UNIT 6: Civil War, enslavement, and abolition
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

19 Terms
Civil War (1861-1865)
deadliest war in American history; conflict between north (union) and south (confederacy); 11 southern slave states wanted to secede from Union

Secede
To leave or withdraw from a political union or organization.
abolish
to put an end to

Abolitionist
A person who wanted to end slavery in the United States

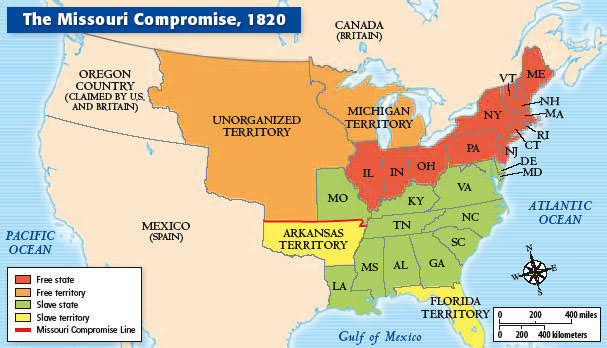
Missouri Compromise of 1820
Focused on maintaining a balance of power in Congress by admitting Missouri as a slave state and Maine as a free state, while also prohibiting slavery in the remaining Louisiana Purchase territory north of a specific parallel.
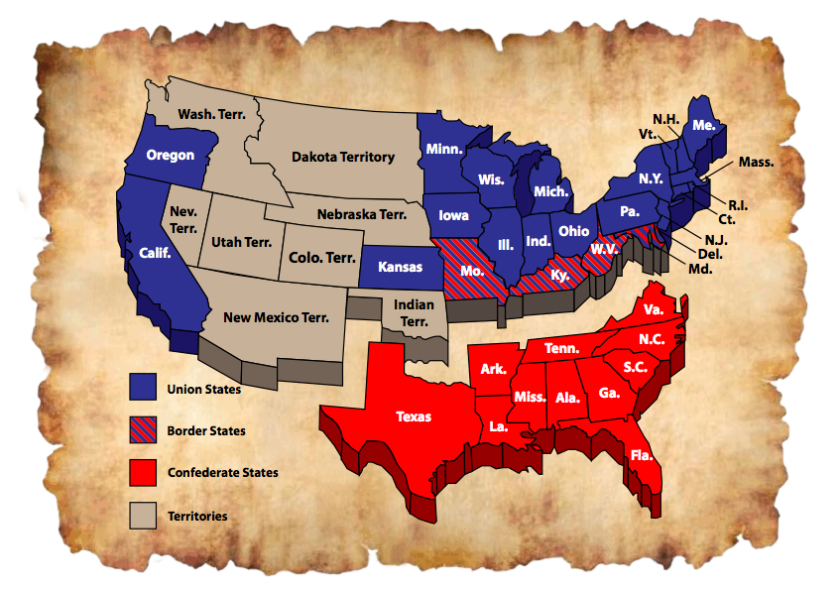
The Union
The Northern States during the Civil War that fought against the Confederacy.
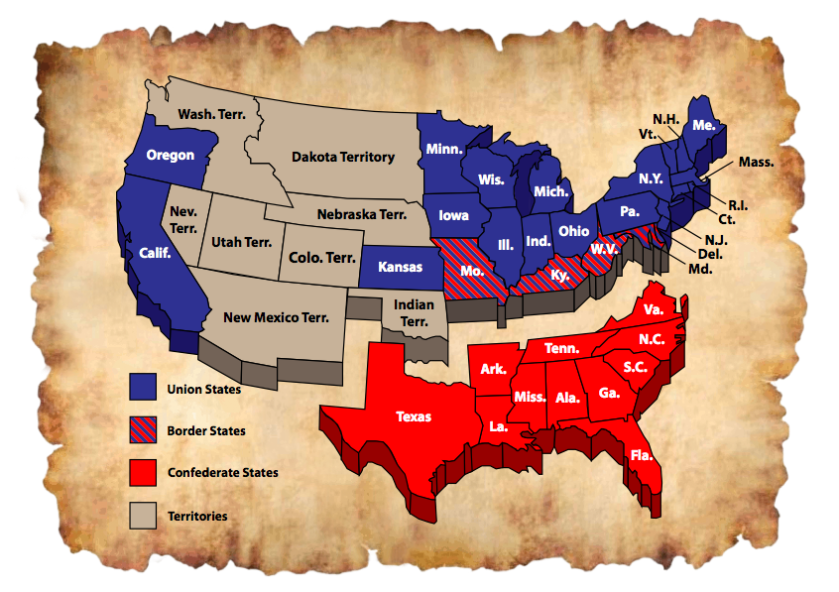
The Confederacy
the southern states that seceded from the United States in 1861. They fought against the Union in the Civil War.
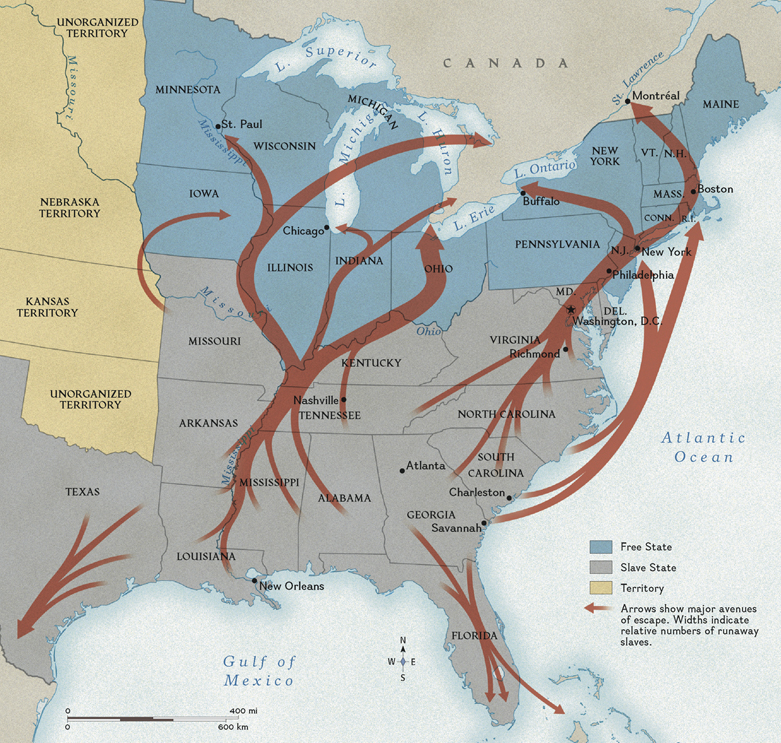
Underground Railroad
a system of secret routes used by escaping enslaved people to reach freedom in the North or in Canada (not a real railroad!)
Emancipation Proclamation (1863)
Declared all slaves in rebelling states to be free but did not affect slavery in non-rebelling Border States. The Proclamation closed the door on possible compromise with the South and encouraged thousands of Southern slaves to flee to Union lines.

emancipate
to set free
Juneteenth
June 19th, 1865 - the date celebrated as the anniversary of Emancipation Day for enslaved people in Texas

13th Amendment to the Constitution
An amendment passed in 1865 that declared that slavery was completely illegal.

Gettysburg Address
A 3-minute speech by Abraham Lincoln during the American Civil War (November 19, 1963) at the dedication of a national cemetery on the site of the Battle of Gettysburg

Abraham Lincoln
16th president of the United States; helped preserve the United States by leading the defeat of the secessionist Confederacy; an outspoken opponent of the expansion of slavery (but not against slavery itself).

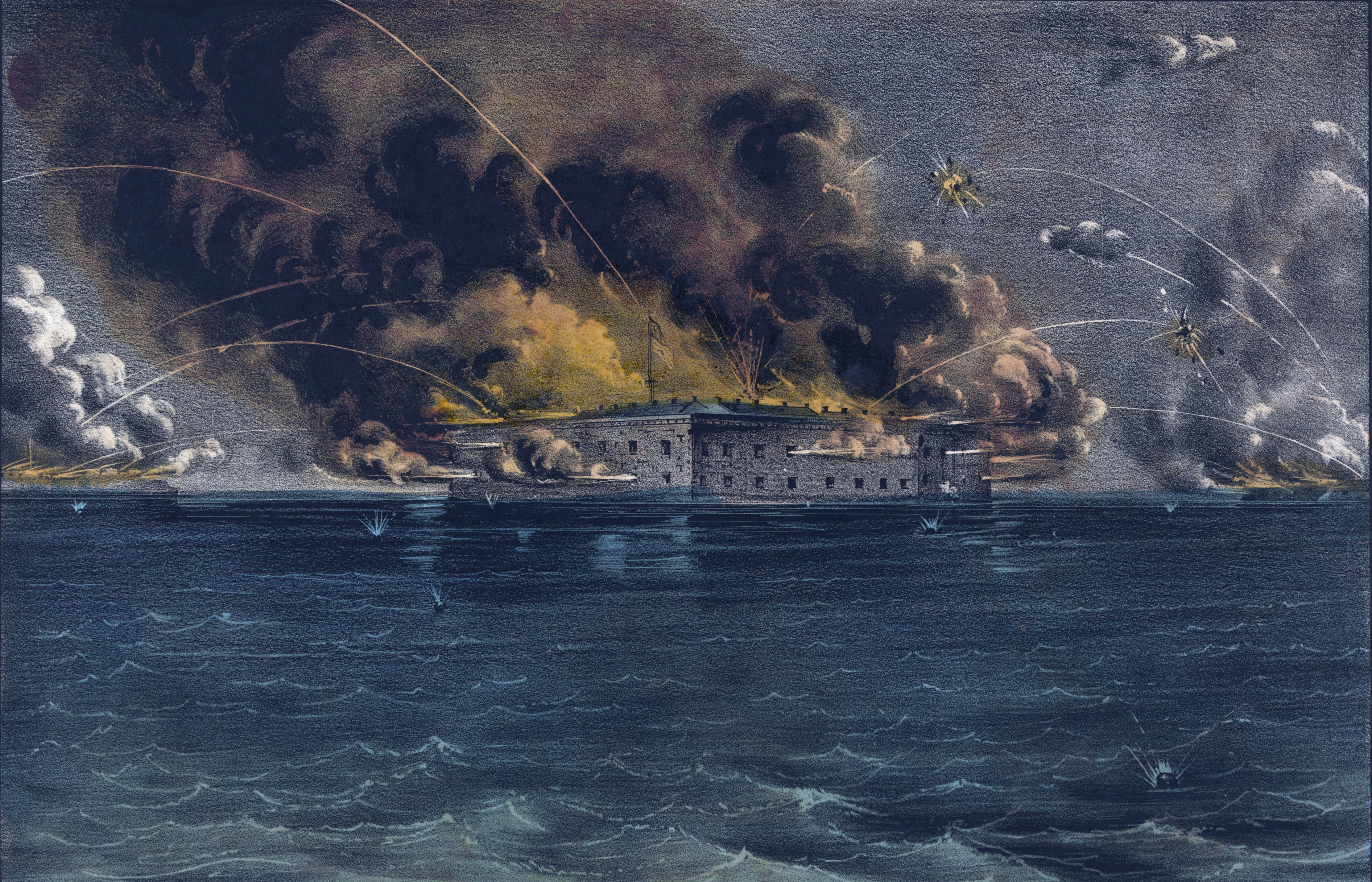
Fort Sumter
The first shots of the Civil War were fired at this fort in South Carolina.

Frederick Douglass
(1817-1895) American abolitionist and writer, he escaped slavery and became a leading African American spokesman and writer. He published his biography, The Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, and founded the abolitionist newspaper, the North Star.

Popular Sovereignty
A government in which the people rule by their own consent.
Missouri Compromise of 1850
Addressing issues related to the status of new territories acquired from Mexico, including California's admission as a free state, popular sovereignty in New Mexico and Utah, and the Fugitive Slave Act.
Kansas-Nebraska Act
Passed in 1854, it created the territories of Kansas and Nebraska, allowing residents to decide on the issue of slavery through popular sovereignty. The act led to violent clashes “Bleeding Kansas” between pro-slavery and anti-slavery groups in Kansas as both sides sought to influence the vote on slavery.
