quiz 5 - Animal Repro
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
During rectal palpation, what part of the beef cow reproductive tract is palpated to determine whether or not the cow is pregnant?
uterine horns
Which of the following is the placental type used by swine and horses?
diffuse
You have graduated from UCM and have been hired by a purebred Angus breeder as a cow/calf manager. One of your responsibilities is to ultrasound the cows in the herd after the breeding season because your boss culls all open cows. One day your boss walks into the barn while you are ultrasounding a cow and wants to know how the ultrasound works. You explain that prior to 100 days of gestation, the fetus is basically in a fluid-filled sac, and that fluid-filled objects appear as black on the ultrasound machine screen. Your boss then asks why fluid-filled objects appear as black on the screen. How do you respond?
Fluid-filled objects absorb many of the sound waves and echo few back.
For what species of farm animal livestock are the offspring weaned after approximately 21 days after birth? The female will then show estrus and be re-bred approximately 4 to 7 days after weaning.
swine
Sheep and goats are ___ -day seasonal breeders, which means that sheep and goats will have estrous cycles and estrus in the USA during the fall of the year.
short
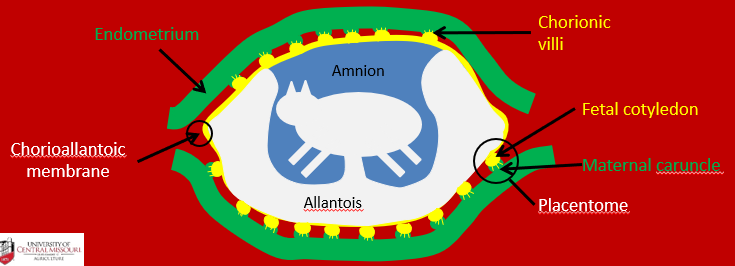
The ____ is the name of the structure that forms from the fusion of the fetal cotyledon with the maternal caruncle
placentome
The gonads and structures of the reproductive tract begin to develop in the male and female embryo during the ___ trimester.
first
In class lecture we discussed that the location where the fetal component and the maternal component of the placenta attach together is where the ‘metabolic exchange’ occurs. Please explain what is mean by the term metabolic exchange.
Metabolic exchange’ describes nutrient uptake, waste elimination, and gas exchange via the mother's blood supply to and from the fetus’ blood supply.
This question is worth two points and partial credit may be given. During embryonic development of the reproductive tract structures and gonads of the male and female, two ducts will begin to develop around the gonads. Please identify these two ducts and explain what happens to each duct if the embryo is male.
If the embryo is male, the fetal testicles will produce a hormone called Anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) which will cause the paramesonephric duct (aka Müllerian duct) to degenerate and be reabsorbed by the embryo. In addition, the fetal testicles will produce testosterone which will stimulate further growth of the mesonephric duct which will become the epididymis and male reproductive tract.
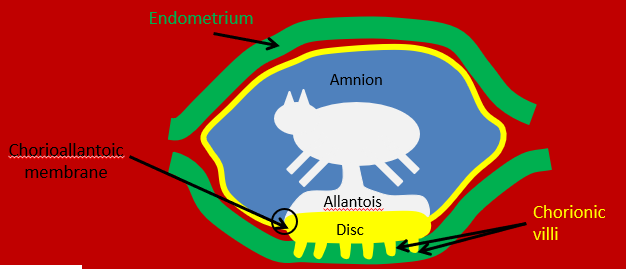
What placenta type do rodents and humans have?
discoid (a disc on one side of the placenta that contains the chorionic villi)
What does the placenta produce?
progesterone
In what species does progesterone produced by the placenta replace the progesterone produced by the CL(s) to maintain the pregnancy?
cattle, horses, sheep
Length of gestation and time of placental take-over of progesterone for each species
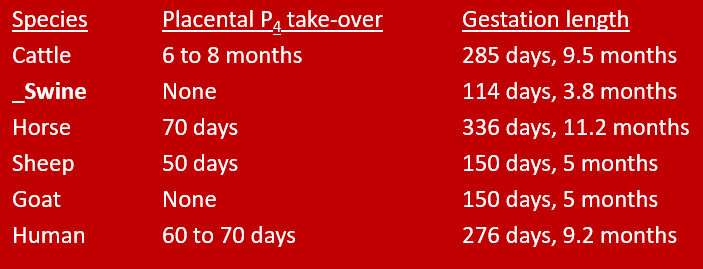
–In the species that have placental take-over of progesterone, the CL(s) remains on the ovary(ies)
The CL(s) will be removed during the parturition cascade
true or false
true
–When do the gonads and structures of the reproductive tract begin to develop in the male and female embryo?
•The gonads and associated structures of the reproductive tract in the male and female embryo develop during the first trimester of gestation in the farm animal livestock species and humans.
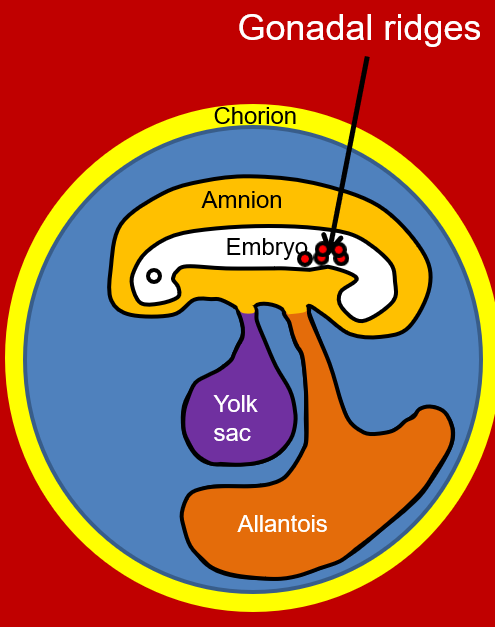
–There are three important events that occur during development of the gonads and structures of the reproductive tract
1.Migration of the primordial germ cells from the yolk sac to the gonadal (aka genital) ridges of the embryo
2.Development of the sex cords (i.e. epithelial cords in males and females)
3.Development of the reproductive tract structures and gonads of the male and female.
What are the primordial germ cells?
•the cells that will become the round spermatid cells in the male and the primary oocytes in the female
What happens to the primordial germ cells during migration to the gonadal ridges?
undergo mitotic divisions which causes the number of primordial germ cells to greatly increase
How do the primordial germ cells know how to get the gonadal ridges of the embryo?
•The primordial germ cells use chemotaxis
–Remember that chemotaxis is when a cell migrates in response to chemical signals released by another cell(s)
•The primordial germ cells follow the chemical signals released by the cells of the gonadal ridges.
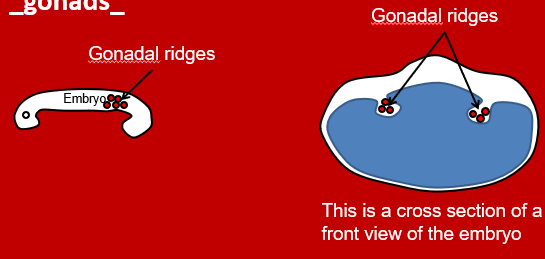
What do the gonadal ridges become?
gonads
What happens in the 2nd step and when the cells arrive at the gonadal ridges?
the primordial germ cells organize into sex cords_
What happens in step three of development of gonadal structures?
–Two ducts will begin to develop around the gonads: the mesonephric duct and the paramesonephric duct (aka Müllerian duct)
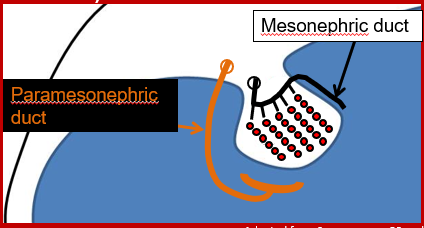
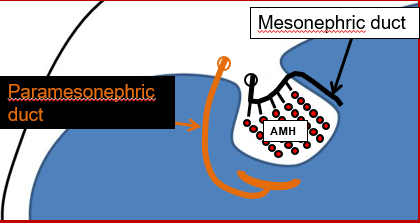
What happens the ducts if fetus is male?
The mesonephric duct will become the epididymis if the embryo is male.
If the embryo is male, the fetal testicles will produce a hormone called Anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) which will cause the paramesonephric duct (aka Müllerian duct) to degenerate and be reabsorbed by the embryo.
(red dots do not disperse, develop into seminiferous tubules)
If the embryo is male, the fetal testicles will produce testosterone which will stimulate further growth of the mesonephric duct which will become the epididymis and male reproductive tract.
The paramesonephric duct (aka Müllerian duct) will become the infundibulum, oviduct and uterus if the embryo is female.
If the embryo is female, there will not be any fetal testicles and therefore no testosterone. If no testosterone is produced, then the mesonephric duct will degenerate due to lack of testosterone and be reabsorbed by the embryo.
If the embryo is female, there will not be any fetal testicles and therefore no AMH produced. If no AMH is produced, then the paramesonephric duct will not degenerate and will continue to grow.
If the embryo is female, the primordial germ cells will disperse from the sex cords and space themselves out around the fetal ovary.
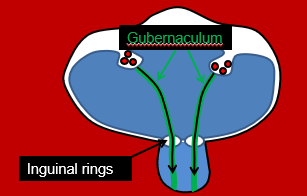
–How do the testicles get outside of the body?
•The testicles descend into the scrotum in the third trimester
•Basically, a structure called the gubernaculum attaches to each testicle and pulls the testicles into the developing scrotum through the inguinal rings in the peritoneum.
–From a livestock production perspective, it is very important to determine pregnancy as early as possible in the female
•Why?
–Because we need to eliminate as many ‘non-productive days’ as possible
»In other words, the female animal is being productive when she is either getting ready to be bred, gestating or lactating
»If the female animal is not doing one of these activities listed above, then she is ‘non-productive’ and is incurring extra cost to the livestock producer.
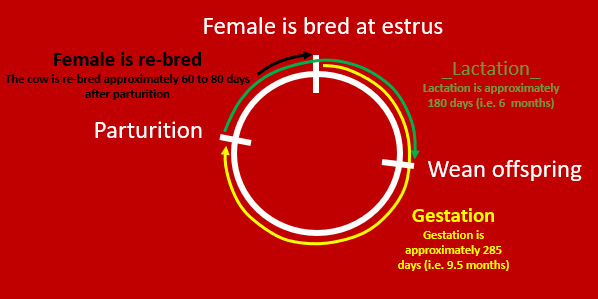
Reproductive cycle for beef cattle
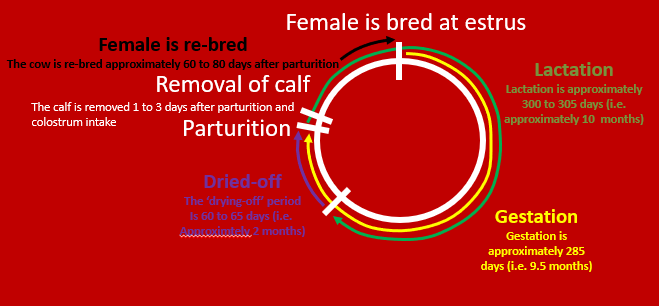
Reproductive cycle for dairy cattle
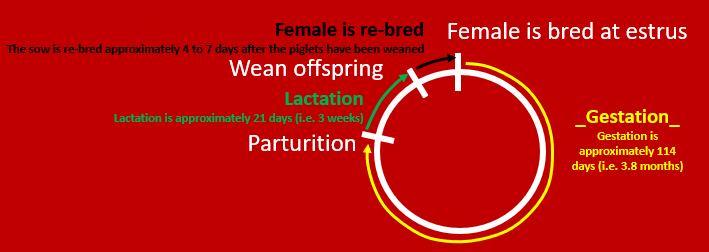
Reproductive cycle for swine
How soon are piglets able to eat solid food after parturition?
Piglets (monogastrics) are ok to eat solid food after 3 weeks. 3 weeks is also how long it takes for female repro tract to reset, so they can have about 2 to 2.5 litters per year
•Reproductive cycle for sheep and goats
–Sheep and goats are short-day seasonal breeders
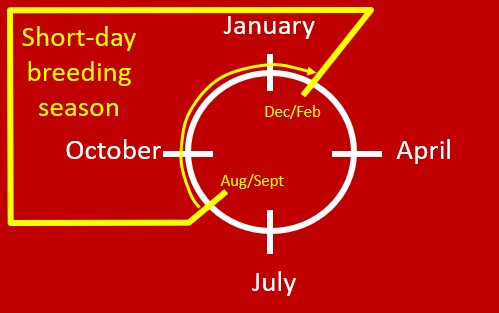
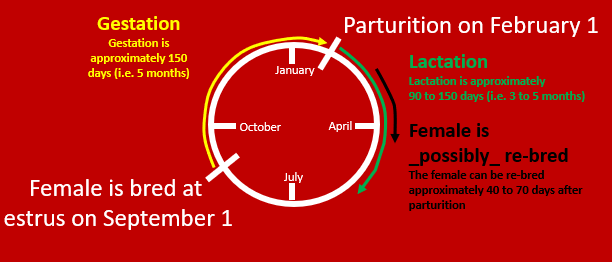
–It is possible for a ewe or a doe to reproduce twice in 365 day period?
•Yes, if the ewe or doe conceives early in the breeding season, she can lamb or kid during the mid to late part of the breeding season and be bred again at the end of the breeding season
–Example: ~150 days gestation + ~30 days until rebreeding = ~180 days (the breeding season is ~180 days long).
•Reproductive cycle for horses
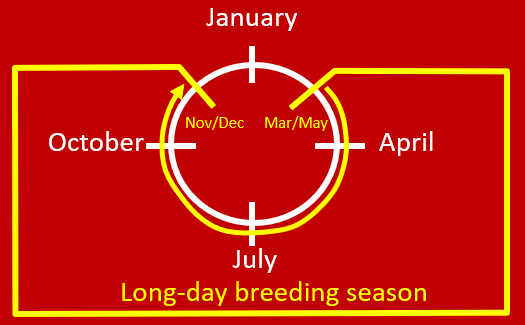
If producers wants a foal every year from mare, she will need to get bred during foal heat
–There are four basic procedures used to check for pregnancy in the different livestock species
1.Checking for estrus
2.Rectal palpation
3.Ultrasound machine
4.Pregnancy tests that determine the presence of pregnancy associated hormones or chemical compounds in the blood and/or urine.
What is considered the ‘easiest’ and lowest cost method?
checking for estrus (•i.e. heat) from day 18 to day 24 after insemination
When does female naturally show estrus if she did not get bred?
–show estrus again 18 to 24 days after insemination
What is rectal palpation?
•when the individual inserts their arm into the female’s rectum and palpates (i.e. examines by touch) the uterine horns of the reproductive tract to determine the presence of absence of a fetus
rectal palpation in cattle
»An experienced veterinarian can detect pregnancy by rectal palpation as early as 45 to 50 days following insemination
fectal palpation in horse
»It is highly recommended that a veterinarian perform rectal palpation for horses due to the risk of tearing the tissue of the rectal wall in horses
»An experienced veterinarian can detect pregnancy by rectal palpation as early as 20 to 60 days following insemination.
How does ultra sound machine work?
an ultrasound probe emitting sound waves_ that bounce off the uterine horns of the reproductive tract.
What are the two types of ultrasounds?
1.A-mode ultrasound (aka amplitude mode ultrasound)
2.B-mode ultrasound (aka Real-time ultrasound)
Which ultrasound is more reliable?
B-mode
Explain how A- mode ultrasound works?
»A-mode uses sound waves to detect the accumulation of fluids in the uterine horns
»If fluid is detected in the uterine horns, then the machine will make a long continuous beeping sound and likely the female is bred
»If fluid is not detected in the uterine horns, then the machine will make a series of short beeps and likely the female is not bred
»It is very easy to get a ‘false positive’ if the probe is incorrectly aimed at the bladder.
Explain how B- mode ultrasound works?
»B-mode ultrasound converts the sound waves that bounce off the uterine horns into a visual picture that is transmitted onto a computer screen
•Fluid-filled objects in the uterine horns, such as a early stage fetus, absorb many of the sound waves and echo few back
Fluid-filled objects are displayed as black on the screen
•Hard tissues absorb few sound waves and echo many back
Hard tissues are displayed as white on the screen
During the first 15 to 40 days after insemination, with B-mode ultrasound, what does technician look for?
looking for small dark_circles_ on the ultrasound screen
»These circles are the fluid surrounding the embryos that are located in the uterine horns
»The white tissue of the developing embryo can also (usually) be seen inside the small dark circles
Example of ultrasound image
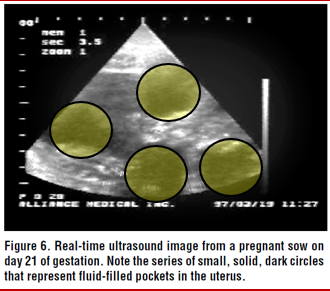
»Examples of ultrasound images in swine
»There are 4 embryos in this picture.
What are two different ways to ultrasound?
probe with ultrasound/rectal ultrasound by hand, or placing rear flank
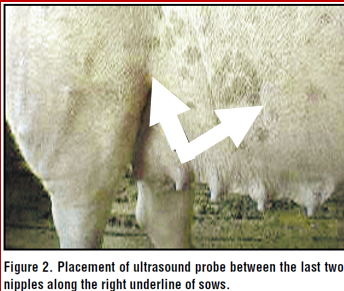
Where should ultrasound be placed for swine, goats, and sheep ?
•This picture shows where the probe should be placed between the last two nipples on the underline of the sow
•The probe should be aimed toward the opposite leg or the opposite shoulder to avoid the bladder
What do pregnancy tests do?
determine the presence of pregnancy associated hormones or chemical compounds in the blood and/or urine
Example of pregnancy test for cattle
PAG test = Pregnancy Associated Glycoproteins
How does a PAG test work?
–glycoproteins produced by binucleate giant cells
»Binucleate giant cells are cells from the fetal chorion that migrate from the fetal cotyledon into the maternal caruncle
»The Binucleate giant cells produce PAGs that are released into the blood of the dam
»One specific type of PAG is Pregnancy-specific protein B.
Example of pregnancy test for horses
eCG = Equine Chorionic Gonadotropin
How does a eCG test work?
–eCG is produced by the endometrial cups located all over the placenta
»The eCG can then be detected in the blood of the dam.
What are the two methods for synchronizing estrus in farm animal livestock?
natural and artificial estrus synchronization
Explain natural estrus synch in cattle
–Cows will naturally show estrous cycles and estrus 60 to 90 days after calving
Explain briefly natural estrus synch in cattle
Use hormones to artificially manipulate the female’s estrous cycle to synchronize estrus
What are the three main hormones are used to synchronize estrus?
GnRH, progestin, prostaglandin F 2 alpha
Purpose of GnRH
stimulates release of LH to cause ovulation
Purpose of progestin (synthetic progesterone)
is produced by the CL to promote gestation (i.e. progesterone) which means that estrus is suppressed after ovulation
Purpose of Prostaglandin F2α
removes the corpus luteum (CL) from the ovary, which allows the growth of a new follicle which stimulates estrus.
Give example of prostaglandin product and dosage?
lutalyse → 5ml
Give example of progestin product and dosage?
CIDR → 1/hd, intravaginally
Give example of GnRH product and dosage?
cystorelin → 2ml
What does CIDR stand for?
controlled internal drug release
What is a CIDR?
•have progestin coated on the rubber surface of the CIDR
What is the purpose of the CIDR?
progestin is slowly released from the CIDR into the vagina of the female usually over a 7 day period
How is the CIDR held into place when placed in vaginal vault?
wings of the CIDR are folded in and the blue applicator placed in the vaginal vault. The wings are released to hold CIDR in place in the vagina next to the cervix when the applicator is removed