DAT practice
1/237
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
238 Terms
Saphrophyte
An organism that feeds on dead matter
Force (for gases) is equal to
pressure x area
Pribnow box
the TATAAT sequence that is often found at the -10 region of bacterial promoters
When is 5 prime cap added to mRNA strand during protein synthesis
mRNA processing
What makes up the 5' cap end of mRNA in eukaryotes?
GTP
What region of mRNA allows ribosomal attachment?
5' cap
Huntington's disease
autosomal dominant condition characterized by forgetfulness and irritability
density centrifugation
In contrast to differential centrifugation, density centrifugation only separates cell contents on the basis of density. Unlike the multiple spin steps of differential centrifugation, density centrifugation involves one spin step that creates multiple layers separated by density.
❖ Centrifugation can also be used to separate proteins based on solubility (insoluble proteins pellet out, soluble proteins remain in the supernatant).
differential centrifugation
separates the cellular components by size and density
differential centrifugation levels
Nuclei pellets out first
then mitochondria and chloroplasts
3rd is ER
4th is ribosomes
TRUE
While plants do have mitochondria and use them to produce ATP through cellular respiration, they generally produce less ATP per unit of glucose compared to animals because plants primarily rely on photosynthesis for energy production through their chloroplasts, meaning their mitochondria are not as heavily utilized for energy generation as in animal cells
simple interest
Interest earned only on the original principal amount invested
Simple Interest Formula
I=PRT (Interest = Principal x Rate x Time)
Compound Interest Formula
A = P(1 + r/n)^(n x t)
r is the rate, n is the number of times compounded, t is time
permutation
An arrangement, or listing, of objects in which order is important
Permutation Formula
nPr = n!/(n-r)!
combination
a grouping of items in which order does not matter
Combination Formula
nCr = n!/r!(n-r)!
Cru di chat
microdeletion of short arm of chromosome 5
PCR (polymerase chain reaction)
A laboratory technique for amplifying DNA in vitro by incubating with special primers, DNA polymerase molecules, and nucleotides.
C NMR Spectroscopy
uses 13-C isotope, very similar to H-NMR with regard to deshielding, in order determine the type and number of carbon atoms
-alkane- 0-70
-alkene- 90-120
-aromatic- 110-160
-carbonyl- 160-200
Body's main source of energy
carbohydrates
body' least preferred source of energy
proteins
antigenic shift vs antigenic drift
Shift: Changes HA and NA spikes; probably due to genetic recombination between different strains infecting the same cell.
Drift: Point mutations in genes encoding HA or NA spikes; may involve 1 amino acid. Allows virus to avoid mucosal IgA antibodies.
"Antigenic shift" refers to a sudden, major change in a virus's genetic makeup, often resulting from the mixing of different viral strains, while "antigenic drift" describes a gradual, minor change in a virus's genetic makeup caused by small mutations accumulating over time; both terms are primarily used in the context of influenza viruses, where shift can lead to pandemic outbreaks due to the emergence of a completely new strain, while drift causes more subtle changes that require yearly vaccine updates
antigenic shift
the process by which two or more different strains of a virus, or strains of two or more different viruses, combine to form a new subtype having a mixture of the surface antigens of the two or more original strains.
antigenic drift
a mechanism for variation in viruses that involves the accumulation of mutations within the genes that code for antibody-binding sites.
allele vs gene
A gene is a part of DNA that determines a certain trait; genes can take two or more alternative forms; an allele is one of these forms of a gene.
Ex: gene for eye color (has several variations); allele for blue eyes (specific version of the gene)
A "gene" is a section of DNA that codes for a specific trait, while an "allele" is a variant form of that gene, meaning different versions of the same gene that can lead to variations in a trait; essentially, a gene is the basic unit, and alleles are the different options within that gene, like different color variations for eye color, where the eye color gene has multiple alleles for blue, brown, green, etc.
the laws of genetics
1. Law of Dominance
2. Law of Segregation
3. Law of Independent Assortment
Law of segregation
During gamete production, each hereditary factor's two copies separate so that offspring receive one factor from each parent.
Law of independent assortment
Traits inherited through one gene are inherited independently of traits inherited through another gene.
Law of dominance
In a heterozygote, a dominant trait will mask the expression of another trait for the same characteristic.
Intermediate dominance
In a heterozygote, there is no dominant or recessive allele, so the features are a mix of the two alleles.
law of dominance
In many traits one allele is dominant over the other allele. The "weaker (recessive" allele is only expressed when it is paired with another recessive allele
law of segregation
Mendel's law that states that the pairs of homologous chromosomes separate in meiosis so that only one chromosome from each pair is present in each gamete
law of independent assortment
Mendel's law, stating that allele pairs separate from one another during gamete formation
true
Gregor Mendel is the scientist that is considered the pioneer of the field of heredity because he established the fundamental laws of inheritance. Mendel worked with pea plants, and observed their traits. From his work he discovered the law of dominance, law of segregation, and law of independent assortment.
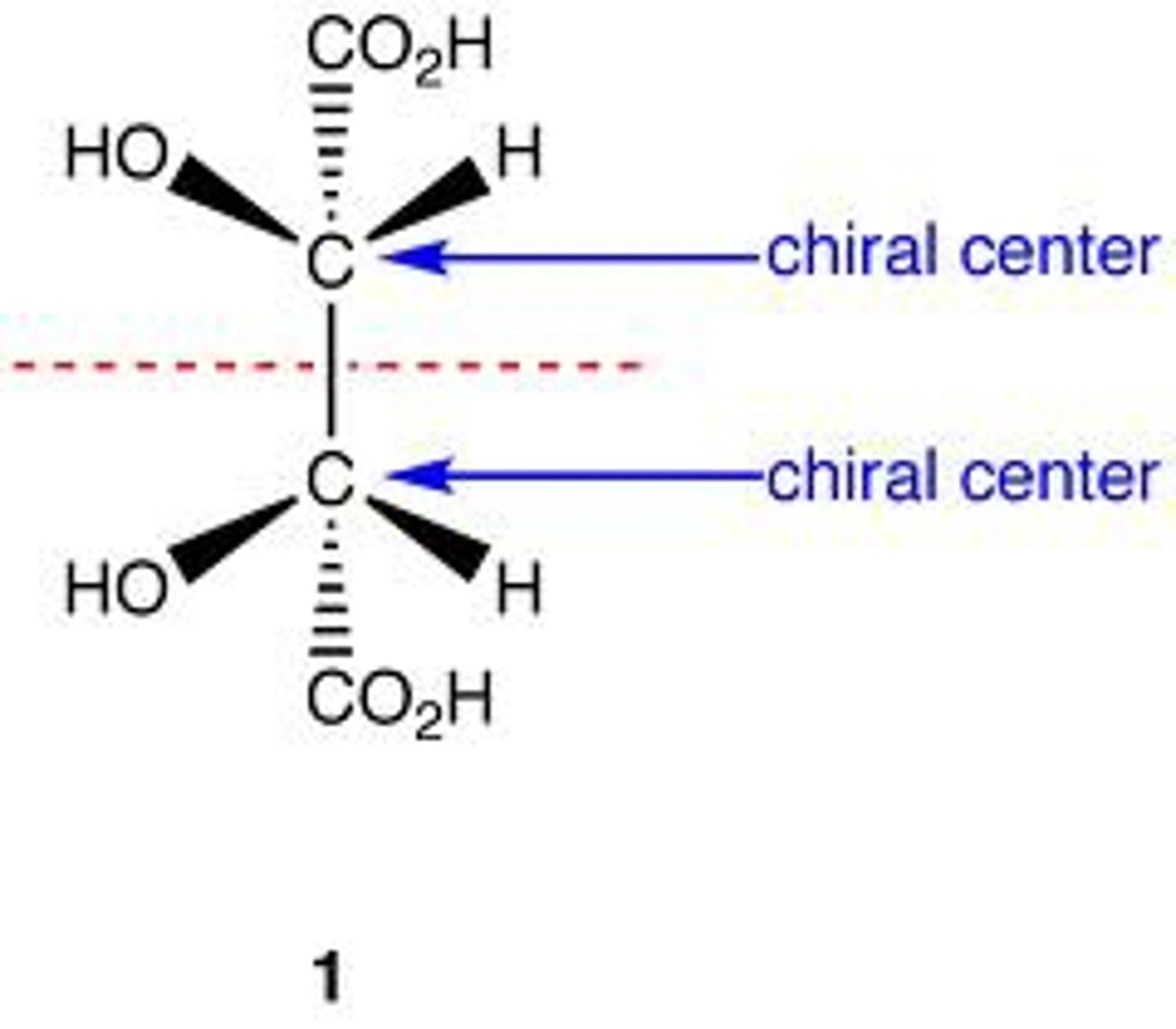
Meso compounds are optically
inactive
meso compound has
multiple stereocenters but optically inactive
meso compound
-multiple chiral centers
-optically inactive
-has a plane of symmetry
-achiral
-to identify a meso compound, you can look for an internal plane of symmetry and determine the R or S configuration of each chiral center. If the molecule has an internal plane of symmetry and the chiral centers have opposite configurations, then it is a meso compound.
true statement
ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is indeed the most abundant type of RNA in a cell, while messenger RNA (mRNA) is considered the least abundant
calorimetry
The precise measurement of heat flow out of a system for chemical and physical processes
calorimetry equation
q=mcΔT
dna replication steps
1) Helicase- unwinds the parental double helix
2) DNA topoisomerase - upstream of helices alleviating torsional strain
3) Single-strand binding proteins (SSBP) stabilize unwound DNA, aided by DNA gyrase.
4) Primase synthesizes a short RNA primer for DNA polymerase to bind to in the 5' to 3' direction to start replication on each strand.
5) DNA polymerase synthesizes the leading strand in 5' to 3' direction while the lagging strand is made discontinuously by primase making short pieces and then DNA polymerase extending these to make Okazaki fragments.
6) DNA ligase joins the Okazaki fragments together
dna replication
initiation, elongation, termination
first ionization energy
the energy required to remove the first electron from an atom
second ionization energy
the energy needed to knock off the second valence electron
third ionization energy
the energy required to remove the third electron
fourth ionization energy
the energy required to remove the fourth electron
the amount of energy needed to remove the fourth electron from a gaseous atom, essentially measuring the energy required to create a +4 charged ion from a neutral atom by taking away four electrons; it is typically significantly higher than the first, second, and third ionization energies due to the increasing difficulty of removing electrons from a progressively more positively charged ion
"First ionization energy" refers to the energy needed to remove the first electron from a neutral atom, while "second ionization energy" is the energy needed to remove the second electron from a +1 ion, and "third ionization energy" is the energy needed to remove the third electron from a +2 ion, with each successive ionization energy always being higher than the previous one because it becomes increasingly difficult to remove an electron from a positively charged ion; essentially, the more positive the ion, the stronger the pull on the remaining electrons making them harder to remove.
true
electron affinity
the energy change that occurs when an electron is acquired by a neutral atom
nucleosomes make up chromatin and chromatin makes up chromosome
nucleosomes are the basic repeating units that make up chromatin, and chromatin is the complex of DNA and proteins that ultimately forms chromosomes within a cell nucleus
true
peroxisome vs lysosome
Lysosomes
Break down excess or damaged cell parts, and can destroy viruses and bacteria. They are the cell's recycling centers. They are also generally large but can vary in size and shape.
Peroxisomes
Break down long chain fatty acids and harmful hydrogen peroxide. They are involved in energy metabolism and lipid biosynthesis. Generally small
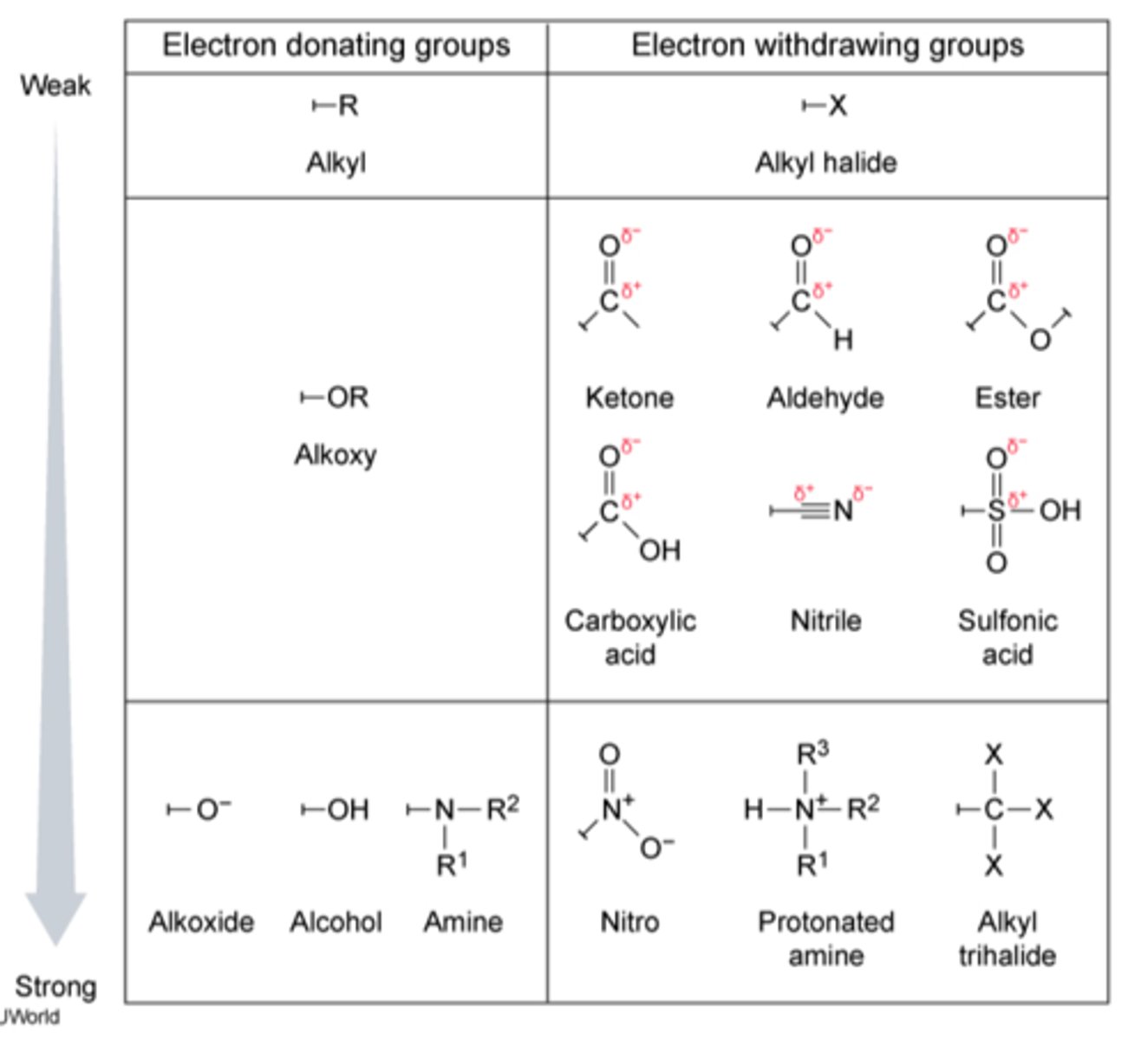
electron donating groups
Groups that push (donate) electron density towards another functional group through sigma or pi bonds.
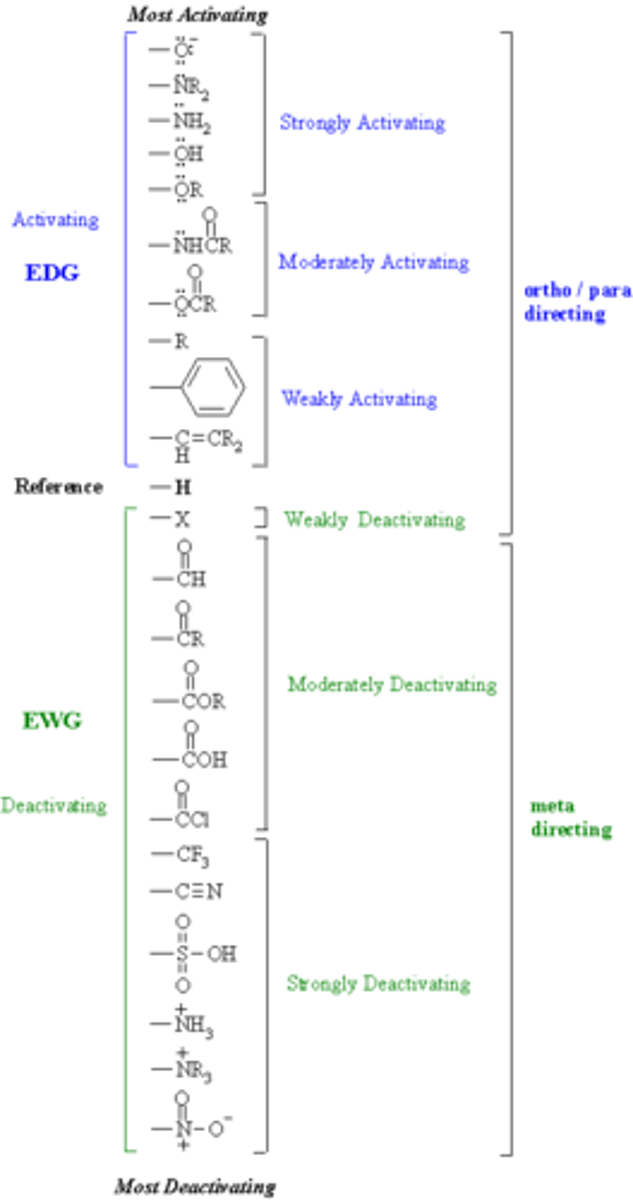
electron withdrawing groups
An electron withdrawing group or EWG draws electrons away from a reaction center. Makes it less nucleophilic
When this center is an electron rich carbanion or an alkoxide anion, the presence of the electron-withdrawing substituent has a stabilizing effect
Nitro groups, cyano groups, sulphano groups, carbocylic acids, esters (unless attached to Oxygen of an OR, then EDG), quanterary amines,
degree of unsaturation
U = (2C - H + N + 2)/2
molecule is saturated if it contains no pi bonds or rings
saturated alkane has formula of CnH2n+2
"Degrees of unsaturation" in chemistry refers to the total number of rings and multiple bonds (double or triple bonds) present in a molecule, essentially indicating how many "unsaturated" sites exist within a compound, calculated based on its molecular formula and used to help deduce a molecule's possible structure; each ring or double bond counts as one degree of unsaturation
linear, quadratic, and cubic
"Linear," "quadratic," and "cubic" refer to the degree of a polynomial, with linear meaning a degree of 1, quadratic meaning a degree of 2, and cubic meaning a degree of 3; essentially, how high the exponent of the variable is in the equation.
In cellular respiration, the sequence goes from glycolysis to pyruvate decarboxylation (also called pyruvate oxidation), then to the Krebs cycle (also known as the citric acid cycle), and finally to the electron transport chain (ETC) - essentially breaking down glucose into energy through a series of steps, with pyruvate decarboxylation acting as the transition phase between glycolysis and the Krebs cycle; all of these stages, except for glycolysis, require oxygen to function properly.
cellular respiration
plants
Plants perform more photosynthesis than cellular respiration because photosynthesis is the process by which they create their own food (glucose) using sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide, while cellular respiration is the process of breaking down that glucose to release energy, meaning plants only need to respire to the extent necessary to utilize the glucose they produce through photosynthesis; during daylight hours, the rate of photosynthesis significantly exceeds the rate of respiration, resulting in a net production of glucose and oxygen.
standard state of elements
Elements in their most stable form at standard conditions
standard states of major elements
Hg and Br are liquid
H2, He, N2, O2, F2, Ne, Cl2, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn are gas
the rest are mostly solid
peregrination
(n.) the act of traveling; an excursion, especially on foot or to a foreign country
PCR can be used to discover all of the following
single nucleotide polymorphisms
short tandem repeats
specific DNA sequences
mutation detection
what is used to detect restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs)
restriction enzymes
Restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs) are the DNA variations among individuals at restriction sites. Restriction enzymes are used to discover RFLPs since they will cut the RFLPs differently in each individual and produce DNA fragments of varying lengths. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) cannot be used to discover RFLPs.
northern blot
Similar technique [to Southern], except that Northern blotting involves radioactive DNA probe binding to sample RNA .
Southern Blotting Technique
The procedure used to isolate and identify DNA fragments from a complex mixture. The isolated denatured fragments are transferred from an agarose gel to a nylon filter and identified by hybridization with probes.
Western blotting
procedure that uses labeled antibodies to detect specific antigens in a mixture of proteins separated according to their molecular weight
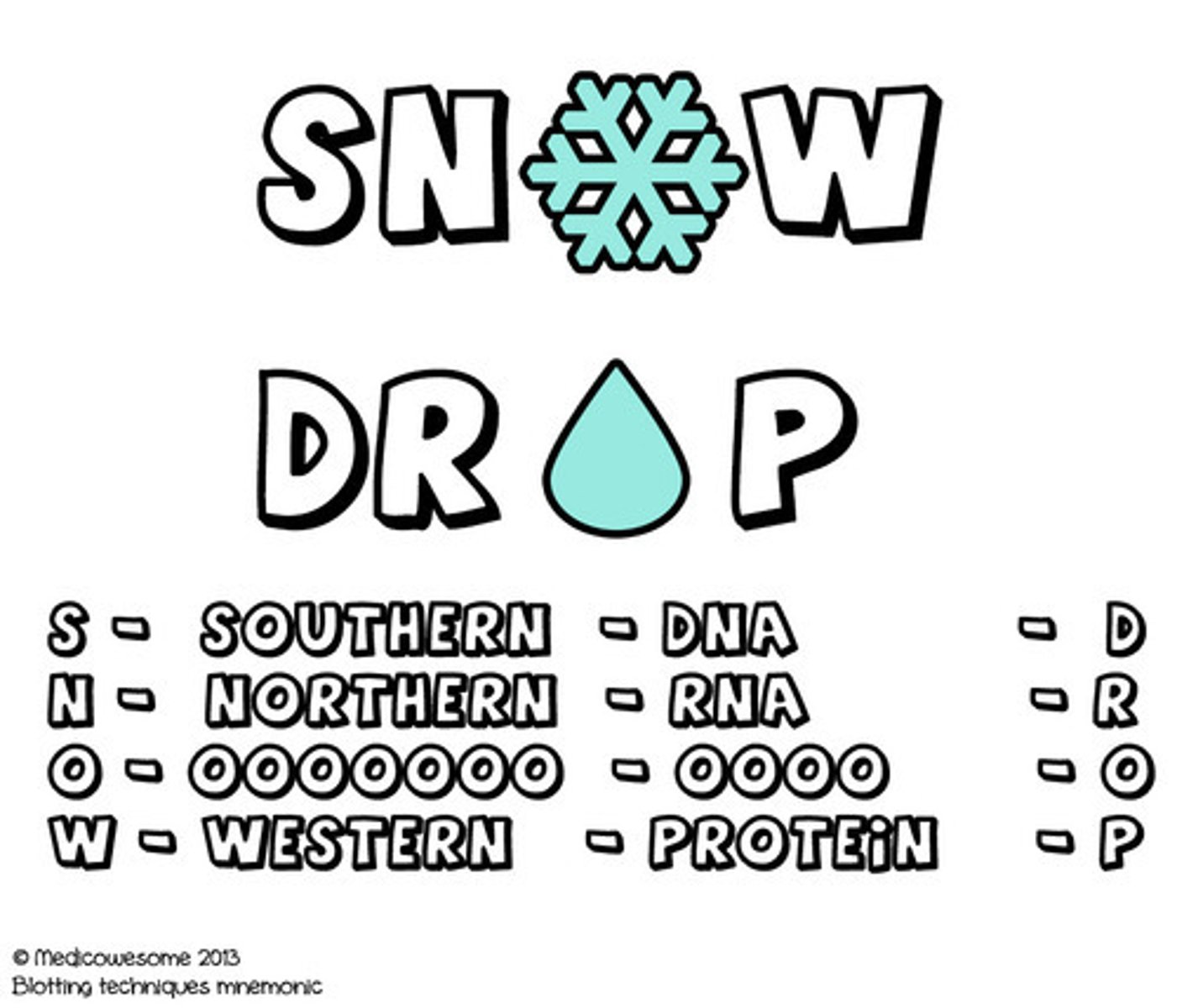
acronym for blotting techniques
The most common acronym used to remember the different blotting techniques is "SNOW-DROP," where "S" stands for Southern Blot (DNA), "N" for Northern Blot (RNA), "W" for Western Blot (protein), and "D" for the molecule being detected (depending on the blot type).
PCR
(polymerase chain reaction) a method used to rapidly make multiple copies of a specific segment of DNA; can be used to make millions of copies of DNA from a very small amount of DNA
Which of the following will most likely be used to study the expression of a large sample of genes in the genome?
DNA microarray assays
A method to detect and measure the expression of thousands of genes at one time. Tiny amounts of a large number of single-stranded DNA fragments representing different genes are fixed to a glass slide. These fragments, ideally representing all the genes of an organism, are tested for hybridization with various samples of cDNA molecules.
next-generation sequencing
group of automated techniques used for rapid DNA sequencing
A scientist would like to study multiple mutation hot spots in the genome of a patient suffering from breast cancer. Which DNA technology should he use to do so?
DNA microarray assay
Sanger sequencing
A procedure in which chemical termination of daughter strands help in determining the DNA sequence.
DNA microarray assays
The DNA microarray assay consists of thousands of DNA probes representing different genes. Reverse transcriptase is an enzyme that synthesizes cDNA from an mRNA template. The cDNA is then fluorescently labeled and hybridizes with the DNA probes.
horizontal transmission
disease is spread through a population from one infected individual to another
vertical transmission
parent to offspring
functional group priorities
1. Carboxylic acid
2. Anhydride
3. Ester
4. Amide
5. Aldehyde
6. Ketone
7. Alcohol
8. Alkene
9. Alkyne
10. Alkane
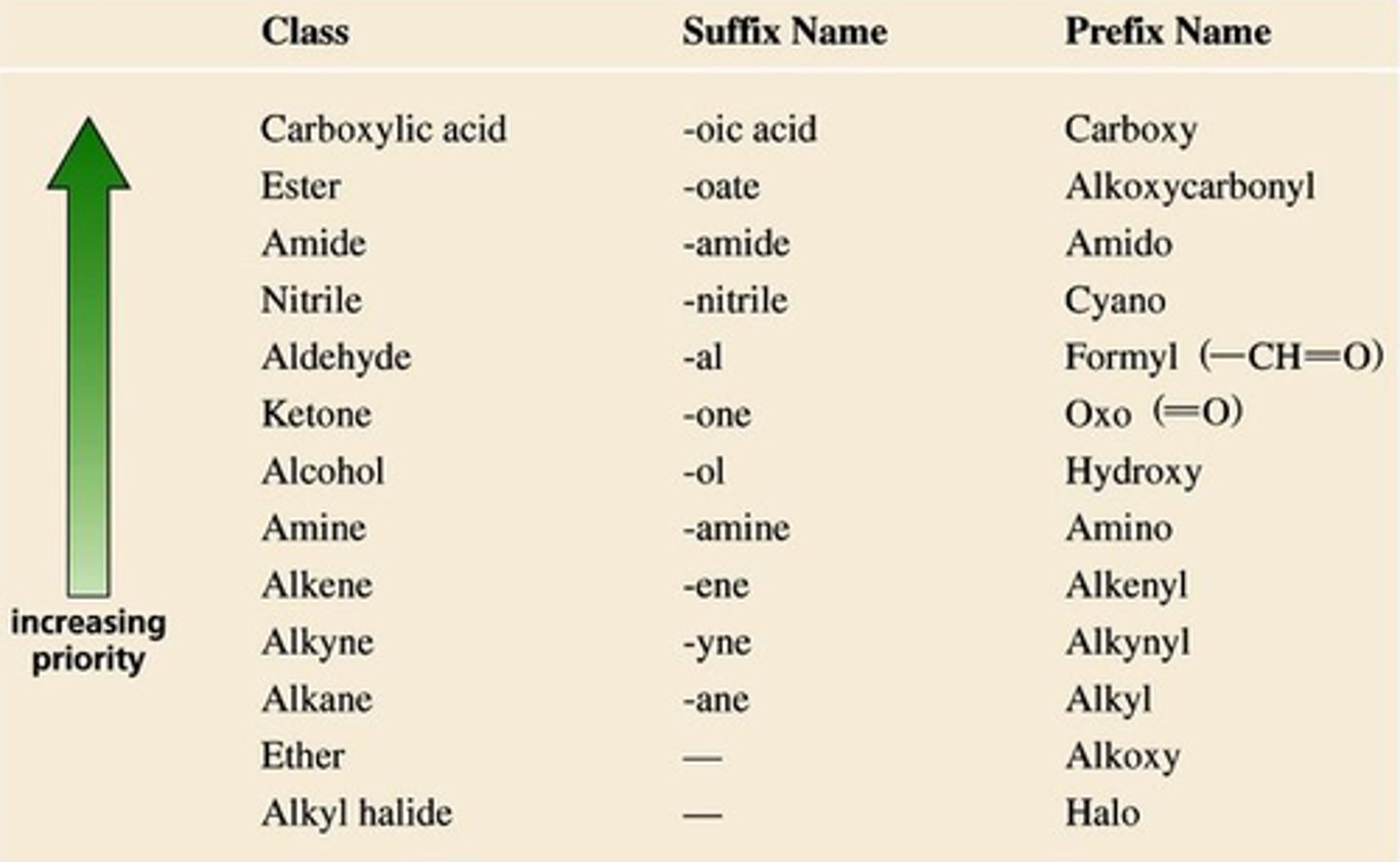
IUPAC rules
IUPAC Rules:
1) Find the longest carbon chain.
• If there is a tie, the one with the most substituents is the parent chain.
2) The terminal carbon closest to a substituent is numbered #1.
• If there is a tie, look at the second substituent.
3) Order the substituents alphabetically and give each one a number to match the carbon to which it is attached
4) If more than one of the same substituent is present, use the prefixes di, tri, tetra, etc. (i.e., 2,2- dimethylbutane).
5) When to use hyphens:
• Hyphens are placed before and after substituent numbers, but NOT between standard prefixes.
6) Rules for alphabetizing:
• Do NOT consider the prefix when alphabetizing the substituents if:
1) it represents a number (di-, tri-, etc.) or 2) it includes a hyphen (sec-, tert-, etc.). Do alphabetize other prefixes (isopropyl, isobutyl, etc.).
aromatic compound derivatives
organic compounds derived from benzene or other aromatic compounds
benzene derivatives
Compounds derived from benzene structure
toluene, ethylbenzene, xylenes, phenol, aniline, nitrobenzene, benzoic acid
Aromaticity Rules
1. cyclic or polycyclic
2. all the atoms in the ring must be spy or sp hybridized
3. the number of pi electrons in a ring must equal 4n + 2 = huckles rule
xylene
The most commonly used clearing agent, particularly in histology as it effectively mixes with both alcohol and paraffin wax, making it a preferred choice for tissue prep in microscopy prep
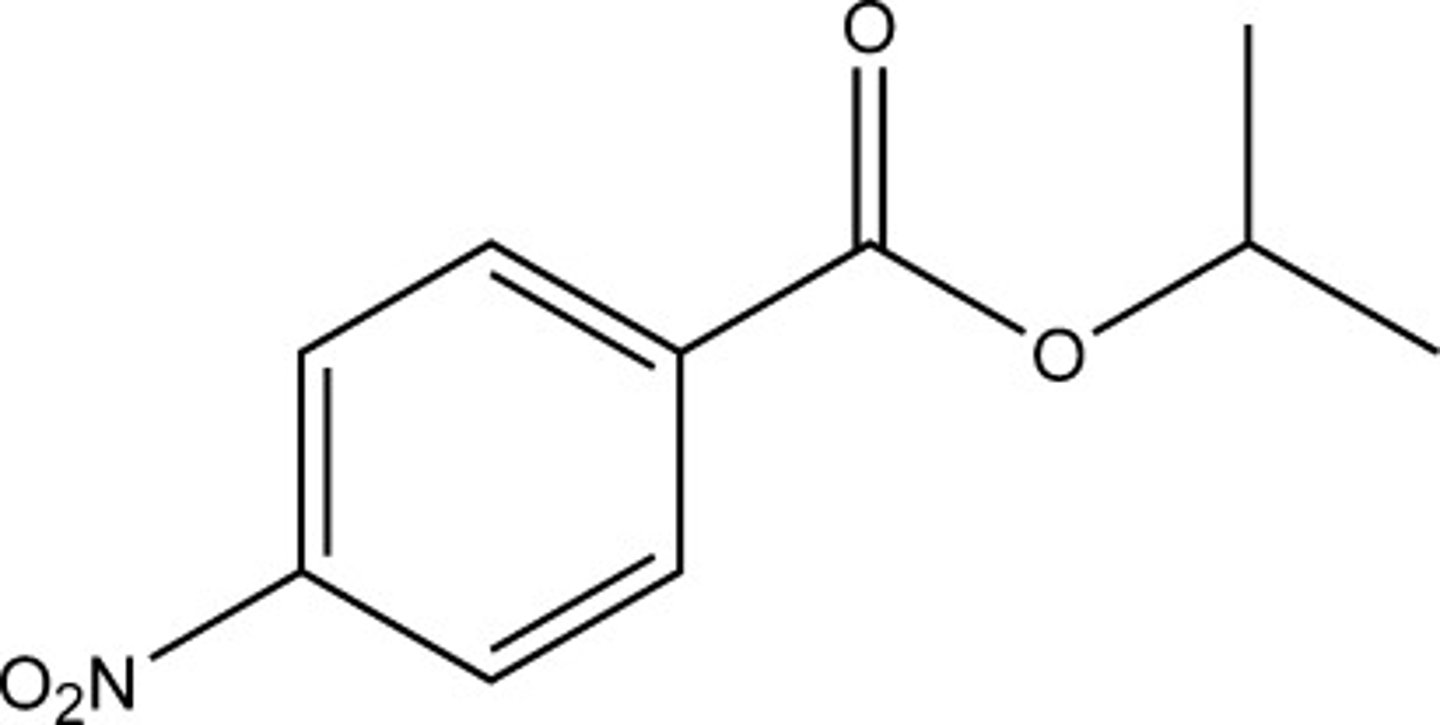
p-nitrobenzoic acid (pKa = 3.41)
At pH 4.5, which of the following acids would be most dissociated?
A) p-nitrobenzoic acid (pKa = 3.41)
B) acetic acid (ethanoic acid) (pKa = 4.74)
C) hexanoic acid (pKa = 4.88)
D) octanoic acid (pKa = 4.89)
dna microarray assay
A method to detect and measure the expression of thousands of genes at one time. Tiny amounts of a large number of single-stranded DNA fragments representing different genes are fixed to a glass slide and tested for hybridization with samples of labeled cDNA.
binary fission
A form of asexual reproduction in single-celled organisms by which one cell divides into two cells of the same size
single parent cell divides into two identical daughter cells without involvement of gametes (sex cells)
A scientist is performing a DNA microarray assay and uses red fluorescence for healthy tissue cDNA and blue fluorescence for malignant tissue cDNA. During analysis, he notices one of the wells has no fluorescence. This means ___________.
The gene in the DNA microarray is not expressed in either healthy or malignant tissue
Blotting techniques in research can be used to identify all of the following EXCEPT one. Which one is the EXCEPTION?
cell density
needed to start a southern blot
gel electrophoresis
bacteria and archaea primarily reproduce through
binary fission
HIV is a
single stranded RNA virus
western blotting uses ___ while southern blotting does not
antibodies
mad cow prions
diseased cow's brain tissue (misfolded proteins)
use western blot as it deals with identifying proteins
southern blotting uses ______ and northern blotting uses ______
DNA probes; RNA probes
genomic library
A genomic library contains a copy of an organism's complete genome. By screening a genomic library, specific genes can be located within the genome.
first step of gene cloning
plasmids are removed from bacterial cells to be used as vectors
after plasmids are removed from bacteria cells, which step needs to follow in the process of gene cloning
extraction of gene of interest from cell
in situ hybridization
A technique using nucleic acid hybridization with a labeled probe to detect the location of a specific mRNA in an intact organism.
in vitro mutagenesis
A technique to discover the function of a gene by introducing specific changes into the sequence of a cloned gene, reinserting the mutated gene into a cell, and studying the phenotype of the mutant.
If a mutation occurs within a gene, its function can be altered. In vitro mutagenesis takes advantage of this by introducing mutations into a cloned gene. Phenotypic changes are observed and can be used to determine the function of the gene of interest.
Basic procedure of in vitro mutagenesis: introduce mutations to cloned gene
true
in vivo mutagenesis
The process of introducing mutations inside living cells using mutator strains
three domains of life
Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya
DAT
Dental Admissions Test
Karyotype
A display of the chromosome pairs of a cell arranged by size and shape.
knockout mice
created by deleting a gene of interest
transgenic organism
Organisms that contain functional recombinant DNA from a different organism