Criterion A biology
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
diffusion
The net movement of particles within a fluid from a high concentration of particles to a lower concentration of particles(down a concentration gradient) as a result of their random movement until an equilibrium is reached. How: all molecules have energy(KE) which causes them to bounce off of each other and transfer the energy.
SA
the larger the SA the higher the rate of diffusion because it gives the particles more oppertunity to diffuse in and out of cell at any given point in time.
temperature
higher temperature gives the particles more energy making them move around faster so they diffuse more quickly since they can push harder and push the solute faster around.
concentration-osmosis
the amount of H2O as compared to other solute molecules that are dissolved in the water.
Concentration gradient
The difference in concentration between two places affects the rate because the greater the difference of concentration gradient the more molecules and the faster the molecules diffuse across the membrane because there is greater need for them to do so.
Molecular mass
the larger the molecule and the greater its molecular weight the slower the rate of diffusion since they move more slowly(and the water molecules can’t push them as easily)
diffusion distance
if the diffusion distance is small, diffusion happens faster because the particles do not have as far to travel-also why cells can’t be enormous because otherwise diffusion doesn’t happen in time.
permeability of membrane
Affects efficiency of diffusion processes within cells. When a membrane has high permeability, it means that it allows a greater number of molecules to pass through it at a faster rate. This is because the molecules encounter less resistance and can move freely across the membrane that has more “holes” in it so more molecules can move in and out at once.
When equilibrium is reached…
it only means the particles ar evenly spaced out, they still conctinue randomly moving since they all have KE energy. 0
difusion is a …
Passive process- doesn’t require any energy from the cell, instead its just the random movement of the molecules that results in diffusion(all cells do this for free)
dissolving vs diffusion
Diffusion refers to the “net movement” of particles moving from and are of high coencentration to low concentration whilst dissolving is when solvent forces apart the solute molecules, mixing and forming a solution.
osmosis
The diffusion of water through a semi-permeable membrane. Water moevs from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration, and tries to balance out the number of water molecule sper solute particle.(SOLUTE CANNOT MOVE ACROSS MEMBRANE IN THIS CASE)
solution
the products formed by a solute dissolving into a solvent.
solvent
the substance that the solute dissolves into
solute
the substance dissolving into the solvent
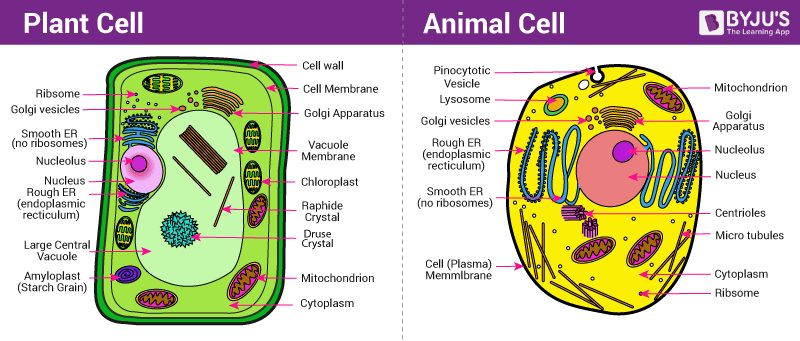
Animal cell- size and contents
nucleus
mitochondria
ribosomes
cytoplasm
cell membrane
endoplasmic reticulum
Golgi apparatus
lysosomes
40 micrometers
Plant cell- size and contents
nucleus
mitochondria
cytoplasm
cell membrane
ribosomes
Golgi apparatus
endoplasmic reticulum
chloroplasts
permanent vacuole
cell wall
Hypertonic
Higher concentration of solute compared to the other side. As the water molecules get attached (bond) to the larger molecules in the solution the number of free water molecules decreases. If a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution it will shrivel and shrink(in plant cells its inside shrinks away from the cell wall).
Net movement of water out of cell.
Hypotonic
Lower concentration of solute compared to other side. Makes cells turgid(swollen) if placed in a hypotonic solution.
Net movement of water into cell.
Isotonic
Molecules will move in and out of cell with random KE but at the same rate so the cell stays the same size, for plant cells gives a flaccid(droopy) look. Net movement of water=0
plasmolysis
cell contraction as the water moves out fo the sell making it shrivel (material away from cell wall).
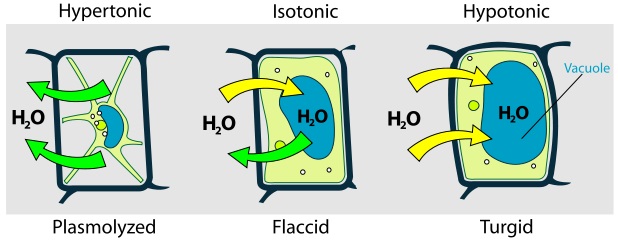
Cytolisis
the bursting of a cell as it grows in size after a lot of water diffuses into it by osmosis.
cell membrane- function and where found-size
Lines the shape of the cell, and controls what goes in and out of the cell and how much of a given substance can come in. Selective by size and charge of particles. It’s made of phospholipids. Thickness: 5-10nm
nucleus- function and where found
Controls the activities of a cell, because it stores the genetic material(DNA) of the cell in the form of chromosomes. Contains Nucleolus(compact/denser). Diameter: 5 to 20 μm
mitochondria- function and where found
Responsible for ATP(energy) production via the process of aerobic respiration in the cell: Glucose+O2=water and CO2 It has an inner membrane folded into cristea to increase SA: volume ratio. 0.5–1 μm.
cytoplasm- function and where found
A jelly like fluid that holds all the organelles (protects them too) and is where all the reactions take place. Made of mainly salts and sugars(solutes) water(solvent) and proteins.
ribosomes- function and where found
An intercellular structure made of RNA and protein. Its the site of protein synthesis in a cell. 20 to 30 nm
lysosomes- function and where found
They are like recycling trucks, as they have digestive enzymes that break down molecules into the elements so they can be reused. Found only in animal cells. 0.1 μm-1.2 μm (smaller than mitochondria tho)
Golgi Apparatus - function and where found
An assembly of folded membranes responsible for material secretion. Materials are sorted, modified and then exported from within the cell vesicles.
Endoplasmic reticulum
Plasma membrane found inside the cell that folds itself to create the lumen(attatche dto nuclear envelope). 10% of cell volume
Smoother endoplasmic reticulum- function and where found
It has no nodes, and it synthesises lipids and steriods.
Rougher Endoplasmic reticulum- function and where found
A studded surface with ribosomes, a membranous network that transports materials via vesicles.
chloroplasts- function and where found
Found only in plants. It is repsonsible for photosynthesis(ocnverting light energry into chemical energy) and uses chlorophyll to absorb and utilise light energy. They move around in the cell to maximise light absorption. 5 to 10 μm long
permanent vacuole- function and where found
Essentially a sack with a membrane and it contians cell sap which is a store of water and dissolved sugars and salts. up to 40 μm diameter
cell wall- function and where found
Made of cellulose(lose network of fibres) its giving a rigid structure to plant cells and determines their shape. Helps plant root hair cells not burst during cytolysis, and keeps plant structure during plasmolysis. Thickness: around 0.1-2 µm thick
4 rules when drawing cells:
Draw to proportion
No shading
Use a ruler to label with a line directly touching the organelle being labeled.
Connected lines(crisp)
what are Differences between animal and plant cell
Differences
Plant cells have a cell wall, chloroplasts, and a large central vacuole.
Animal cells have lysosomes, lots of small vacuoles and none of those above because animals get sugar from the food they eat, they do not need chloroplasts: just mitochondria, and don’t need to absorb water form soil.
fixed shape in plant cells whilst round irregular shape in animal cells (lacks rigidity).
sizes:
prokaryotes
single celled organisms
Eukaryotes
Eukaryotes are organisms whose cells have a nucleus enclosed within membranes, unlike prokaryotes.
compartmentalisation
A cell
A building block of an organism, smalles unit of life that can replicate independently.
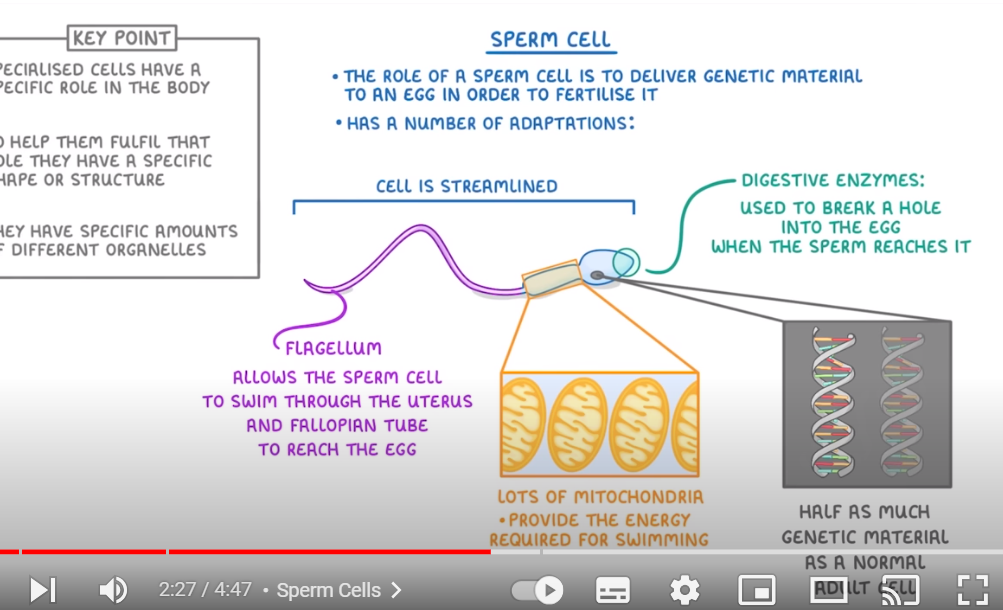
Specialised cell- sperm cell
Role: to deliver genetic material to an egg to fertilise it. It has a streamlined body shape- thin and is lightweight. The flagellum helps it travel quickly and easily and in different directions to the egg. Its nucleus only contains half as much genetic material as a normal adult cell(combines). Its front has lots of digestive ensymes that are used to break a hole into the egg when the sperm reaches it. It has many Mitochondria to get the energy required when swimming.
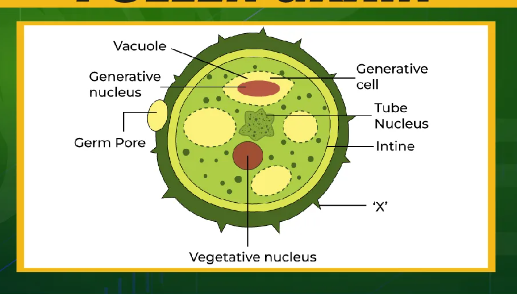
Specialised cell-pollen grain
Role: to transfer male gametes to the female gametes on a flowe, facilitate sexual reproduction in a plant. To be carried by pollinator. Its cell is very small and circular making them very easy to transport by the wind, water or animals. Because the exterior exine is rigid protecting what’s inside and water proof, resistant to deterioration. The cell wall has spikes, creases to make it stick easily to pollinators.
Specialised cell- Root hair cell
Role: to absorb water and minerals from the soil to be transported to the rest of the plant. Large SA to maximise water and mineral absorption through diffusion from soil- osmosis speeds it up. Cell wall to keep it from bursting during cytolysis and maintain its shape during plasmolysis. Lots of mitochondria for acitve transport. NO CHLOROPLASTS.
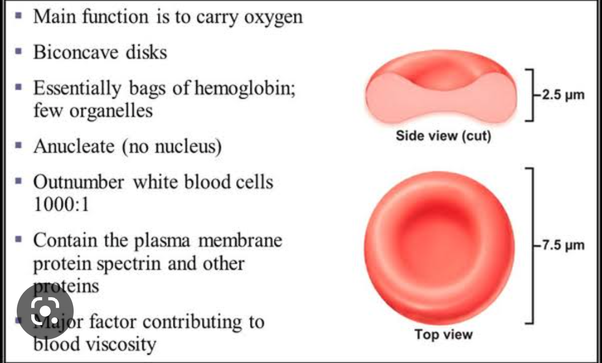
Specialised cell-Red blood cell
role: to carry oxygen from the lungs and deliver it throughout the body and bring back waste products. It has a biconcave disc shape to increase SA and no nucleus so it can absorb more O2, uses haemaglobin to bind to the O2. Has a thin outer membrane to let O2 easily diffuse through and make it flexible (bendable).
Specialised cell-Paliside cell
role:photosynthesis for plants-providing energy and absrobing light to convert into glucose and oxygen. Has an elongated shape to increases SA for light absorption(first cells facing light upwards), and lots of chloroplasts.
Light microscope
they possess low magnification and resolution(max x2000 without losing resolution).
2D image, see things in relation to eachother
Views specimens in natural colours and can be alive(preserved too)
Uses visible light that is sent from the light source through the actual specimen and the glass lenses then magnify the image of the specimen through refraction.
Electron Microscope:
possesses high magnificationa nd resolution
Can only view dead specimen and in monochrome(false colouring)
Uses a laser scanninf which pass through(transmission) or move over the surface of (scan) the dried specimen kept within a vacuum.
Produces 3D version/image- more detail
magnifciation
how many times bigger something appears(image) compared to actual size
resolution
smallest distance that items can be apart while still seeming seperate(two distignuishable points).
How have microscopes helped us understnad cells:
scientists were able to observe the structure and function of cells, leading to groundbreaking discoveries about the complexity of living organisms.
Allowed us to see the intricate details of cells(organelles).
Observe how cells divide and differentiate, as well as how they interact with each other and their environment.
Microscopes have enabled us to study the effects of diseases and treatments at the cellular level.