new economics 💵
1/119
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover essential economic concepts, definitions, and principles, providing a comprehensive resource for exam preparation.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
Economic Problem
Unlimited wants and limited resources.
Opportunity Cost
The cost of forgoing the next best alternative when one choice is made instead of another.
Supply
The quantity of a good that producers have available for sale.
Demand
The quantity of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to buy.
Equilibrium
The point at which the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded.
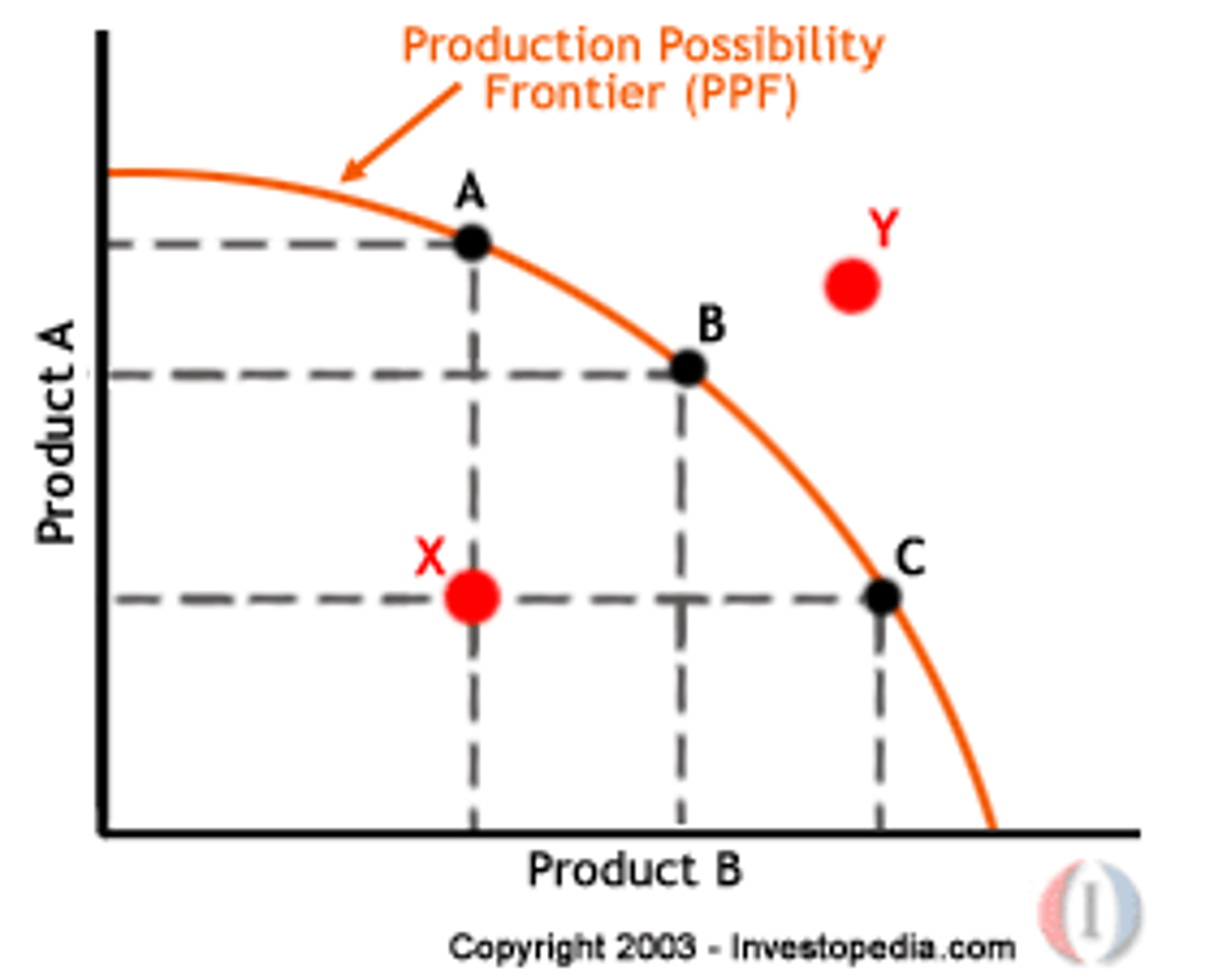
Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF)
A graph showing the combinations of output that the economy can produce at the current time if all resources are fully employed.
Inward Shift of the PPF
A reduction in economic growth.
Outward Shift of the PPF
An increase in economic growth.
Economic Questions
Questions such as What to produce? How to produce? How much to produce? Who receives what is produced?
Complementary Wants
Desires for goods or services that naturally go together.
Recurring Want
A desire that is never fully satisfied and keeps arising over time.
Individual Want
Desires held by each person.
Collective Want
Desires shared by the entire community.
Factors of Production - Land
All natural resources used in the production of goods and services (e.g. raw materials, agricultural land, water, minerals).
Factors of Production - Labour
The human effort, both physical and mental, used in producing goods and services.
Factors of Production - Capital
Physical assets or resources used in the production process that are not directly consumed.
Factors of Production - Enterprise
The ability and willingness to combine land, labour, and capital to produce goods and services, typically involving risk-taking and innovation.
Business Cycle
A graph showing fluctuations in economic activity over time.
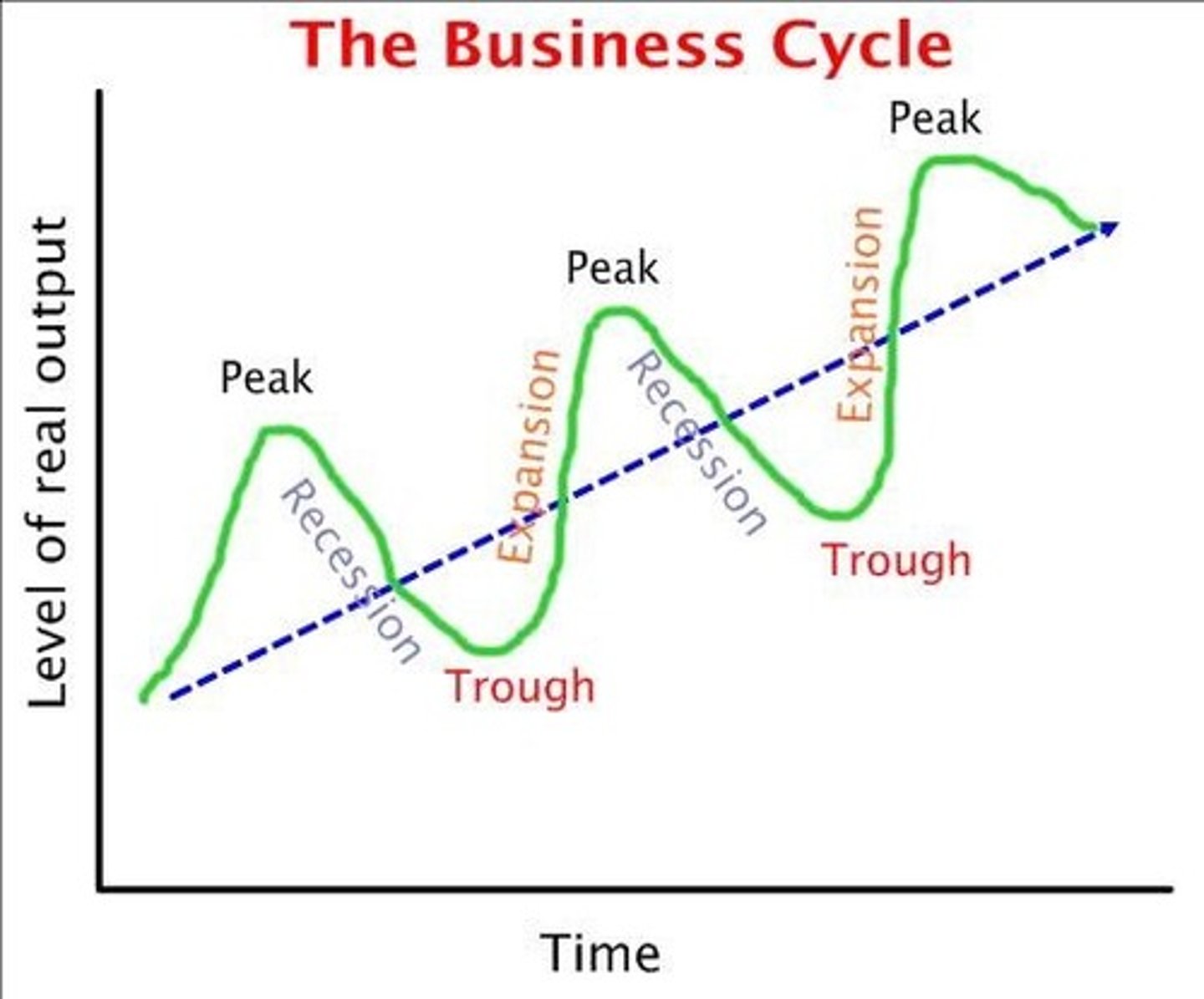
Expansion (Business Cycle)
An increase in demand and sales, inflation, business confidence, employment, wages, and production.
Contraction (Business Cycle)
A decrease in demand and sales, inflation, business confidence, employment, wages, and production.
Wealth
The value of assets owned.
Macroeconomics
The study of the economy as a whole.
Microeconomics
The study of individual firms and their decision-making.
Aggregate Demand (AD)
The total demand for goods and services in the economy (C + I + G + [X – M]).
Aggregate Supply
The total amount of goods and services produced by the economy.
Five-Sector Circular Flow Model
Describes interactions between different sectors in the economy.
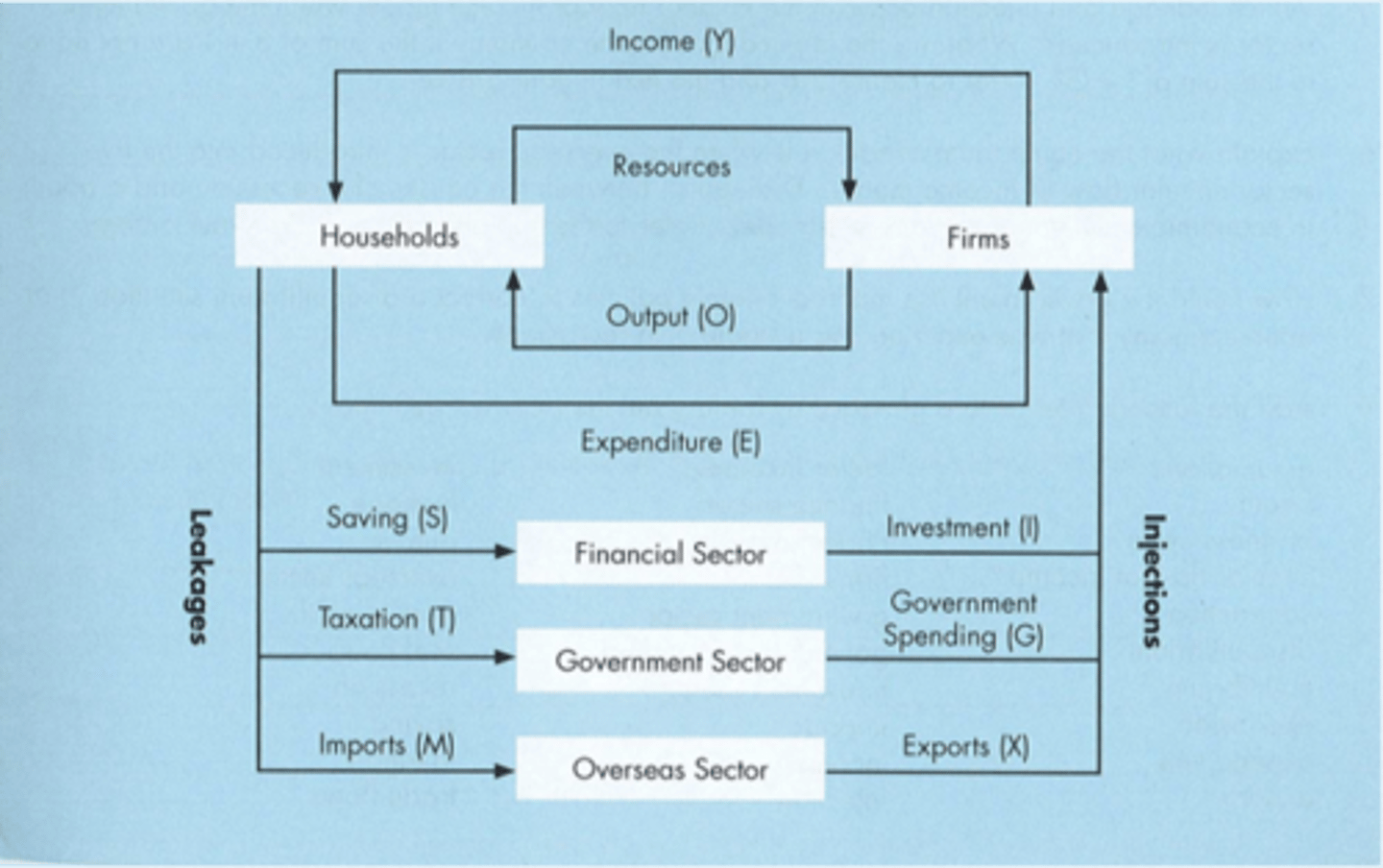
Income (Y)
Earnings from work or investments (Y = C + S).
Leakages
Transactions that remove money from the economy.
Savings (S)
The portion of income not spent on consumption.
Taxation (T)
Money paid to the government.
Injections
Transactions that introduce money into the economy.
Imports (M)
Goods and services purchased from other countries.
Investment (I)
Spending on capital goods for future production.
Government Expenditure (G)
Spending by the government on goods and services.
Exports (X)
Goods and services sold to other countries.
Standard of Living
A measure of an individual’s material well-being.
Income/Wealth Distribution
How a country’s total income or wealth is divided among its population.
Inflation
A continuous rise in the general level of prices over time, eroding purchasing power.
Stagflation
A period marked by rising inflation coupled with rising unemployment.
Comparing Economies
Economies are compared using factors such as inflation, GDP, HDI, wellbeing/happiness, unemployment, GNI, income/wealth distribution, environmental quality, quality of life, size, government role, and economic growth.
Purchasing Power Parity
A method that compares currencies by measuring the cost of a basket of goods in different economies, with equilibrium reached when the basket is priced the same in each.
Gini Coefficient
A statistical measure of income inequality ranging from 0 (perfect equality) to 1 (maximum inequality).
Lorenz Curve
A graphical representation of income distribution, where the Gini coefficient is derived from the area between the line of equality and the curve.
Average Propensity to Consume (APC)
The fraction of total income that is spent on consumption (APC = C/Y).
Average Propensity to Save (APS)
The fraction of total income that is saved (APS = S/Y).
Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC)
The proportion of each extra dollar earned that is spent on consumption (MPC = ΔC/ΔY).
Marginal Propensity to Save (MPS)
The proportion of each extra dollar earned that is saved (MPS = ΔS/ΔY).
The Multiplier Effect
The change that occurs in the overall economy when an external force (like added money) affects other parts, calculated as K = 1/MPS.
Consumer Sovereignty
The power that consumers have in determining what and how much is produced through their purchasing choices.
Factors Affecting Saving and Spending
These include personality, culture, future expectations, specific plans, tax policies, credit availability, and age.
Planned Obsolescence
The practice of altering products so that those already sold become outdated before they actually require replacement.
Monopolies
Corporations that gain complete control over the production of a single good or service.
Misleading or Deceptive Conduct
Actions by a manufacturer or seller that are unfair, dishonest, or likely to mislead consumers when making a purchase.
Anti-Competitive Behaviour
Strategies (such as predatory pricing) that limit competition within a market.
Factors Influencing Consumer Choices
These include the level of income, the price of a good or service, prices of substitutes or complements, consumer tastes/preferences, and advertising.
GDP
The total monetary value of all final goods and services produced within a country over a specific period (typically one year).
HDI (Human Development Index)
A composite statistic based on life expectancy, education, and per capita income that ranks countries into tiers of human development on a scale from 0 to 1.
GNI (Gross National Income)
The total income earned by a nation’s residents and businesses, regardless of whether the income is generated domestically or abroad.
Measuring Wealth Distribution
Often measured by metrics like the Gini coefficient or statistical measures of wealth shares among population segments.
Measuring Economy Size
Typically measured by the total value of all goods and services produced within a country over a given period.
Scarcity
The fundamental economic problem arising because resources are limited while wants are unlimited, forcing trade-offs in resource allocation.
Wants
Desires for goods and services that are not essential for survival but enhance quality of life.
Needs
Essential requirements for survival (such as food, water, shelter, and clothing) that must be met before other desires.
What Does ‘Land’ Refer To?
All natural resources used in production, including raw materials, agricultural land, and natural resources like water and minerals.
Defining Labour
The human effort (both physical and mental) used in producing goods and services, including work by employees and entrepreneurs.
Defining Capital
Physical assets or resources used in production that help facilitate the process without being directly consumed.
Defining Enterprise
The capacity to combine the factors of production—land, labour, and capital—to create goods and services, often involving risk and innovation.
Individual Want
A desire for a specific good or service that satisfies personal needs.
Collective Want
A desire shared by a group for goods or services that address common needs (for example, a community resource).
Recurrent Want
A need for goods or services that arises repeatedly over time, such as food or clothing.
Complementary Want
A desire for a good or service that is used together with another (for example, a printer with ink cartridges).
The Four Production Choices
What to produce, How to produce (using labor intensity, capital intensity, or machinery), How much to produce, How to distribute what is produced.
Asia’s Economic Growth
True – Asia is the fastest growing economic region, driven by significant development and rising trade interactions.
Australian Welfare Spending Compared to Asia
Australia spends more on welfare than most nations in Asia.
Assumptions of the PPF
The economy produces only two goods, Technology remains constant (no technological advances), The quantity of resources is unchanged, All resources are fully employed.
Main Types of Economies
Traditional, command, market, and mixed economies.
Traditional Economy
An economic system in which decisions are based on long-established customs, traditions, and beliefs.
Command Economy
An economic system where a central authority makes all decisions about production and distribution rather than relying on market forces.
Market Economy
An economic system where supply and demand determine production and distribution, with little central control.
Mixed Economy
An economic system that blends free market practices with government intervention.
Disadvantages of a Traditional Economy
Change is discouraged (or even punished), and production methods tend to be inefficient.
Disadvantages of a Command Economy
There is little incentive to work hard or innovate, and consumer choice is limited.
Disadvantages of a Market Economy
There may be inadequate support for those unable to work (such as the very young, elderly, or sick), potentially leaving them vulnerable without external assistance.
Disadvantages of a Mixed Economy
Overregulation can lead to inefficiency, reduced innovation, increased bureaucracy, and a higher risk of corruption or social unrest.
Government Intervention in the Economy
The process by which the government provides services or regulates markets to correct failures or supply public goods and services.
Market Concentration
Refers to the number of competitors operating in a particular market.
Australian Economic Growth Compared to Asia
Australia’s economic growth is slower on average than that of Asian economies.
Asia’s Industrialisation
True – Asia industrialised quickly.
Australia’s GDP per Capita
It is high—approximately $102,000.
Australia’s HDI Ranking in Asia
Australia ranks third in the Asian region.
Australian Unemployment Rate
It is quite low, around 4.1%.
COVID-19 Unemployment Recovery in Asia
No, Asia did not recover slowly; it recovered very quickly.
Employment in Services (Australia)
About 80% of the workforce is employed in the services sector.
Agricultural Employment in Indonesia
Approximately 30%, although this figure is declining.
Agricultural Employment in Australia
Roughly 2% of the workforce is employed in agriculture.
Income Inequality: Asia vs. Europe
Income inequality is generally higher in Asia than in Europe.
Australia’s Income Inequality Compared to Asia
Australia’s income inequality is relatively low; it ranks second in the region behind New Zealand.
CO₂ Emissions in Australia (Per Capita)
Yes, Australia emits high CO₂ per capita.
Australia’s Government Expenditure (2022)
Government spending was about 38% of GDP.
Spending on Education and Health in Australia
Approximately 13.2% of GDP is spent on education and health combined.