PSY 150 - Biopsychology
1/106
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
Where is the adrenal gland located?
On top of kidneys
What kinds of hormones does the adrenal gland secrete?
Stress response hormones(epinephrine/adrenaline, norepinephrine/noradrenaline)
What system is the adrenal gland a part of?
Endocrine System
What is the all or none phenomenon?
A nerve or muscle cell will respond with maximum energy to incoming neuron signal if it reaches threshold of excitation, or it will not respond at all
Allele
Specific version of a gene
What are the three most significant parts of the limbic system?
Hippocampus, Amygdala, Hypothalamus
Primary function of amygdala
experience of emotion, attaching emotional meaning to memories
Where is the auditory cortex located?
Temporal lobe
What is the peripheral nervous system?
Bundles of axons/nerves linking central nervous system to rest of body
Parts of the Peripheral nervous system
Somatic and Autonomic nervous systems
Function of the Autonomic nervous system
Controls our inner organs and glands. Out of control.
Parts of the Autonomic nervous system
Sympathetic and Parasympathetic nervous systems
Function of Sympathetic nervous system
Preparing the body for stress. Fight or flight response.
Function of parasympathetic nervous system
Day to day operations, maintaining homeostasis. Calming body down after fight or flight response.
Parts of Somatic nervous system
Motor and Sensory neurons
Function of Somatic nervous system
Conscious and voluntary activities, relaying information to and from central nervous system.
Function of motor neurons
Carrying instructions from central nervous system to muscles. Efferent.
What does efferent mean?
“away from”
What does afferent mean?
“moving towards”
Function of sensory neurons
Carry sensory information to central nervous system. Afferent
Axon
Major extension off soma
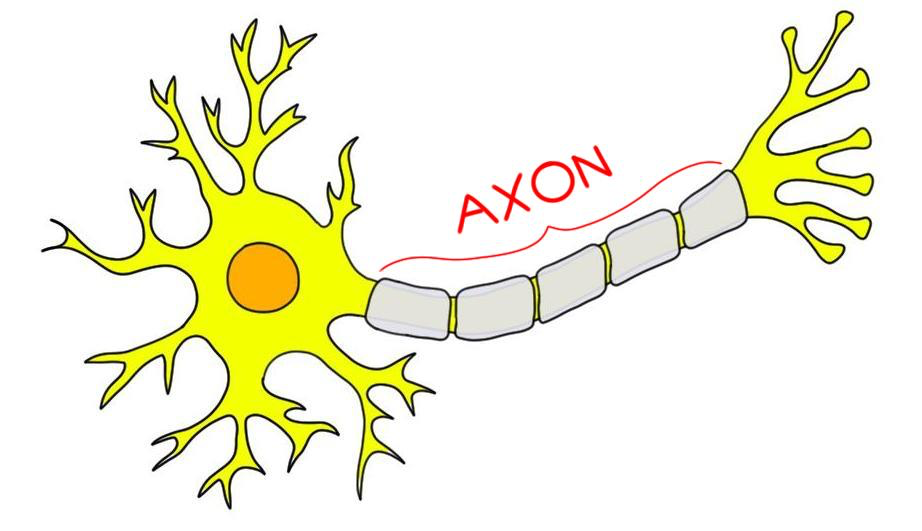
Where does the axon of a neuron end?
At the terminal buttons
What is the biological perspective?
Theory that mental disorders are caused by neurotransmitter imbalances
Function of Brocas area
Essential to language
Where is Brocas area located?
In the left hemisphere
What is the central nervous system?
The brain and spinal cord
Structures in the hindbrain
Medulla, Pons, Cerebellum
Function of the Cerebellum
Balance and coordination, procedural memory(learning task performance)
What is the cerebral cortex?
Surface of the brain, highest mental capabilities
What is a chromosome?
Long strand of genetic information
Computerized Tomography Scan(CT)
Computer takes multiple x rays of a given area, coordinating and integrating. Brain structure.
Corpus callousum
Thick band of neural fibers connecting brains hemispheres
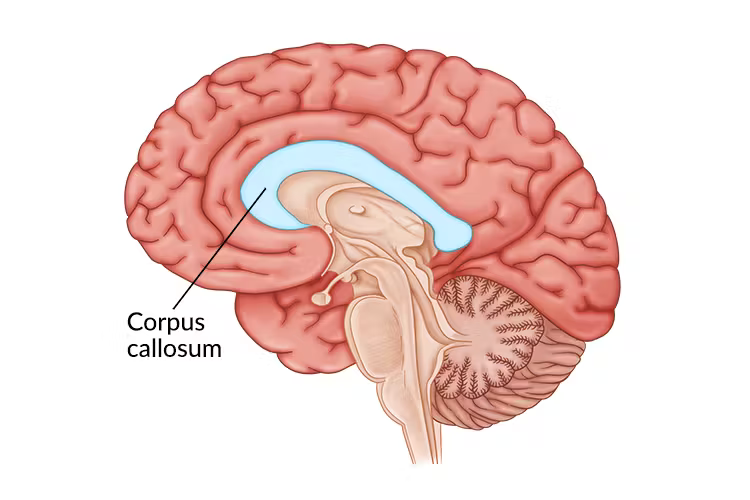
Why is the corpus callousum severed?
Prevent the spread of seizures
What is split brain?
Severance of corpus callousum. Unable to name picture shown to left side of brain(information stored in right side)
Dendrite
Extension of soma, recieves incoming signals from other neurons
Soma
Nucleus of neurons. Information processor.
Semipermeable Membrane
Allows smaller/less charge molecules to pass, blocking bigger/higher charge ones
Types of cells in the nervous system
Glial cells and neurons
Glial cells
Support neurons, scaffold on which nervous system is built.
Myelin Sheath
Fatty substance. Insulator increasing signal travel speed across cell. Not continuous(leapfrog)
How is the Myelin Sheath formed?
Glial cell activity
What is the shape of DNA?
Helix
What is DNA made of?
Nucleotide base pairs
What causes diabetes?
Insufficient insulin production
Role of Insulin
Lower blood sugar
Role of glucagon
Increase blood sugar
Role of Pancreas
Secrete blood sugar regulation hormones
What system is the pancreas a part of?
Endocrine system
Electroencephalography(EEG)
Monitoring of electrical activity in brain, brainwaves(electrodes placed on head). Sleep disorders
Positron Emission Tomography(PET)
Individual drinks radioactive tracer. Amount of tracer in different brain regions monitored. Often replaced by fMRI.
What is the Forebrain?
Largest part of the brain
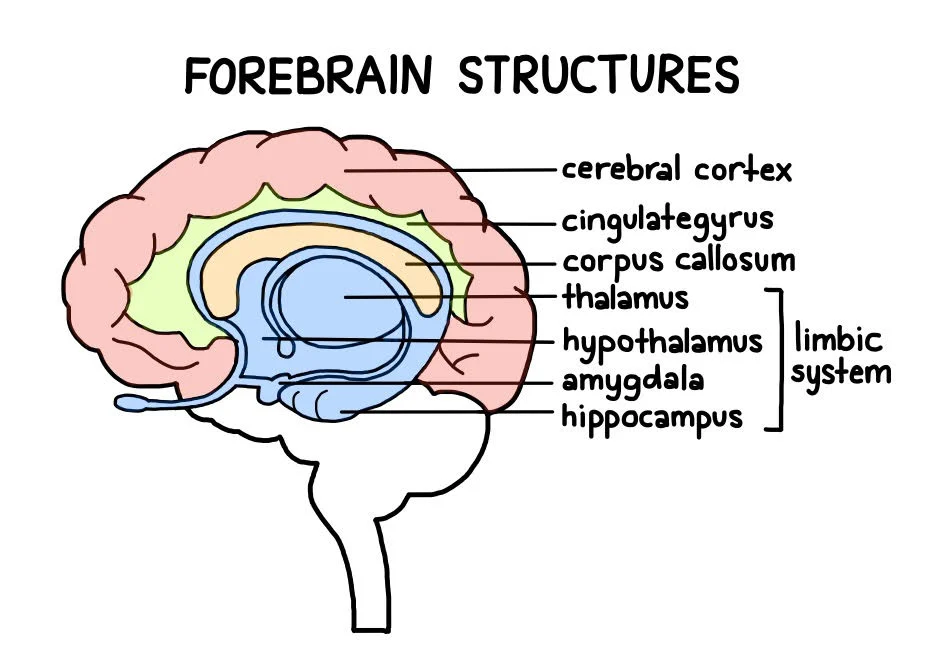
Structures of the forebrain
Cerebral cortex, thalamus, limbic system, etc
Lobes of the cerebral cortex
Frontal, Temporal, Occipital, Parietal
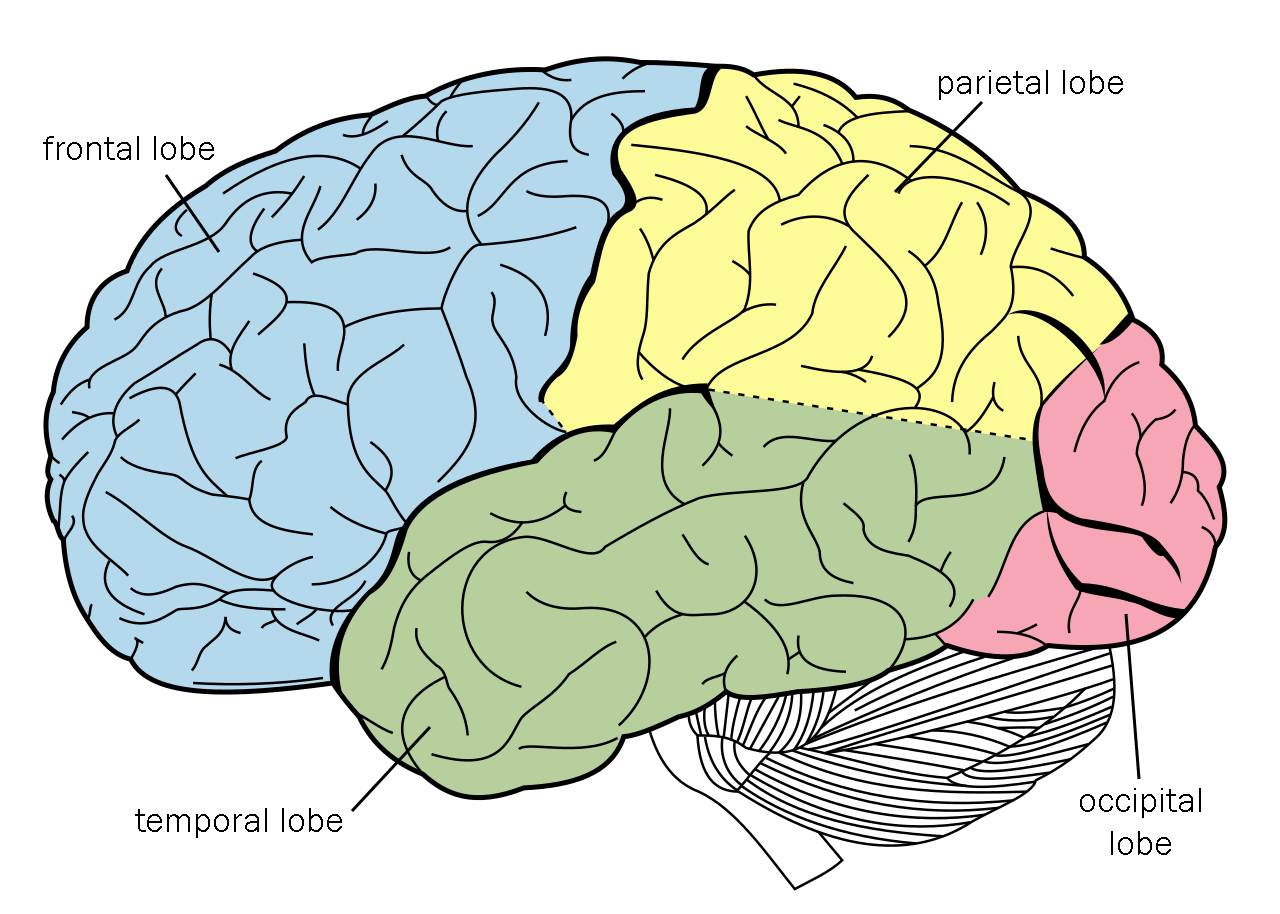
Frontal lobe role
Reasoning, motor control, emotion, language
Parts of the Frontal lobe
Brocas Area, Motor cortex, prefrontal cortex
Role of the Prefrontal cortex
Higher level cognition
Role of Motor cortex
Planning/coordinating movement
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging(fMRI)
MRI showing metabolic changes in brain.
Gene
Sequence of DNA
Genetic Environmental Correlation
View that genes affect our environment, environment influences makeup of our genes
Epigenetics
Study of how same genotype can be expressed in different ways
Parts of the Temporal Lobe
Auditory Cortex, Wernickes Area, Limbic system
Function of Wernickes Area
Speech comprehension(not understanding, only speaking)
Function of hippocampus
Learning and memory
Function of Hypothalamus
Sexual motivation and homeostatic processes. Interface between nervous and endocrine systems.
Lateralization
Concept that each brain structure is associated with a special function
Longitudinal Fissure
Deep groove in brains cortex. Most prominent sulcus
Function of Medulla
Automated processes. Breathing, blood pressure, heart rate.
Membrane Potential
Difference in charge across the neuronal membrane. Provides energy for the signal
Resting Potential
Between signals. Membrane potential is at readiness.(like a rubber band, ions line up ready to rush across)
Structures of the midbrain
Reticular Formation, Substantia Nigra, Vental Tegmental area
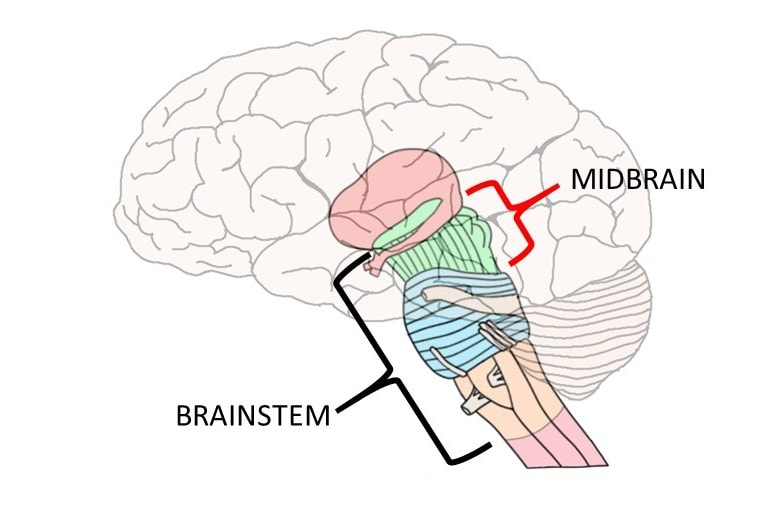
Function of the Reticular Formation
Sleep and wake cycle, arousal, alertness and motor skills
Function of the Substantia Nigra
Dopamine production, mood, reward, addiction
Function of the Vental Tegmental Area
Reward and motivation
Location of the Reticular Formation
Centered in midbrain, extends into fore and hind brain
Where is the Motor Cortex located?
Frontal lobe
Motor Cortex
Strip of cortex, planning and coordination of movement
Nodes of Ranvier
Gaps in the Myelin Sheath
Where is the Occipital lobe located?
Cerebral cortex, very back of brain
Most important part of Occipital lobe
Primary visual cortex(Brodmann area 17)
Where is the Parietal Lobe located?
Right behind the frontal lobe
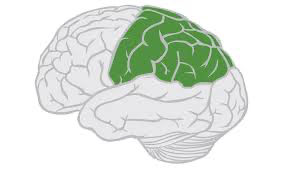
Function of the Parietal Lobe
Processing sensory information
Most important structure of Parietal lobe
Somatosensory Cortex
Function of Somatosensory Cortex
Processing sensory information(touch, temperature, etc)
Location of Pituitary Gland
Right below hypothalamus at brain base
What is the “master gland” of the endocrine system?
Pituitary gland
Function of the Pituitary Gland
Carry out messages from hypothalamus to body, secrete growth hormone, fluid regulation and endorphins(pain relief)
Polygenic
Multiple genes affecting a trait
Function of Pons
Regulation of brain activity during sleep, connects brain and spinal cord
What disease is degeneration of Midbrain structures most commonly linked to?
Parkinsons disease
Psychotropic Medication
Treats disorders by regulating neurotransmitter balance
Range of Reaction(theory)
Genes set the boundaries in which we can operate, and environment interacts with genes to determine where in that range we will fall
Receptor
Protein on the cell surface where neurotransmitters attach
Reuptake
Neurotransmitter pumped back into neuron that released it
Sulcus(plural = Sulci)
Depressions or grooves in cerebral cortex
Gyrus(plural = Gyri)
Folds/bumps on cerebral cortex
Synaptic Cleft
Small gap between two neurons where communication happens(receptors and neurotransmitter binding)
Synaptic Vesicle
Storage site for neurotransmitters
Function of Temporal Lobe
Hearing, memory, emotion and some language
Terminal Button
Axon terminal containing Synaptic Vesicles