cognition psychology
1/184
Earn XP
Description and Tags
memory & intelligence
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
185 Terms
memory researcher that shown that recovered memories may be false recollections of events
4 months | |
1st year | |
18 months |
babbling stage | 4 months |
holophrastic stage / one-word stage | 1st year |
telegraphic speech / two-word stage | 18 months |
rule that guarantees the right solution by a fool-proof method
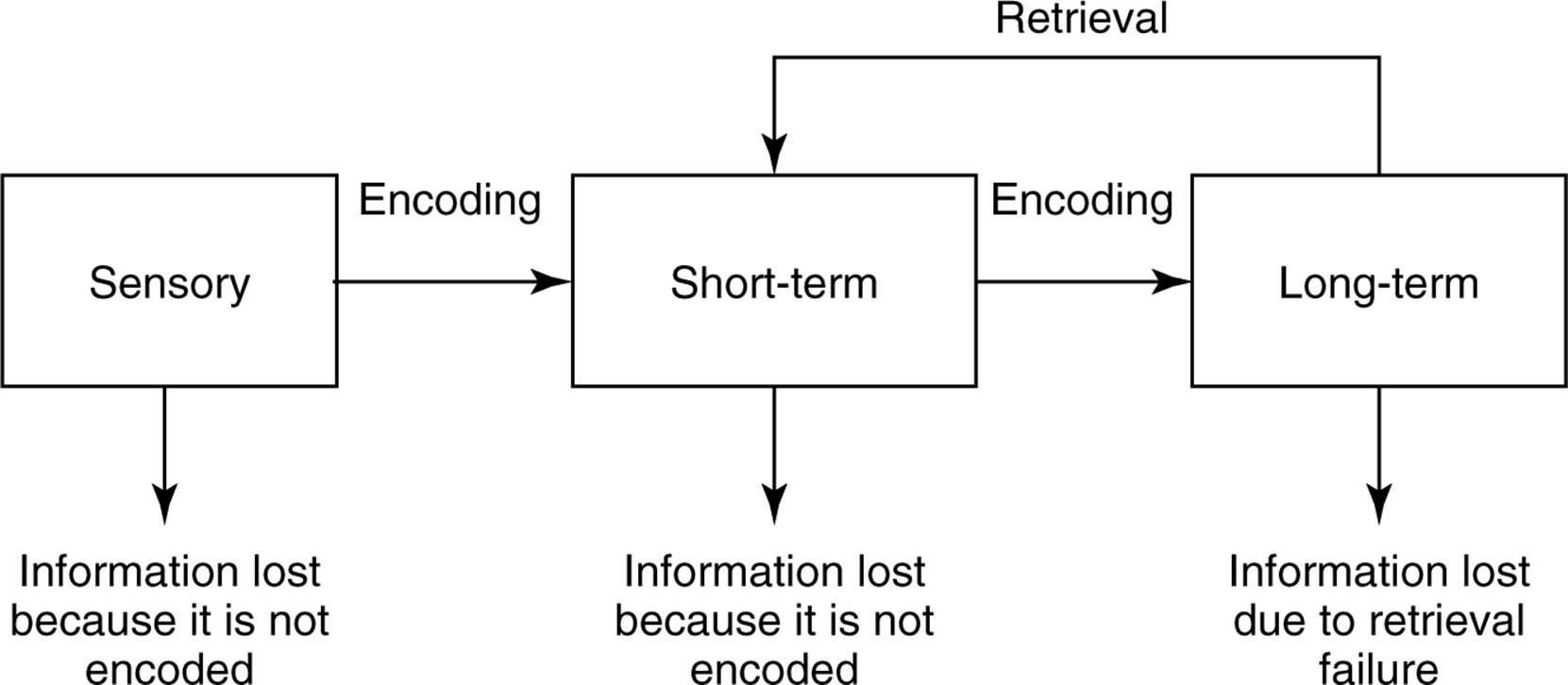
information processing model
three stages that information passes through before it is stored (memory)
face validity
extent to which a test does what it needs to do on the surface.
the representative population for the actual population of the test
argued that intelligence could be expressed by a single factor; g
Howard Gardener’s multiple intelligences | meaning |
linguistic, logica-mathemeatic, spatial (able to visualize w/ minds eye) | |
ability to play a instrument or make a symphony | |
ability to manipulate body and objects | |
ability to understand oneself. // ex. introspection, those insane Instagram poems | |
ability to get along with people and be sensitive to others // ex. my mom | |
ability to recognize & organize natural environment // ex. my mom’s gardening skills |
Howard Gardener’s multiple intelligences | meaning |
traditional | linguistic, logica-mathemeatic, spatial (able to visualize w/ minds eye) |
musical | ability to play a instrument or make a symphony |
bodily-kinestthetic | ability to manipulate body and objects |
intrapersonal | ability to understand oneself. // ex. introspection, those insane Instagram poems |
interpersonal | ability to get along with people and be sensitive to others // ex. my mom |
naturalist | ability to recognize & organize natural environment // ex. my mom’s gardening skills |
theory | summary |
spearman’s general intelligence | |
intelligence is broken down into 7 distinct factors. still an underlying g factor | |
garderner’s multiple intellligences | |
sternburg’s triarchic theory | |
social intelligence is an important indicator of life success |
theory | summary |
spearman’s general intelligence | basic intelligence predicts our abilities in varied academic areas |
thurstone’s primary mental abilities | intelligence is broken down into 7 distinct factors. still an underlying g factor |
garderner’s multiple intellligences | abilities are classified into independent intelligences, beyond traditional academic ones |
sternburg’s triarchic theory | intelligence is best classifed in 3 areas for world-success: analytical, creative, and pratical. |
goleman’s emotional intelligence | social intelligence is an important indicator of life success |
retrieve informaiton that is not currently in your conscious awareness but that was learned at an earlier time // ex. fill in the blank test
measure of memory in which the person identifies items previously learned. // ex. multiple choice test
learning something more quickly when learning it again. // ex. when studying ofr a final exam, engaging in a language from early childhood
pioneer memory researcher. did study on himself with recalling syllables
students should use ___ for effective studing
recall
1. sensory memory
2. short-term memory (now added working memory)
3. long-term memory
activated memory that holds items briefly. // ex. digits on a phone # while calling.
newer understanding of short term memory that adds conscious active processing of incoming auditory/visual information and information retrieval from long term memory. // ex. when you are studying for ap psych you talk and see terms and exmaples