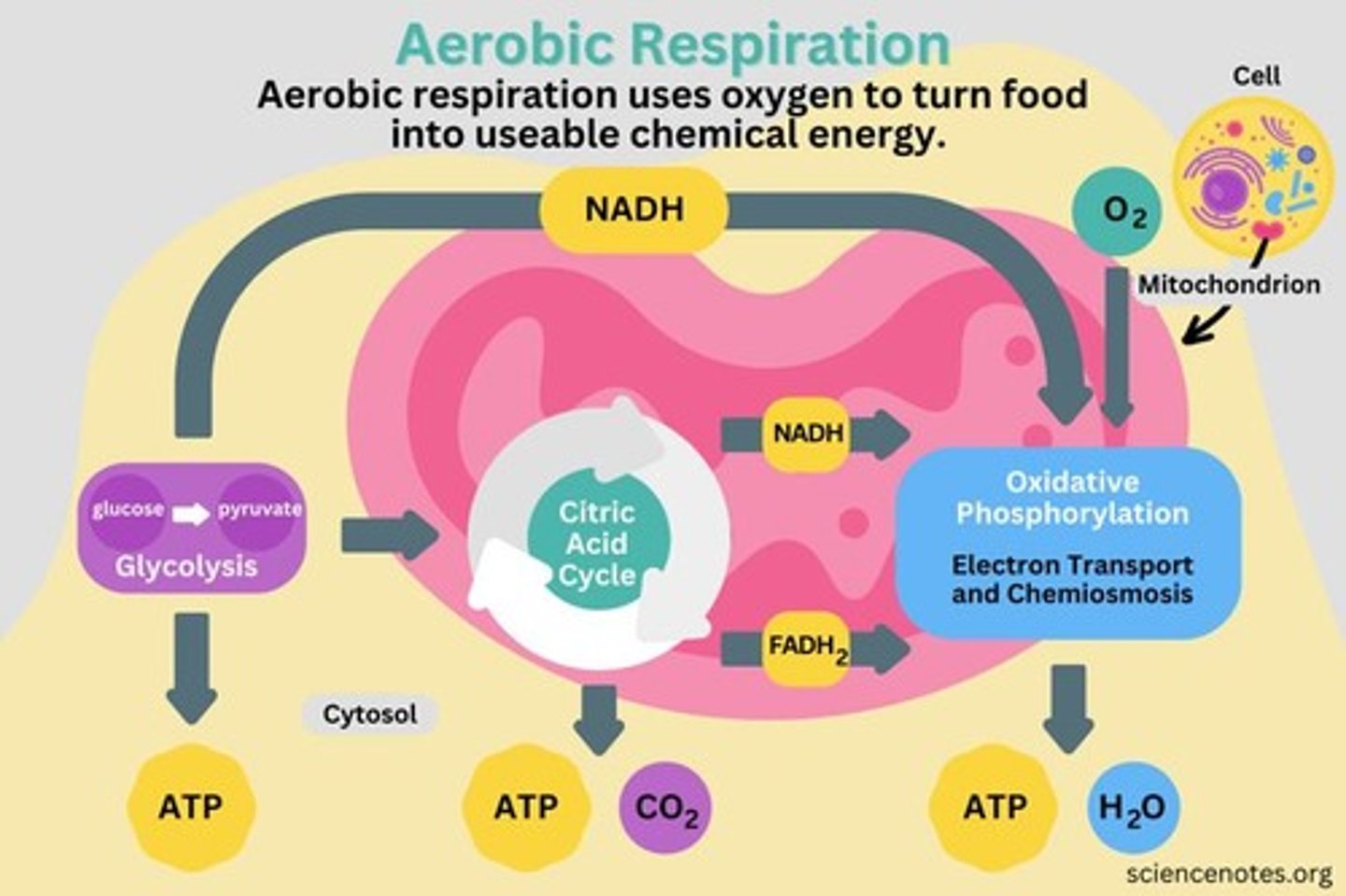
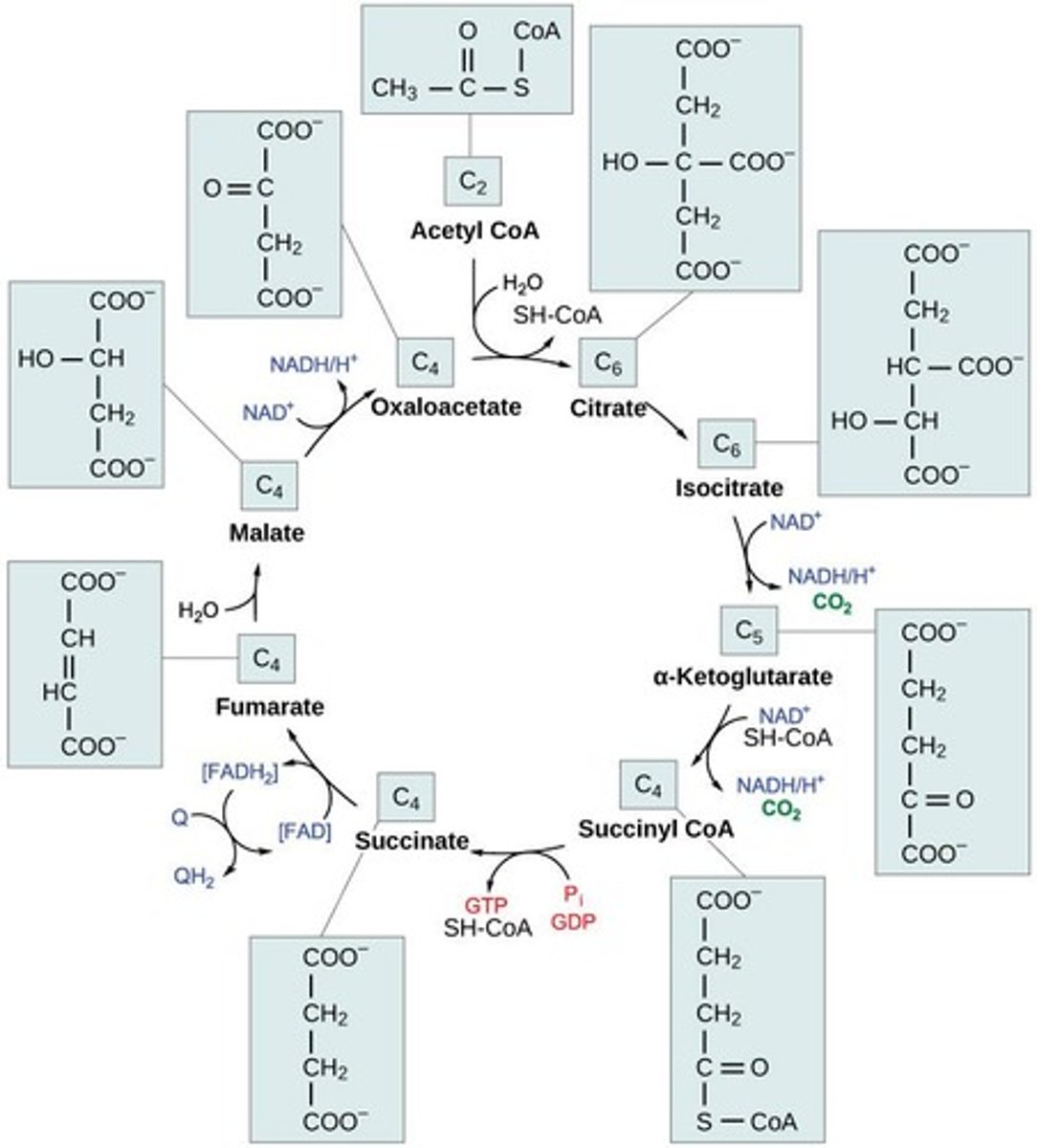
Citric Acid Cycle
Processes Acetyl CoA to produce ATP and electron carriers.
Glycolysis
First step of respiration, converts glucose to pyruvate.
Pyruvate oxidation
Converts pyruvate to Acetyl CoA, releasing CO2.
Krebs Cycle
Oxidizes Acetyl CoA, producing ATP and electron carriers.
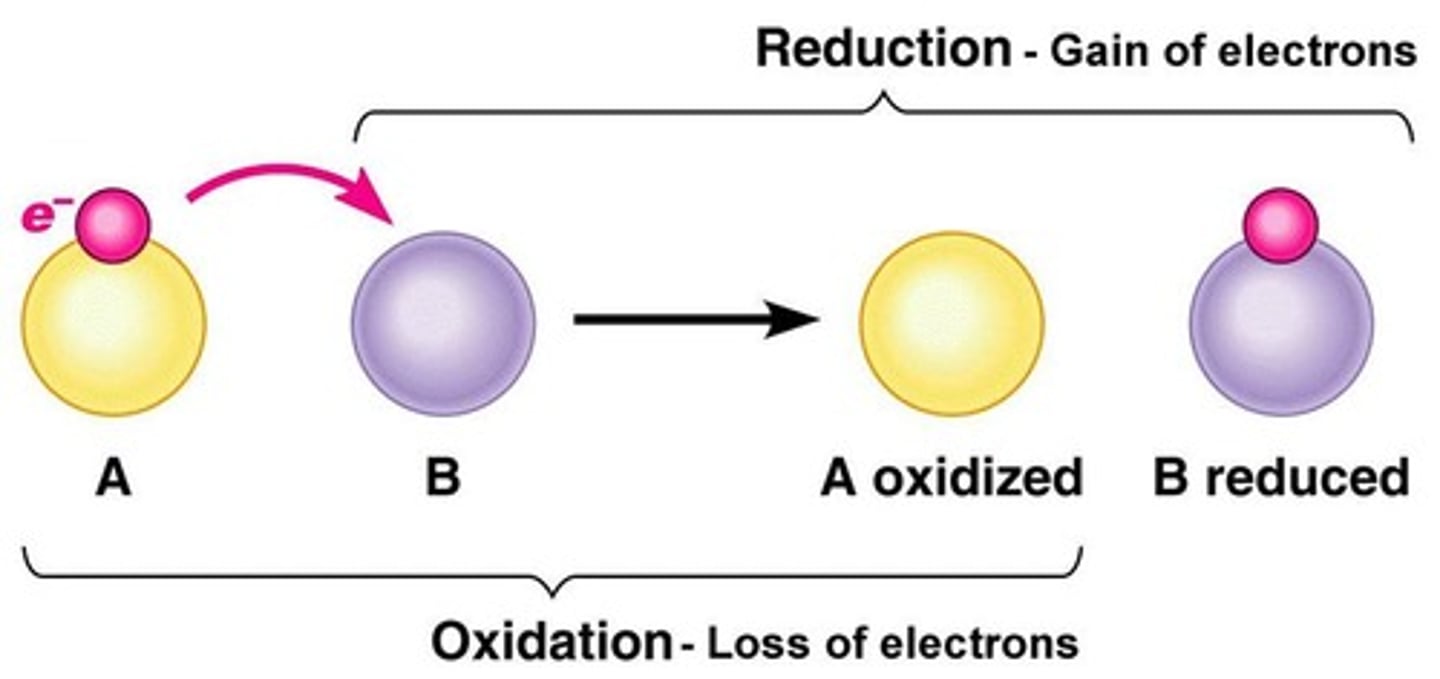
Redox reactions
Reactions involving electron transfer between molecules.
Endergonic
Reactions that require energy input to proceed.
Exergonic
Reactions that release energy during the process.
Cytosol
Fluid-filled interior of the cell, excluding organelles.
Cristae
Folded inner membrane of mitochondria, increases surface area.
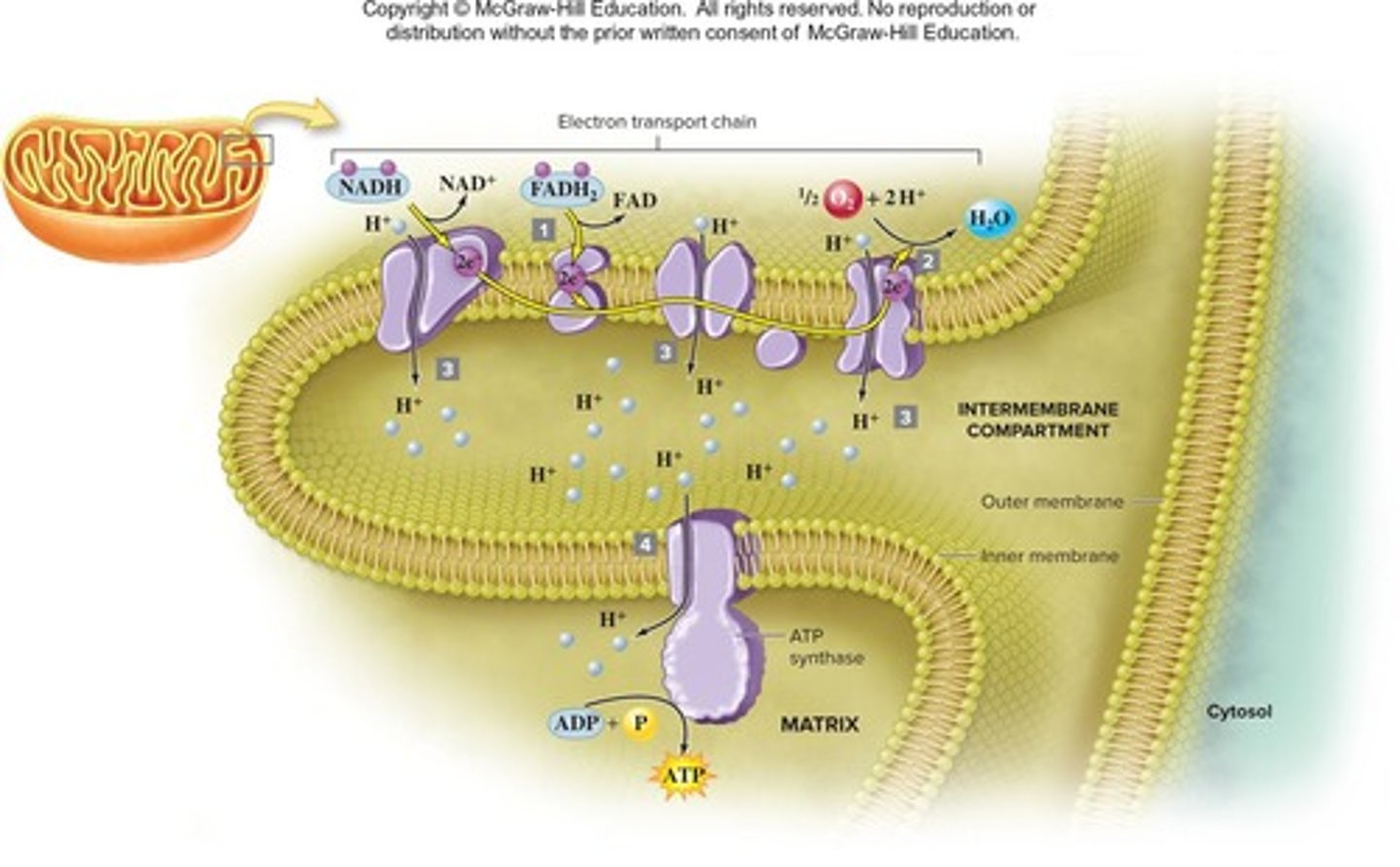
ATP synthase
Enzyme that synthesizes ATP using proton gradient.
Cofactors
Vitamins and minerals required for enzymatic reactions.
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
Final step in cellular respiration producing ATP.
NADH
High-energy electron carrier donating electrons to ETC.
FADH2
Another electron carrier contributing to ATP production.
O2
Final electron acceptor forming H2O in ETC.
Pyruvate
3-carbon molecule produced from glucose in glycolysis.
Anaerobic
Process that does not require oxygen for glycolysis.
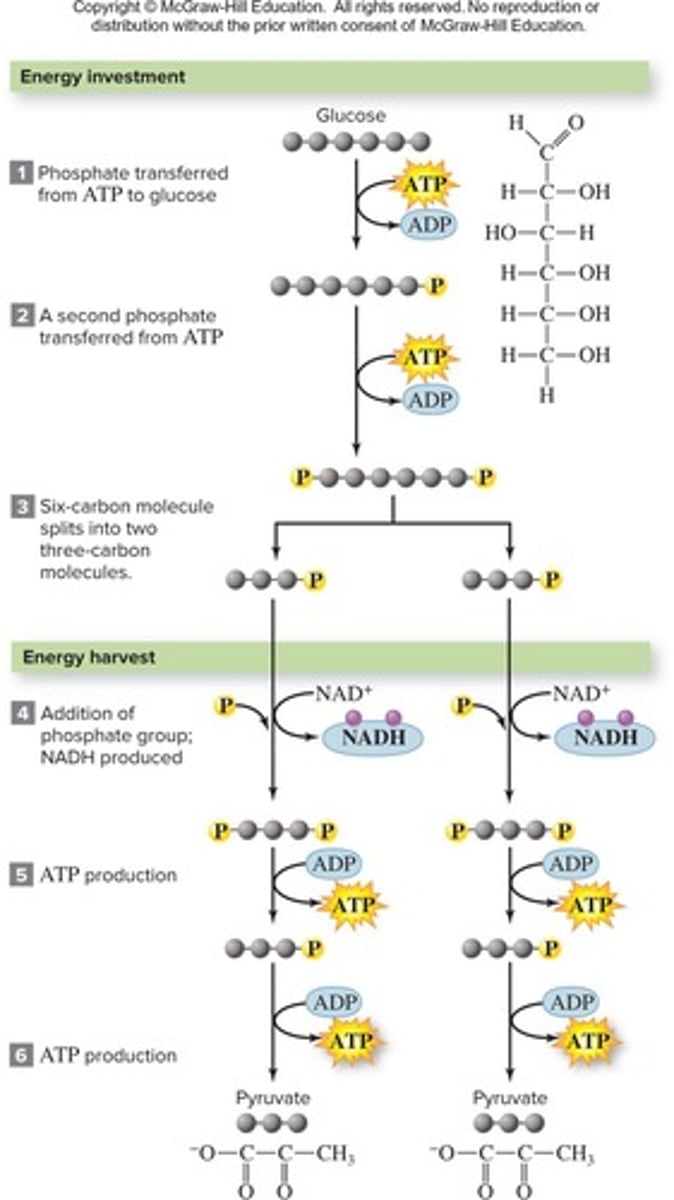
Energy Investment Phase
Initial phase of glycolysis consuming 2 ATP.
Energy Harvest Phase
Phase of glycolysis producing 4 ATP and 2 NADH.
Acetyl CoA
2-carbon molecule entering Krebs cycle after pyruvate oxidation.
Redox Reactions
Reactions involving oxidation and reduction of molecules.
Proton Gradient
Difference in H+ concentration driving ATP synthesis.
ATP Synthase
Enzyme synthesizing ATP using proton motive force.
Metabolic Water
Water produced as a waste product in ETC.
Inputs of Glycolysis
1 glucose, 2 ATP, 2 NAD+, 4 ADP.
Outputs of Glycolysis
4 ATP, 2 NADH, 2 pyruvate (net gain 2 ATP).
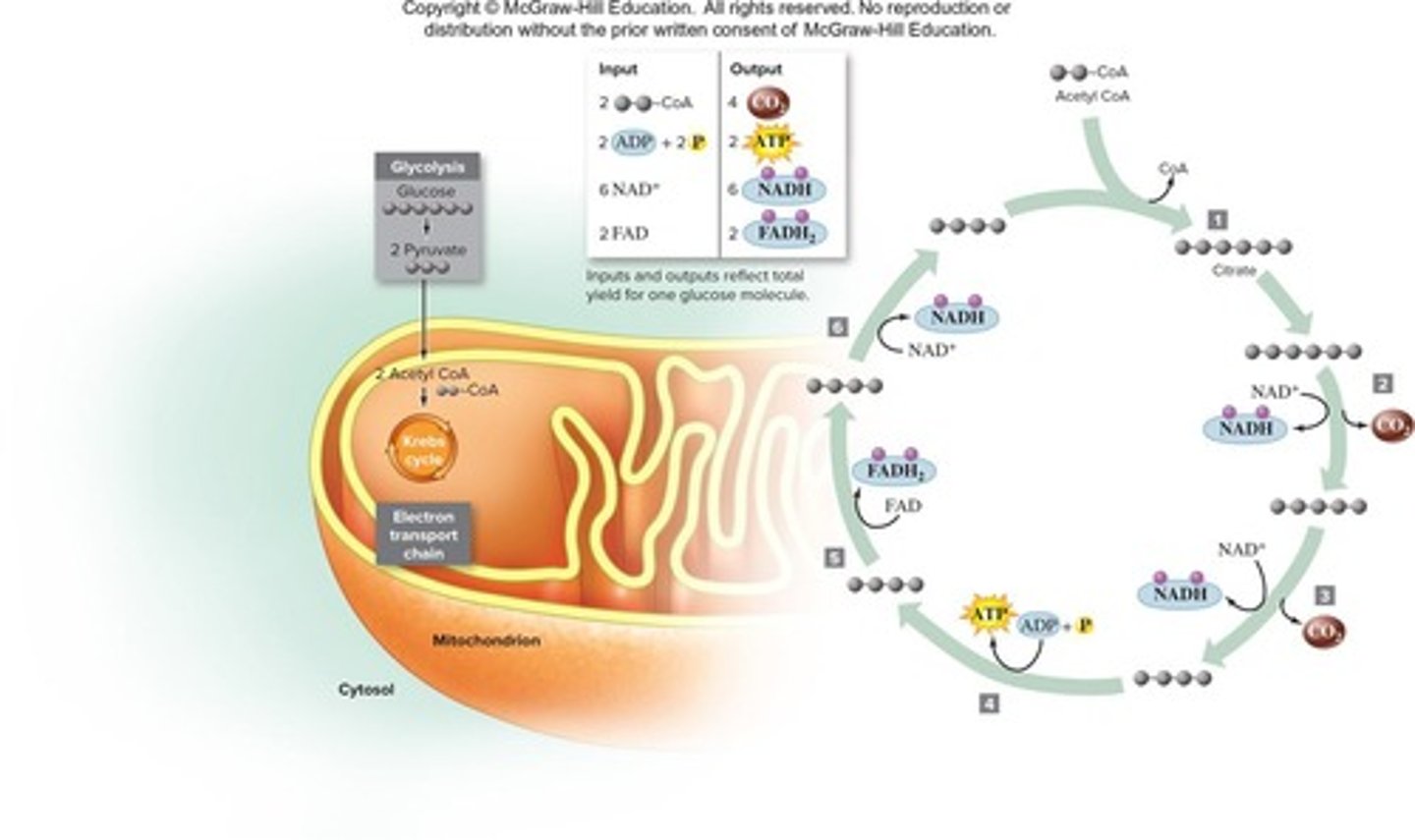
Inputs of Pyruvate Oxidation
2 pyruvate molecules entering mitochondrial matrix.
Outputs of Pyruvate Oxidation
2 NADH, 2 CO2, 2 Acetyl CoA.
Theoretical ATP Yield
Up to 36 ATP produced from 1 glucose.
Actual ATP Yield
Approximately 30 ATP produced per glucose.
Cellular Respiration
Process converting glucose into usable energy.
Cytoplasm
Location of glycolysis in the cell.
Mitochondrial Matrix
Location of pyruvate oxidation and Krebs cycle.
Waste Products
CO2 and H2O produced during cellular respiration.
ATP Transport
Energy currency used to move NADH.
Pyruvate Transport
Process of moving pyruvate into mitochondria.
H+ Ion Leakage
H+ ions bypass ATP synthase, reducing efficiency.
ATP Yield from Glucose
1 glucose yields approximately 30 ATP.
Energy Efficiency
Cellular respiration is 32-37% efficient.
Macromolecule Fuels
Proteins and lipids can fuel respiration pathways.
ETC Location
Electron Transport Chain occurs in inner mitochondrial membrane.
Oxidation and Reduction
Identify components oxidized or reduced in reactions.
Active Transport
Energy-dependent movement across membranes in ETC.
Facilitated Diffusion
Passive transport of molecules across membranes.
Fermentation Pathways
Allow cells to survive without oxygen.
Anaerobic Organisms
Organisms that do not require oxygen for survival.
NAD+ Regeneration
NAD+ is recycled from NADH during fermentation.
Lactic Acid Fermentation
Pyruvate converts to lactic acid, regenerating NAD+.
Ethanol Fermentation
Pyruvate converts to ethanol and CO2, regenerating NAD+.
Energy Transformation Efficiency
37% of glucose energy converted to ATP.
Glycolysis Efficiency
Glycolysis alone is only 2% efficient.
Fermentation as Last Resort
Used by organisms under oxygen-limited conditions.
Cellular Respiration Steps
Includes glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, Krebs cycle, ETC.
Inputs and Outputs of Fermentation
Inputs: NADH, Outputs: NAD+, lactic acid or ethanol.