American Pageant Chapter 16 APUSH Review
Slavery in America
- Bacon' s Rebellion in Virginia (1676) leads to shift from indentured servants to black slavery.
- 1780s: Slavery issue of debate at the Constitutional Convention
- 3/5th Compromise
- Slave Trade ends in 1808
- Fugitive Slave Act
- Following the American Revolution slavery slowly ends in Northern and middle states.
- Slavery band in northwest territory with northwest ordinance 1787.
- The north and South were able to postpone a major sectional crisis with the Missouri compromise in 1820.
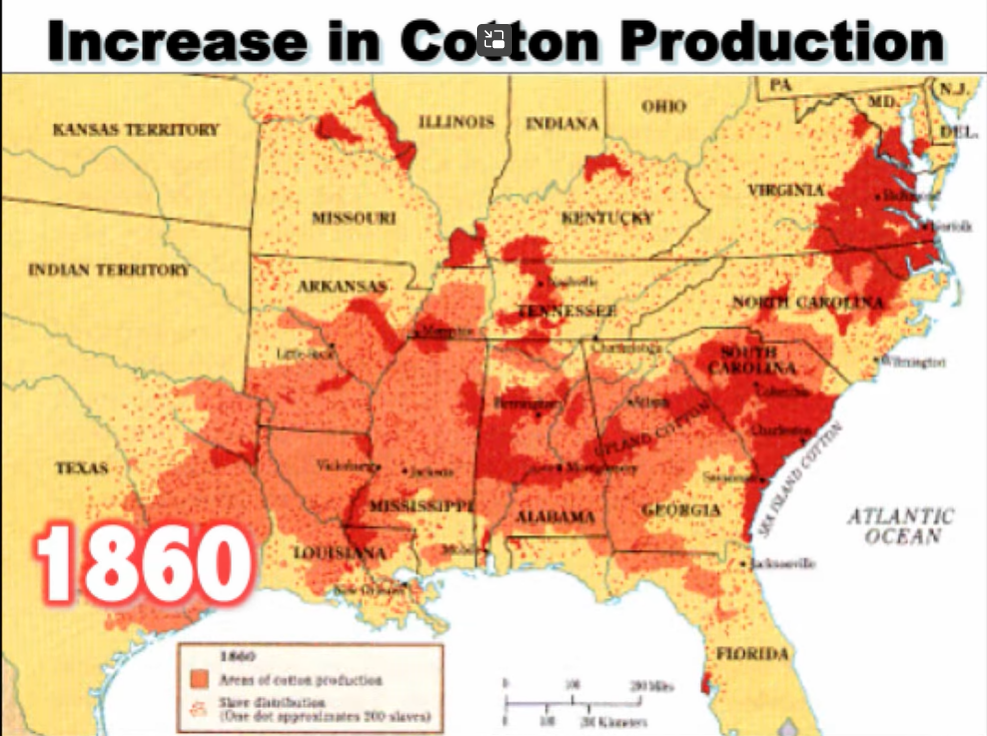
King Cotton
- Southern economy reliant on cash crops such as tobacco, rice, and cotton
- Eli Whitey cotton gin makes the cash crop economy profitable.
- Demand for land for cotton production leads to huge increase in demand for slave labor
- Market Revolution: northern industry demand for southern cotton
- Prosperity of North, South, and England built on backs of slaves
Increase in Cotton Production

Expansion of Slavery
Western expansion and the issue of slavery will cause an increase in sectional conflict.
Missouri compromise of 1820.
Compromise of 1850.
Kansas Nebraska Act 1854.

Antebellum South:
- Primarily agrarian society: "King Cotton"
- Lack of industrialization
- $$$ invested in slave labor
- 25% of population owned slaves
- Majority of southerners were not slave owners
- Southern whites support and defend institution of slavery
- Hopeful they will one day own slaves
- Racism: Felt higher than slaves in southern society
- Southern politics was in many ways a oligarchy
- Government by the few wealthy
- Plantation owners
- Southern large slave holders control southern politics
- Southern plantation owners 2) Small slaveholders 3) Yeoman farmers 4) people of the pine barrens
- Contrast with the north
- Lack of immigration to the south
African American Communities
- African American population in the North
- About 250,000
- Tensions with Irish immigrants
- Competition over low skilled jobs
- Free black population in the South
- About 250,000
- Many restrictions on daily life
- Especially after Nat Turner's rebellion in 1831
Slavery
Chattel slavery
- Slaves were treated as property
- “Uncle Tom's Cabin": brought the issue of families being broken up to a mass audience
By the eve of the civil war most slaves were in the deep south
Slaves were not afforded any social, political, or civil rights
- Illegal to learn to read or write
African American culture emerged as a blending of African and American cultural influences
- African American religion (especially after 2nd GA)
- Black Christianity [Baptists & Methodists]:
- African practice of responsorial style of preaching.
- Drawing on West African traditions
- Importance of music in black culture. [esp. spirituals].
Resistance to Slavery
- Forms of Resistance
- Work slowdowns
- Negligence
- Break equipment
- Run away: Underground Railroad
- Slave Revolt
- Slave revolts were not common
- Stono Rebellion (1739): South Carolina slaves runaway to Florida
- Denmark Vesey (1822): massive revolt planned in South Carolina
- Nat Turner (1831): Revolt in Virginia killed 60 people
- Southerns react
- Harsher laws: “Black Codes”
- Slave Patrols
Abolitionist Movement
- Quakers were earliest opponent slavery
- American Colonization Society: transport freed slaves back to Africa (1822 Monrovia, Liberia)
- David Walker- "Appeal to thee Colored Citizens of World" (1829 called for violent uprising
- William LIoyd Garrison (1833) American Anti-Slavery Society called for immediate uncompensated emancipation. - Published "The Liberator"
- Sojourner Truth & Frederick Douglas: former slaves who advocated for abolitionism.
- Liberty Party (1840)
Southern Reaction: Defense of Slavery
- Gag Resolution in Congress (1836-1844)
- Ban on anti-slavery petitions being discussed in Congress
- Repealed by John Quincy Adam in 1844
- Bans on teaching slaves to read or write
- Southern states adopt strict slave codes
- Nat Turner revolt
- Anti-slavery messages banned from Southern mail
- Pro-slavery argument by George Fitzhugh
- Slaves as family
- Better than "wage slavery"
- civilized inferior people