AP Chem Unit 2: Compound Structure and Properties🧪
2.1: Types of Chemical Bonds🔗
electronegativity: measure of an atom(or a group of atoms) to attract shared electrons
Fluorine is the most electronegative element
partial charges: created in a polar covalent bond when one atom is more electronegative than another
region with high electron density will have a partial negative charge while a region with low density will have a partial positive charge
higher electronegativity=partial negative
lower electronegativity=partial positive
covalent | covalent | ionic | |
nonpolar | polar | ionic | |
sharing of electrons | equal | unequal | transferred |
visual of electron sharing | A—:—B | A —:-B | A :B |
bond dipole moment | no | partial | positive & negative |
electronegativity diff. | <0.5 almost no difference, electrons shared equally | 0.5-1.7 slight difference, electrons shared unequally | >1.7 large difference, electrons transferred |
Ionic bonds:
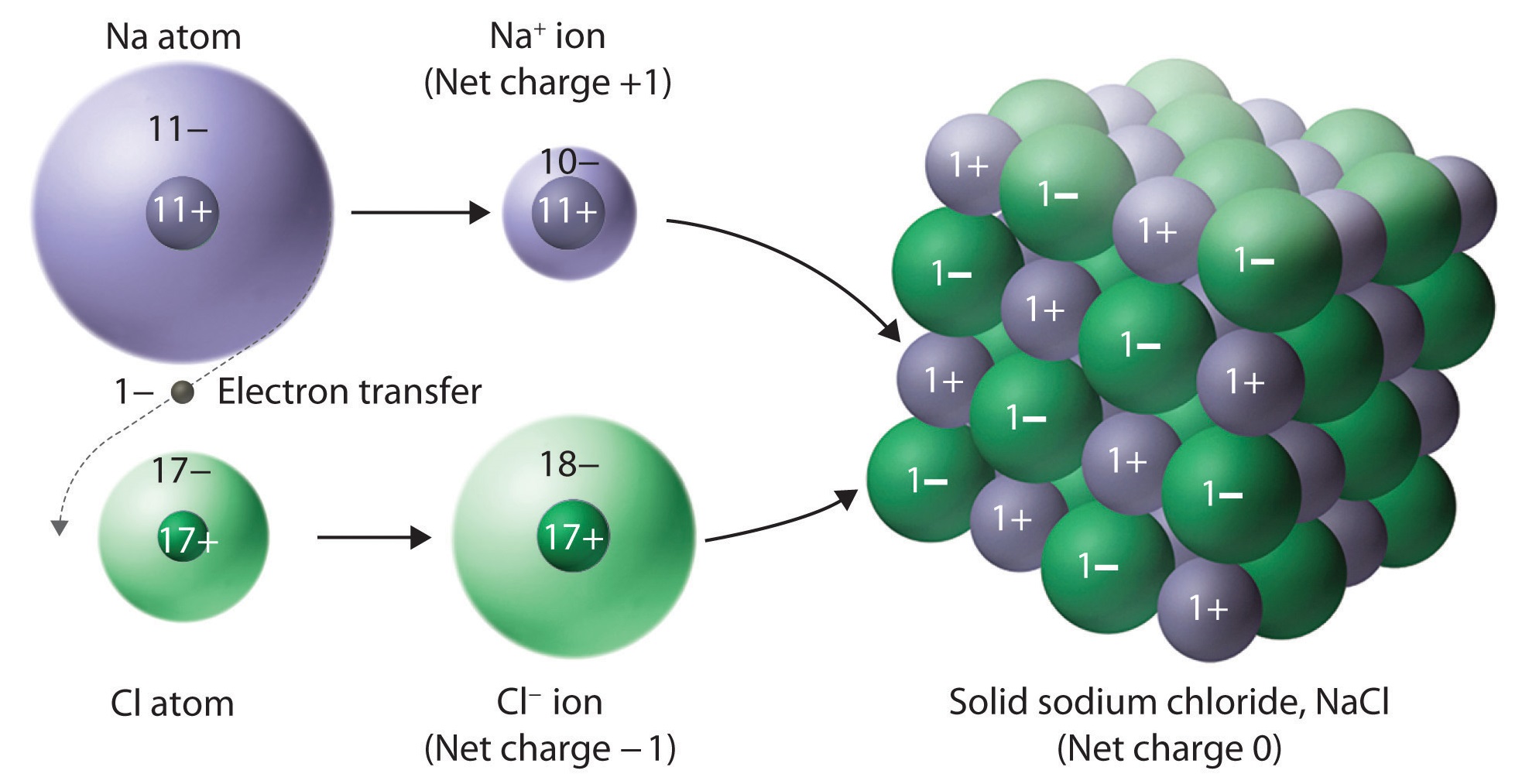
Ionic interactions occur between metal and nonmetal atoms when they lose or gain electrons to form ions
coulombic or electrostatic attraction🧲
Stronger when the charges are larger and the ions are smaller
Properties:
forms crystals🔮
high melting/boiling points
hard & brittle
conducts electricity when dissolved
good insulators as a solid

Metallic bonds:
Occurs between metal atoms🪙
Due to multiple metallic cations being attracted to a delocalized sea of valence electrons
IMF is stronger💪 when there are smaller metallic cations and more valence electrons
Properties:
shiny✨
malleable & ductile
conducts heat🔥 & electricity
metallic oxides are basic and ionic
lose electrons to form cations
Covalent bonds:
Electrons are shared between two or more atoms(typically nonmetals)
Properties:
non-lustrous, various colors
brittle, hard or soft
poor conductors
nonmetallic oxides are acidic and covalent
form anions by gaining electrons
Polar covalent bond🐻❄:
when atoms are shared unequally in a covalent bond

Nonpolar covalent bond🚫🐻❄:
when atoms are shared equally in a covalent bond

2.2: Intramolecular Force & Potential Energy🔋
Covalent bonds:
Can be single, double, triple(or an average if there are resonance structures)
Occur at the lowest energy state
Happens when the attraction between the nuclei is greatest for the shared electrons and repulsions between electrons and nuclei is the least
If atoms are too close the nuclei will repel, if atoms are too far apart the attraction is not enough to hold them together
Bond enthalpy: the energy required to break a bond, or the energy released when a bond is formed
larger radii increases the bond length
longer bond length decreases the bond energy
more electrons & shorter bond length = greater coulombic attraction
Lattice energy: the energy to separate ions in ionic compounds
larger charges = higher lattice energy
bigger radii = smaller lattice energy
increasing the bond order = increasing the bond energy
2.3: Structure of Ionic Solids🪨
Ionic solids:
Consist of cations and anions
molecules are held together by coulombic forces
higher ion charges = stronger bonds
larger atoms = weaker bonds
properties:
nonvolatile & high melting points
ionic bonds need to be broken to melt the solid, which separates oppositely charged particles
do not conduct electricity🚫⚡
charged ions are fixed in place
when melted or dissolved, ions are free to move, which enables electrical conduction⚡
many are soluble in polar solvents and insoluble in nonpolar
2.4: Structure of Metals & Alloys🪙
Metals:
composed of cations that are embedded in delocalized sea of valence electrons
electrons do not stay with one atom, move throughout the entire substance
cations and electrons are attracted through coulombic attraction
# of valence electrons determines amount of electrons in the delocalized sea of electrons
increased charge & increased # of electrons = greater attractions
decreased ionic radius = increased attractions
Alloys:
Mixtures of metals🪙
interstitial alloys: small atoms added to the metal
that fit in between the metal atoms(often H,B,C,N)
substitutional alloys: atoms added to the metal have smaller radii so they replace atoms in the lattice

2.5: Lewis Diagrams📊
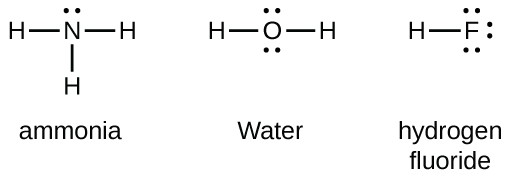
lewis structures:
Covalent bonds are formed between atoms sharing electrons
lewis structures are a simple way of representing covalent bonds
2.6: Formal Charge & Resonance⚡︎
formal charge: method that helps determine what resonance structure is the most valid
sum of lone electrons & bonds connected to the atom - valence electrons
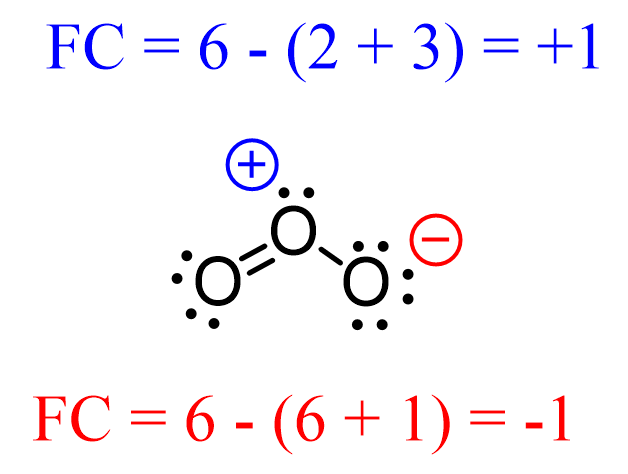
2.7: VSEPR Theory & Bond Hybridization💡
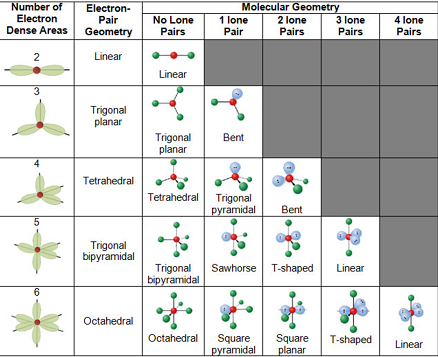
VSEPR theory: predicts the geometrics of molecules and polyatomic ions
the shape, or geometry, of a molecule is determined by lone pairs or bonds on the central atom of a molecule
electron-electron repulsions are minimized by positioning themselves as far apart as possible
lone pairs tend to repel more than bonds
Bond hybridization:
to explain molecular geometries, we assume that the atomic orbitals on an atom mix to form hybrid orbitals
the shape of a hybrid orbital is a mix of the shapes of the original atomic orbitals such as s(spherical) and p(dumbbell)
the total # of atomic orbitals on an atom remains constant, so the # of hybrid orbitals on an atom equals the # of atomic orbitals that are mixed
in CH4, the 2s and 3 2p orbitals of carbon mix to form 4 sp3 hybrid orbitals
Sigma and Pi bonds:
Sigma bonds(σ) are always the first bond between two atoms - a single bond
Pi bonds(π) are second and third bonds resulting from the overlap of p orbitals🥧
single bond | 1 sigma bond |
double bond | 1 sigma, 1 pi bond |
triple bond | 1 sigma, 2 pi bonds |