ECG - Anatomy and Physiology Recap
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
Contrition of the heart is know as ..
Systole - Blood pushed out of the heart
Relaxation of the hearth is know as ..
Diastole - Chambers fill with blood
Contraction of the heart occurs due to ..
Electrical activity in the cardiac muscle cells
Specialised areas of cells within the heart control the rate in which the heart contracts, also known as ..
Pacemakers
No heartbreak
Asystole
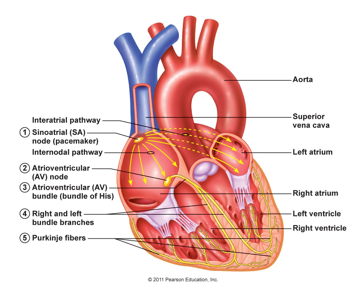
Sinoatrial Node
Generates regular impulses leading to depolarisation
Begins the heartbeat
Initiates a wave of contraction in the atria (R to L)
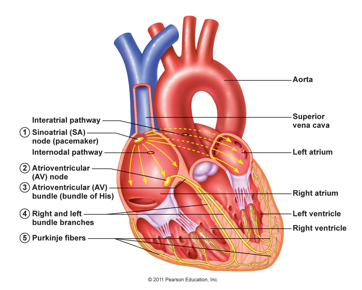
Atrioventricular Node
Electrical impulses from SAN passes through to the AVN
Impulse travels down interventricular septum in the bundle of His
Impulse distributed to ventricles via the Purkinje fibres
Ventricles contract
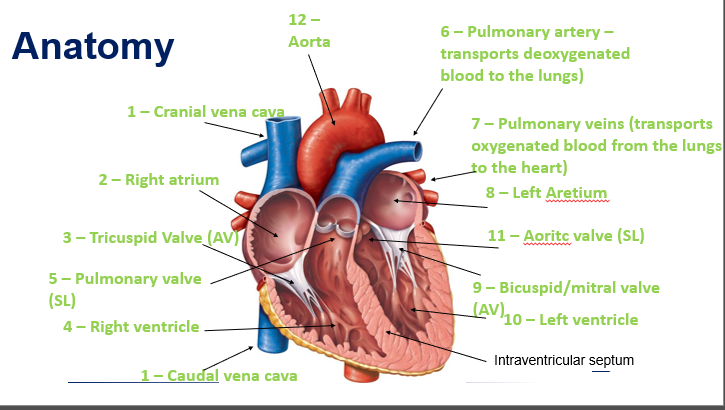
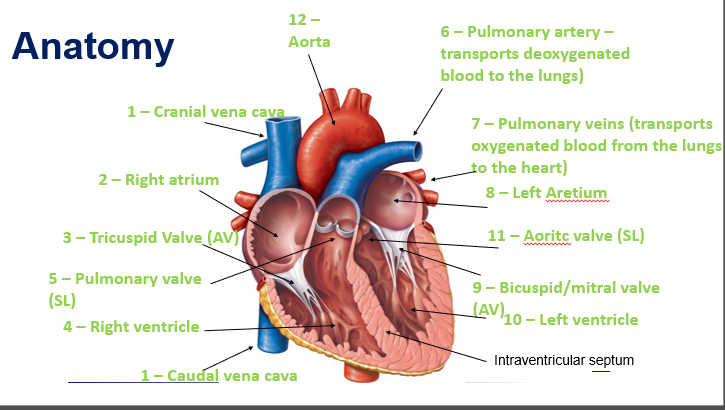
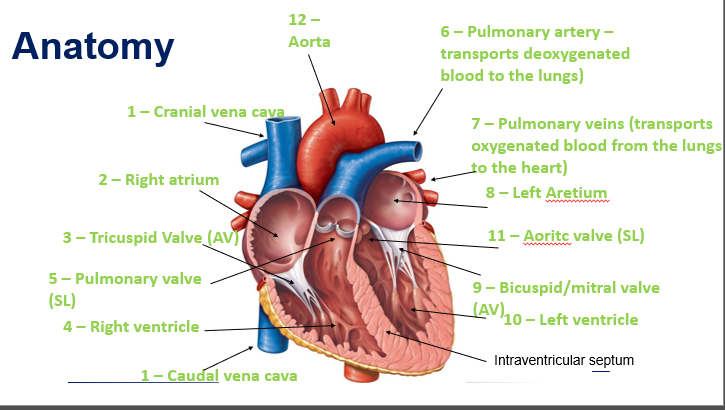
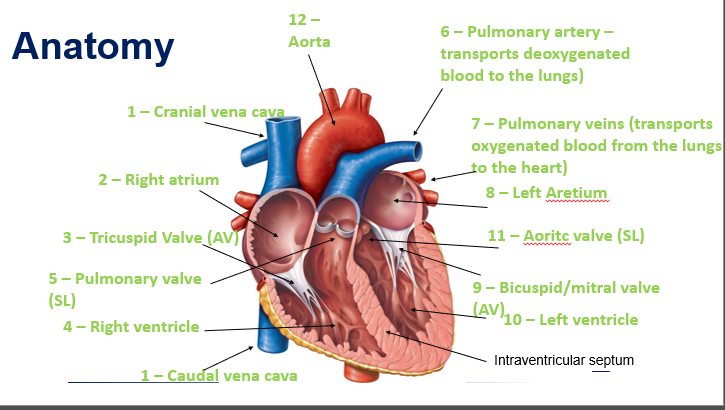
SA node
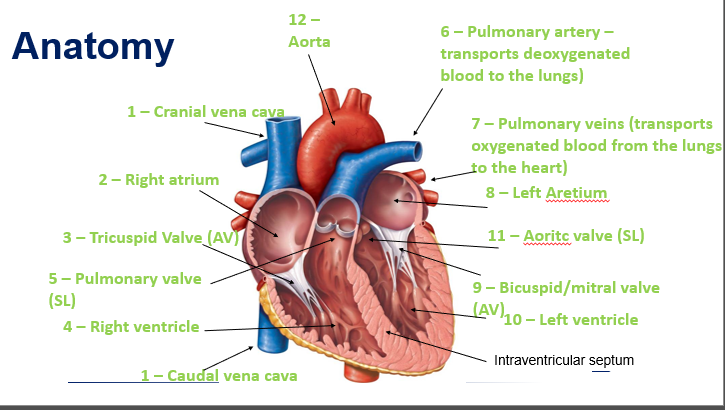
Lies within the wall of the RA atrium near the opening of the cranial vena cava
Also known as the ‘pacemaker’
Causes emptying of the atria and filling of the ventricles
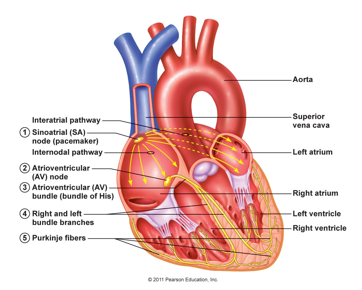
AV node
Lies within the wall of the atrial septum
The AV node briefly slows down the electrical signal to allow the ventricles time to receive the blood from the atria
Impulse pushes blood into the pulmonary arteries and aorta
When the ventricles contract, the right ventricle pumps blood to the lungs and the left ventricle pumps blood up through the aorta and to the rest of the body