CNIT 344 Final Exam
1/81
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
OSI Layer 1
Physical Layer, Data Type: Bits
OSI Layer 2
Data Link Layer, Data Type: Frames
OSI Layer 3
Network Layer, Data Type: Packets
OSI Layer 4
Transport Layer, Data Type: Segment
Ethernet, USB, Bluetooth, Hub, Repeater are associated with what layer?
OSI Layer 1
PPP, ALIP, ATM, Switch, Bridge, Wireless AP (WAP) are associated with what layer?
OSI Layer 2
IP, ARP, ICMP, Routers are associated with what layer?
OSI Layer 3
TCP and UDP are associated with what Layer?
OSI Layer 4
OSI Layer 5
Session Layer, Establish Interhost communication
OSI Layer 6
Presentation Layer, Formats data for viewing
OSI Layer 7
Application Layer, End user application
HTTP, DNS are associated with what layer?
OSI Layer 7
JPEG, GIF, ASCII, SSL, IMAP are associated with what layer?
OSI Layer 6
NFS, RFC, SQL, and NetBIOS are associated with what layer?
OSI Layer 5
OSI Stands for
Open System Interconnection
Analog Bandwidth calculation
Fmax - Fmin
Serial Transmission
one bit at a time
Parallel Transmission
multiple bits at a time
Synchronous Transmission
Time based (clock based) no gap between data items
Asynchronous Transmission
Signal based (start & stop bits)
Common implementations of Serial Transmission
Telco/ISP links
Ethernet
SATA
Common implementation of Parallel Transmission
PCI, Memory bus, Many HDD Interfaces, Older Printers & some scanners.
Timing and transmission for Serial & Synchronous
T-Carrier system, SONET
Frame Relay, xDSL, ISDN
USB, Firewall
Timing and transmission for Serial & Asynchronous
Most “Terminal“ applications, keyboard, mice
ATM
Firewall
Timing and transmission for Parallel & Synchronous
Internal buses
Printers & Scanners
Timing and transmission for Parallel & Asynchronous
Not many communications protocols or standards
Reviewed for HPC
Simplex Communication

Full-Duplex Communication

Half-Duplex
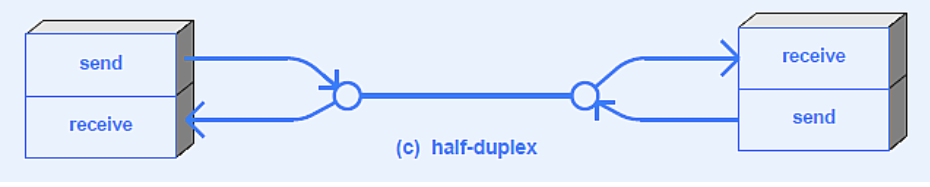
What does Duplex Auto-negotiation do?
Set link speed and duplex mode
What is Modulation?
The process of converting digital bits into an analog signal so it can be sent over an analog medium
What is Demodulation?
The process of converting an analog signal into a digital bit stream is called Demodulation
Devices that preform Modulation and Demodulation
modems
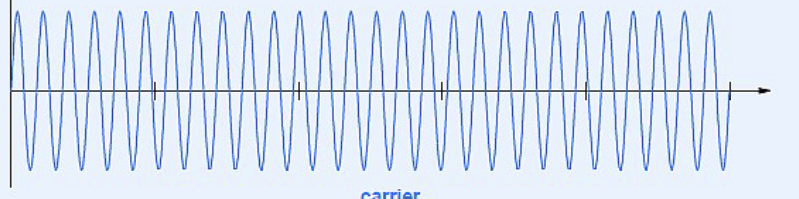
Amplitude Modulations: Carrier
Carrier
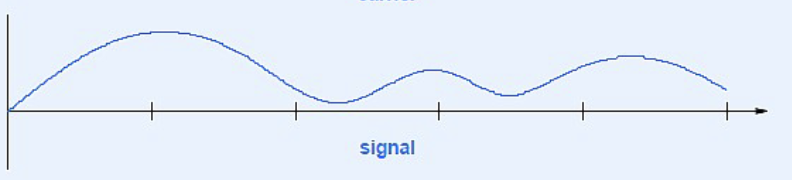
Amplitude Modulations: Signal
Signal
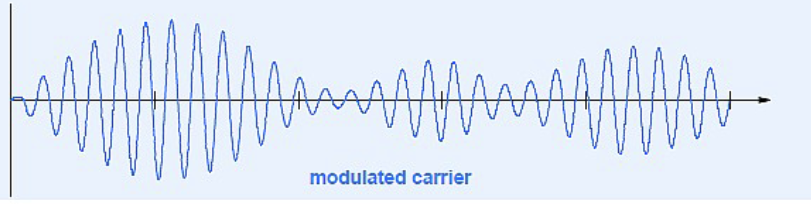
Amplitude Modulations: Modulated Carrier
Modulated Carrier
What is Frequency Modulation?
Manipulate the frequency of the carrier wave in order to indicate data
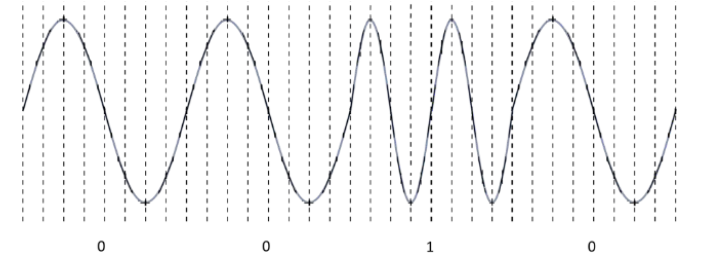
What is Phase Modulation
Manipulation of the phase of the carrier wave in order indicate data
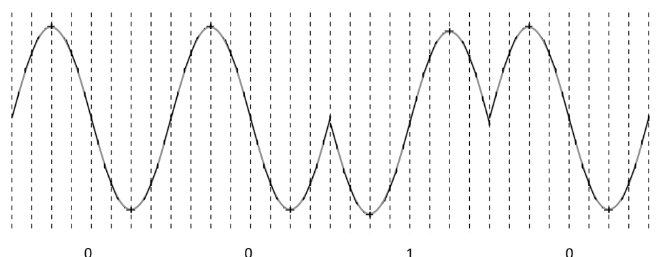
What is Shift Keying
The term that is used when the signal is digital rather than modulation.
What is Frequency Division Multiplexing?
Each source data stream is assigned to a specific sub-frequency of the channel
A guard band is required to minimize adjacent channel interference.
What is Time Division Multiplexing
Data can only be sent during assigned timeslots.
Each source data stream is assigned to a timeslot in the channel
What is Code Division Multiplexing
Each source data stream is assigned a unique orthogonal code for use in the entire channel
Any overlapping data streams are seen as noise in the system and is ignored.
How do the OSI Layers communicate with each other?
Adjacent layers only
What does open interconnection mean for the OSI model?
Multi-vendor environments can be supported due to connection between layers
What do layers rely on for layers above/below them?
To perform their layers specific functions
Responsibility of OSI Layer 1: Physical
Transmission and receipt of the bit stream to and from nodes; concerned with signaling techniques
Responsibility of OSI Layer 2: Data Link
Providing point to point validity of the data and reliable operation of communication links
What are the two sub-layers of the data link layer?
MAC
LLC
Responsibility of OSI Layer 3: Network
Enables Internetworking
provides globally-unique addressing and routes
Responsibility of OSI Layer 4: Transport
Host to Host integrity of transmissions and detecting damaged or lost packets and generating retransmit requests.
Responsibility of OSI Layer 5: Session
Establishing, Maintaining and terminating host to host interactive sessions.
What are ports used for in Layer 5?
To uniquely identify a service/application/function on a host
Responsibility of OSI Layer 6: Presentation
Managing the way data is presented, encoded, translated (ASCII/Unicode), encrypted and compression.
Responsibility of OSI Layer 7: Application
Interface between user applications and network services
What is encapsulation?
Wrapping data with headers/trailers as it moves down in the OSI Model/Layers
What is decapsulation
Removing headers/Trailers as data moves up the OSI Model/Layers
What is Multiplexing?
Combining multiple data streams into one channel
What is IEEE?
Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers, A professional organization that defines the standards for many LAN protocols
What is the standard TIA (Telecommunications Industry Association) and EIA (Electronic Industries Association)
A standards organization covering structured voice and data wiring for LANs
Common means for connecting network devices
Copper Media (Fluorescent Lighting, Radio waves, and Electric motors)
Wiring pattern for T568A (Ethernet)
Striped Green
Green
Striped Orange
Blue
Striped Blue
Orange
Striped Brown
Brown
Wiring Pattern for T568B (Ethernet)
Striped Orange
Orange
Striped Green
Blue
Striped Blue
Green
Striped Brown
Brown
Wiring for a straight through cable
Same pattern throughout the cable (T568B or T568A)
Wiring for a crossover cable
Used both cable types one for each end of the cable (T568B or T568A)
Purpose of a Straight-Through cable
Connecting a device to a switch/hub
Purpose of a Crossover cable
Connecting two of the same devices to the same device (Switch to Switch/Router to Router)
What is a coaxial cable?
Used in wireless and cable access technologies
What is the use case for a rollover cable?
Connecting a workstation serial port to a Cisco networking device console port using a nine-pin adaptor
What are shielded twisted pairs
Shields the entire bundle of wires within the cable as well as the individual wire pairs to provide better noise protection that UTP
What are Hybrid Fiber-Coax
Cable structure used to provide two-way communication over a coaxial cable (i.e. cable connection to the internet
Standard IEEE 802.11
Wireless LAN (WLAN); Uses a contention system with Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Avoidance (CSMA/CA)
Standard IEEE 802.15
Wireless Personal Area Network (WPAN); Uses a device pairing process to communicate over distances from 1-100 meters
Standard IEEE 802.16
Wireless broadband access; uses a point to multipoint topology to provide wireless broadband access
Minimum frame lengths
512 bits / 64 bytes
Maximum frame length
12144 bits / 1518 bytes
What happens if the first bit is 0 in an address
It is a unicast, if not it is a multicast
Standard Ethernet is how fast?
10 Mbps
Fast Ethernet is how fast?
100 Mbps
Gigabit Ethernet is how fast
1 Gbps
Ten-Gigabit Ethernet is how fast?
10 Gbps
What is a Ad Hoc
Wireless networks can operate without access points
client stations which are configured to operate in ad hoc mode configure the wireless parameters between themselves