BMSC 220 MIDTERM
1/320
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
321 Terms
What accounts for most of the wet weight of the cell?
Water (70%)
What is one of the key characteristics of water molecules?
Its polar nature.
Why is water so important to living organisms?
Because it has various biological roles, both passive and active
What are the four major categories of organic molecules?
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Nucleic Acids
Proteins
What sort of bond links carbohydrates?
Glycosidic bonds
What roles do carbohydrates play in cells?
-Major source of nutrients in a cell
-Major structural molecule (ex plant cell wall)
-Signalling and cell recognition (blood typing)
Cellular monosaccharides contain how many carbon atoms?
3 to 7
What number of carbon atoms are most common in cellular monosaccharides?
3,5 and 6
What type(s) of monosaccarides are most common in the cell?
Cyclic forms of 5 and 6 carbon sugars
Structure and function of glycogen?
Structure : branched alpha glucose polymer
Function : Major storage polysaccharide in animal cells
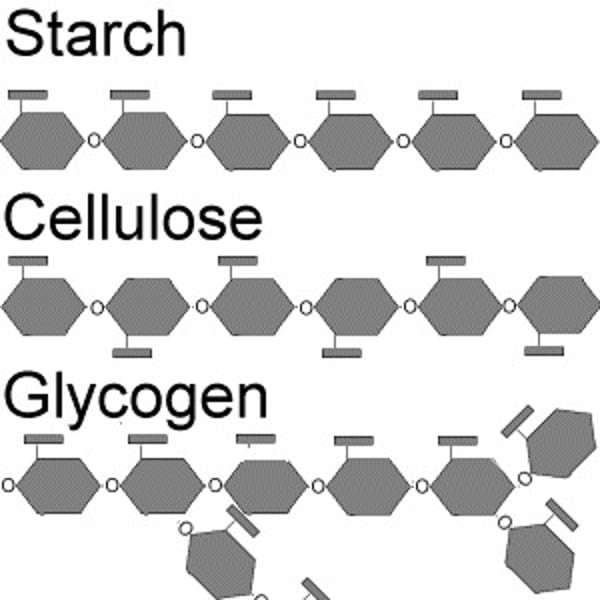
Structure and function of starch?
Structure: branched or unbranched alpha glucose polymer
Function : Major storage polysaccharide in plants
What is the structure and function of cellulose?
Structure : unbranched polymer of beta glucose molecules
Function : Principal structural component of plant cell walls
What is the function of lipids in a cell?
-Major component of cell membranes **
-Cell signalling
-Cell recognition
What are the simplest lipids and what is their general structure?
Fatty acids are the simplest lipids and consist of long hydrocarbon chains
What is the basic formula of all monosaccharides?
(CH2O)n
What is a saturated fatty acid?
One with no double bonds in the carbon main chain. These molecules are linear
What is an unsaturated fatty acid?
One with double bonds (one or more) along the carbon main chain. These molecules are kinked
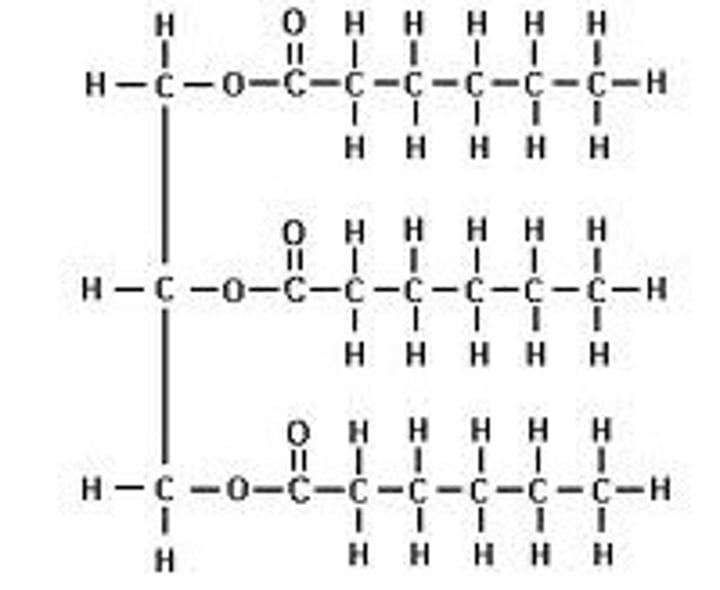
What is the general structure of triacylglycerols?
Three fatty acids linked to a glycerol molecule
What is the general structure of phospholipids?
-Two fatty acids (hydrophobic) attached to a polar phosphate head group (hydrophilic)
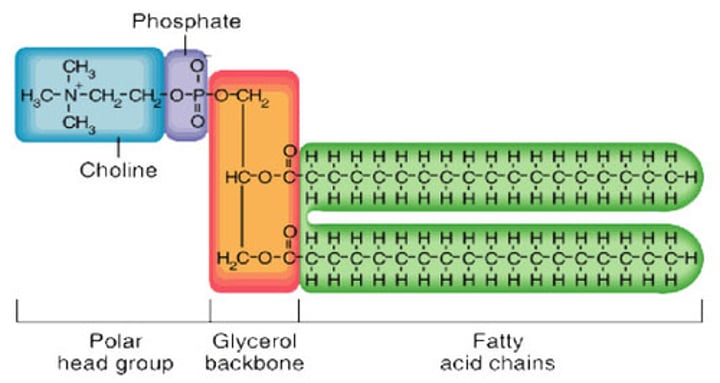
Phospholipids are ____________________________ molecules that are part water soluble and part water insoluble
amphipatic
Apart from phospholipids, what other sorts of lipids do cellular membranes contain?
-Glycolipids (carbohydrate linked to a lipid)
-Cholesterol
Steroid hormones (estrogen, testosterone) are derivatives of _______________ and act as _____________________ both within and between cells
cholesterol
signalling molecules
What is the genetic molecule of the cell and where is it located?
DNA
It is located in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells
What cellular activities do RNA molecules participate in?
-mRNA carries info from DNA to ribosomes
-rRNA and tRNA are involved in protein synthesis
-Other specialized RNAs are involved in gene regulation and others in catalytic functions within the cell
What are DNA and RNA polymers of?
Nucleotides
Nitrogenous bases (purine vs pyrimidine). These bases provide the identity of nucleotides
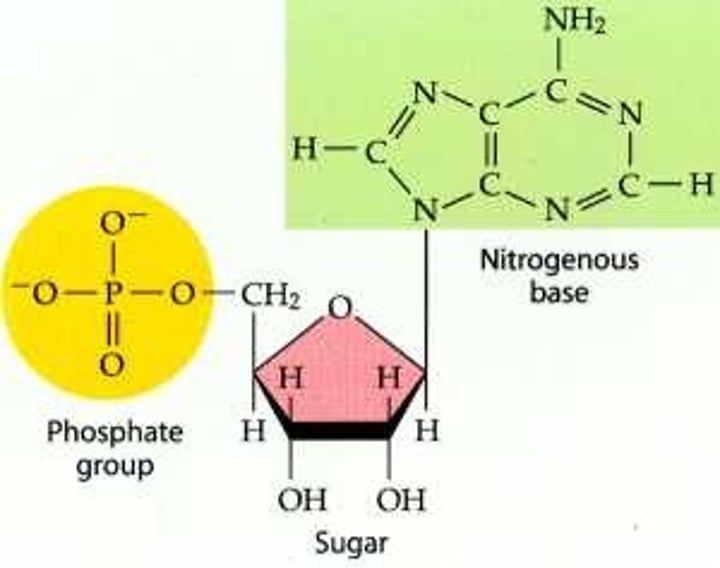
What are the purines?
Adenine
Guanine
What are the pyrimidines?
Cytosine
Thymine
Uracil ** used in place of thymine in RNA
What are nucleosides?
A nitrogenous base linked to the ribose and deoxyribose sugar. They do not have a phosphate group like nucleotides
Do DNA and RNA use the same sugar?
No
DNA - deoxyribose
RNA - ribose
How do nucleotides polymerize to form DNA/RNA?
-Phosphodiester bonds form between the 5' phosphate of one nucleotide and the 3' hydroxyl on the sugar of another
RNA is _____________ - stranded
DNA is ____________ - stranded
Single (but there can be double stranded secondary structure, these are used in specialized functions such as RNA catalytic functions)
Double
How is information in DNA conveyed?
In the order of the bases in the polynucleotide chain
Base pairing in DNA and RNA
A with T (or U in RNA)
G with C
Apart from their role in DNA and RNA formation, what else do nucleotides do in the cell?
-Cellular energetics (ATP)
-Signalling molecule (cyclic GTP)
What is the most fundamental property of proteins?
Their ability to act as enzymes, which catalyze nearly all chemical reactions in biological systems. Without this catalysis, reactions would proceed too slowly to allow for life
All proteins are ___________________________________________
linear chains of amino acids
What is the general structure of amino acids?
A central alpha carbon bonded to an amino group, a carboxyl group, a side chain and a hydrogen atom
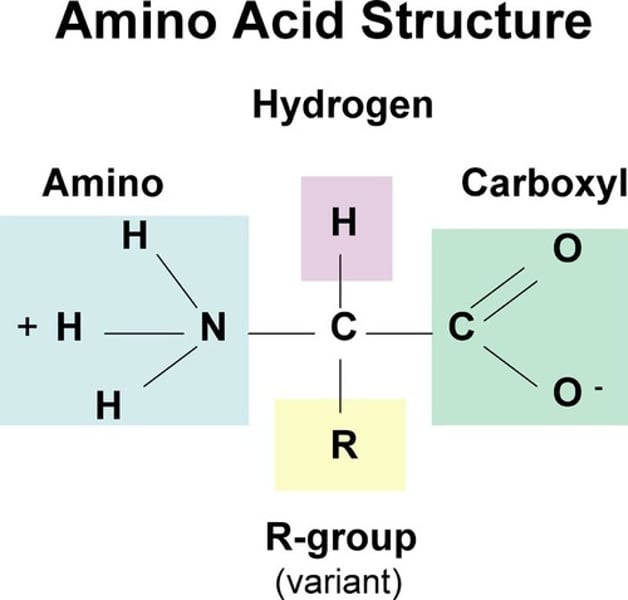
What are proteins polymers of?
Amino acids
How many amino acids are their?
20
What are the four broad groups that amino acids can be categorized into?
-Those with nonpolar side chains (varying degrees of hydrophobicity)
-Those with polar chains (hydrophilic)
-Those with basic (positively charged) side chains
-Those with acidic (negatively charged) side chains
Where are nonpolar amino acids found in a protein?
Since they are hydrophobic they are usually buried in the core of proteins to be kept away from the aqueous environment in and around cells
What sort of bonds join amino acids together?
Peptide bonds
What property of proteins define their characteristics?
Their unique linear sequence(s) of amino acids
What are the different levels of protein structure?
-Primary
-Secondary
-Tertiary
-Quaternary
What is the primary structure of proteins?
The linear sequence of amino acids in the protein's polypeptide chain
What is the secondary structure of proteins?
The regular arrangement of amino acids within localized regions of the polypeptide
What are two types of common secondary structure?
Alpha helices and beta sheets. Both are held together by hydrogen bonds
What is the tertiary structure of proteins?
The folding of the polypeptide chain as a result of interactions between the side chains of amino acids that lie in different regions of the primary sequence
What is the tertiary structure of proteins stabilized by?
-Hydrophobic interactions within the protein
-Hydrophilic interactions on the surface of the protein
-Disulfide bonds between cysteine residues
What is the quaternary structure of proteins?
The interactions between different polypeptide chains in proteins composed of more than one polypeptides
What is the shared and fundamental organization of all cell membranes?
A bilayer of amphipatic phospholipids with associated proteins and other specialized lipids
What are the functions of cellular membranes?
-Separate the interior of the cell from its environment
-Define internal compartments of eukaryotic cels (ex: nucleus, organelles)
-Facilitate the creation of specific internal environments within compartments via selective permeability. This allows for many different sorts of (potentially opposing) chemical reactions to take place within a cell
What is the fundamental building blocks of cell membranes?
Phospholipids
What is the structure of phospholipids?
Two hydrophobic fatty acid chains and a hydrophilic phosphate head group
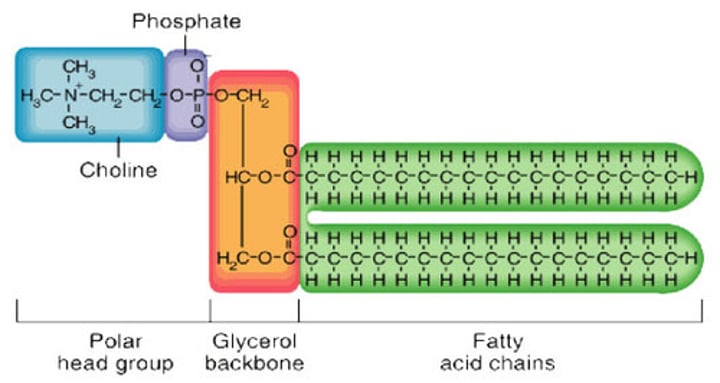
Apart from lipids, what else is part of cell membranes?
Proteins
Are molecules fixed within a cell membrane?
No, individuals molecules are free to rotate and move in lateral directions. Lipid bilayers are dynamic and fluid
What are integral membrane proteins?
Proteins that are embedded directly within the lipid bilayer
What sort of molecules can and cannot pass through cell membranes via simple diffusion?
Small non-polar (hydrophobic) molecules can
Ions and large polar molecules cannot
What are channel proteins?
A group of proteins that form open pores through the membrane and allow free passage of any molecule of appropriate size and structure.
They can be thought of as open doorways since they directly link the extra and intra cellular spaces
What are carrier proteins?
A group of transport proteins found in cell membranes that selectively bind and transport specific small molecules. Ex: glucose
They can be thought of as revolving doors. Although they allow molecules through, they never cause a direct opening between the extra and intra cellular spaces
What is passive transport?
A process in which molecules are transported by either channel or carrier proteins across membranes in the energetically favourable direction
What is active transport?
A process in which molecules are transported in energetically unfavourable directions across a membrane by using ATP hydrolysis as a source of energy
What is systems biology?
A large scale 'whole picture' approach to biology problems. The core tenet of the approach is that complex biological behaviors / systems cannot be reduced to the linear sum of their parts' functions
What is the general role of the nucleus?
It plays a central role in gene expression and the regulation of genome activity
Apart from having membrane bound organelles, what is a key feature that distinguishes eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic cells?
The presence of a nucleus
What biochemical processes happen in the nucleus?
- DNA replication
-RNA synthesis
- RNA processing
- Ribosome assembly
__________________ information is found in the _____________________
Genetic
nucleus
Why is having a nucleus important to eukaryotic life?
A nucleus allows for the separation of the genome from the site of protein synthesis (happens in the cytoplasm). This plays a central role in eukaryotic gene regulation that otherwise wouldn't have been possible
What separates the contents of the nucleus from the cytoplasm?
The nuclear envelope
What establishes the nuclear composition and controls the traffic of proteins and RNAs through the nucleus?
Nuclear pore complexes
What are nuclear pore complexes?
Large macromolecular complexes that differ significantly from typical membrane channels and transporters
What is the composition of the nuclear envelope?
-Two phospholipid bilayer membranes
- Underlying nuclear lamina (protein framework)
-Nuclear pore complexes
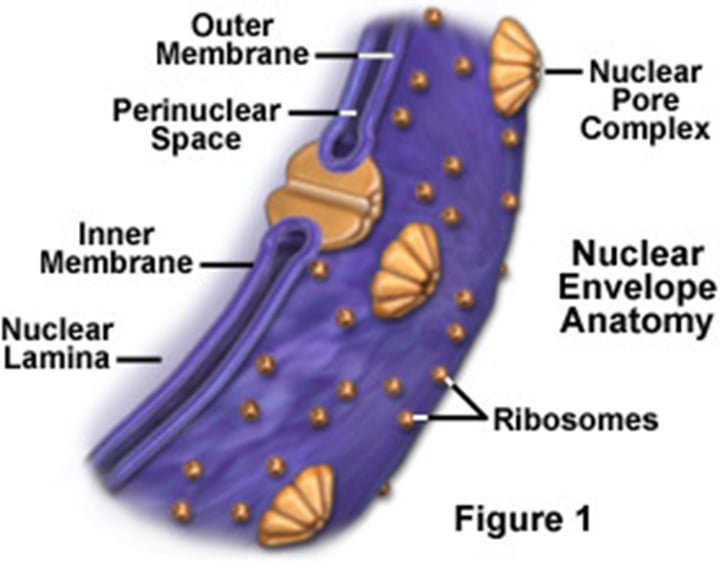
The inner nuclear membrane has __________________ that bind
_________________________
Proteins
the nuclear lamina
What sort of proteins can be found on the outer nuclear membrane?
The outer nuclear membrane is enriched with proteins that bind the cytoskeleton
What is the relationship between the nuclear membrane and the endoplasmic reticulum?
The outer nuclear membrane is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum
What is the nuclear lamina?
A fibrous mesh that provides structural support to the nucleus
What is the composition of the nuclear lamina?
It consists of fibrous proteins called lamins (several types) and other proteins
Who discovered the classical principles of genetics?
Gregor Mendel
What is an allele?
One or two or more alternative forms of a gene. One allele of a gene is inherited from each parent
What does genotype refer to?
The genetic composition of an organism
What does phenotype refer to?
The physical characteristics of an organism. Classically, this was limited to physical appearance, but nowadays includes biochemical and physiological traits
What are chromosomes?
The carriers of genes. They consist of long DNA molecules and associated proteins
What is the central dogma of molecular biology?
DNA --> RNA --> protein
DNA is used to synthesize RNA molecules which are used to synthesize proteins
What is replication?
The synthesis of a duplicate copy of a DNA molecule. It is driven by the action of DNA polymerase. This process relies on DNA/DNA base pairing
What is transcription?
The synthesis of an RNA molecule from a DNA template. It is driven by the action of RNA polymerase. This process relies on DNA/RNA base pairing
What is translation?
The synthesis of a polypeptide chain from an mRNA template. This process is facilitated by ribosomes. This process relies on RNA/RNA base pairing
DNA replication is ___________________________________
Semiconservative
What enzyme catalyzes the synthesis of RNA from a DNA template?
RNA polymerase
What are the types of cellular RNAs and what are their functions?
Messenger RNAs (mRNAs):
-Serve as templates for protein synthesis
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
-Component of ribosomes
Transfer RNAs (tRNAs)
-Adaptor molecules that align amino acids along the mRNA template
Are mRNA, rRNA and tRNA the only types of RNAs?
No, other types of regulatory and catalytic RNAs are also present in cells.
Ex: microRNA (miRNA)
What are codons?
The basic units of the genetic code. They are a three base code that specifies one of the twenty amino acids, a start codon or one of three stop codons
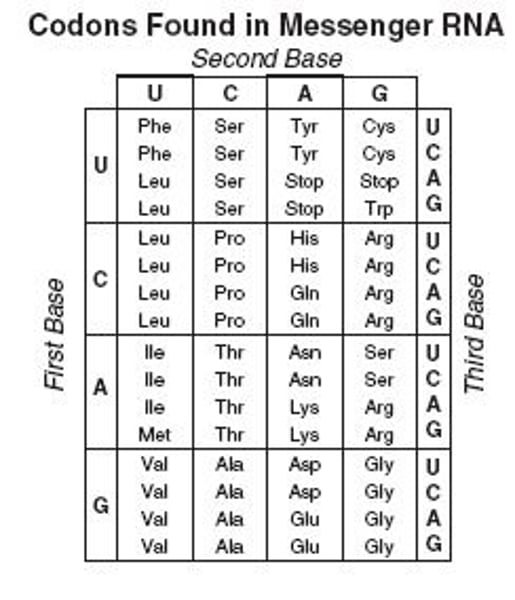
What is the genetic code?
Corresponding information from nucleotide triplets called codons that encode individual amino acids in proteins
How do most genes act on and exert any influence on what happens in the body?
Most genes act by encoding proteins. These proteins are responsible for directing most cellular activities
How do mutations to the genetic code lead to changes in proteins?
Mutations can lead to changes in which an amino acid is inserted within a given position. Mutations can also introduce a premature stop codon leading to a shortened protein
What is a very general trend between an organism's complexity and the size of its genome?
Increased organism complexity = increased genome size
*This is not a direct relationship*
For example, insect and plant genomes vary by several orders of magnitude depending on the species being examined
What is a gene?
A segment of DNA within a chromosome that is expressed to yield a functional product
What do most genes encode?
Most genes encode mRNAs that are subsequently translated into proteins but some genes also encode regulatory and structural RNAs
Genes are made up of what two sorts of segments/sequences?
Exons and introns
What are introns?
Segments of non-protein-coding nucleotide sequences
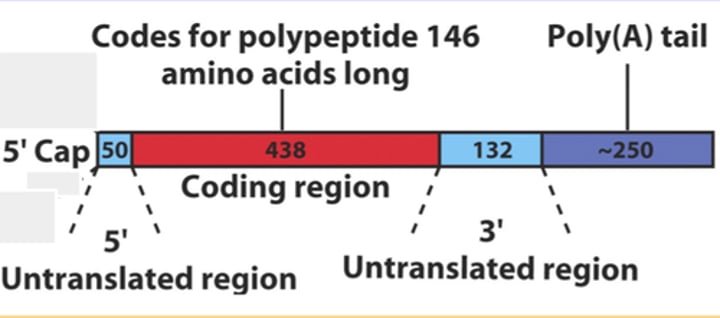
What are exons?
Segments of protein-coding nucleotide sequences. Exons also contain untranslated regions (UTRs) that are not involved in protein encoding