Chapter 2 Bio
1/80
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
Subatomic particles are _____, _______, and ________
protons, neutrons, and electrons
Electrons exist on the shells…
closest to the nucleus
The lower the atomic number…
the lower the pull; more likely to form bonds with other atoms
1 mol of a substance is the amount whose mass in _____ equals its molecular mass in _______.
grams; amu
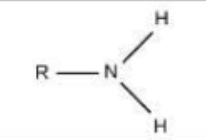
In covalent bonds, electrons are ________
shared
In ionic bonds, atoms _____ or _____ electrons
lose; gain
What consist of anions and cations held together by ionic bonds?
salts
Covalent bonds in which there is unequal sharing of the electrons are called _______.
polar bonds
Covalent bonds in which there is equal sharing of the electrons are called _______.
non-polar bonds
Both bond type and molecular shape determine if a molecule is ____ or _____.
polar; nonpolar
Weak attractions between two or more molecules in close proximity due to changes in electron density are called _______.
Vand der Waals interactions
Weaker bonds between a proton in one atom, and an electronegative atom in the other are called _________.
hydrogen bonds
In liquid water hydrogen bonds are constantly _____, _____, and _______.
made, broken, and remade
In _______, water is heated, kinetic energy increases, causing hydrogen bonds to break + water molecules escape as gas
gas
In _______ temperature is lowered and crystalline structure is maintained.
solid water
______ and ______ molecules can dissolve in water
Ions; Polar
Compounds dissolved or mixed in with the water are called _____.
solutes
Water molecules at the liquid-gas interface stick together due to hydrogen bonding (an attraction between water molecules and other water molecules) is called ______.
cohesion
Surface tension is caused by _______.
cohesion
An attraction between water molecules and other molecules is called ________.
adhesion
Capillary actions is caused by ________.
adhesion
Solutions with high H+ concentration are ______.
acidic
Solutions with high OH- concentration are _______.
alkaline (basic)
Normal human pH is _______
7.4
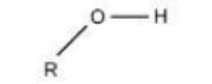
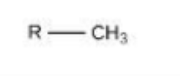
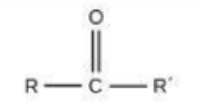
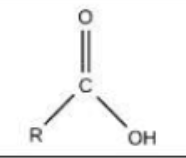
Carbon is a key component of ________.
macromolecules (proteins, carbohydrate, lipids and nucleic acids)
\
This allows it to achieve the octet rule
When hydrocarbons are burned, energy is ________.
released
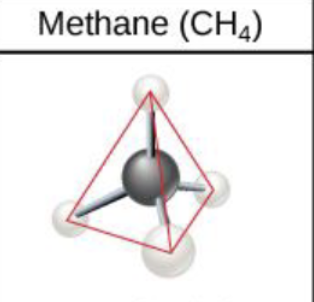
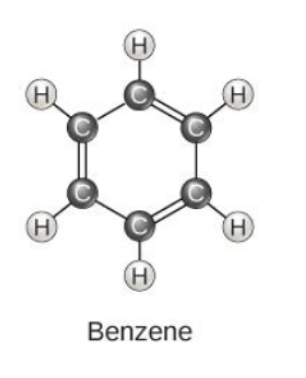
An important hydrocarbon ring used in some amino acids, cholesterol and its derivatives is called ________.
benzene
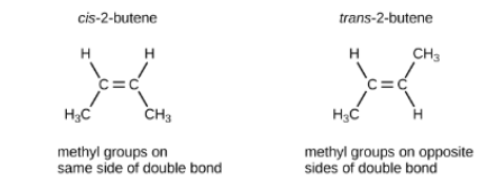
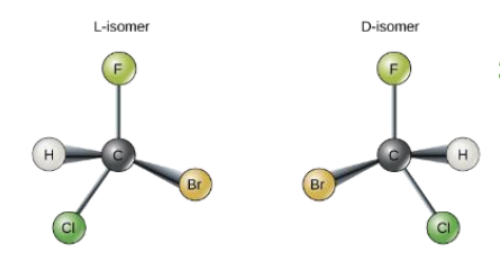
Fatty acids with double bond are _______
unsaturated
Fatty acids with no double bonds are _______
saturated