Resolution : principles and applications of science
resolution is the ability of a microscope to distinguish between 2 objects that are close together
the limiting factor of a light microscope is the wavelength of light
the theoretical limit to resolution microscope is 20
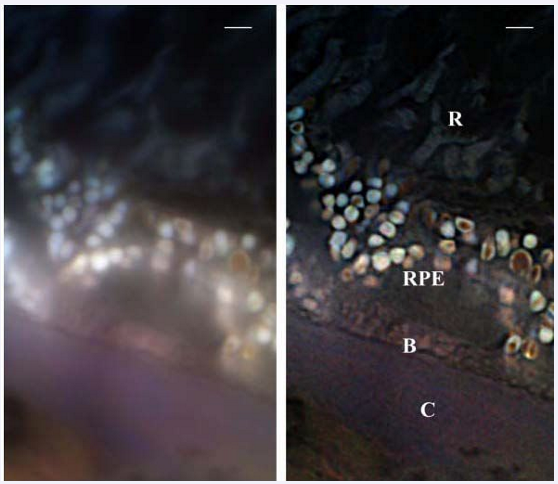
The electron microscope
Much better resolution
uses a beam of electrons instead of light
electrons have a shorter wavelength and therefore greater resolution
resolution is 0.1m,much better than a light microscope
there are two types of electron microscopes
scanning electron microscope
- produces images that are reflected from the electrons/specimen
- also produces a 3D image /looks like a photograph
transmission electron microscopes
produces images from electrons that have passed through and they produce a 2D image
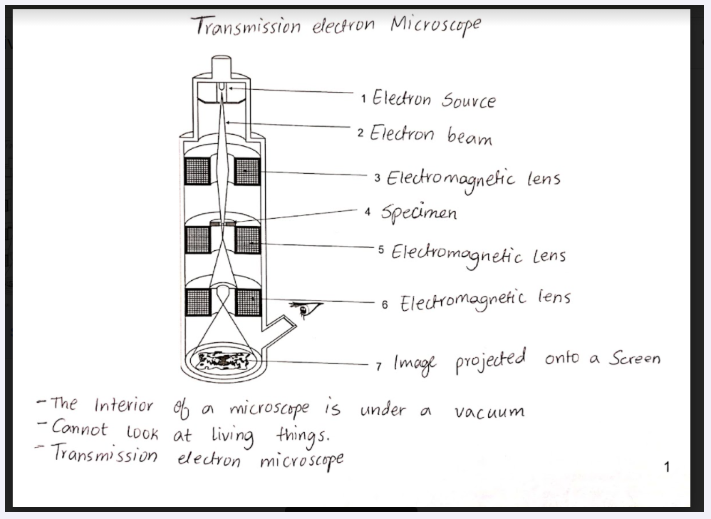
bacteria and blue green algae
- these type of cells are prokaryotes that are prokaryotic organisms
- cells are very small,smaller than red blood cells
- 0.1 to 10 micro meters in length
- they differ from eukaryotic cells in a number of ways
- no nucleus
- they usually have a single circular DNA molecule that acts as their chromosomes
- bacteria only have 3000 types of genes
bacteria
in addition to the main chromosome they have much smaller loops of DNA called plasmids
they have cell membrane and a cell wall
they have a smaller ribosomes than eukaryotic cells (70’s rather than 80’s in eukaryotes)
some have flagella - which differs depending on the structure of the prokaryotic cell
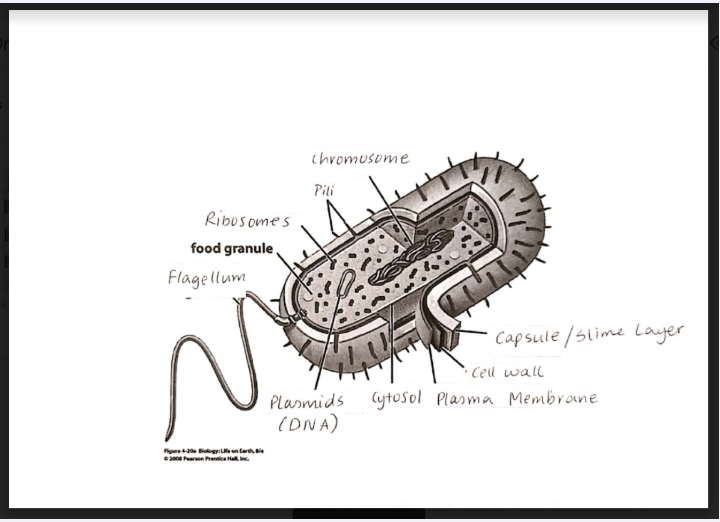
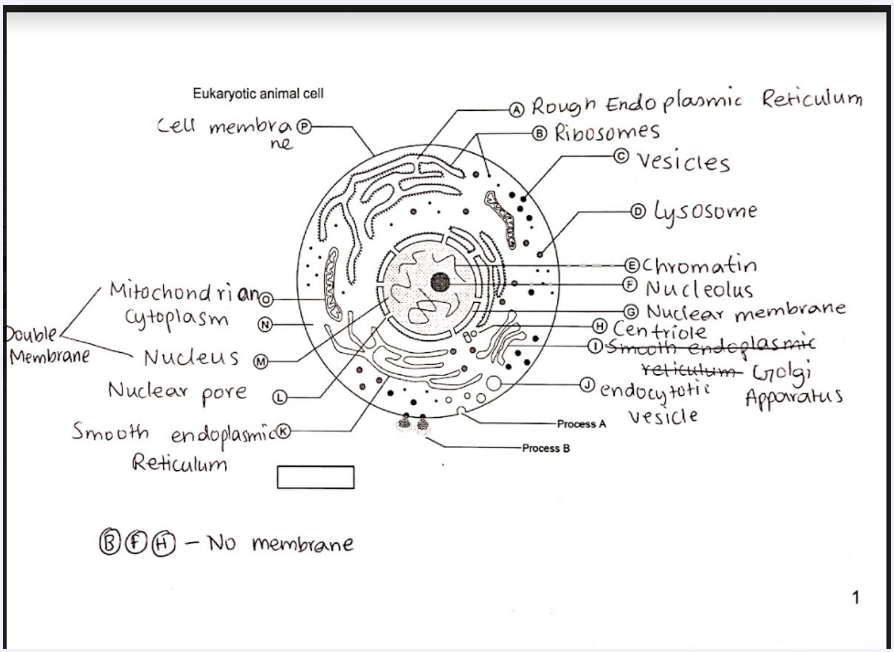
Eukaryotic cells
larger than bacteria,prokaryotes
have a nucleus with membrane
have a membrane bound organelle within the cell
division of labour within the cell
each organelle has a specific function
plant cell