Introduction to Evolution and Natural Selection
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Evolution
Results from a heritable change in one or more characteristics of a population from one generation to the next.
Microevolution
Evolution resulting from a succession of relatively small genetic variations or mutations (to single genes) within a population over time.
Macroevolution
Evolution that results in the formation of a new species or groups of related species.
Natural Selection
The process by which organisms better adapted to their environment tend to survive and produce more offspring.
Survival of the Fittest
A phrase that relates to natural selection, indicating that the most fit individuals are more likely to survive and reproduce.
Genetic Variation
Differences in DNA among individuals within a population.
Darwin's Finches
Different species of finches observed by Darwin that played a crucial role in his formulation of the theory of evolution.
Selective Breeding
The process by which humans breed plants and animals for particular genetic traits.
Biogeography
The study of the distribution of species and ecosystems in geographic space and through geological time.
Convergent Evolution
The process where organisms not closely related evolve similar traits as a result of having to adapt to similar environments.
Fossil Record
The history of life as documented by fossils, which provide evidence of past organisms.
Homologies
Similarities in structure or function that indicate a common ancestry, including anatomical, developmental, and molecular homologies.
Atoms
The smallest unit of an element; all matter is composed of atoms.
Molecules
A group of two or more atoms chemically bonded together.
Macromolecules
Large molecules typically composed of thousands of atoms.
Organelles
Structures or 'organs' of the cell.
Cells
The simplest unit of life.
Tissues
Many cells of the same type that perform a specific function.
Organs
Two or more types of tissues performing a specific function.
Organisms
Individual living 'things' made up of a collection of different organs.
Population
A group of organisms of the same species occupying the same environment.
Community
All organisms (i.e. different species) that interact with one another in a particular environment.
Ecosystem
Interactions of a community of organisms with their physical environment.
Biosphere
The worldwide ecosystem (i.e. Earth) including in the air, in bodies of water, on the land, and in the soil.
Darwin's Finches
A group of birds observed by Darwin in the Galapagos Islands, instrumental in his theory of evolution.
Natural Selection
The process by which differences among species, caused by inheritance and variation of traits, lead to competition and survival of the fittest.
Common Ancestor
The shared ancestor of different species, from which they evolved.
Genetic Variation
Differences in traits among individuals of a species, resulting from genetic mutations.
Modification of Species
The process by which organisms evolve from pre-existing organisms over time.
Survival of the Fittest
The concept that individuals with advantageous traits are more likely to survive and reproduce.
Evolution
The change in the inherited characteristics of biological populations over successive generations.
Beak Size Variation
Differences in beak sizes and shapes among Galapagos finches that affect their feeding efficiency.
Reproductive Success
The ability of an individual to survive and reproduce, passing on advantageous traits to offspring.
Inheritance of Traits
The process by which genetic traits are passed from parents to offspring.
Galapagos Islands
The location where Darwin spent five weeks and made significant observations for his theory.
Species Modification
The idea that species can change over time from a common ancestor.
1859 Publication
The year Darwin published 'On the Origin of Species', discussing his theories on evolution.

Genetic Basis of Traits
The underlying genetic factors that determine traits, which were not understood in Darwin's time.
Environmental Adaptation
The process by which species evolve traits that better suit them to their environment.
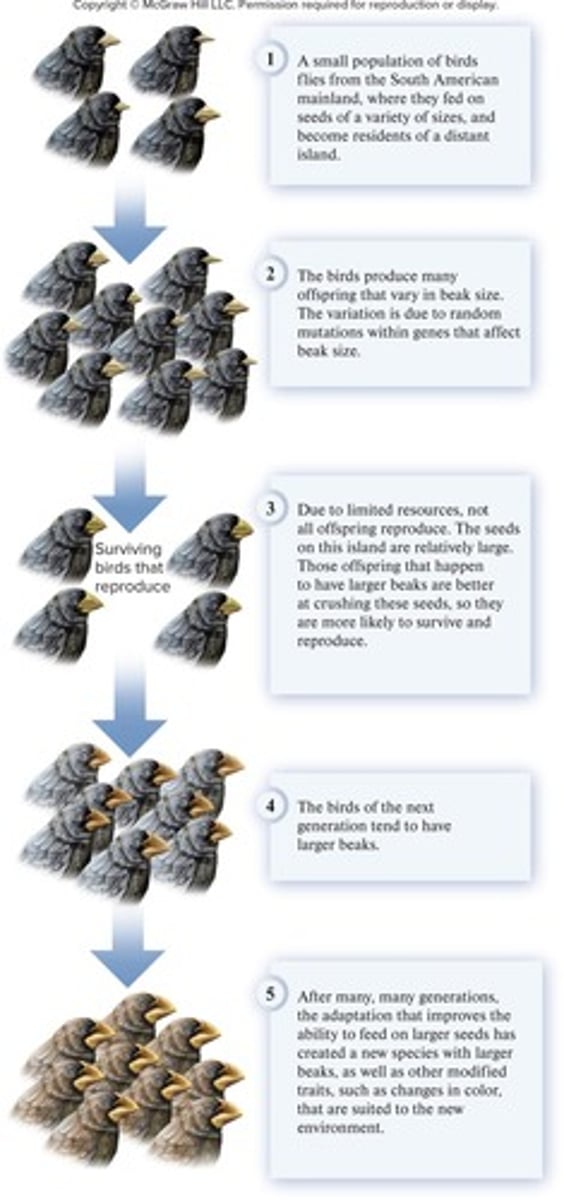
Competition for Resources
The struggle among individuals for limited resources, influencing natural selection.

Evolutionary Change
The gradual development of species over long periods due to natural selection.
Ancestral Species
The species from which modern species have descended.
Feeding Behavior
The different ways species obtain food, influenced by their physical adaptations.
Heritable Traits
Traits that can be passed from one generation to the next, influencing survival and reproduction.
Natural Selection
The process by which better adapted individuals survive and reproduce, passing on their adaptations to the next generation.
Survival of the Fittest
A phrase used as an alternative to natural selection, indicating that those best adapted to their environment are more likely to survive.
Negative Trait(s)
Traits that decrease an individual's ability to survive and reproduce, which can be passed to offspring.
Biological Evolution
The process that leaves marks of evidence to compare relatedness between organisms, supporting the theory of evolution.
Phylogenetic Tree
A diagram that links all life by showing the passage of genes along branches representing evolutionary relationships.
Homologies
Similarities in anatomy, development, or molecular structure among different organisms indicating common ancestry.
Selective Breeding
Programs and procedures designed to modify traits in domesticated species, also known as artificial selection.
Artificial Selection
A process where breeders choose parents to enhance desirable traits in offspring.
Genetic Variation
The diversity in gene frequencies within a population, which is essential for selective breeding.
Desirable Phenotypes
Traits that are chosen by breeders during selective breeding to enhance specific characteristics.
Biogeography
The study of the geographic distribution of extinct and living species.
Endemic Species
Plants and/or animals that are naturally found only in a particular location.
Convergent Evolution
The process where two different species from different lineages develop similar characteristics due to occupying similar environments.
Aerial Rootlets
Structures found in English ivy and wintercreeper that demonstrate convergent evolution.
Fossils
Preserved remains of past life that provide information regarding evolutionary change among related organisms.
Evolutionary Relationships
Hypotheses about how extinct organisms relate to present-day counterparts based on fossil evidence.
Age Comparison of Fossils
The method of comparing fossils based on their age to reveal successive evolutionary changes.
Extinct Organisms
Species that no longer exist, which can be studied through fossils to understand evolutionary history.
Present-day Counterparts
Current species that can be compared to extinct organisms to hypothesize evolutionary relationships.
Homology
A similarity between organisms that occurs due to descent from a common ancestor.
Anatomical homologies
The comparison of body structure between different organisms.
Developmental homologies
The comparison of the process and structures involved in the development of different organisms.
Molecular homologies
The comparison of molecular level aspects (DNA, RNA, and proteins) of different organisms.
Molecular evolution
The process of evolution at the level of genes and proteins.
Phenotype
The physical characteristics of every organism mainly determined by the proteins they possess.
Genotype
The genetic constitution of an organism, specified by the order of nucleotides in their DNA.
Nucleotides
The basic building blocks of DNA and RNA.
Amino acids
The building blocks of proteins, with most proteins for every organism based on the same 20 amino acids.
Chromosome structure
The arrangement and organization of DNA within a chromosome.
Chromosome number
The total count of chromosomes in a cell, which can change during evolution.
Common ancestor
An ancestral organism from which multiple species have descended.
Similarity %
A measure of how closely related two organisms are based on genetic comparisons.
Human chromosome 2
A large chromosome in humans that is a fusion of two separate chromosomes found in other primates.
Inversion
A chromosomal rearrangement in which a segment of a chromosome is reversed end to end.
DNA → RNA → Protein
The central dogma of molecular biology describing the flow of genetic information.
p53
A protein involved in regulating the cell cycle and is compared in molecular homology studies.
Molecular homology relationships
Relationships determined by comparing DNA, RNA, and/or protein sequences among organisms.
Evolutionary change
The process through which species undergo changes over time, often evidenced by homologies.