lab 6
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
what type of epithelium is the cervix
stratified squamous
what area of the cervix is most susceptible to HPV infection
squamous columnar junction (SCJ) or transition zone
because columnar up inside and squamous on the outside - squamous cells taken in smear
how does the cervix change over a womans life
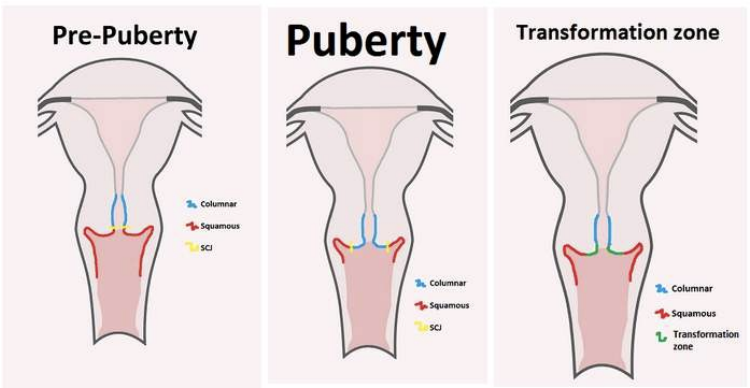
SCJ becomes more exposed in puberty → so need to make sure vaccinated before then
is HPV alone enough for cancer
probably not - need a second hit which we dont really understand yet
cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN)
potentially premalignant transformation and dysplasia of squamous cells on the surface of the epithelium

pleomorphic
when the cells are dysplastic and are different sizes
CIN 2 and 3 cytology
reduction in size of some cells
increase in nuclear/cytiplasmic ratio
hyperchromatic nuclei
pleomorphism
halos around nuclei - koilocytes
neutrophils or bacteria
CIN 2 and 3 carcinoma in situ - histology
loss of maturity of basal cells that extends to various levels of epithelial thickness
loss of cellular orientation
hyperchromatic nuclei
increase in nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio
pleomorphism
koilocytes
what causes halo effects
less protein being produced as the virus does not care about trying to preserve cell function
immunocytochemistry
use of antibodies to label specific antigens in cells
antibody-antigen reaction binding is identified by a number of labelling methods and enzyme substrate reaction produced colourful product
important tumour suppressor genes
p53, RB, BRCA1, PTEN
p53 mutations involved in breast and brain but not cervical cancer
BRCA1 in breast and ovarian cancer
why test for p53
can label cells for p53 using immunocytochemistry
tightly negatively regulated in cells - so mutations mean there are high levels of p53 in cells as mutant is more stable (labels both wild type and mutated p53)
imunocytochemistry - how
treat cells with DNA damaging agent → should see an increase in p53 to fix damage and then go back down as it is negatively regulated
DNA damage → primary antibody to p53 (mouse) → excess washed off → secondary antibody conjugated to a chromagen
FISH is used
to label specific DNA or mRNA (transcript sequences) using a labelled single strand probe targeting the sequence
often there are gene or chromosome abnormalities (amplification) in cancer cells
what is the most commonly amplified gene in cervical cancers
PIK3CA
what looking for in FISH
one colour highlights one gene so should see two of each colour in a nucleus
if see more than 2 of each colour in nucleus know that the gene has been amplified