serology, ELISA, and infectious agent
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Serology
the scientific study of blood serum and other bodily fluids
Pregnancy Testing
detecting of the hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in urine
Pros of Pregnancy Testing
convenience, privacy, affordability, ease of use, early detection, wide availability, improved accuracy
Cons of Pregnancy Test
timing sensitivity, human error, false positives, false negatives, no medical guidance, anxiety or misinterpretation, lack of sensitivity to rare conditions
Blood Typing
determines an individual’s blood group based on the presence of specific antigens on the surface of red blood cells
Clumps in blood testing
positive
No clumps in blood testing
negative
ELISA Testing
detect and quantify specific biomolecules, such as antibodies, antigens, proteins, or hormones
ELISA Testing commonly used for
HIV, Covid-19, Hepatitis, Pregnancy Hormones, Allergies
Tool used in ELISA Testing
transfer Pipet
Person-to-Person
skin-to-skin: ring worm
sexual contact: HIV
Droplet Spread
COVID-19
Airborne Transmission
chickenpox
Fomite Transmission
norovirus
Vector-Borne Transmission
plague
Contaminated Food or Water
cholera
Poor Hygiene
rotavirus
In Utero
rubella
During Birth
herpes simplex virus
Breastfeeding
HIV
Direct Contact
rabies
Consumption of Contaminated Animal Products
Salmonella
Bloodborne Transmission
Hepatitis B
Sexual Transmission
Chlamydia
Contaminated Sol
tetanus
Waterborne Pathogens
legionella
prevention of transmission
hygiene, vaccination, protective measure, vector control, quarantine and isolation
Inactivated Vaccines
contain killed pathogens
Live-Attenuated Vaccines
use weakened forms of the pathogen
Subunit, Recombinant, and Conjugate Vaccines
include specific pieces of the pathogens
mRNA Vaccines
deliver genetic instruction for the immune system to produce and antigen
Vector-Based Vaccines
use harmless virus to deliver genetic material coding for an antigen
Endemic
regularly found among particular people or in a certain area
Sporadic
a disease that occurs infrequently and irregularly
Epidemic
a widespread outbreak of an infectious disease where many people are infected at the same time
Pandemic
an epidemic that affects multiple geographic areas at the same time
Herd Immunity
immunity in MOST of the population
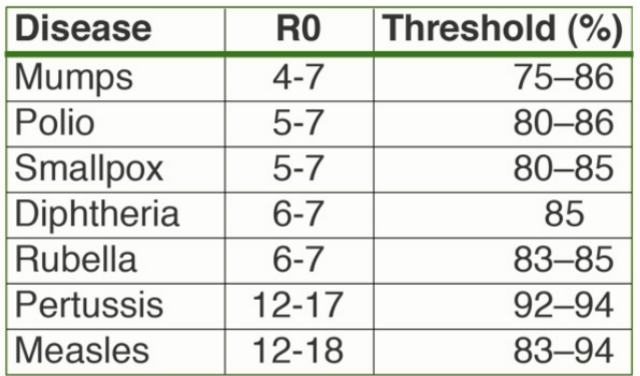
R0 (reproductive number)
is how many people 1 person can infect
Threshold %
is the amount of the population vaccinated in order to obtain Herd immunity
Direct ELISA
test for antibody
uses one antibody
signal is generated and measured
Indirect ELISA
test for antibody (or antigen)
2 antibodies
signal is generated and measured
Sandwich ELISA
test for antigen
2 antibodies
for complex samples
Competitive ELISA
test for antigen
sample antigen competes with the known one
signal inversely correlates with the amount of antigen in the sample
Voriolation
inoculation of smallpox into the skin
vaccine
substance used to stimulate the
production of antibodies that provide immunity against one or several diseases or their products; treated to act as
an antigen without inducing disease