1.11 Assessment of Mitral Regurgitation
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
What is the first thing that must be done when regurgitation is present?
Finding out what is causing the regurge (MAC, MVP, MS, Flail leaflets, etc.). This is also known as the etiology.
What views should MR be viewed in?
Parasternal LAX
Apical 4
Apical 2
Apical LAX
2-D measurements should be performed to assess what when MR is present?
LV sizem systolic function, and LA size.
How can we determine the severity of the regurgitation? (4)
Colour Doppler-ing the jet area
Vena contracta width
PISA shell
Pulmonary vein Doppler
It is important to place what kind of Doppler on every view the MV is seen to look at the regurgitant jet?
Colour.
It is important to use all views the MR is seen in, why?
Small and eccentric jets can be missed if multiple windows are not used.
Central jets are typically seen with secondary MR due to what?
LA dilatation.
Ischemic MR often results in an what type of jet?
Eccentric posteriorly directed jet.
What is important when determining the degree of MR?
The area of the jet in relation to the size of the LA.
Colour Flow makes detection of MR…?
Easier and quicker.
What is the vena contract width?
The smallest width of the jet as it leaves the regurgitant orifice and it also reflects the regurgitant orifice area.
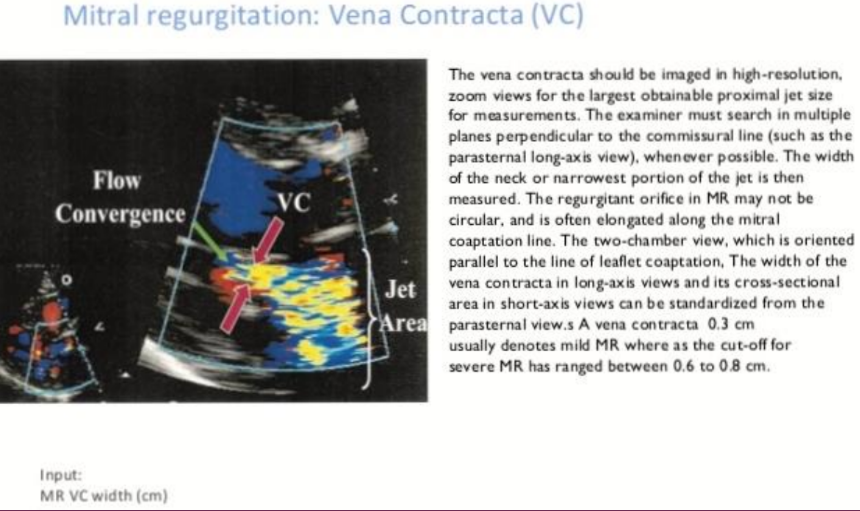
How do you obtain the vena contracta width of the MR jet?
When looking at the colour Doppler cineloop of the MR, cineloop through to systole where the MR occurs. Zoom this area and measure the area right below the PISA shell.
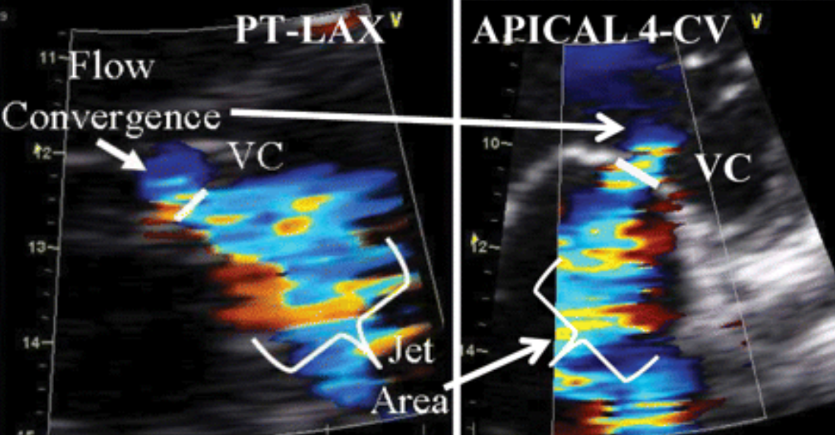
A vena contracta of < 3 mm indicates what?
Mild MR.
A vena contracta of > 7 mm indicates what?
Severe MR.
A vena contracta > 3 mm but < 7 mm defines what?
These values are intermediate and are not accurate for identification of the severity of MR.
What is the preferred method for assessing MR?
PISA.
What does PISA stand for?
Proximal Isovelocity Surface Index.
PISA is also known as what?
The flow convergence method.
What does PISA do?
It estimates the area of an orifice through which blood is flowing through.
With MR, what does PISA do?
It determines the effective regurgitant orifice and regurgitant volume.
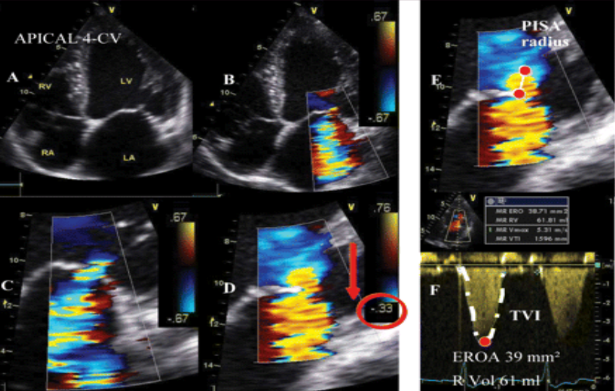
What are the four hallmarks of flow in MR?
Flow convergence (PISA)
Flow acceleration (vena contracta)
Turbulence (what we call the size of the jet)
Downstream (reverse effects in the pulmonary veins)
PISA is appropriate to use when MR has what type of jet?
A central jet.
What view should PISA of MR with central jet be performed in?
A4. (However in the case of prolapse, LAX or SAX can be used if there is AMVL prolapse).
Can you use PISA on eccentric jets with MR?
No, they show to be problematic.
How do you obtain PISA of MR central jet in Apical 4?
Have cineloop of MR zoomed and placed in systole where the regurge is occurring. Lower the baseline of the colour scale to < -0.4 and apply PISA.
An EROA of < 0.20 cm² is what type of MR?
Mild.
An EROA of 0.20 - 0.29 cm² is what type of MR?
Moderate.
An EROA of 0.30 - 0.39 cm² is what type of MR?
Moderate to severe.
An EROA of > 0.40 cm² is what type of MR?
Severe.
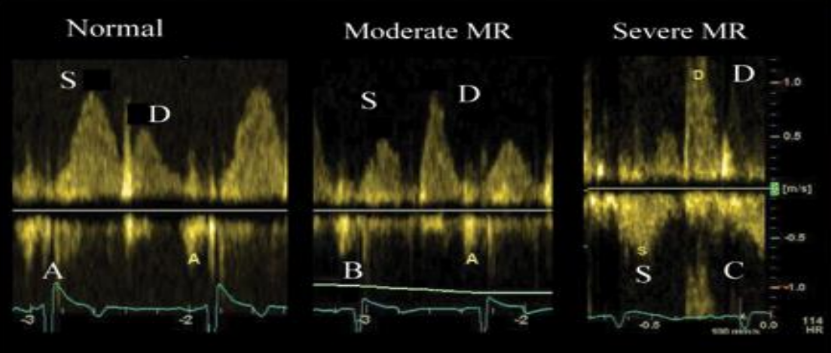
When assessing for MR, it is important to PW the pulmonary vein. Why?
To check if the regurge is going down and reversing flow in the pulmonary veins.
When assessing MV for MVP, what is performed?
A sweep of the MV in parasternal LAX. One with Colour Doppler and one without. Be sure to zoom in on the MV.