Economics Unit 2
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/33
Last updated 1:21 PM on 11/11/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
1
New cards
Law of Supply
as prices rise, so does supply. there is direct relationship between price and quantity supplied.
2
New cards
Law of Demand
as price falls, quantity demanded rises other things being equal. This describes an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded.
3
New cards
Changes in Quantity Demand (Movement)
a movement can only happen when a price change occurs.
4
New cards
Changes in Quantity Demand (Shift)
* a change in a non price factor causes a shift.
* a demand shift occurs when there is a change in a non price factor.
* a demand shift occurs when there is a change in a non price factor.
5
New cards
Supply Movement
a movement along the line that is caused by a price shift.
6
New cards
SUPPLY Shift (GOOD=RIGHT)
* if the company is able to produce goods, the shift will be to the right which is increasing total quantity produced.
7
New cards
SUPPLY Shift (BAD=LEFT)
* if there is an event that reduces the company ability to produce goods, shift will be to the left, decreasing total quantity produced.
8
New cards
(D.D) change in income
when your income goes up you spend more stuff and vis versa.
9
New cards
(D.D) complementary
items that go well together (ketchup and fries)
10
New cards
(D.D) substitute
goods that can be used to replace another good (coke and pepsi)
11
New cards
(D.D) change in taste and preference
as consumer tastes change so does demand.
12
New cards
(D.D) change in expectations
an expected change in the future price will change in demand today.
13
New cards
(D.D) change in the # of consumers
changes of the # of consumers can happen for a variety of reasons for example death, birth, etc.
14
New cards
(S.D) # of producers
if there are more producers, then total production will increase at all levels.
15
New cards
(S.D) resource price
are the inputs for business. if there is a change in the price of a resource it causes a change in the cost to produce goods,
16
New cards
(S.D) state of tech
tech is used to increase productivity and output. (computers robots, machinery)
17
New cards
(S.D) prices of related goods
related goods for producers are tings that the company could also make instead.
18
New cards
(S.D) nature
change in nature (think weather and natural events)
19
New cards
(S.D) producer expectation
if producers expect prices in the future, it changes their behaviour today.
20
New cards
Slope Demand
is generally considered to slope downward at higher prices consumers buy less.
21
New cards
Slope Supply
is generally considered to slope upward as the prices rise meaning suppliers are willing to produce more.
22
New cards
Surplus
when the price is lesser than the equilibrium price then the quantity supplier is greater than the quantity demanded.
23
New cards
Shortage
when the price is lesser than the equilibrium price then the quantity demanded is greater than the quantity supplied.
24
New cards
Equilibrium
refers to a situation in which the price has reached the level where quantity supplied equals quantity demand.
25
New cards
Unemployment
anyone over the age 16 not in school or who don’t have a job but are actively seeking work.
26
New cards
Seasonal
is unemployment due to seasonal changes in employment or labour supply (wonderland)
27
New cards
Frictional
is a brief period of unemployment caused by moving between jobs or into labour market ex. college or university graduates.
28
New cards
Structural
caused by mis match between the skills or location of job seekers and the requirement or location of available jobs.
29
New cards
Cylical
caused by a lack of job opening a poor level of aggregate demand. occurs during recessions and company cut back workers.
30
New cards
Economic Inequality
an unequal distribution of income and opportunity between different groups of society.
31
New cards
Unemployment Equation
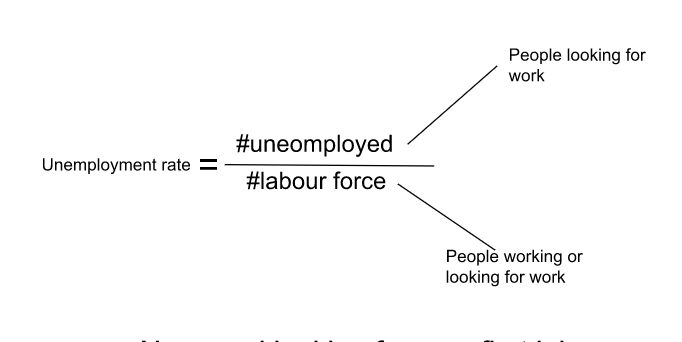
32
New cards
Progressive income tax
the more money you make the more taxes you pay
33
New cards
Regressive taxes
is applied to all citizens no matter what you income is, you still have to pay.
34
New cards
Welfare State
the social safety net is set of government policies to support struggling citizens through taxation and spending.