Proprioception and Vestibulation
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
somatosensation
The body senses, including body position, touch, skin temperature, and pain.
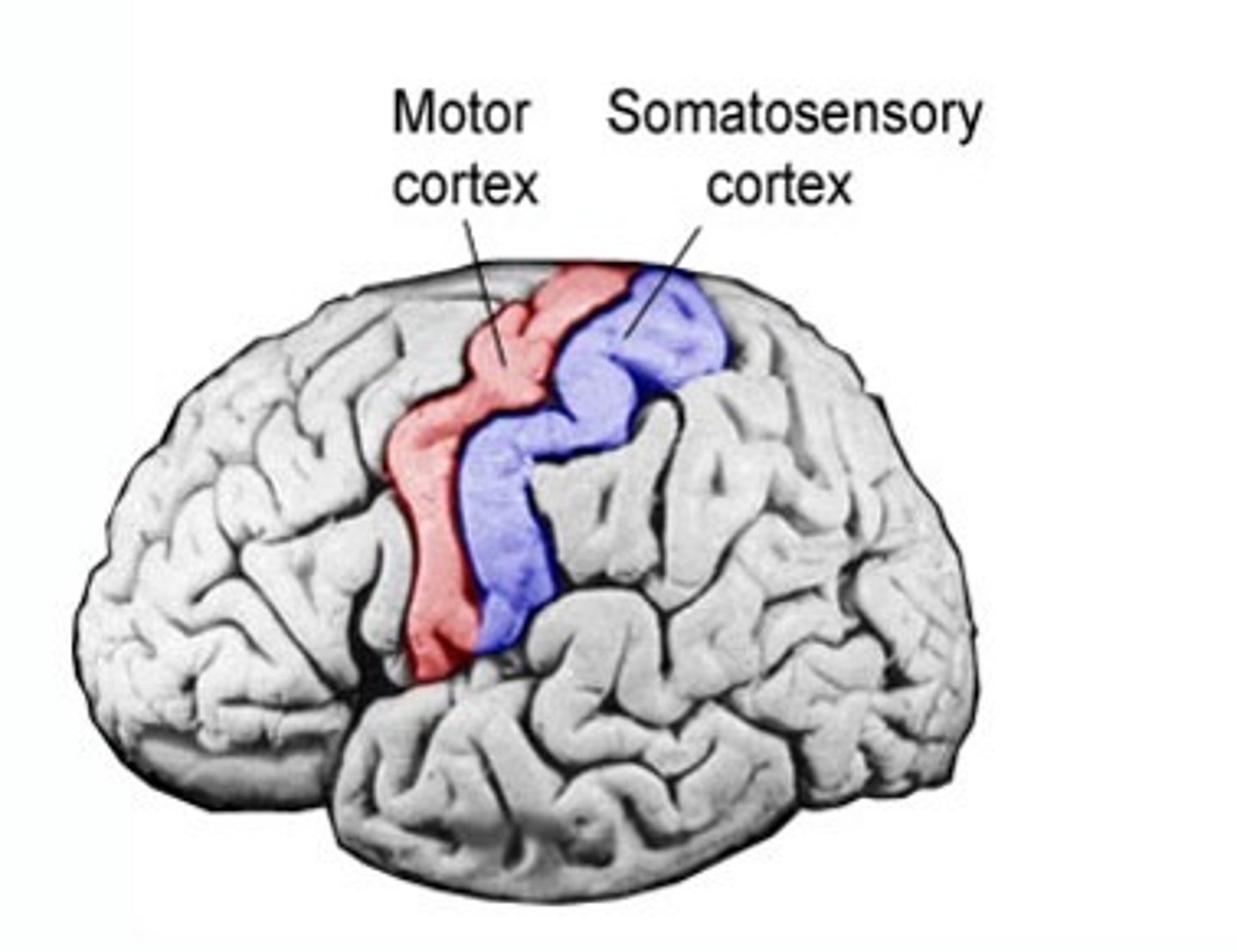
somatosensory and motor cortex (and homunculus)
work together to create awareness of the world; motor cortex (frontal lobe) sends message for action, SS cortex (parietal lobe) confirms action was done through touch
proprioception
ability to tell where one's body is in space

body image
the way you see your body

rubber hand illusion
The false perception of a fake hand as belonging to a perceiver, due to multimodal sensory information.
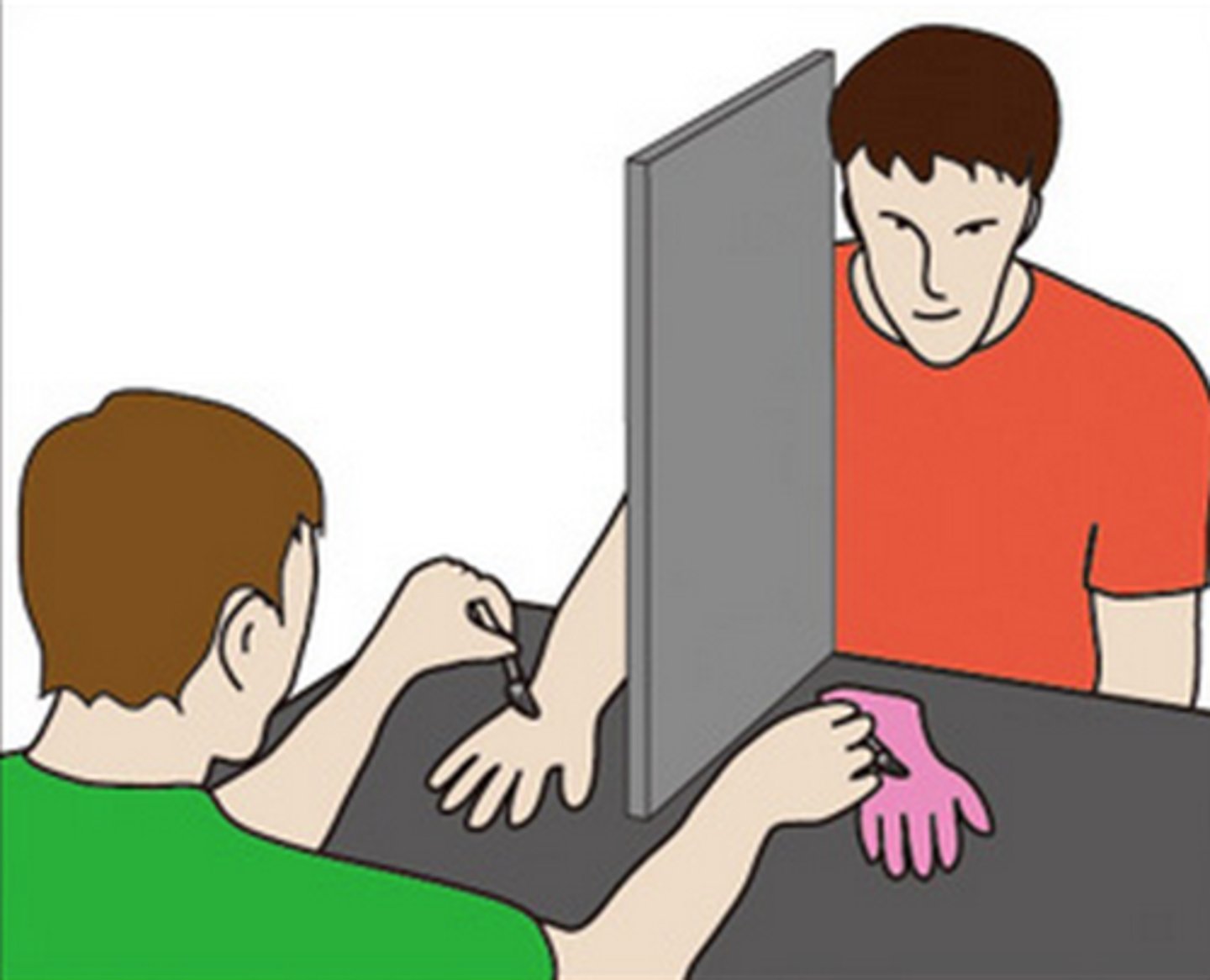
phantom limb syndrome and mirror box treatment
using a mirror to create illusion that missing amputated limb is present to "trick" brain into perceiving phantom limb as moving and reduce phantom pain

vestibulation
sense of balance or spatial awareness
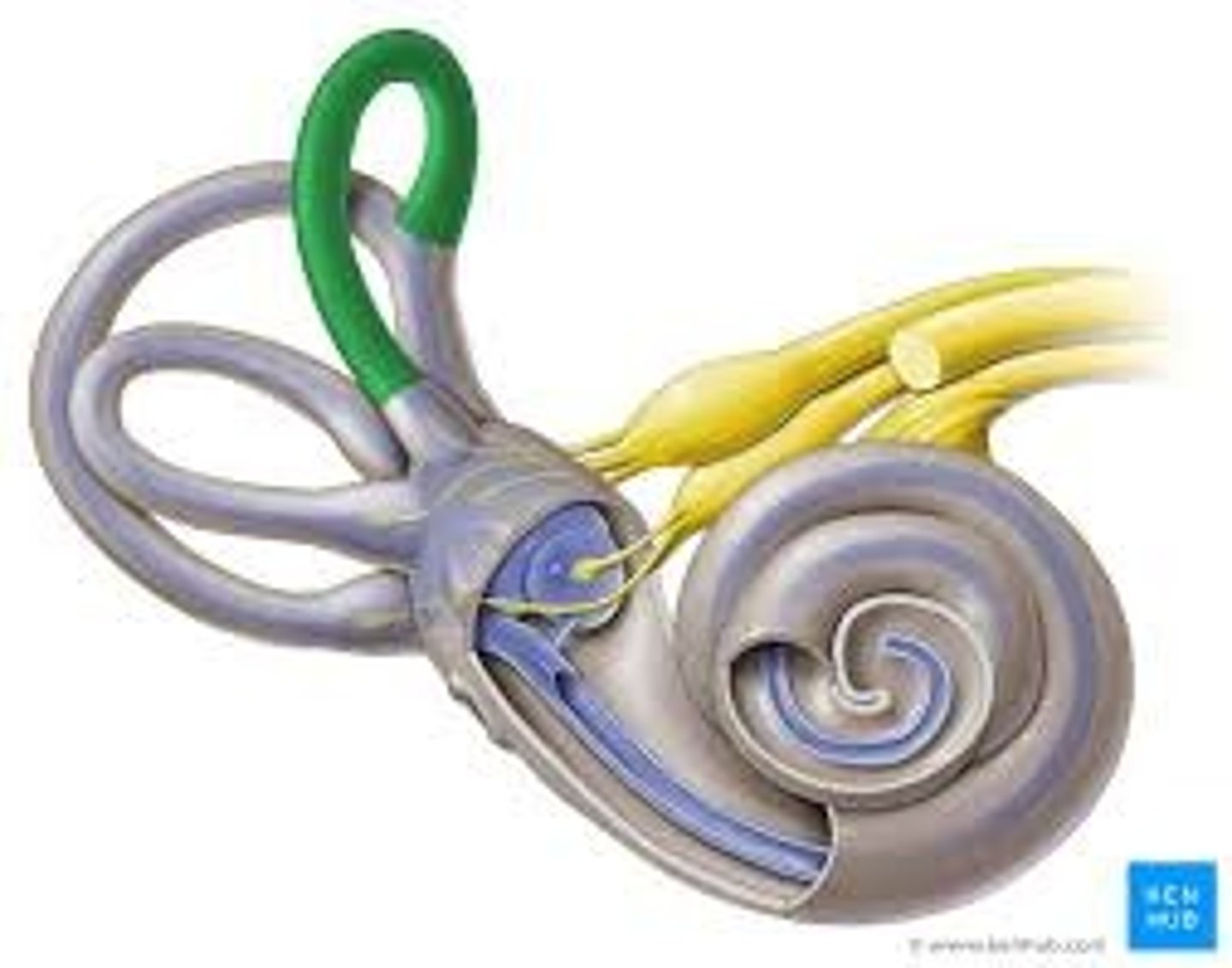
semircircular canals and otolith organs
parts of vestibular system: THREE fluid-filled, looped tubes within ear that detect movements of the head and provide sense of dynamic equilibrium essential for maintaining balance; utricle and saccule in inner ear for detecting linear motion and gravitational forces
orientation, direction, and heading
overall awareness and positioning within environment; specifies path to move to reach destination; indicates direction one is facing
Tumbling room
space for rough-and-tumble play crucial for developing physical skills like balance, coordination, strength, and agility

vection
the illusion of self-motion in the absence of actual physical movement (e.g. seeing a neighboring train moving and feeling movement when actually stationary)
optical flow
The change in patterns of light rays from the environment as they "flow" over the retina during continuous movement of the eye through the environment, allowing perception of motion, position, and timing.

anti-gravity hill
visual illusion where a car appears to roll uphill, defying gravity, when it's actually rolling downhill
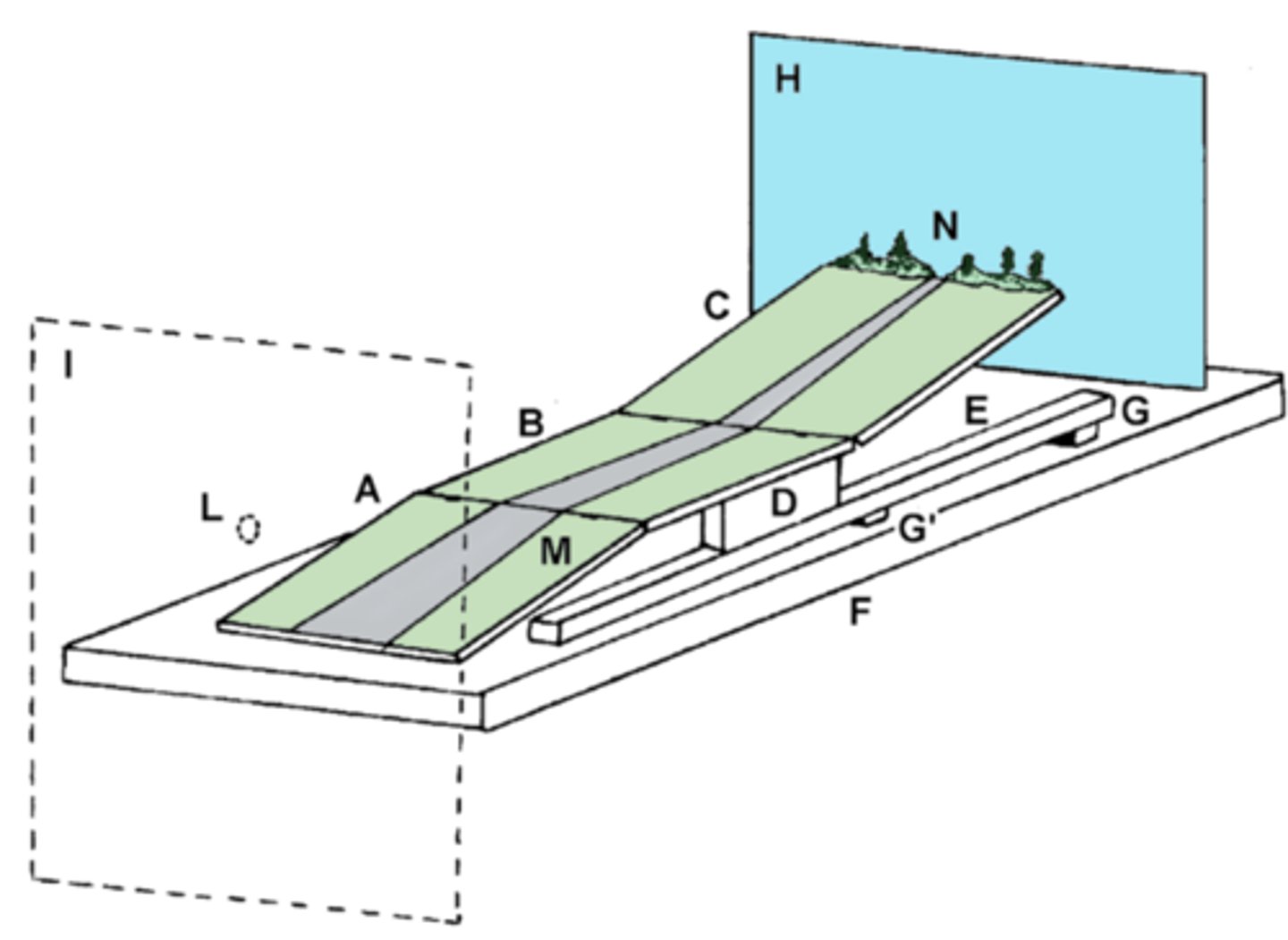
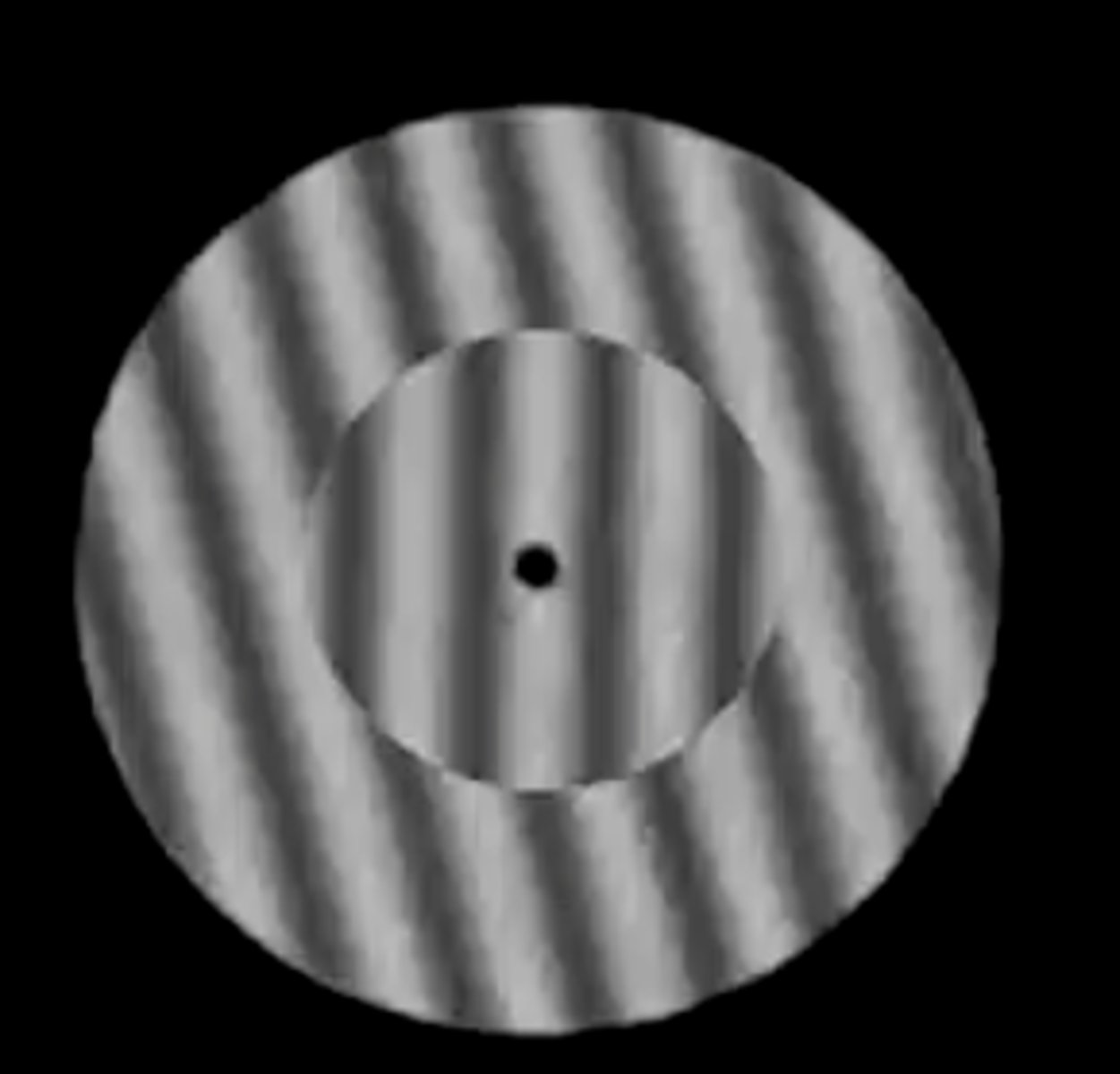
tilt illusion
prolonged adaptation to an oriented stimulus causes shifts in subsequent perceived orientations; surrounding appear tilted due to dysfunction in the central vestibular system (balance and spatial orientation)

mystery spots
locations of psychological and perceptual illusions that are demonstrate how context and environmental cues shape perception and create visual illusions
