BMS 302 11
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
total lung capacity equals
IRV + TV+ ERV+ RV
vital capacity equals
IRV + TV+ ERV
functional residual capacity equals
ERV + RV
inspiratory capacity equals
IRV + TV
Tidal volume
amount of air inhaled per breath during normal breathing
inspiratory reserve volume
amount of air that can be inspired above and beyond that inspired during a normal quiet inspiration
expiratory reserve volume
maximal amount of air that can be expired following a normal quiet expiration
residual volume
amount of air left in lungs after a maximal expiratory effort
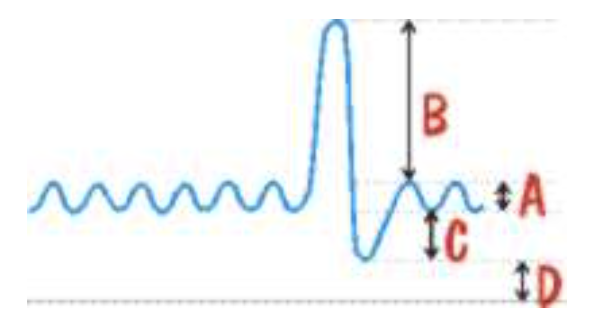
A represents
tidal volume
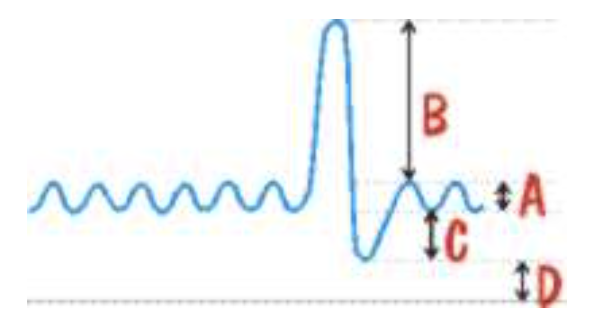
B represents
inspiratory reserve volume
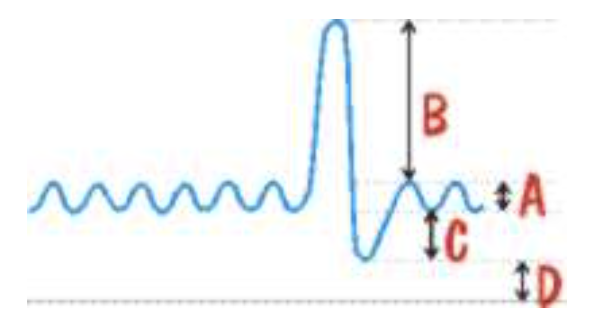
D represents
residual volume
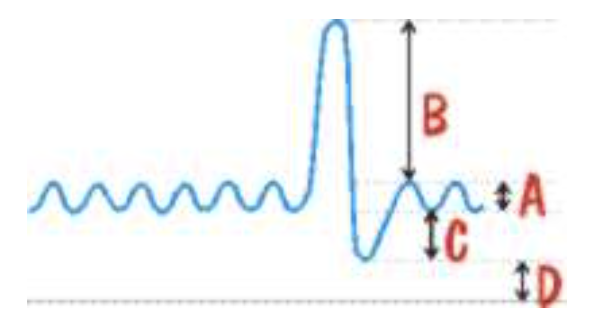
A + B + C represents
vital capacity
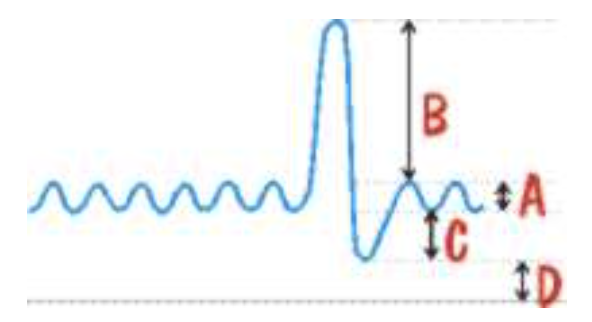
A + B+ C + D represents
total lung capacity
normal volume for tital volume at rest
0.5 L
normal volume for total lung capacity in men
6 L
normal volume for total lung capacity in women
4.6 L
normal volume for FEV1
75-85%
normal volume for FEV3
>97%
BTPS refers to
body temp, ambient pressure, and saturated gas
the composition of room air is
20.93% O2, 0.04% CO2, and 79% N2
stimulus
changes in blood levels of CO2 and O2
receptors
chemoreceptors located in aortic arch and carotid sinus
afferent pathway
sensory neurons from chemoreceptors to respiratory center
integrator
respiratory center in medulla and pons
somatic efferent pathway
neurons to diaphragm and intercostal muscles
autonomic efferent pathway
SANS and PANS neurons to bronchiole smooth muscle
effectors
bronchiole smooth muscle, diaphragm, intercostal muscles
response
change in VE (breath rate and/or tidal volume) to bring CO2 and O2 levels back toward steady state
in subjects with normal lung function at sea level or moderate altitudes, ____ has the greatest effect on increasing ventilation
hypercapnia
hyperventilation results in ____ levels
no change in blood O2
decreased blood CO2
what is the effect of hypocapnia on ventilation
decreases
what is the effect of hypercapnia on ventilation
increases
what is the effect of hypoxia on ventilation
increases
what is the effect of hyperoxia on ventilation
has no effect
what kind of samples can be used to estimate pulmonary capillary blood levels of CO2
Haldane-Priestly end-expiratory samples
Typical values for an end-expiratory sample of gas collected following a one minute breathold might be:
5-6% CO2
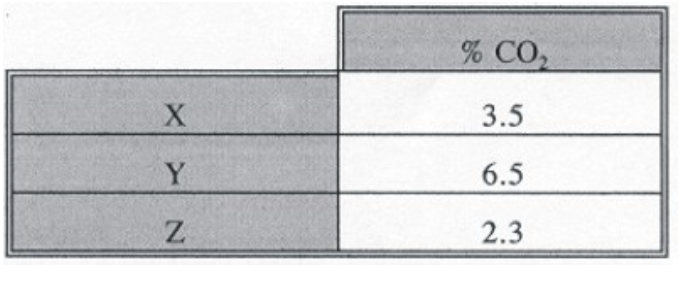
The data in the table below was collected from a subject using a small balloon to collect an Haldane-Priestly end-expiratory gas sample. Sample___ represents an end-expiratory sample collected following a breath-hold, sample ___ represents an end-expiratory sample collected following hyperventilation, and sample ___ is the control resting sample.
y, z, x
What happens to O2 levels in blood during a breath-hold
decrease
what happens to CO2 levels in the blood during a breath-hold
increase
Hyperventilation results in _____blood CO2 levels, which ____ breath-hold time, while breath-holding ______ blood CO2 levels resulting in _____ urge to breath.
decreased; increases; increases; an increased
The Sympathetic Nervous System _____ smooth muscle contraction, which _____ diameter and _____ airway resistance.
decreases, increases, decreases
The Paraympathetic Nervous System _____ smooth muscle contraction, which _____ diameter and _____ airway resistance.
increases, decreases, increases
What is the most appropriate type (cholinergic or adrenergic) of agonist and/or antagonist for decreasing airway resistance? Select all appropriate drug classes.
cholinergic antagonists
adrenergic agonists
bronchitis cause
inflammation of airways caused by pollution, smoking, or chronic infection
asthma cause
inflammatory response accompanied by bronchoconstriction
emphysema cause
smoking (in 90% of all cases) ultimately leading to a loss of surface area and air way collapse especially during exhalation
lung cancer cause
heredity and smoking
bronchitis T/P
remove source of irritation
asthma T/P
anti-inflammatory drugs and bronchodilators
emphysema T/P
stop smoking, supplemental O2
lung cancer T/P
surgery