16. therio- prolapses and dropsical conditions of cattle
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
at what point of gestation do vaginal prolapses in cattle most commonly occur?
in late gestation
vaginal prolapses can occur postpartum, but this is more rare

why do most vaginal prolapses of cows occur in late gestation?
due to high estrogen in late pregnancy causing relaxation of pelvic ligaments

is vaginal prolapse hereditary?
yes

which breeds is vaginal prolapse hereditary in?
herefords
charlois
limousin
shorthorn
bos indicus breeds
(Short, Boss, Charlie, Limo is Here)
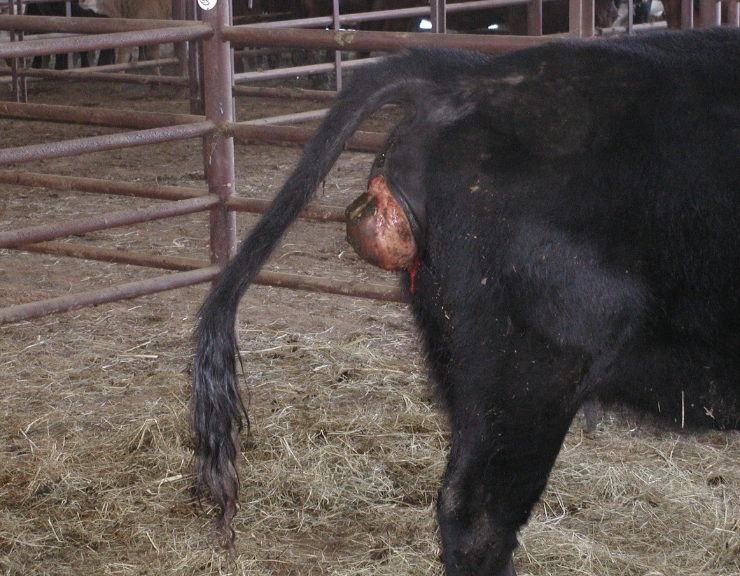

what are other risk factors for vaginal prolapse?
-seen more in older, fat cows
-more common in cold weather
-tends to reoccur each pregnancy
-grazing estrogenic plants
-ET super-ovulated cows (bc of high estrogen from multiple follicles)
does vaginal prolapse predispose animals to uterine prolapse?
no
what is vaginal prolapse usually associated with when seen postpartum?
dystocia
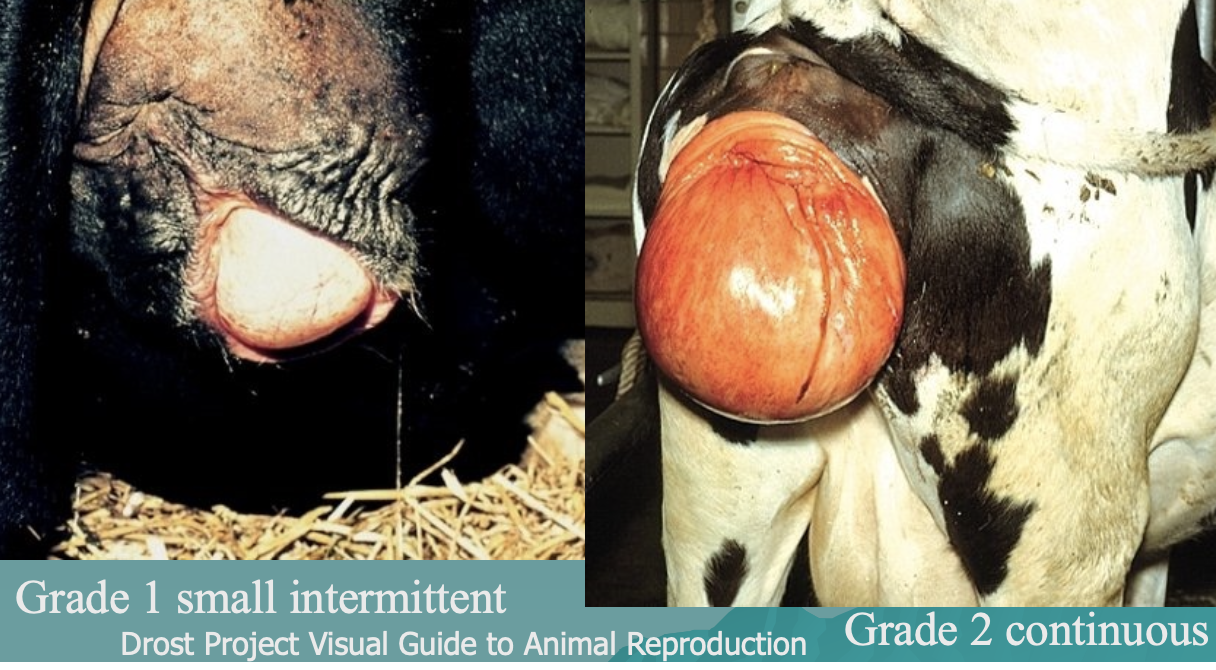
what are the grades of vaginal prolapse?
grade 1
grade 2
grade 3
grade 4
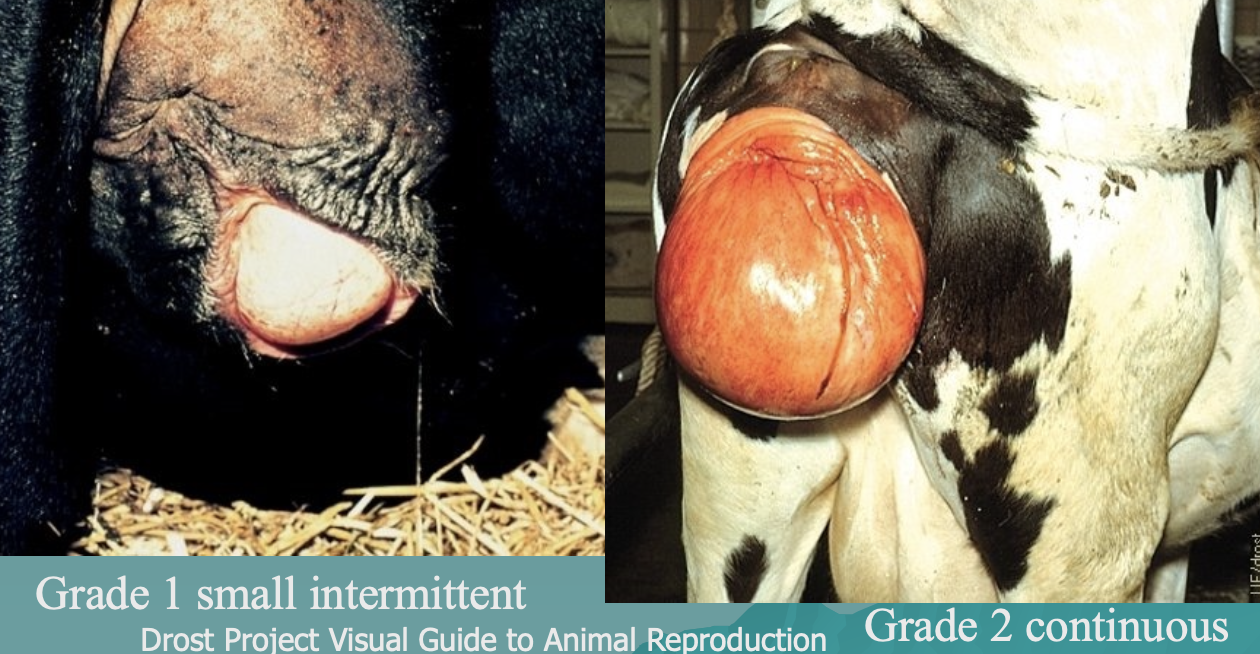
what are grades 1 and 2 vaginal prolapse?
grade 1: small intermittent
grade 2: continuous
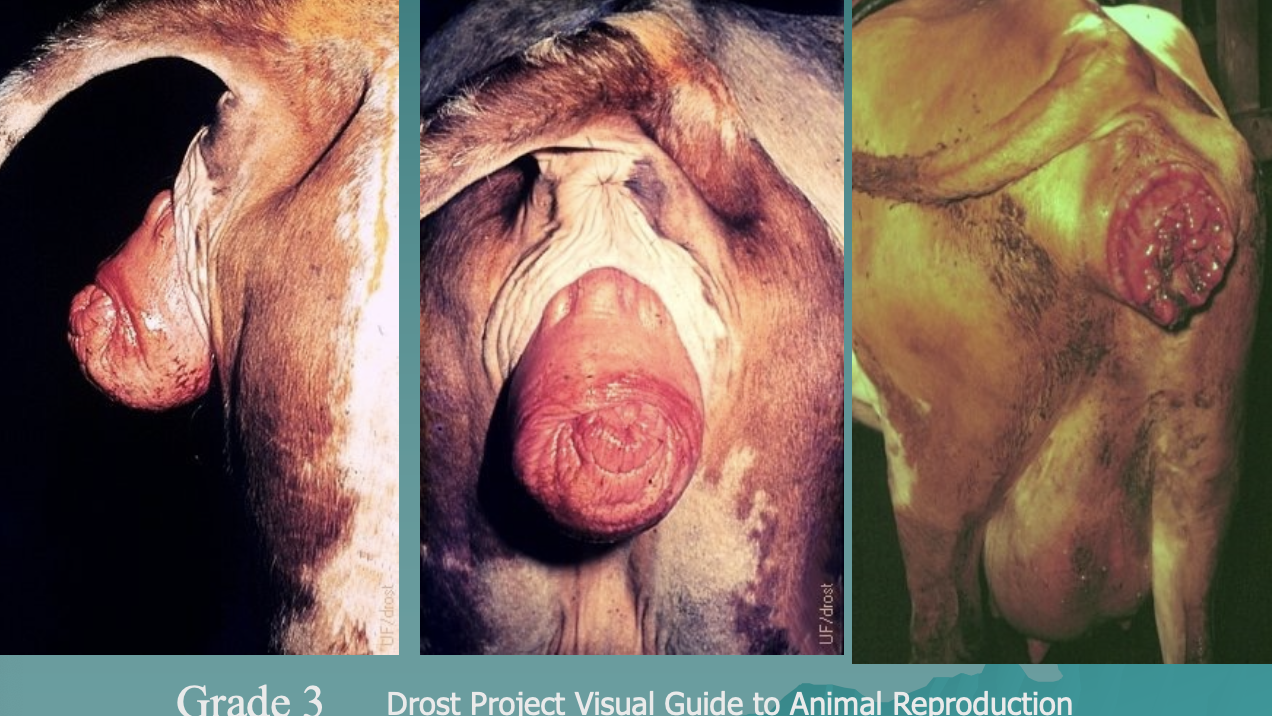
what are grades 3 and 4 vaginal prolapse?
grade 3: vagina, cervix, and bladder prolapse
grade 4: progression of grade 3, leads to necrosis or fibrosis
which breeds are cervicovaginal prolapses common in?
common in bos indicus influenced cattle (santa gertrudis and beefmaster breeds)

what is the goal of vaginal/cervical prolapse correction?
to replace and retain vagina and cervix then calve normally
-permanent or temporary reduction
how are mild cases of vaginal prolapse corrected?
clean and replace:
can place a caslick (but has weak retention): for grade 1 only, non-pregnant
how are moderate/severe cases of vaginal/cervical prolapse corrected?
replacement and retention performed standing under epidural anesthesia
what is the actual procedure for correcting a vaginal prolapse?
1. perform epidural
2. clean with surgical scrub (+/- sugar, 50% glucose)
3. lift dorsally to allow urination if bladder is everted into prolapse
4. coat prolapse tissue with OB lube and massage back into normal position
5. choose a method of retention
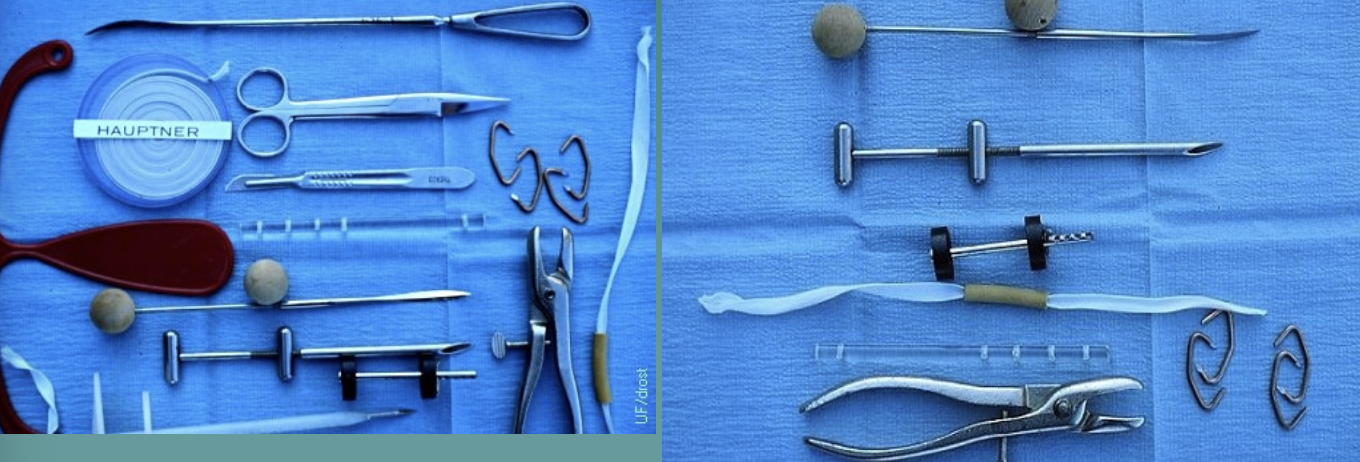
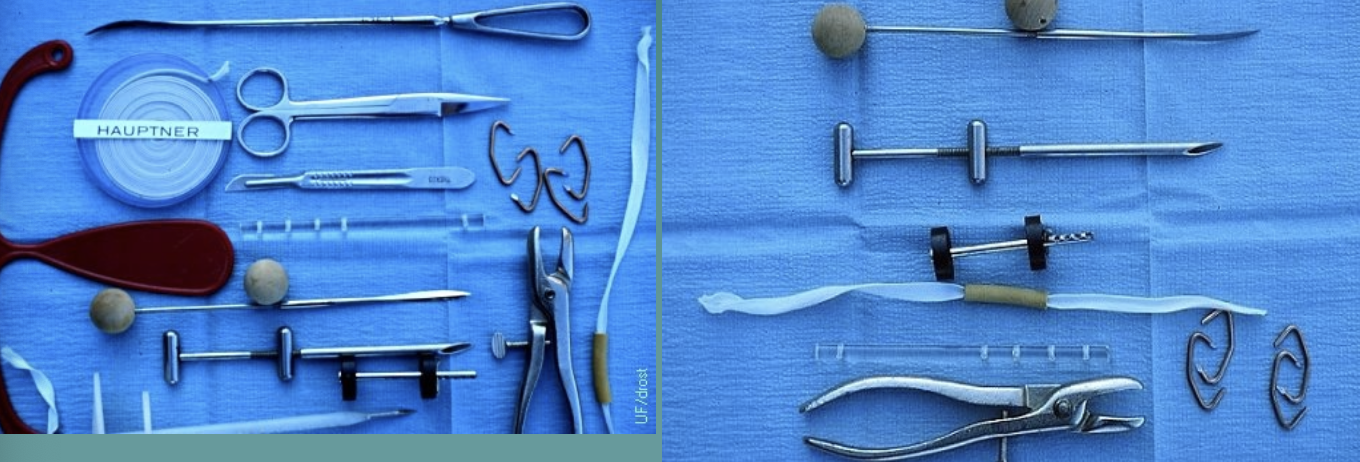
what are different fixation/retention methods for vaginal prolapse corrections?
1. vulvar suture patterns (temporary)
2. hog ring bootlace
3. buhner technique (has to be removed before calving)
4. modified minchev technique (does not have to be removed before calving)
5. cervicopexy
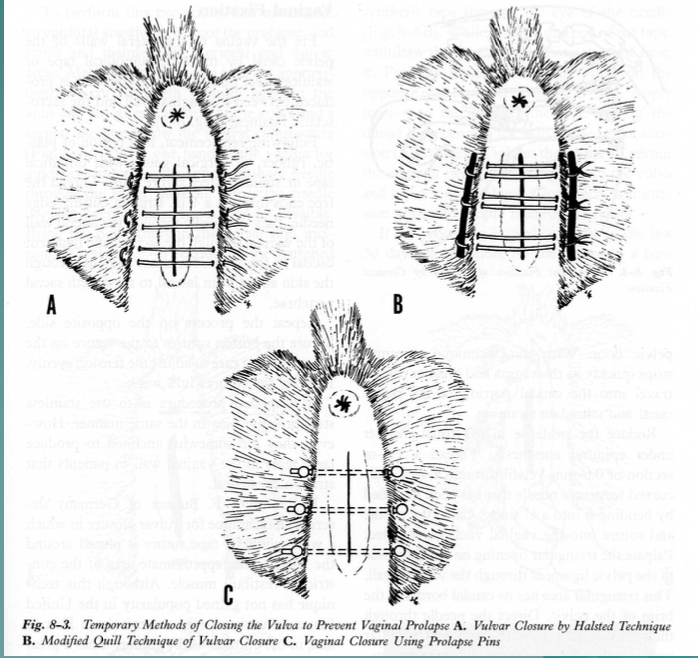
what is this fixation method?
vulvar suture patterns (temporary)
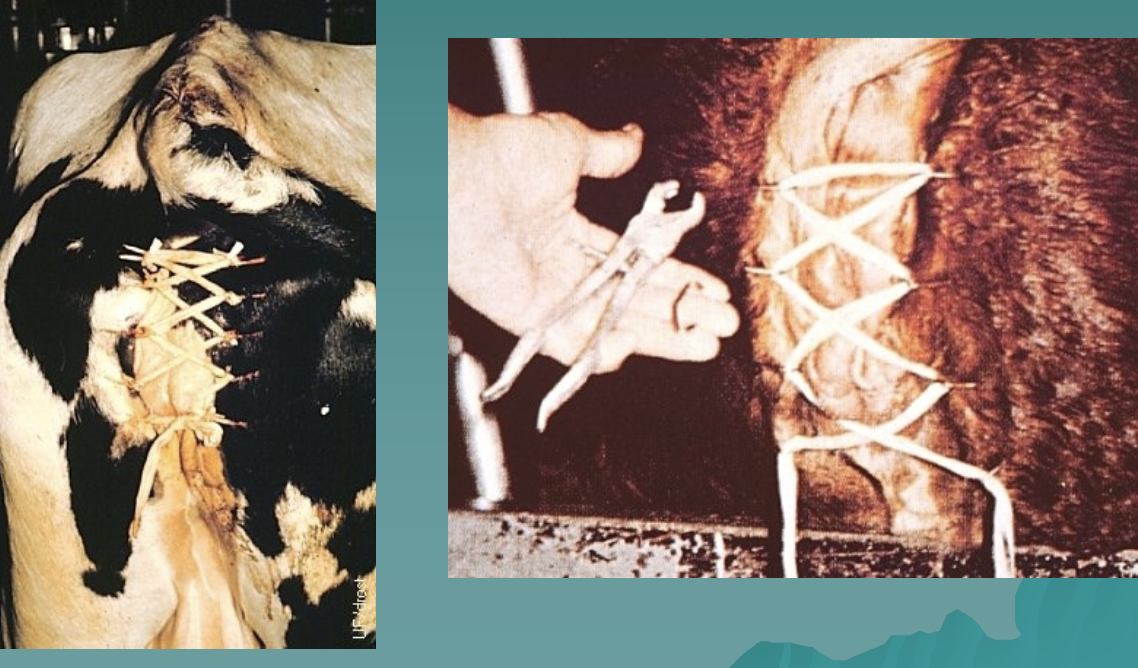

what is this fixation method?
hog ring bootlace
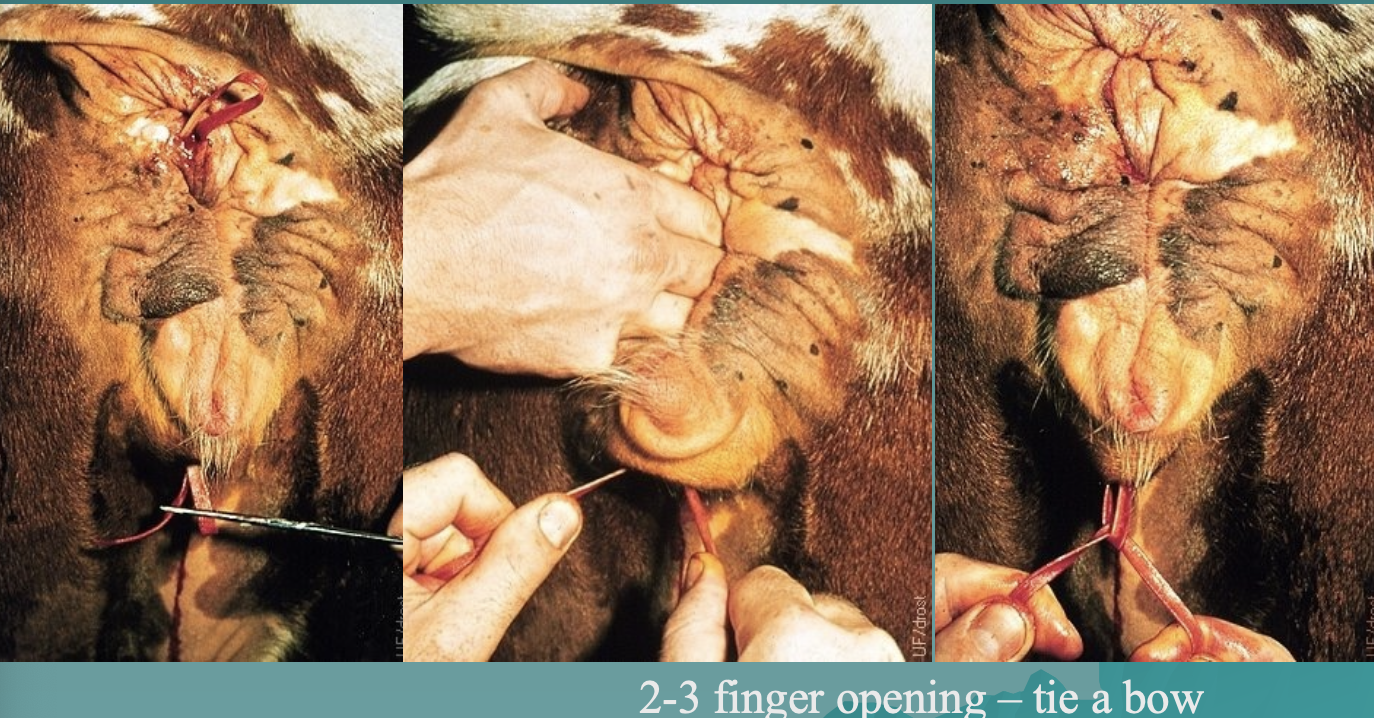
what is this fixation method?
buhner technique (has to be removed before calving)
*Dr. E thinks this is the best method as long as it is removed before calving
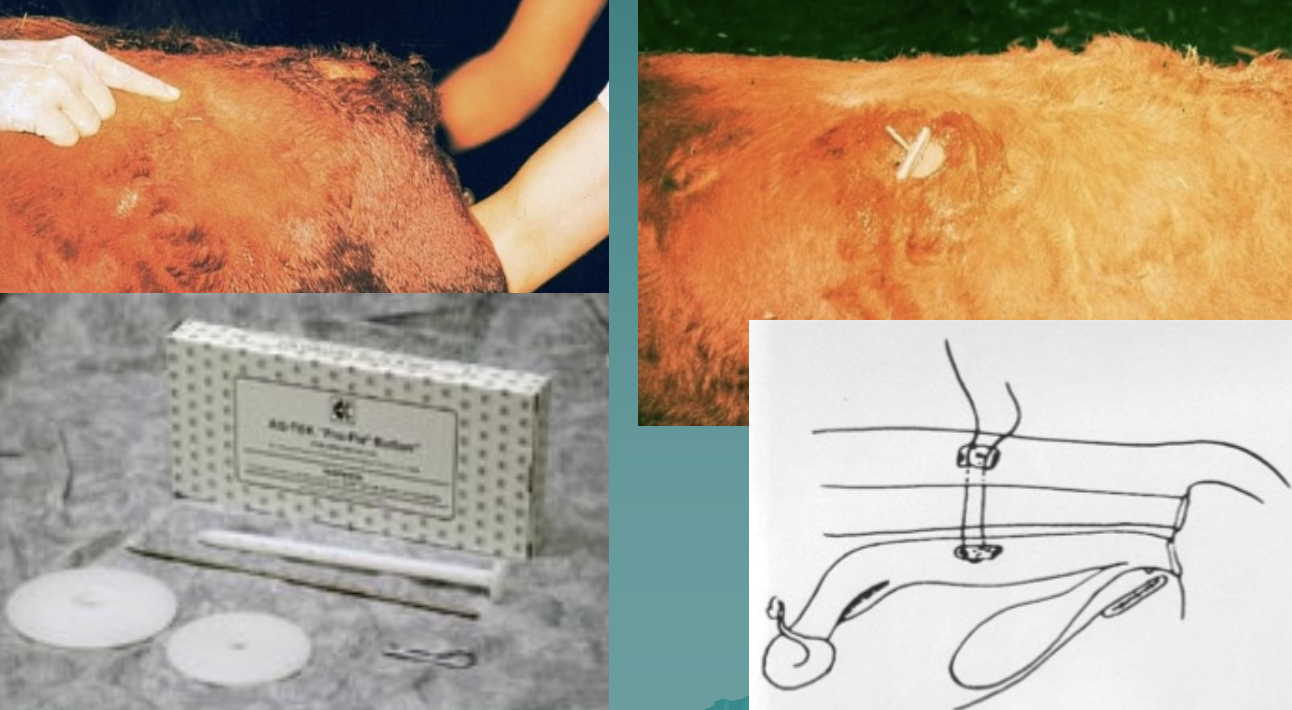
what is this fixation method?
modified Minchev technique (can stay in during calving)
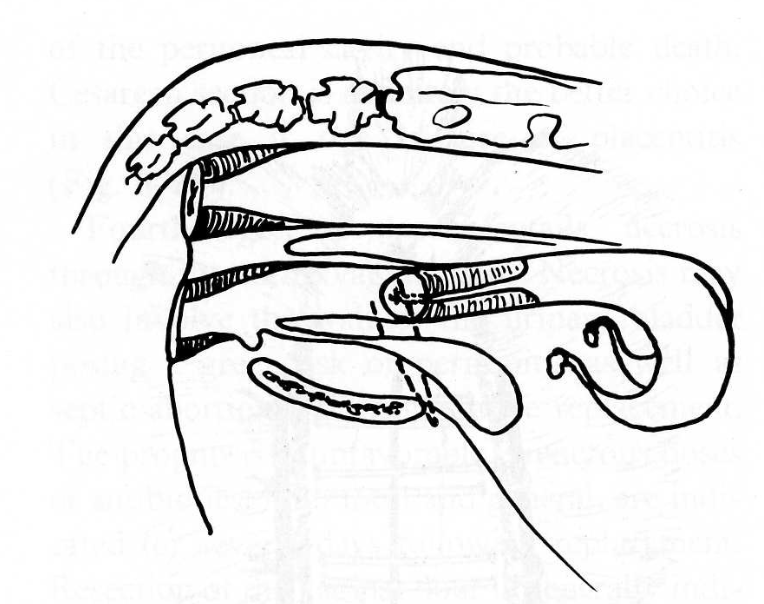
what is this fixation method?
Cervicopexy (Winkler technique)
*if done blindly, can accidentally suture bladder so often do flank approach to prevent this
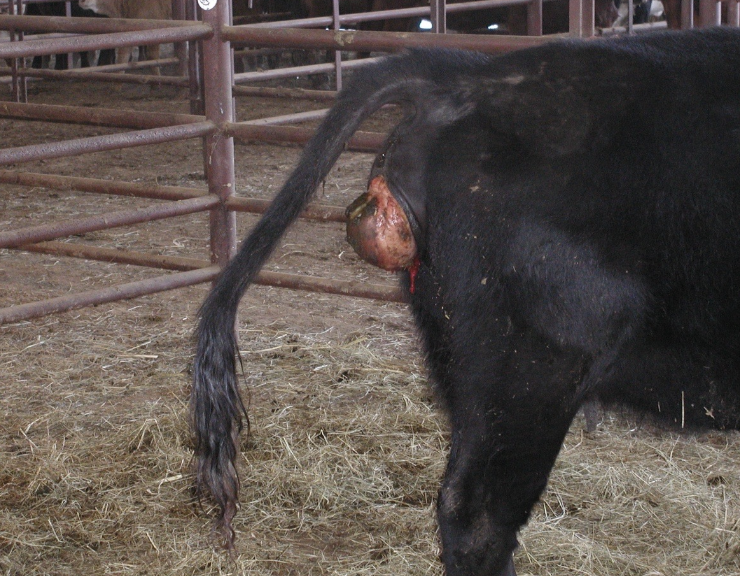
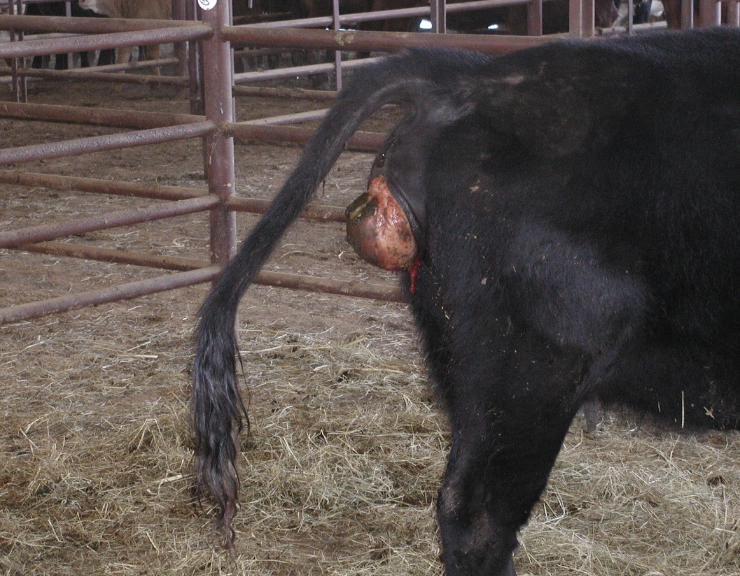
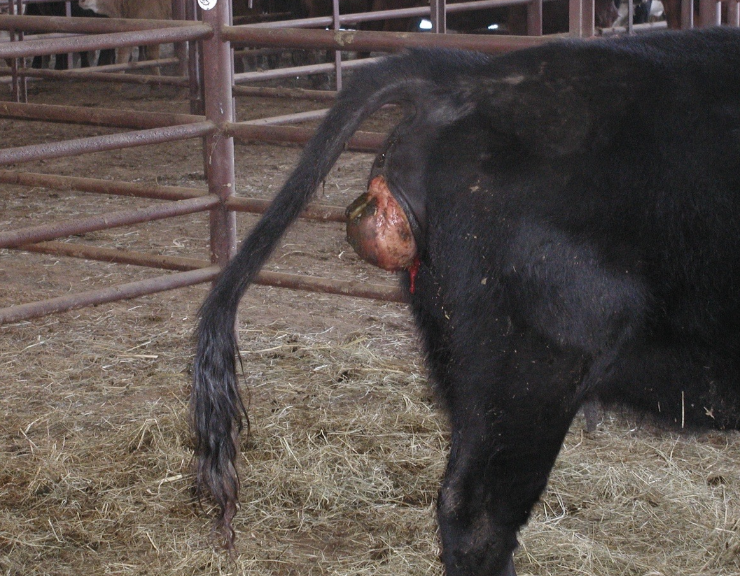
how serious are uterine prolapses in cows?
one of the most life-threatening emergencies that can happen in a cow
what is the incidence of uterine prolapse in cows?
<1% of calvings can result in uterine prolapse
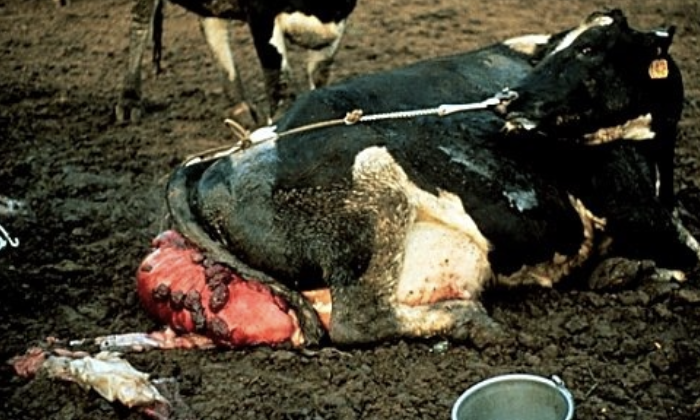
is uterine prolapse heritable?
no
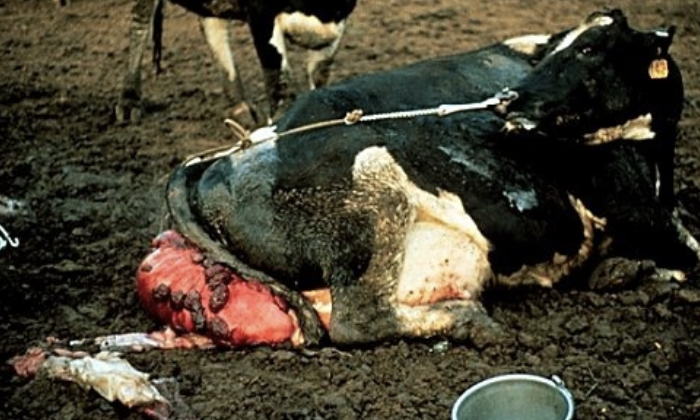
when do most uterine prolapses occur?
within first 24 hours of calving
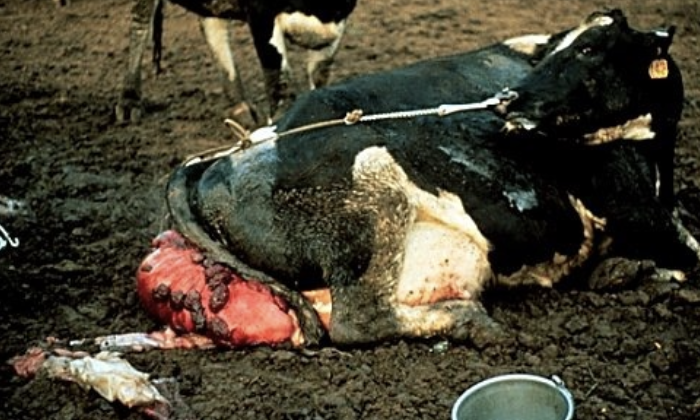
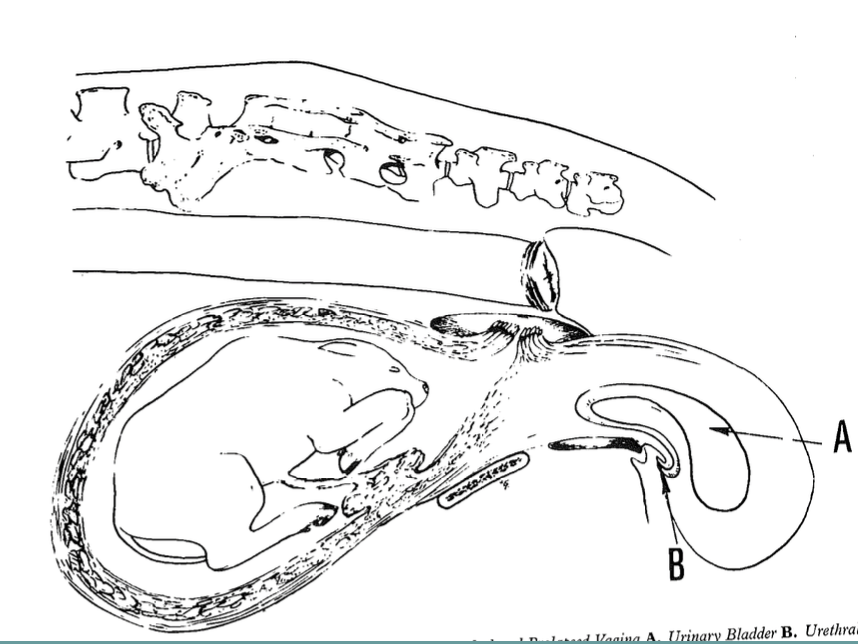
how do uterine prolapses occur?
when cow continues an abdominal press on a flaccid uterus after calf delivery
-dystocia, pelvic irritation, vaginal injury
-hypocalcemia, uterine inertia
-uterus inverts and is forced out thru the cervix
-usually only the gravid horn prolapses
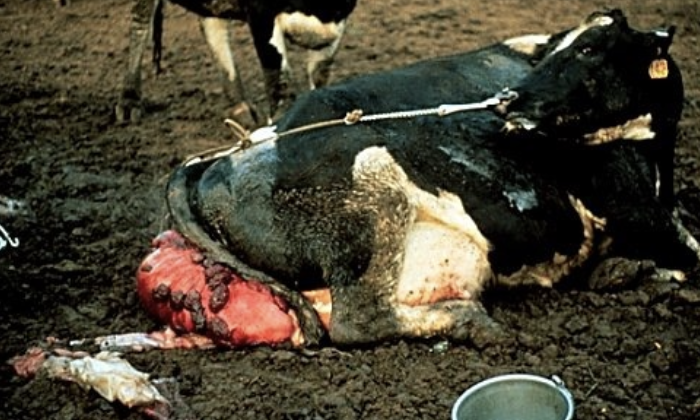
what occurs to the uterine tissues when uterine prolapse occurs?
tissues become edematous and friable, and are often subjected to injury
also prone to vascular rupture and hemorrhage
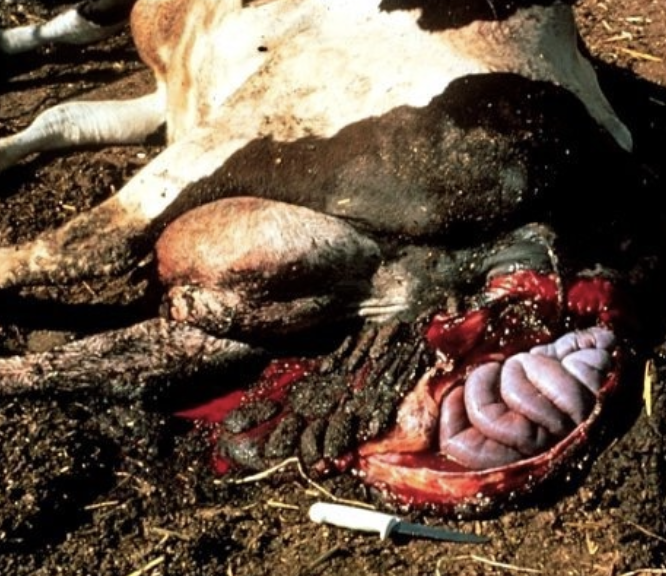
what additional complications may occur with uterine prolapse?
abdominal viscera may strangulate in prolapse or the prolapse could rupture and eviscerate
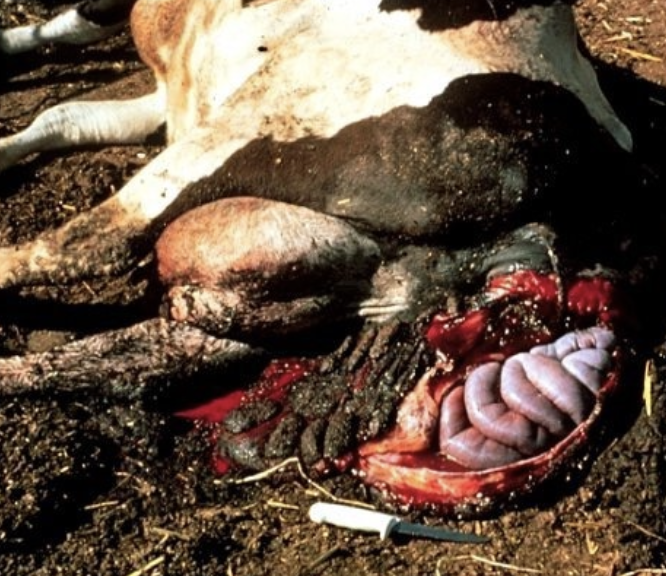
what is the prognosis of uterine prolapse influenced by?
promptness of treatment
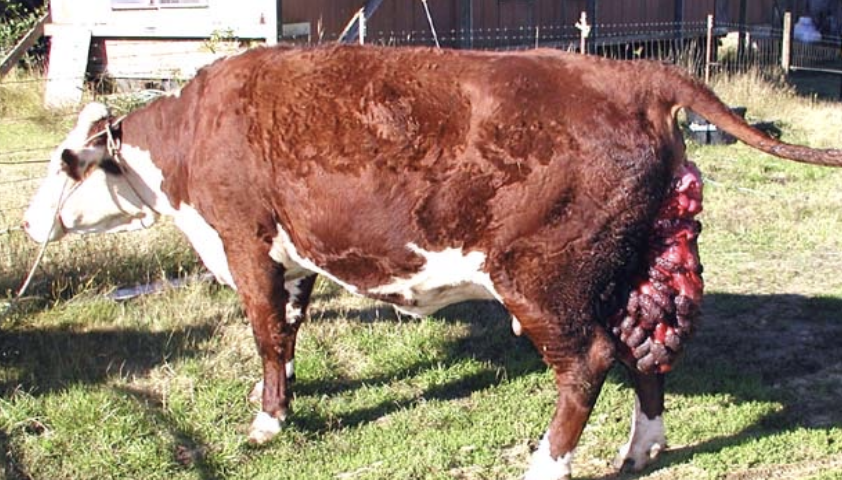
how can uterine trauma be avoided in ambulatory cows with uterine prolapse?
handle ambulatory cows gently to avoid uterine trauma
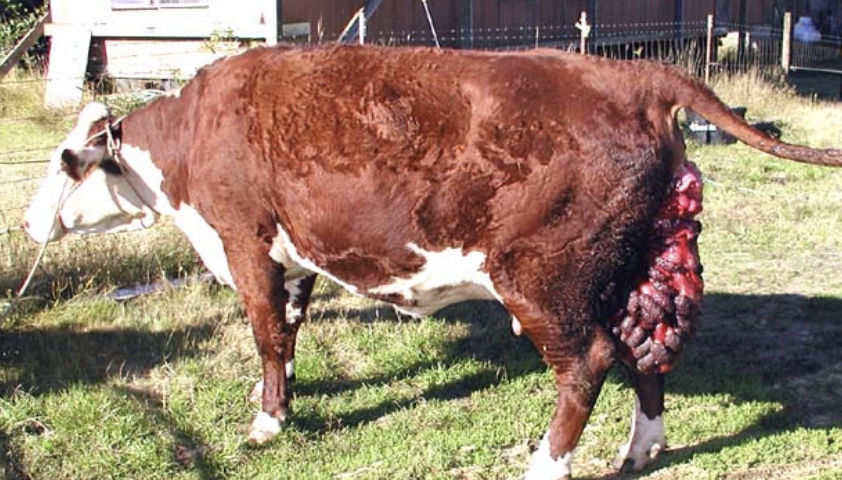
is it okay to remove the attached placenta in cows with prolapsed uteruses?
yes, can remove the attached placenta if it detaches easily
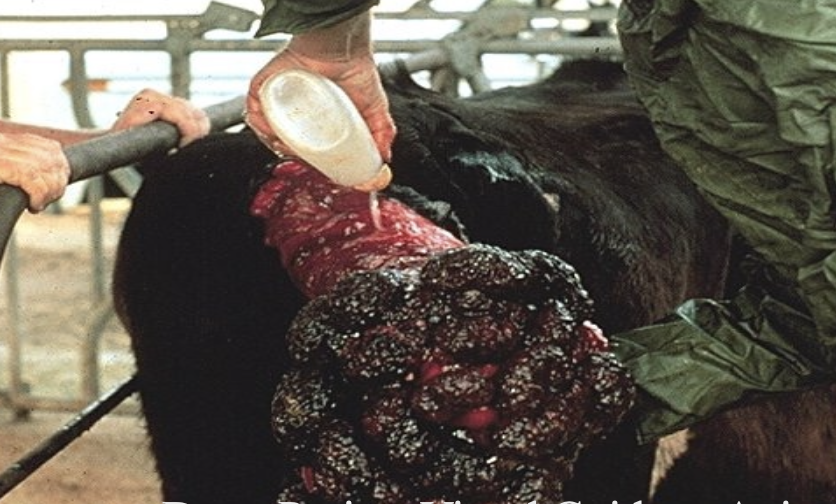
how are cows prepped for treatment of a prolapsed uterus?
epidural and clean prolapse with soap and water
if the cow is recumbent, pull back legs rearward to tilt pelvis to facilitate replacement
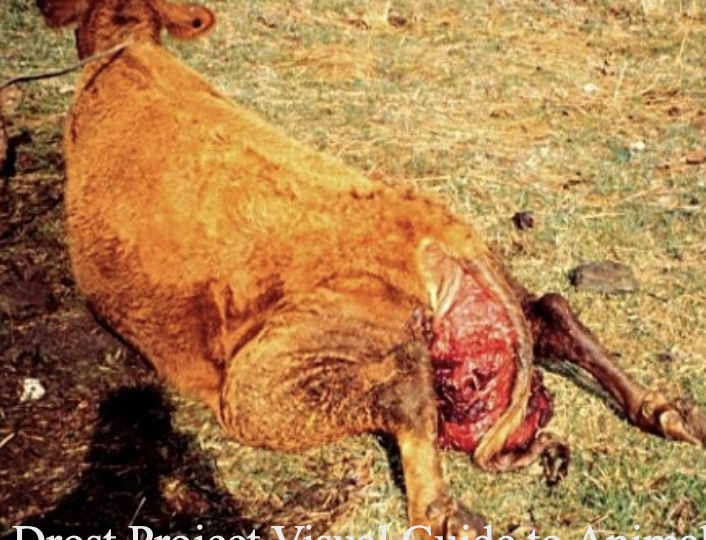
does it matter what way the uterus is replaced back into the body?
yes- the part that came out last goes in first

once the uterus is replaced, how is the uterine horn straightened out?
wiffle ball bat as a probang
infuse large amount of water (3 gallons) + povidone iodine intrauterine to straighten out and prevent intussusception
then give 20 IU oxytocin q30minutes x 3
give 23% calcium gluconate if needed ± antibiotics
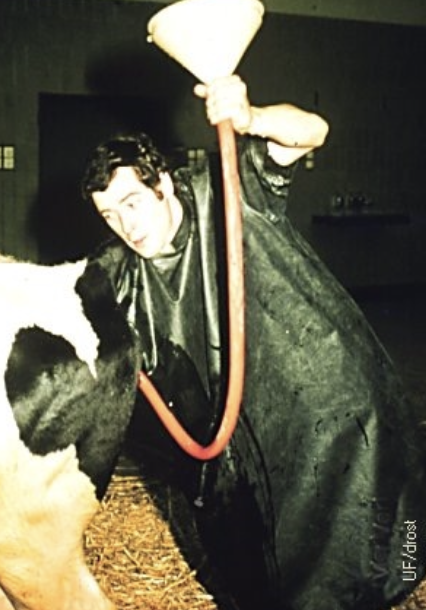

once the uterus is replaced, should you place a suture to prevent re-prolapse?
if the cow is recumbent and/or struggling- yes, put in a buhner suture
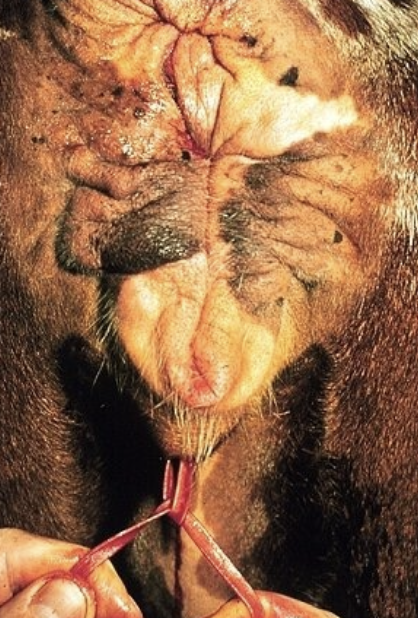
if placing a suture after replacement of a prolapsed uterus, why is it important to recheck the cow after a day?
invagination of the uterus may occur and go unnoticed, so should recheck in a day
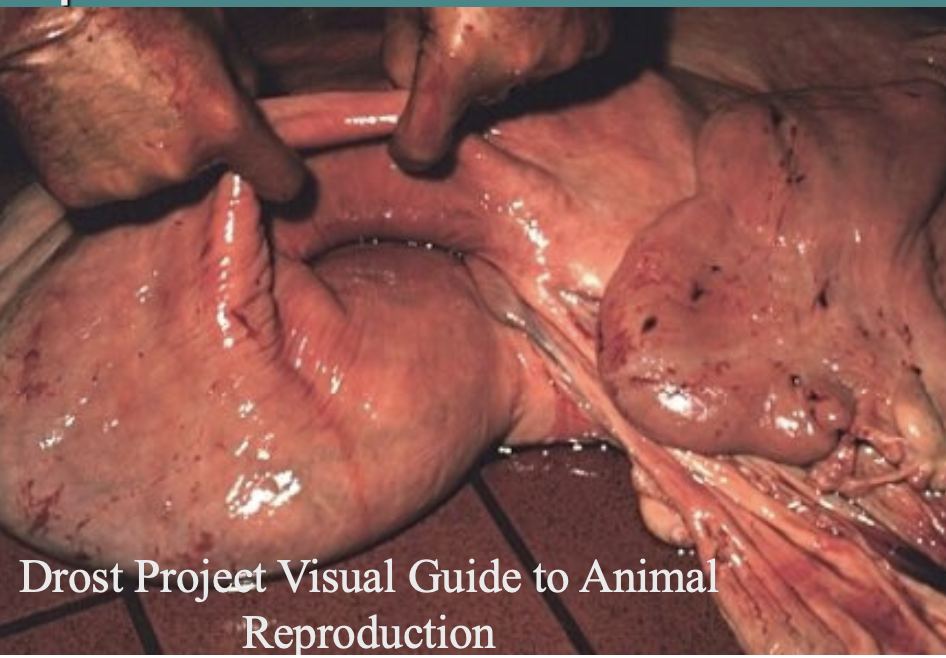
what occurs if the uterus is not completely reverted?
results in continued straining and re-prolapse
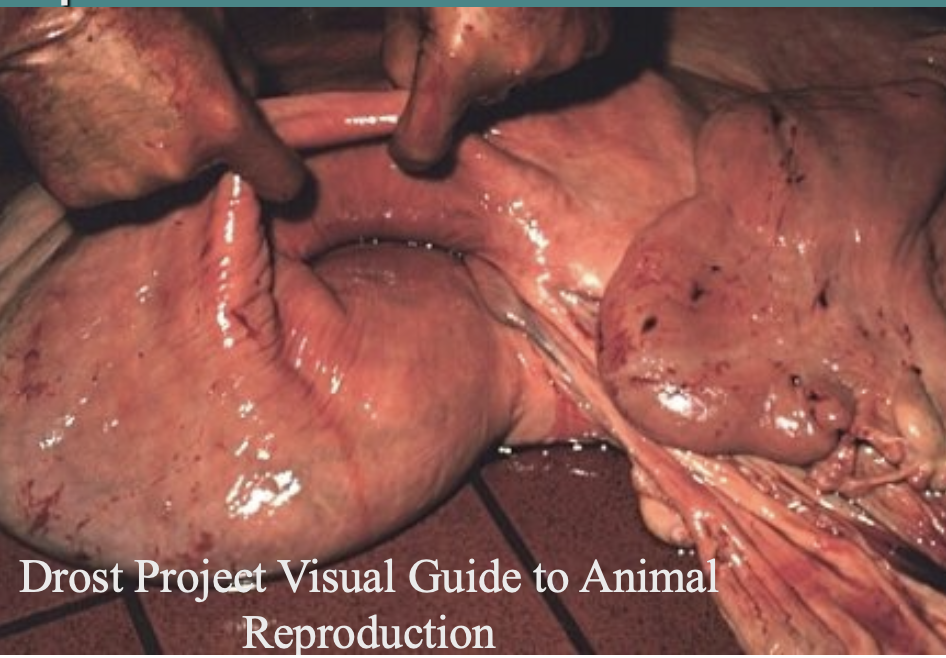
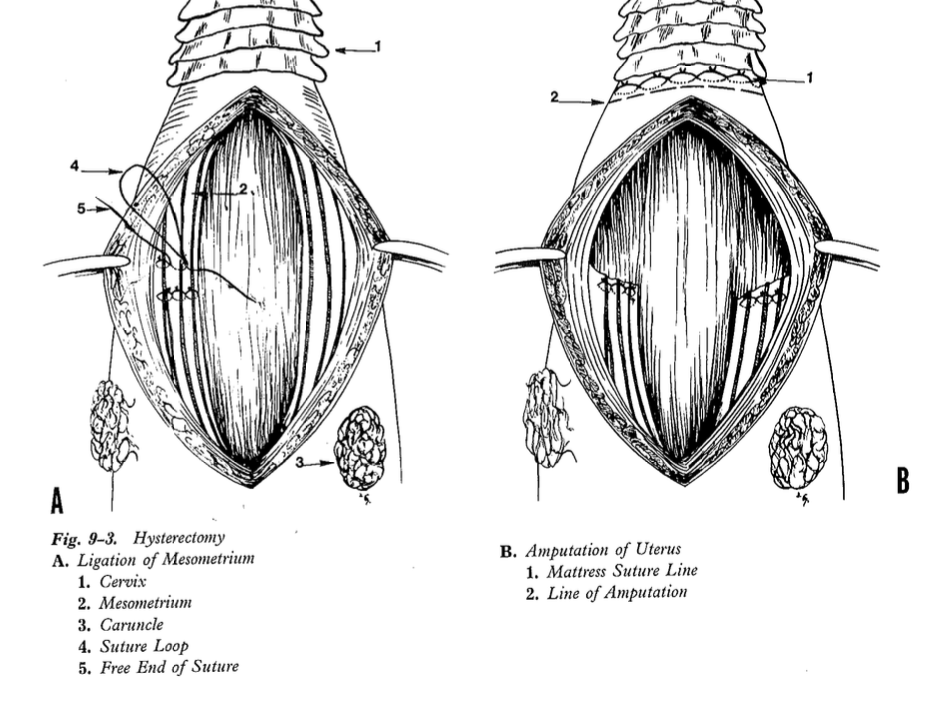
what can be done if uterus unable to be replaced?
amputation of uterus, open vs closed
Can use the Callicrate Prolapse Loop (for uterine prolapse) to band and remove
what is the prognosis for uterine prolapse if the cow survives the first 24-48 hours?
good
which cows with uterine prolapse usually have a poor prognosis?
cows with paresis, stage 3 hypocalcemia, severe uterine trauma, shock, or hemorrhage
what complications may be seen in cows which survive uterine prolapses?
usually are fertile, but expect metritis
what is hydrallantois?
large accumulation (40-70 gallons) or allantoic fluid over 1-3 weeks in late gestation
weight of uterus, fetus, membranes and fluids may be 500lbs
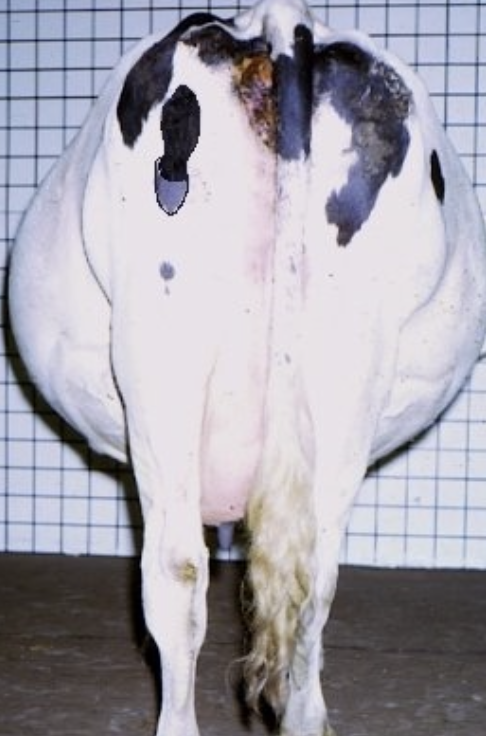
is hydrallantois or hydramnios more common? which is more severe?
hydrallantois is much more common (90% of hydrops cases), and is much more severe
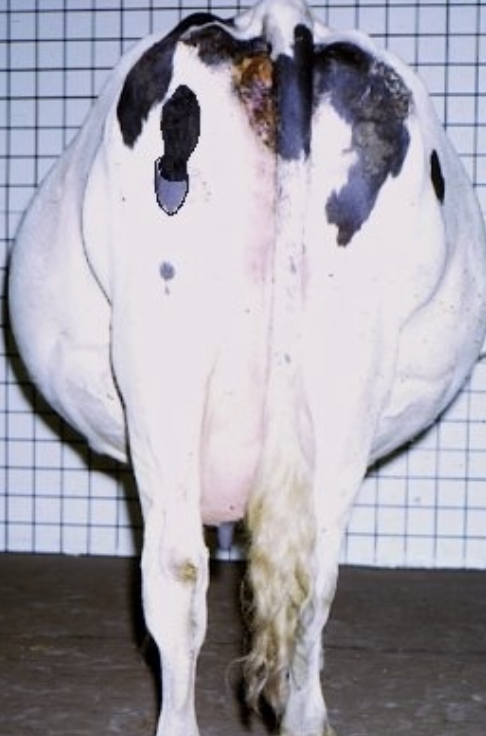
what are clinical signs of mild cases of hydrallantois?
signs may be missed but suspected at parturition when a large quantity of fluid is passed
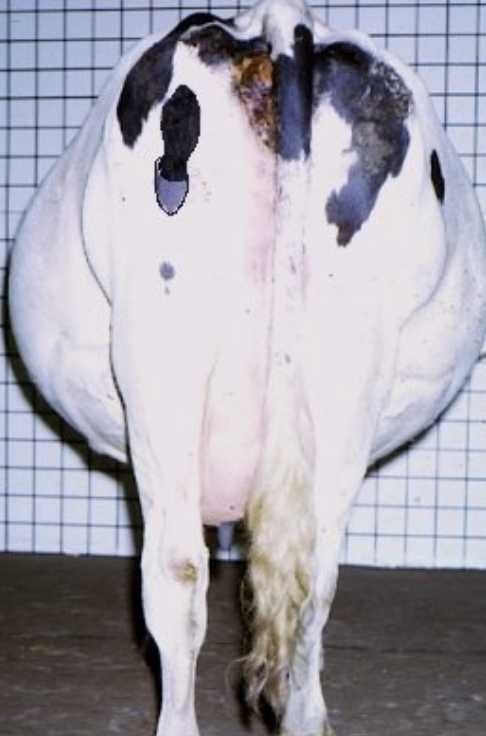
what are clinical signs of severe cases of hydrallantois?
abdominal enlargement noted as early as the 5th month of gestation
may see backward extension of rear legs and recumbency, prepubic tendon rupture
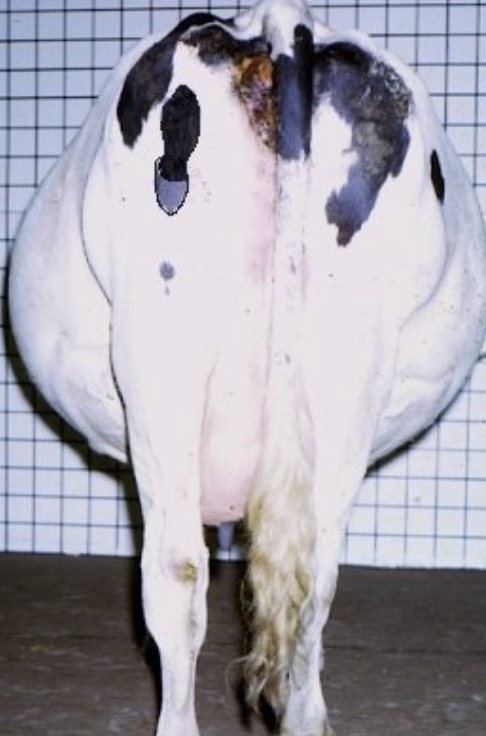
what causes hydrallantois?
placental dysfunction due to uterine or placental disease
-deficient number of caruncles
-more common with twins/triplets

how is hydrallantois diagnosed?
-history and clinical signs
-palpation per rectum reveals a greatly distended uterus
-usually cannot palpate fetus or placentomes
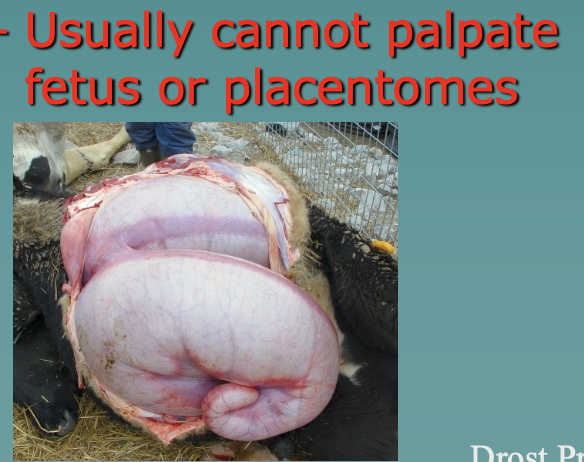
what is the prognosis of hydrallantois?
life: poor
fertility: poor
RFMs and metritis usually follow delivery
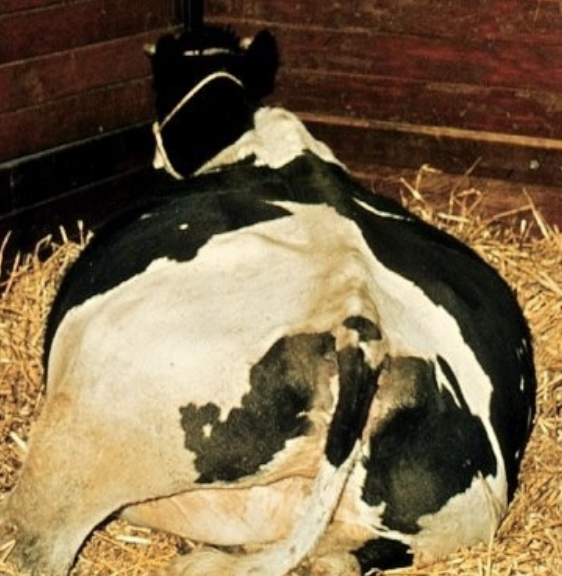
how is hydrallantois treated?
consider salvage by slaughter
if valuable cow, consider inducing abortion
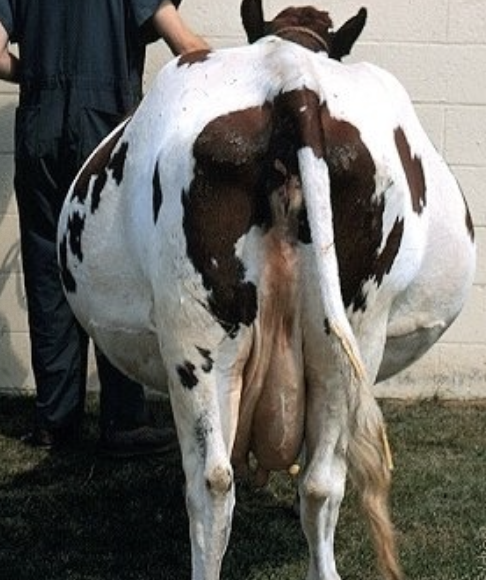

how is abortion induced in cows with hydrallantois?
give dexamethasone and PGF
-check every 12hrs after injection
-as soon as hand can be passed thru the cervix, puncture membranes to release fluid (but not too fast, as the cow can go into hypovolemic shock)
-continue exam and remove calf when possible
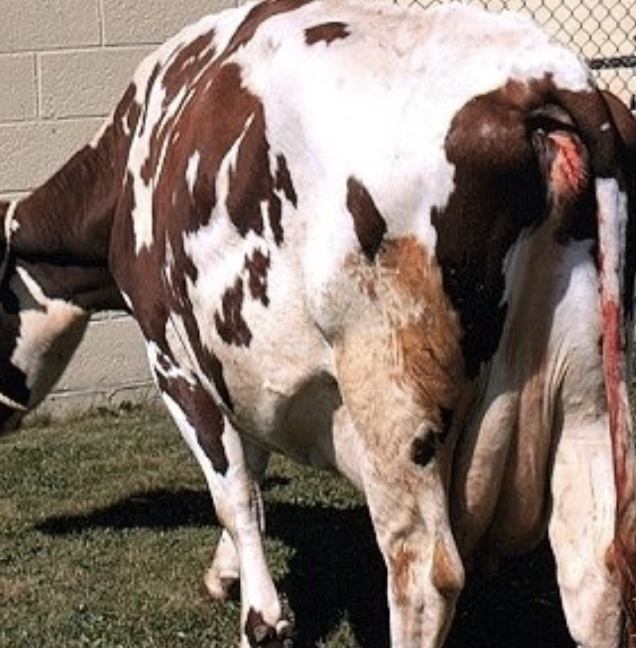

what is hydramnios?
10% of all hydrops cases (less common, less severe)
slow accumulation of large amount (5-30 gallons) of amniotic fluid during the second half of gestation
what causes hydramnios?
usually associated with an anomalous fetus
-may be due to inability of fetus to swallow fluid or renal dysfunction
-several autosomal recessive genes associated with the condition
-seen in bison bull-domestic cow hybrids
what autosomal recessive genes may be associated with hydramnios?
-dexter cattle with bulldog fetus
-muscle-contracture monsters of red danish
-guernsey calves with pituitary hypoplasia producing prolonged gestation
-hydrocephalic hereford calves
how is hydramnios diagnosed?
palpation per rectum revealing a large uterus
fetus and placentomes are usually palpable
what is the treatment for hydramnios?
induce abortion
what is the prognosis for hydramnios?
life: good
fertility: good, usually rebreed
usually do not have RFMs