Lecture 5: Population Ecology
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
what is ecology?
the study of the relationship of organisms to their environment and to other organisms
ecology helps us understand why species…. (5)
live in certain places
eat certain food
interact with other organisms in a specific way
allows us to understand how human activities can harm populations
gives us information on how we can preserve animals and their habitat
what is a population?
a group of interbreeding individuals of the same species in the same location
each individual subpopulation of a population is called a…..
deme
what is a metapopulation?
a group of 2+, spatially separated populations of the same species, which are connected to one another by movement of individuals between them
what is population ecology? what kind of info can it provide?
how populations interact with each other and the environment. can provide info about the processes that affect population size and distribution, which can help maintain and protect populations
how is the geographic range of a population determined?
by what suitable habitats are available
what is dispersion? what are the 3 kinds? what does it reflect?
the spacing of individuals with respect to one another. clumped, uniform, and random. reflects habitat and social interaction

what is uniform dispersion?
usually arises from social interactions between individuals. may result from territoriality during nesting or competition for space and light

what is random dispersion?
can result from dispersal of seeds through wind or birds

what is clumped dispersion?
most common in nature and can be found when populations are clustering around a resource such as food, social family structures, and aggregations such as schools of fish and herds for mutual defense and protections
what is population size (N)? can scientists get a perfect count?
the total number of individuals in a population. no, so they will sample a portion of the population and then estimate the size of the larger population
what are 2 forms of population estimation?
quadrat samping and mark-recapture method
what is quadrat sampling? what is it best for?
use a meter long square to sample different areas and count the number of species in the square and do this many times in an area. best for immobile or slow-moving species
what is the mark-recpature method? what is it best for?
capture an organism, mark them, and sample again, where you will probably find marked and unmarked organisms. find ratio of marked to unmarked individuals to estimate population size. best for organisms that move around
what is the effective population size (Ne)? what is it affected by?
the number of individuals in a population that are actually contributing to the next generation's gene pool
number of breeding individuals
sex ratio
differences in number of offspring
inbreeding
when is the effective population size the greatest?
when there is an equal ratio between male and female organisms
as effective population increases, so does ______
genetic diversity
what are the 3 graphs that model population size change?
exponential growth (j-shaped curve), logistic growth (s-shape), and a realistic growth
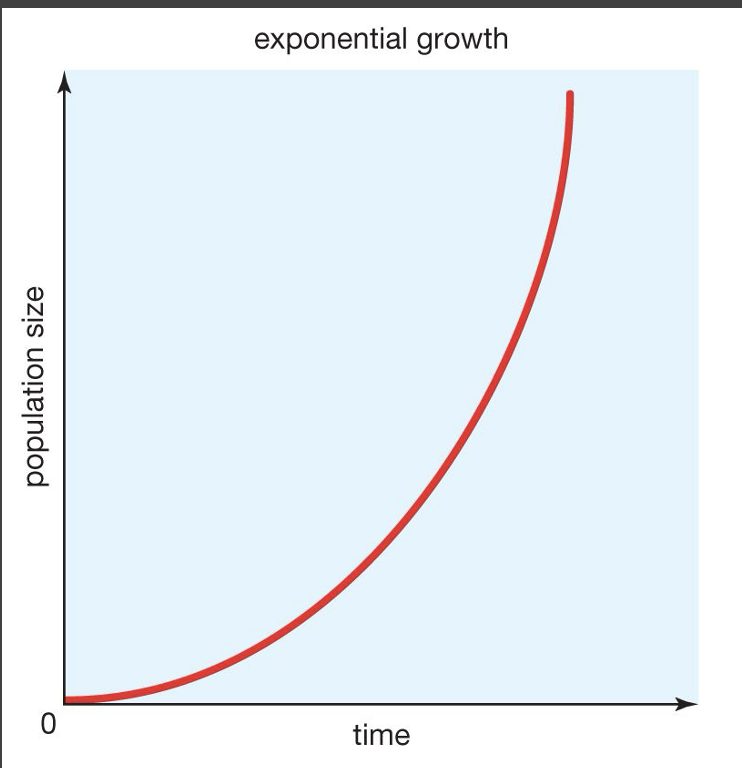
is the exponential growth curve (j-shaped) realistic?
currently, humans are experiencing this kind of growth, but it is extremely uncommon in nature, and we will not be able to sustain it forever because resources are not unlimited
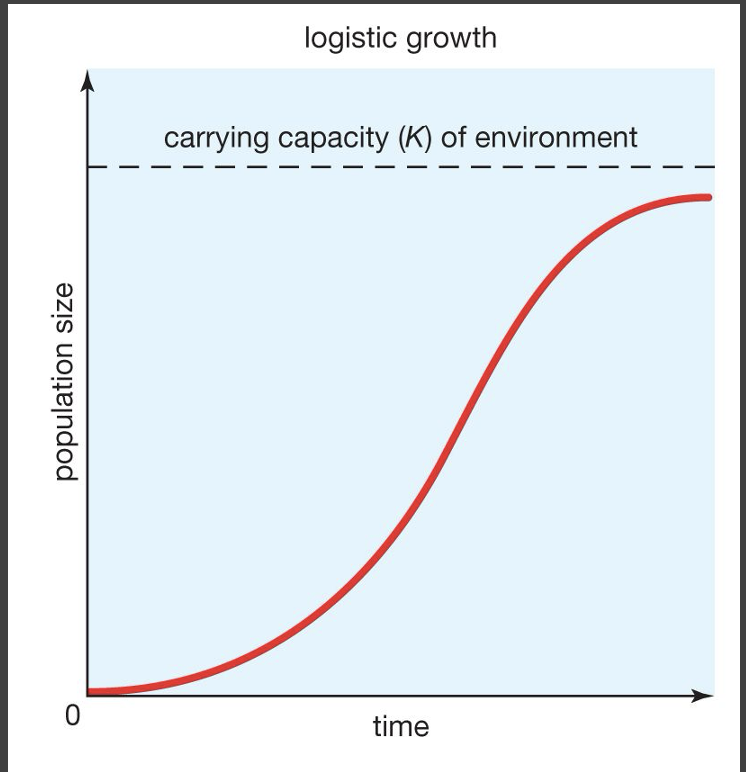
explain the logistic growth curve (s-shaped)
a more realitic growth curve, since resources (food, mates, water, space) in nature are limited
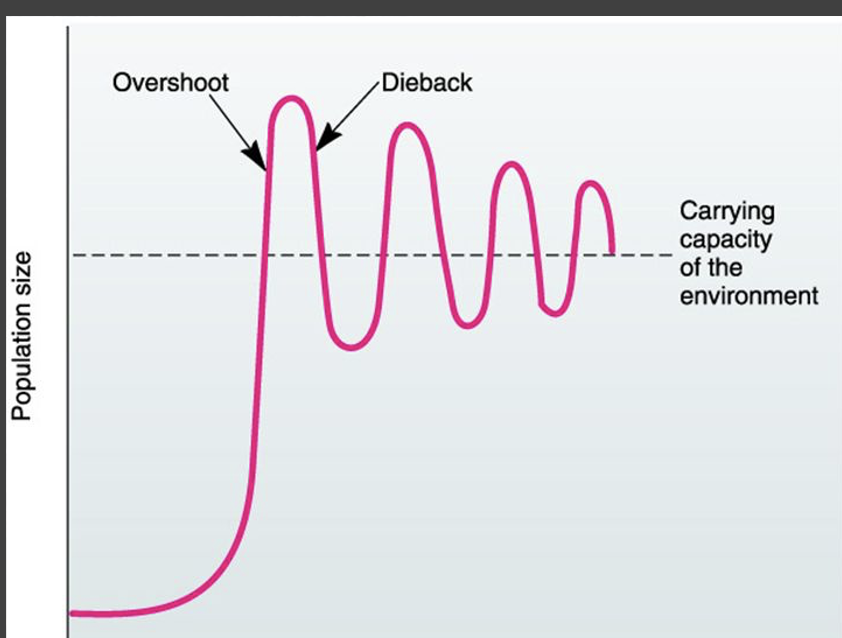
explain the most realistic growth curve
populations may exceed the carrying capacity when resources are good, and eventually are not able to sustain it because resources become limited, leading to more deaths than births. as resources recover, the population increases, and the population continues to oscillate around the carrying capacity
what are the 2 main factors that regulate population growth and density?
density-dependent factors (biotic) - eg. disease
density-independent factors (abiotic) - eg. natural disaster
what are density dependent factors? name 3 of them
environmental factors that affect the population more the larger the population gets
competition for resources
predation
disease
what are density-independent factors? name 3 of them
environmental factors that affect the population growth rate regardless of the size of the population
weather
natural disasters
pollution