Chemistry - macromolecules
1/150
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
151 Terms
3 types of disaccharides
Maltose
Lactose
Sucrose
3 types of polysaccharides
Starch
Cellulose
Glycogen
What does hydrophilic mean
interact with water around it
How are 2-amino acids obtained
protein hydrolysis
Another term for 2-amino acids
alpha-amino acids
What connects glucose molecules
1-4 glycosidic links
what does hydrophobic mean
does not like water
What connects two amino acids
peptide bons
What forms a peptide bond
a nitrogen, hydrogen, and oxygen molecule
Another term for peptide bond
amide bond
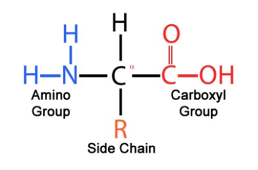
What does polarity of a amino acid depend on
side chain
What is condensation
elimination of smaller molecule when functional groups react - usually water or an alcohol
how do you know if a molecule is polar
if it contains bonds other than CH or has a E0 value greater than 0.4
Difference between addition and condensation in polymerisation
condensation emits a water molecule
Are CH bonds non polar or polar
non polar
If a molecule only has CH bonds, what polarity does it have
Non-polar
2 types of polymerisation
addition and condensation
What position of methyl group in a polymer is best for strength
isotactic as they can pack closer together
What is the difference between alpha and beta amino acids
alpha amino acid will have the amino group attached to the carbon adjacent to the carboxyl group. whereas a beta amino acid will have the amino group attached to the 3rd carbon
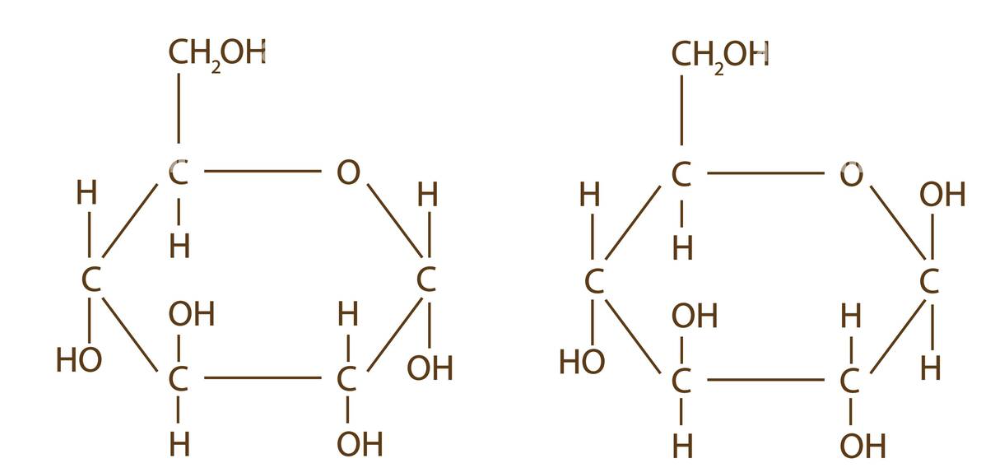
which amino acid is a beta amino acid
2
What is in all amino acids
alpha glucose
what differentiates all amino acids
their side chains
What is the primary structure
the order of amino acids to create the polypeptide chain
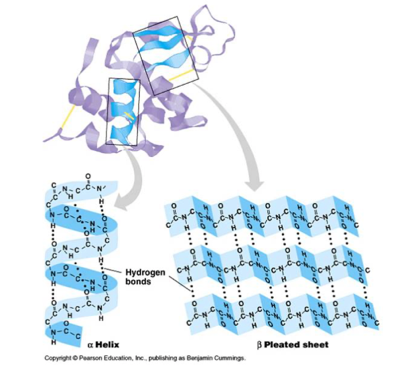
what is the secondary structure
folding of amino acids into either an alpha-helix or a beta-pleated sheet
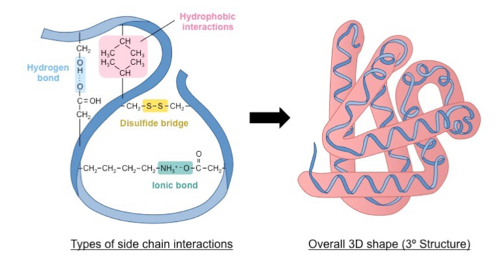
what is the tertiary structure
three dimensional interactions with secondary structures
what is the quaternary structure
several polypeptides combined
what structure is this
primary
what structure is this
secondary
what structure is this
tertiary
different types of reaction in a tertiary structure and where they exist
Hydrophobic interactions exist between non-polar R groups.
H-bonds exist between R groups or between an R group and water
Ionic bonds exist between a negatively charged R group and a positively charged R group.
Disulfide bridge (covalent bond) form between cysteine's R groups, which contain a S atom at the end of the chain.
What is a polyester composed of
dicarboxylic acid and a diol (di-alcohol)
what is a diol acid
di-alcohol, an alcohol with two functional groups (hydroxyl groups)
what is a dicarboxylic acid
a carboxylic acid with two carboxyls
what type of polymerisation occurs if a polymer is formed from an alkene
addition
how can addition polymers can be produced from their monomers
synthesis process initiated by a chemical catalyst which breaks the double bonds in monomers in order to link them together. this develops a long-chain macromolecule
types of polymers produced from addition polymerization
polyethene (LDPE and HDPE)
polypropene
polytetrafluorethene
how can condensation polymers be produced from their monomers
Condensation polymers are produced by two monomers reacting with each other to form bonds and create a polymer chain. water or alcohol is released.
examples of condesation polymers
polypeptides
polysaccharides
polyesters
what is the condensation reaction of 2-amino acids to form polypeptides
In a condensation reaction between two amino acids, the carboxyl group of one amino acid reacts with the amine nitrogen of another amino acid, forming a peptide bond and releasing a water molecule. This process is repeated to form polypeptides.
when are polypeptides formed
when amino acid monomers are joined by peptide bonds
what is the condensation reaction of monosaccharides to form disaccharides and polysaccharides
In the condensation reaction of monosaccharides, a hydroxyl group (-OH) from one monosaccharide combines with a hydrogen atom (-H) from another monosaccharide, forming a glycosidic bond. a water molecule is released
what bond is found between disaccharides or polysaccharides
glycosidic bond
when are polysaccharides formed
when many monosaccharides monomers are joined by glycosidic bonds
what do proteins, carbohydrates, lipids and synthetic polymers display
properties including strength, density and biodegradability
polymer vs. metal strength
Polymers are more resistant to chemicals that their metal counterparts. However, the strength to size ratio of polymers is less than metals meaning heavy structures cannot be made by polymers as the structural rigidity is low
density of polymers
composite materials that are up to 10 times lighter (less dense) than typical metals
Biodegradability of polymers
polymers are often not biodegradable and not recyclable
how is the primary structure created
Amino acids are linked in peptides and proteins by an amide bond between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another 2-amino acid
how is the secondary structure created
by hydrogen bonds between carbonyl groups and 2-amino groups of DIFFERENT amino acids along the stretches of polypeptide chain
how is the tertiary structure created
by the interactions of R groups (side chains) of amino acids in the different secondary structures present in polypeptide chains
how is the quaternary structure created
Larger proteins are made up of multiple polypeptide chains called ‘sub-units’
what are 2-amino acids (α-amino acids)
amino acides obtained from protein hydrolysis
what is an alpha-helix
hydrogen bonds between the oxygen atom of the carbonyl group from one acid and the hydrogen of the amino group which is four amino acids down the polypeptide chain
what is a beta-pleated sheet
Peptide chains lie side by side held together by hydrogen bonds. Hydrogen bonds form between the carbonyl oxygen of one b sheet and the amino hydrogen atom in the polypeptide chain of another b sheet. Wavy/pleated appearance
what do enzymes provide
an activation energy for the reaction which creates a faster rate of reaction, as more of the particles have the required energy to react
why are enzymes specific
only catalyse one reaction for one specific chemical called a “substrate”
how is an ezymes shape disrupted
mild changes of temperature and pH causing the protein to denature (unravel) back to a single chain with no folds
what do enzymes have that helps make products
an active site which binds the reactant molecules (substrate) and puts them in the correct orientation to react and make product
what is the empirical formula of monosaccharides
CH2O
What are the two functional groups in carbohyrdates
hydroxyl group and carbonyl group
what type of polymers are carbohydrates
polyhydroxyaldehydes or polyhydroxyketones
what are monosaccharides
simple sugars and are carbohydrates that cannot be hydrolysed to simpler compounds
how are monosaccharides classified
according to the number of carbon atoms present and according to whether the carbonyl group is present as an aldehyde or as a ketone
what are the two monosaccharides with three carbons
glyceraldehyde and dihydroxyacetone
how the chain numbered in an aldose
from the aldehyde carbon (c=0)
where is the carbonyl group located in a ketose
On the second carbon
difference between alpha and beta glucose
α-glucose has a vertical bond down to the hydroxyl (in the opposite direction of carbon 6 hydroxyl) and β-glucose has an upward diagonal bond to the hydroxyl (in a similar direction to the carbon 6 hydroxyl)
which type of glucose is more stable and why
β-glucose is more stable and less crowded than α-glucose and has a melting point approximately 5 degrees higher due to the hydroxyl position
how are disaccharides produced
a condensation reaction between two monosaccharides. A glycosidic link between the chiral carbon one of one monosaccharide and the hydroxyl group of another monosaccharide is created
what do polysaccharides contain
long chains of monosaccharides linked together though glycosidic bonds
what is starch and structural properties
A polymer of glucose found in plants. It is partially soluble in water and is edible
what are the two different types of polyglucose molecules that starch can be separated into
Amylose and Amylopectin
what does starch contain (type of glucose)
alpha-D-glucose, joined by alpha-1-4-glycosidic links
what is amylose
unbranched glucose polymer with α-1-4-glycosidic links
what is amylopectin
highly branched glucose polymer with α-1-4-glycosidic links and α-1-6-glycosidic links
why is starch soluble in water
has lots of polar hydroxyl groups and can hydrogen bond with water.
the loose packing due to the coils and branching allows solvent to hydrogen bond
what is cellulose
Unbranched polysaccharide (linear chains)
what does cellulose contain
β-D-glucose units are linked together by β-1-4-glycosidic links
why does cellulose’s structure give a higher melting point
Extreme linearity of chain allows hydrogen bonding between hydroxyl groups of adjacent molecule chains
what does high h-bonding in cellulose mean
means there is a high mechanical/tensile strength in its fibres
why is cellulose not soluble
the very close packing of the chain’s limits water’s ability to access and bond with hydroxyl groups
can cellulose be digested by humans
no, because our enzymes do not have the specific active site for β-glucose hydrolysis. Its rigid structure makes it suitable as a structural carbohydrate in trees and the cell wall in plants
another term for triglycerides
lipids
what are lipids
esters made from three carboxylic acids (fatty acids) and glycerol (propan-1,2,3-triol)
another term for the 3 carboxylic acids in lipids
fatty acids
what are triglycerides classified as
fats and oils
structural properties of fats
solids at room temperature, common in animals, high percentage of saturated fatty acids
structural properties of oils
liquids at room temperature, common in plants, contains a high percentage of unsaturated fatty acids
what does the term ‘saturated’ infer about a fatty acid
there are single bonds only
what does the term ‘unsaturated’ infer about a fatty acid
there is 1 or more double bond
two types of unsaturated fatty acids
cis and trans
why do trans fatty acids have high boiling points than cis
trans fatty acids have a straight chain and therefore can pack closer together than cis fatty acids can. this increases the IMF between molecules
what does ‘cis’ refer to in fatty acids
‘H’s are on the same side of double bond
what does ‘cis’ refer to in fatty acids
‘H’s are on the opposite sides of double bond
difference in structure between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids
saturated fatty acids have single bonds only whereas unsaturated fatty acids have 1 or more double bond
what is saponification
the organic reaction between an acidic ester and a strong base to produce a fatty acid salt
another term for saponification
base hydrolysis
what does amphipathic mean
having both hydrophobic – does not dissolve in water, and hydrophilic – dissolves in water, parts
chemical property of soap
amphipathic
what are the cleaning action of soap
Soap dissolves in water because the polar hydrophilic head is attracted to the polar water
Non-polar hydrophobic tail of the soap is not attracted to the water and tries to dissolve in the “like” non-polar substance which is the grease on the clothing.
Agitation (head attaches to water which creates a pull force towards the water) lifts the grease from the surface.
Cleaning action continues.
Completion – small bits of grease float in the water completely surrounded by the embedded soap molecules forming “micelles” with grease trapped in the middle.