IB chemistry HL: S2.2.8 -9 intermolecular forces
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
types of intermolecular forces
London dispersion
Dipole-induced dipole
Dipole–dipole
Hydrogen bonding
Van de leyen forces
London dispersion
Dipole-induced dipole
Dipole–dipole
London dispersion forces/ Temporary dipoles
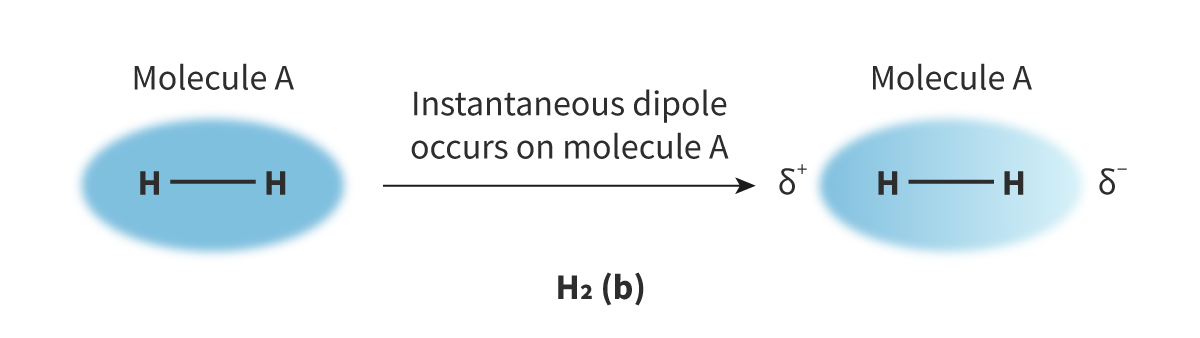
the random, continuous movement of electrons can create asymmetrical electron distribution which causes attraction between neighbouring atoms or molecules.
occurs in both polar and non polar molecules, and can also occur between atoms. the weakest type of intermolecular force
dipole - dipole attraction
when atoms with different electronegativities have an asymetrical shape, they have a permanent dipole
so multiple atoms will be attracted to each other’s charged parts. basically it’s not that deep it’s just not straight polar bond
how does the size of the atoms affect intermolecular forces
As the molecular size of the compound increases, so does the strength of the force.
The greater the number of electrons in a molecule, the greater the probability of electron distribution asymmetry and the more susceptible the molecule is to developing an induced dipole from a charge nearby. As the strength of the attraction is greater, so is the energy required to overcome it.
dipole induced dipole
A weak intermolecular force that occurs when a polar molecule gets close to an atom or non-polar molecule and induces a dipole by disrupting the arrangement of its electrons.
hydrogen bonding
Occurs between molecules with a bond between hydrogen and another very electronegative element ( fluorine, oxygen, nitrogen ),
With the electronegative element having a non bonding pair
the hydrogen has no inner electrons to perform shielding, so the electronegativity difference is very large: the ẟ+ hydrogen is very attracted to non bonding pairs of electrons in other molecules
strongest intermolecular force
intermolecular forces from weakest to strongest
london dispersion forces<dipole induced dipole< dipole dipole forces < hydrogen bonds
how does the size of a molecule impact it’s solubility
in most molecules, the larger the molecule, the relatively smaller the polar part will become, thus reducing it’s solubility
Factors affecting strength of forces
larger molecular size =
bigger van de leyen forces, as greater probability of electron distribution asymmetry and therefore more susceptible to to developing an induced dipole from nearby charge, and therefore strength of attraction increases.
Dipole dipole force relatively less relevant