Bio Lab Exam 1
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
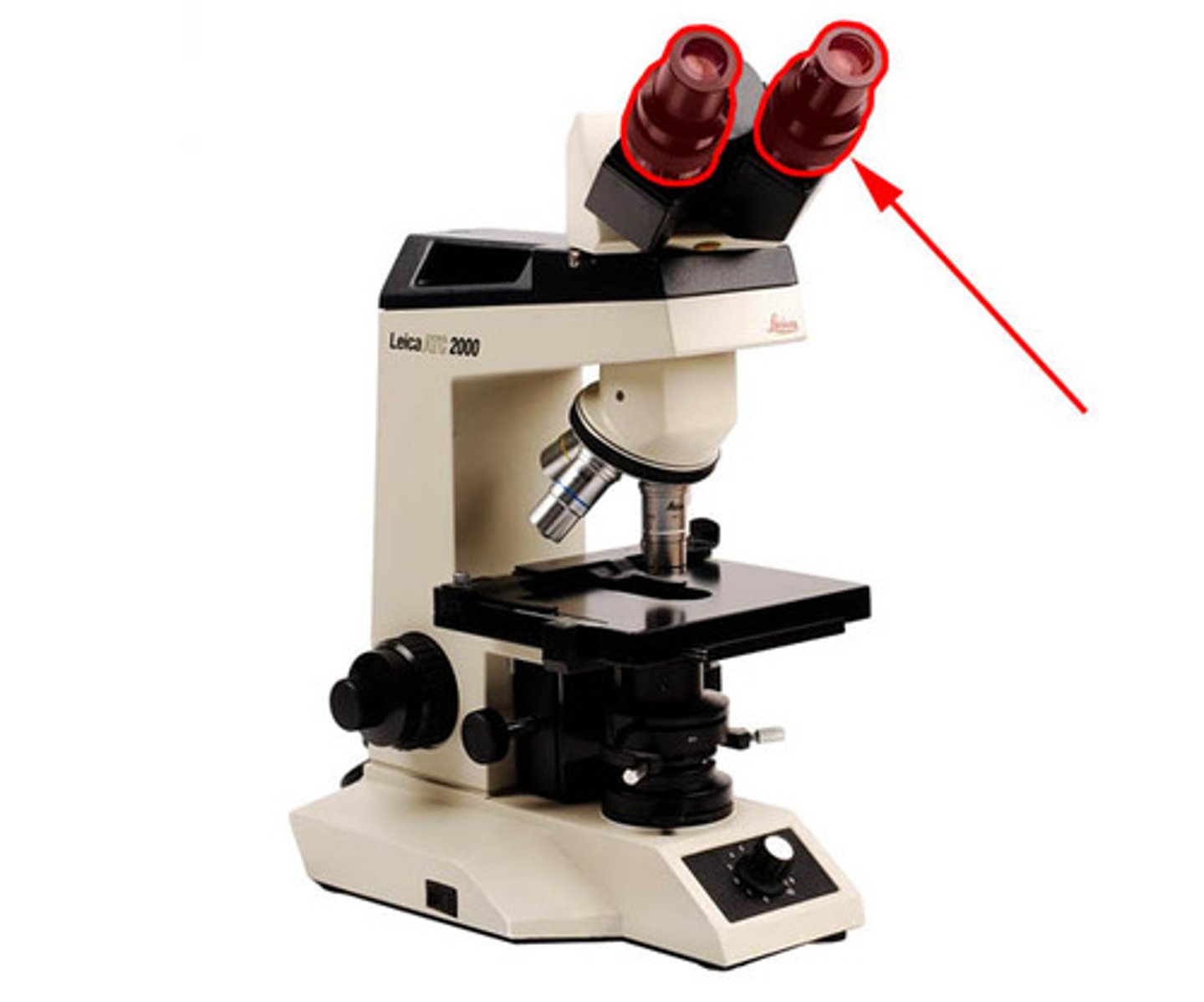
oculars
head
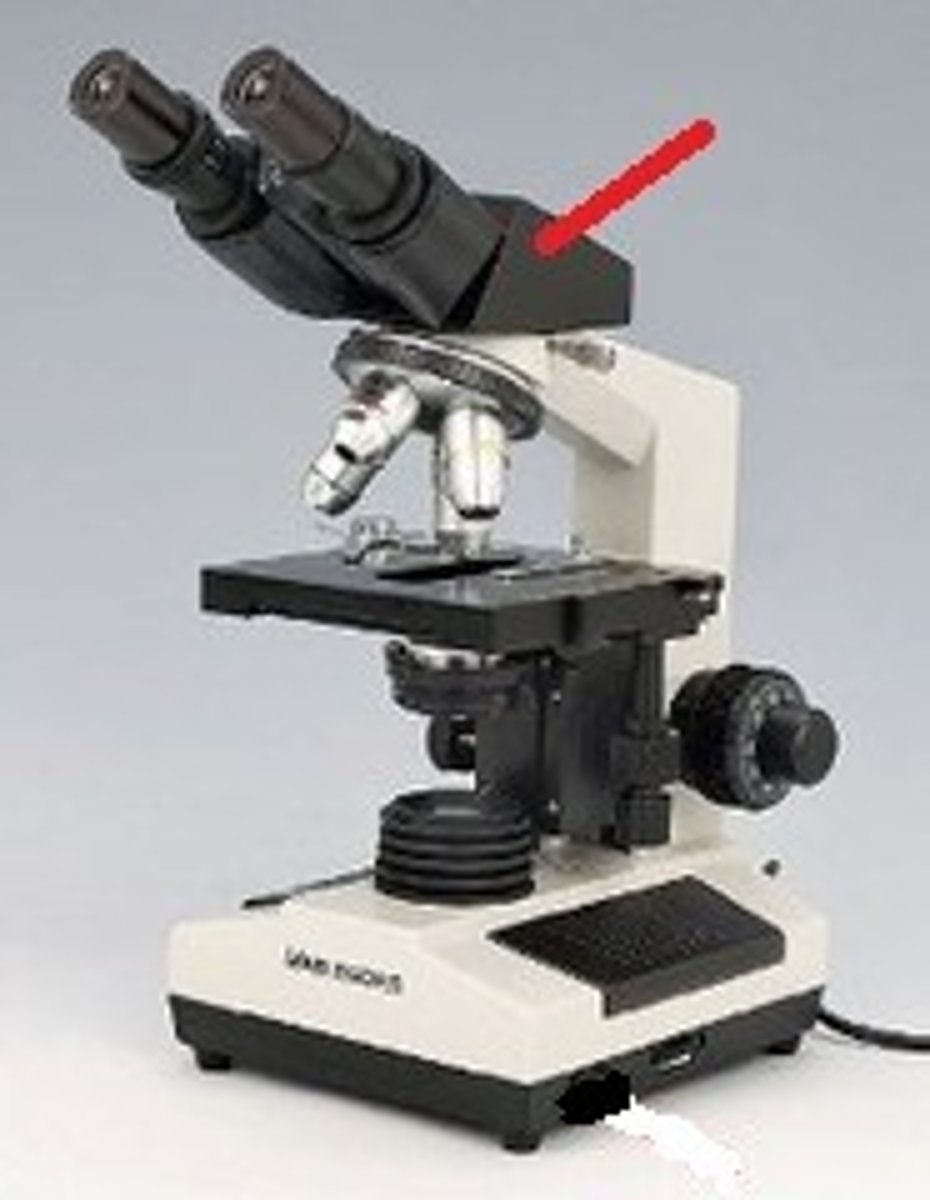

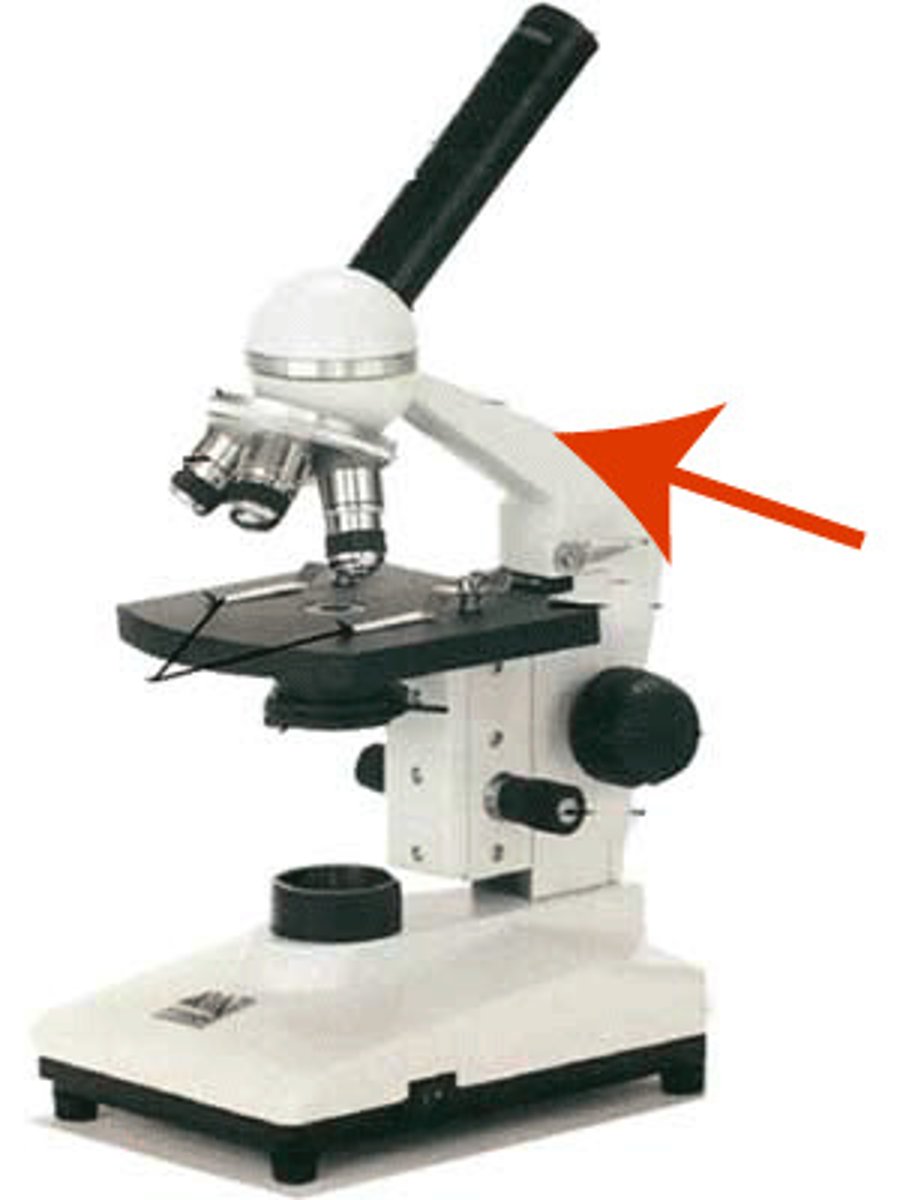
arm
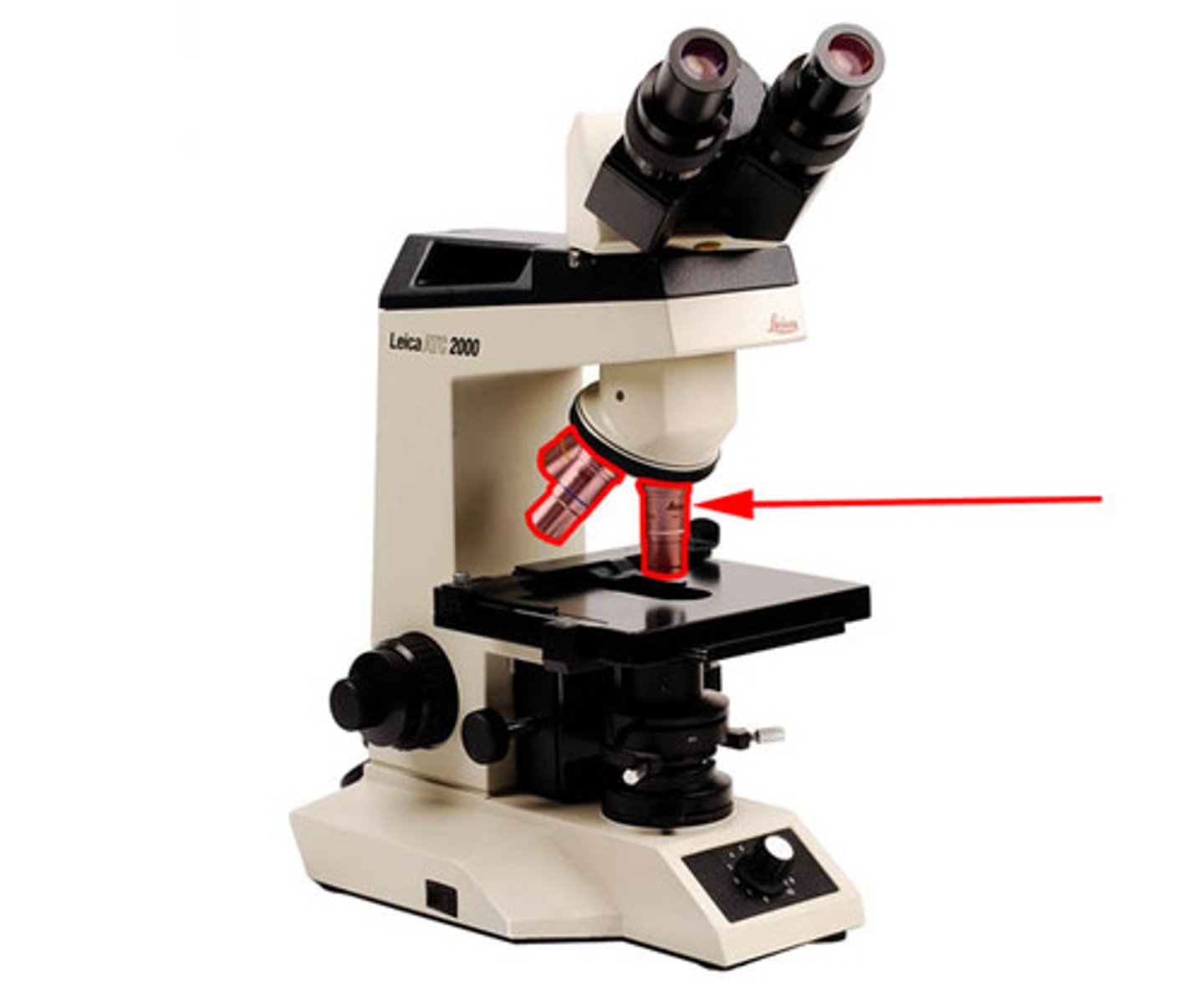
objective lenses
scanning (4x), low power (10x), high power (40x)
coarse focus knob
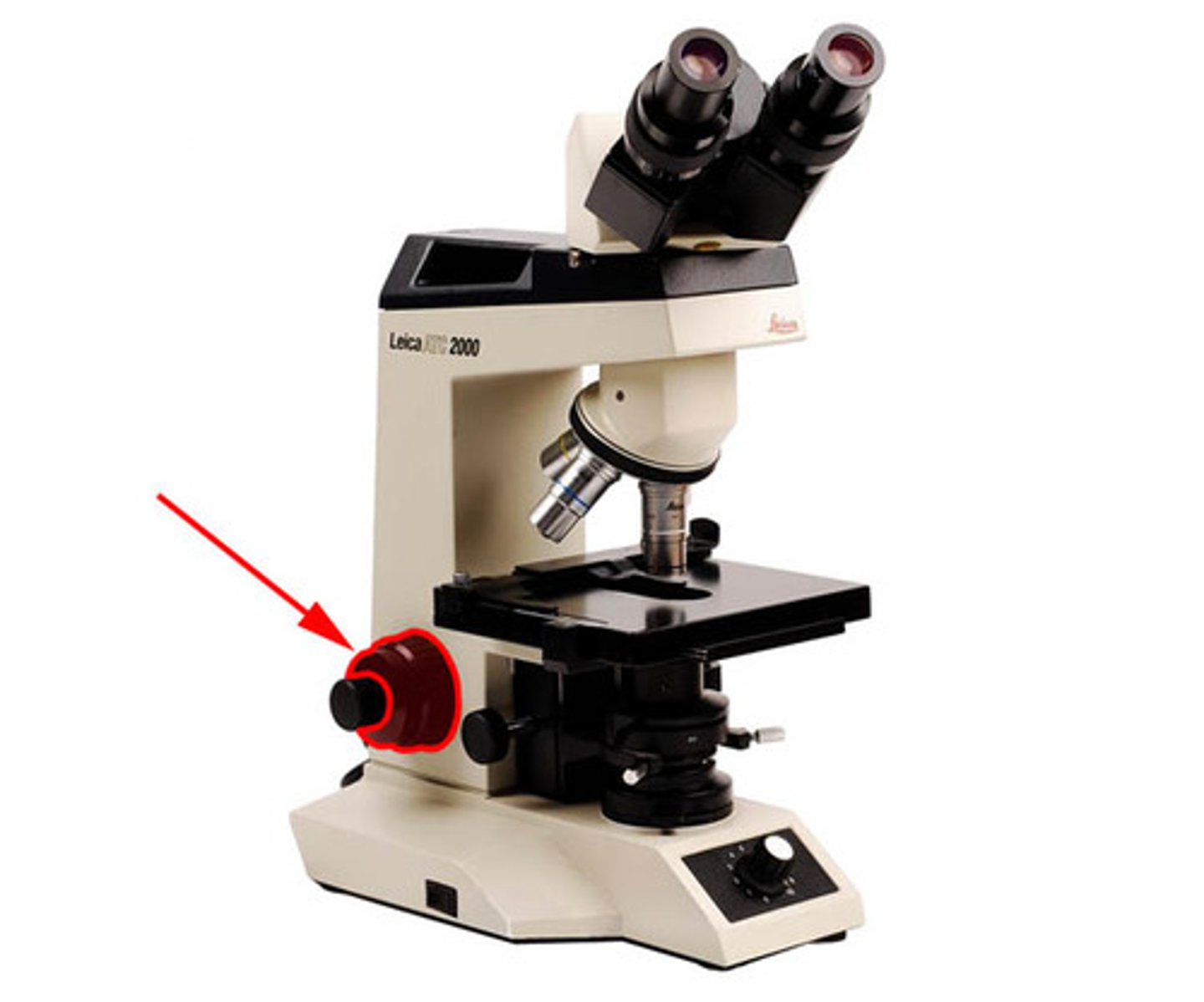
fine focus knob
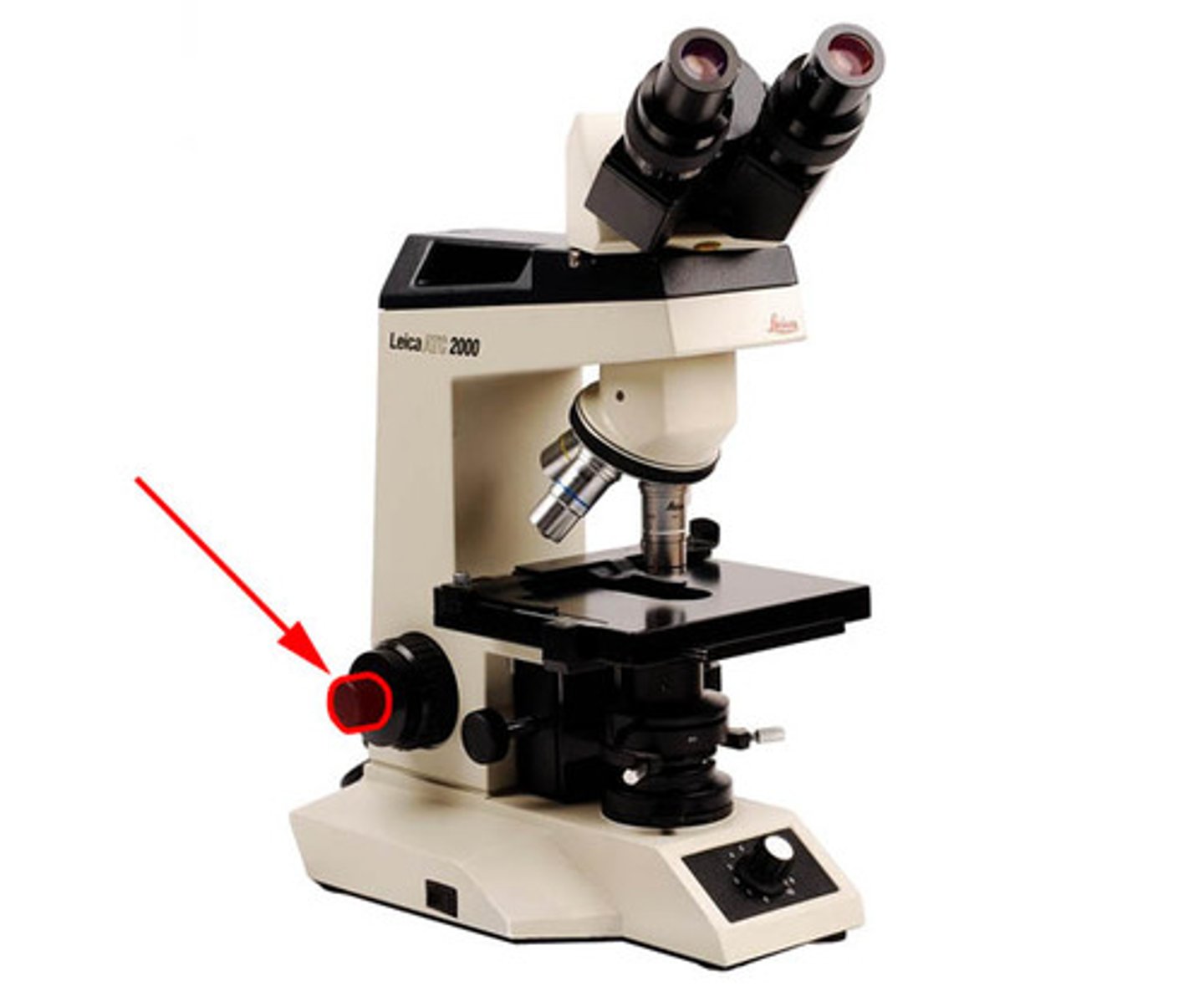
rheostat
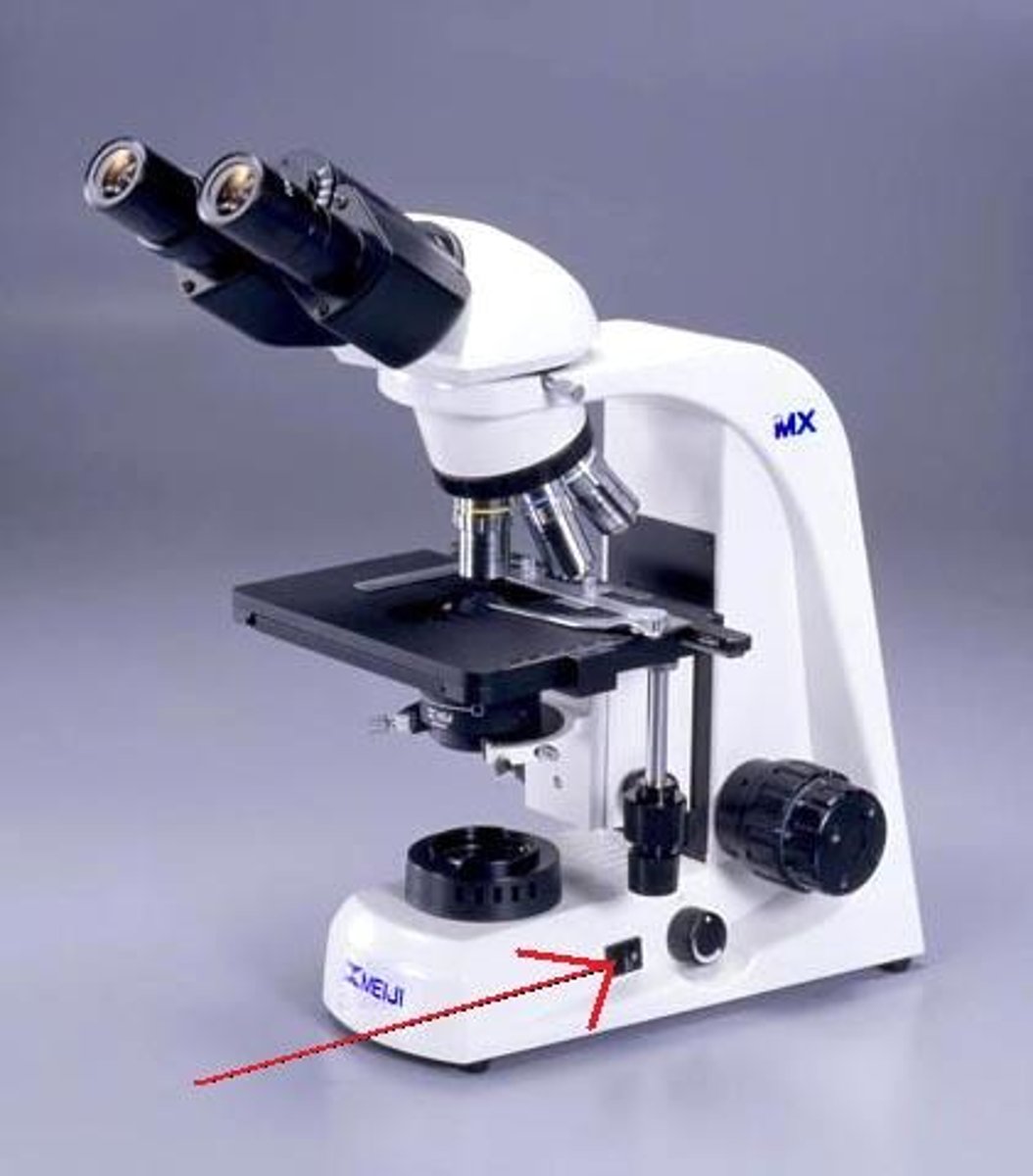
nose piece
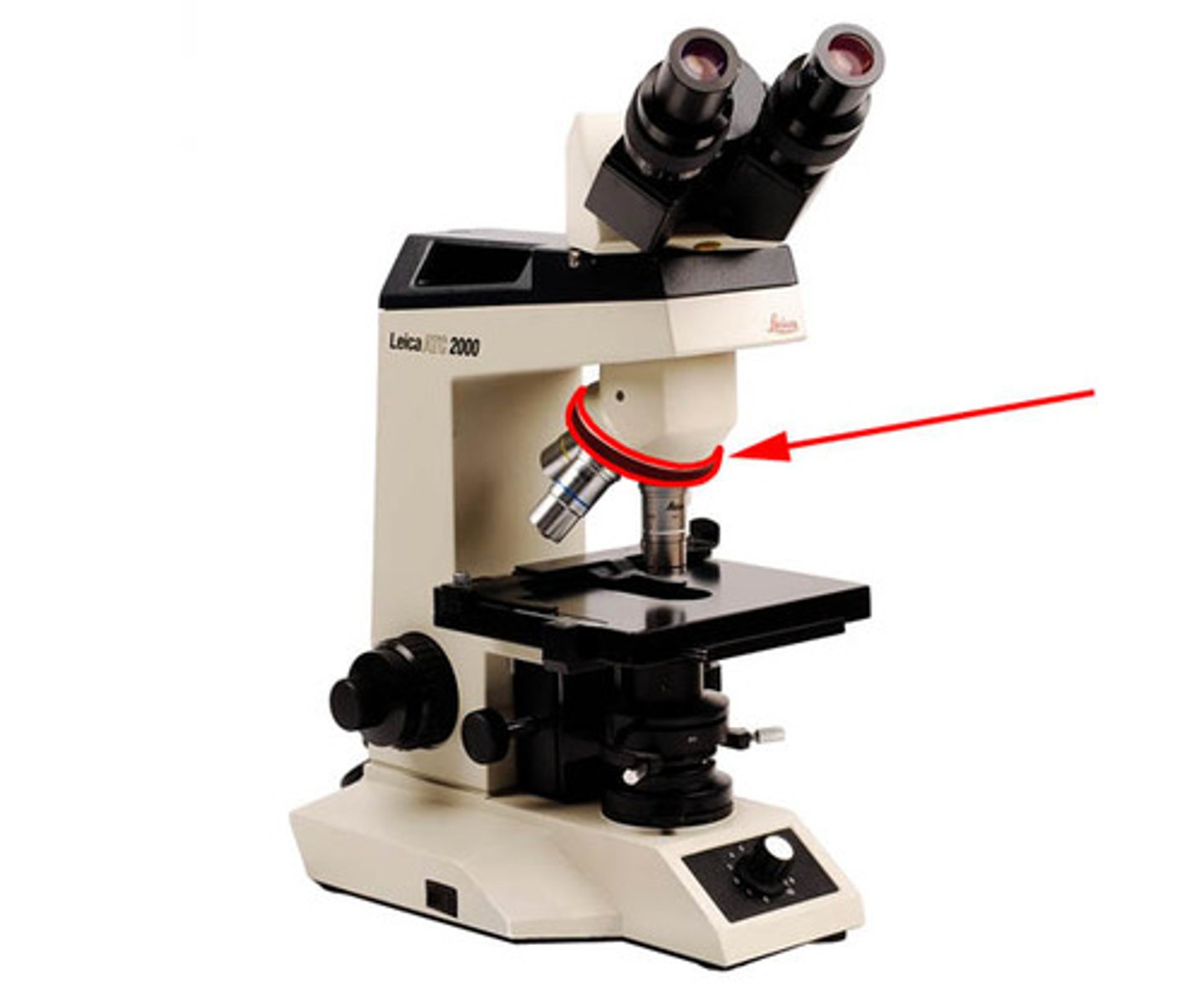
stage
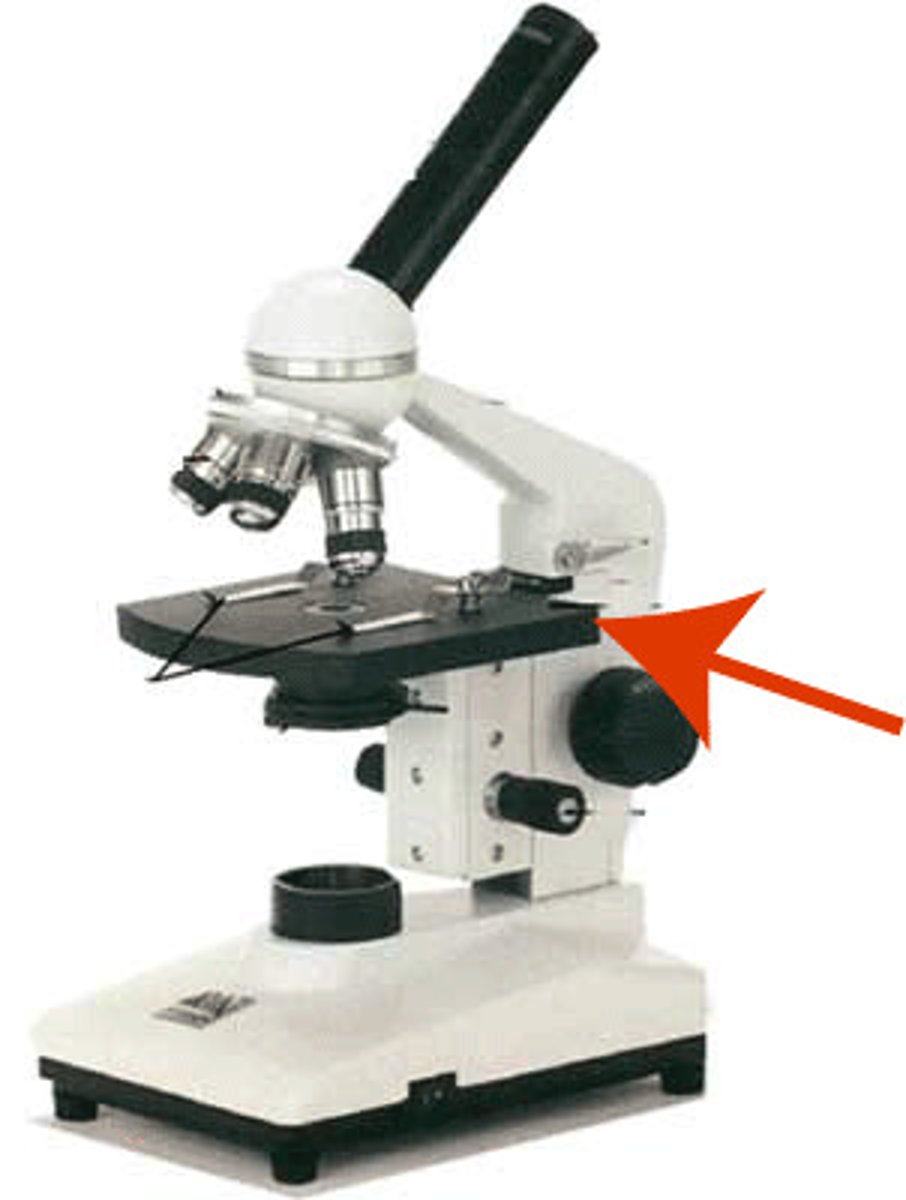
iris diaphragm lever
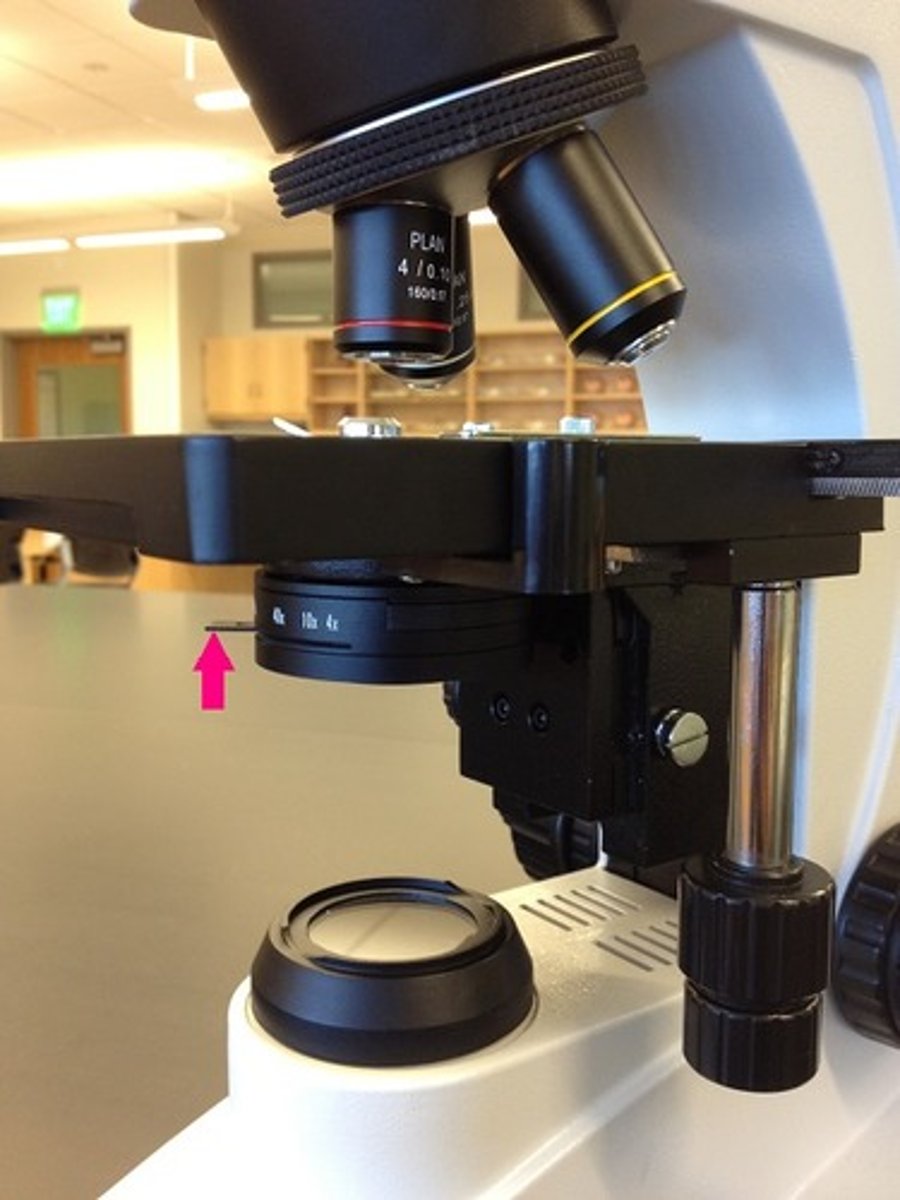

iris diaphragm
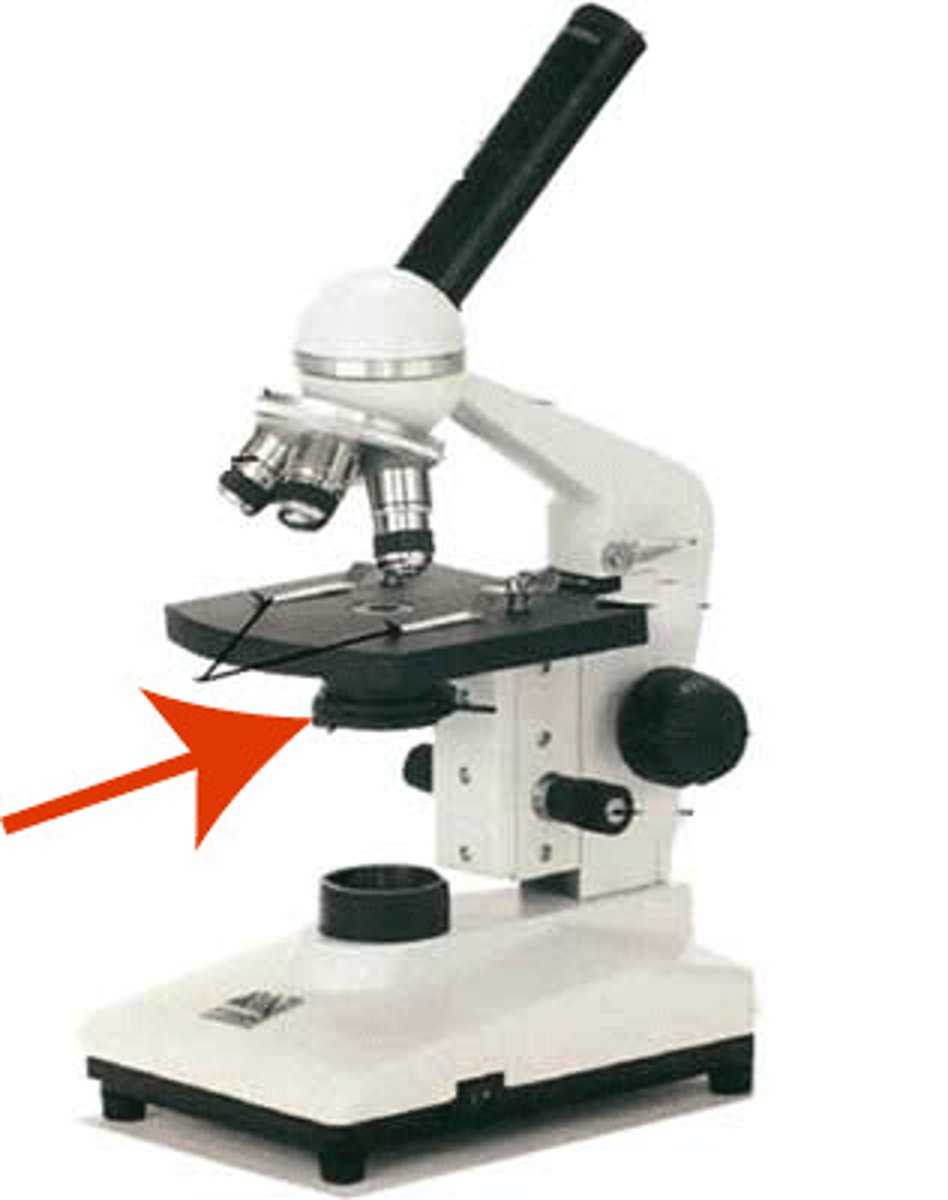
lamp

single celled organism
an organism that is made up of only one cell
Three other categories of organisms composed of one or more cells
filamentous, colonial, and complex multicellular organisms
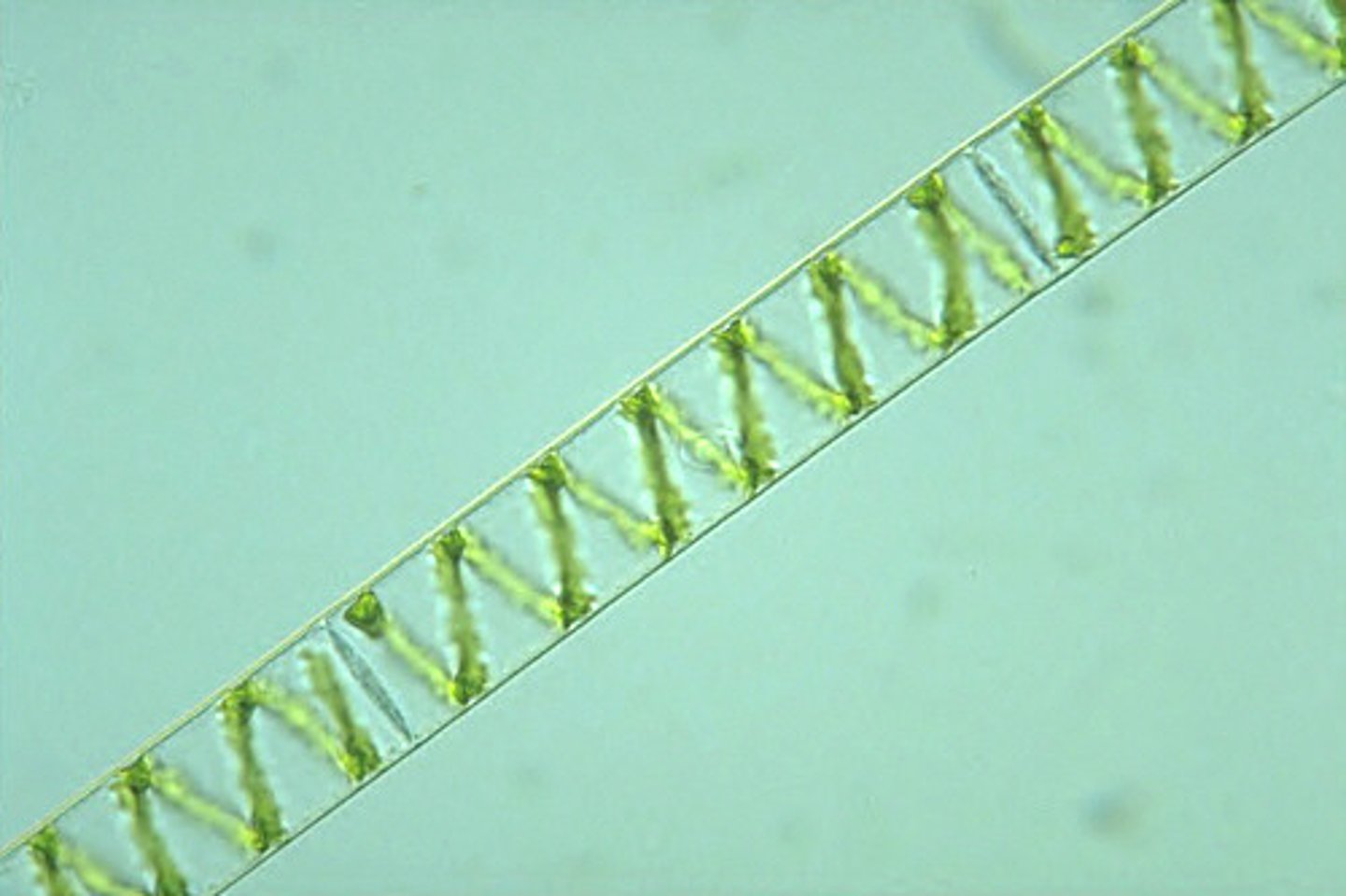
filamentous organisms
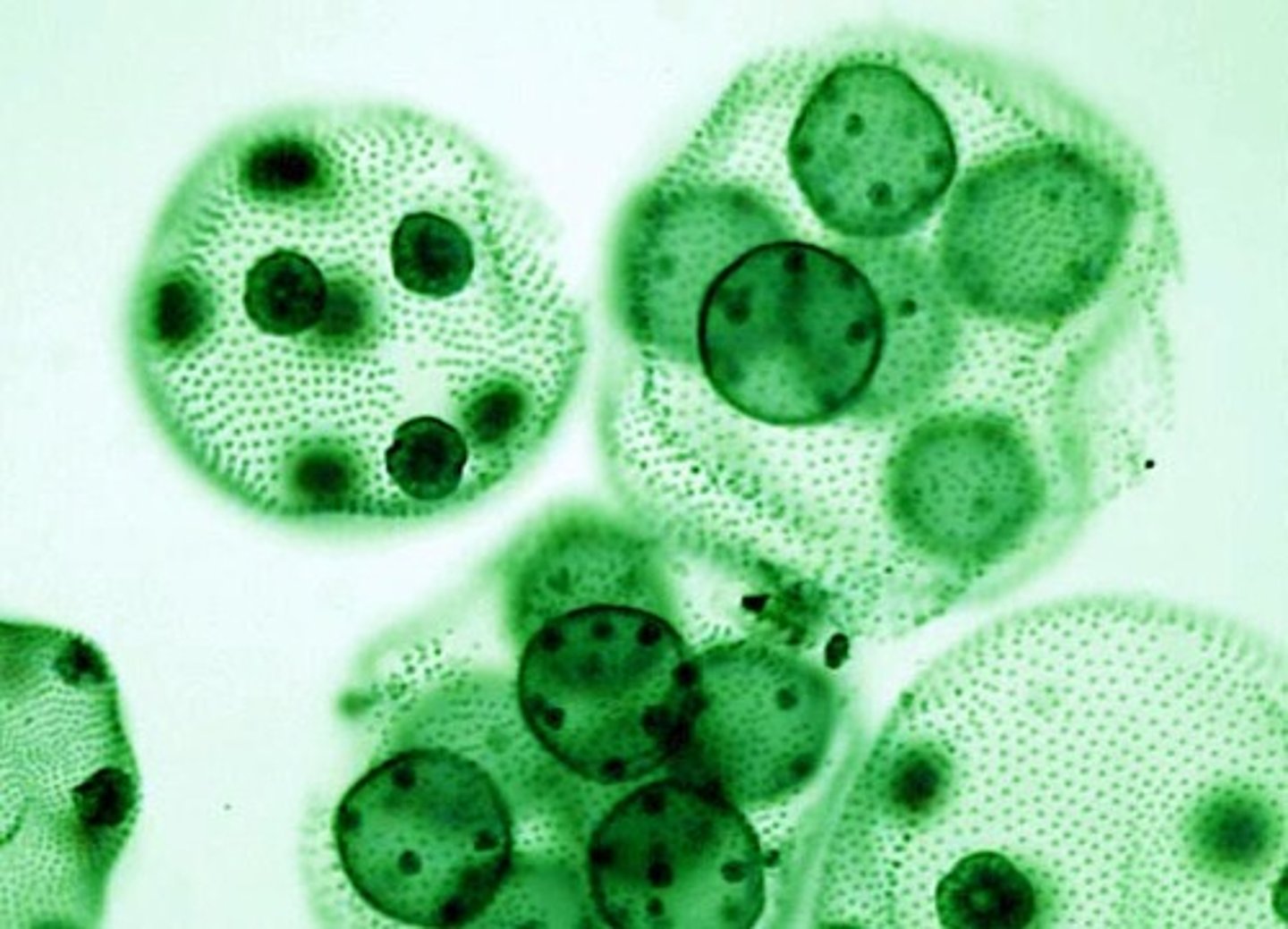
colonial organisms
complex multicellular organisms
exterior plasma membrane
to contain everything and regulate what goes in and out of the cell
DNA
a molecule that contains genetic instructions for the growth, development, functioning, and reproduction of all living organisms and many viruses. It consists of two coiled strands forming a double helix, with nucleotide sequences (adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine) encoding genetic information.
chromosomes
thread-like structures located in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, composed of DNA and proteins. They carry genetic information in the form of genes and are crucial for cell division, heredity, and the regulation of gene expression. In humans, there are 46 chromosomes, arranged in 23 pairs.
cytoplasm
a gel-like substance within a cell, excluding the nucleus, that contains organelles, cytoskeleton, and various molecules. It is the site of many metabolic processes and provides structural support to the cell. The cytoplasm is composed mainly of water, salts, and organic molecules.
cytosol
“cell solution” or the actual cell liquid with various dissolved biochemicals to help the cell function
organelles
distinct chemical assemblages, usually visible on a microscope, that perform particular functions
ribosomes
make proteins
flagella
one to a few hairs that help move or create currents exterior to the cell
cillia
numerous small hairs that help move or create currents exterior to the cell
eukaryotic cells
complex cells that contain a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. They are found in organisms such as animals, plants, fungi, and protists, distinguishing them from prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus.
nucleus
contains the eukaryotes multiple linear chromosomes all enclosed
nuclear membrane
encloses the nucleus
nucleolus
a visible dense area inside the nucleus, is the site of RNA synthesis
electron microscopes
magnify objects to a greater degree than do light microscopes, much larger and more expensive than light microscopes, use a beam of electrons to visualize material
scanning electron microscope (SEM)
illuminate the three dimensional surface of something, such as the outside of a cell
transmission electron microscope (TEM)
allow one to visualize subcellular and macromolecular cell components in a thin section of a cell
bacillus
rod shaped bacteria
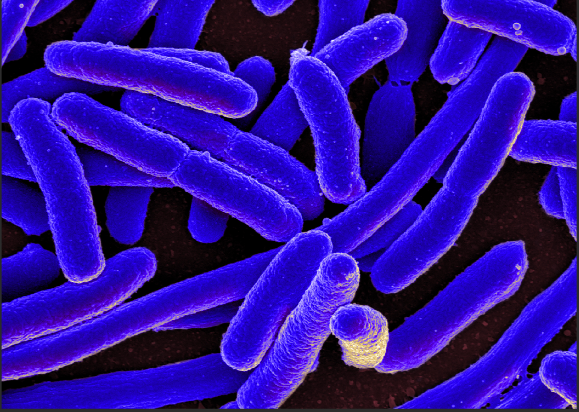
coccus
circular bacteria

spirillum
spiral shaped bacteria

tissue
a distinct group of cells that have the same developmental origin and collectively have a particular function
How many tissue categories are there in animals?
(5) vascular tissues, nervous tissue, muscle tissue, connective tissue, and epithelial tissue
epithelial tissue
lines all organs as well as the exterior of the organism, functioning to hold the organ and organism together, act as a protective barrier by controlling what enters and exits the organism or organs, and it also may have specalized glands that secrete substances
vascular tissue
connects all of the various body parts by transporting materials. In animals, a specific tissue is blood, which distributes gases, foods wastes, and vital elements and chemicals such as calcium ions, enzymes, and hormones
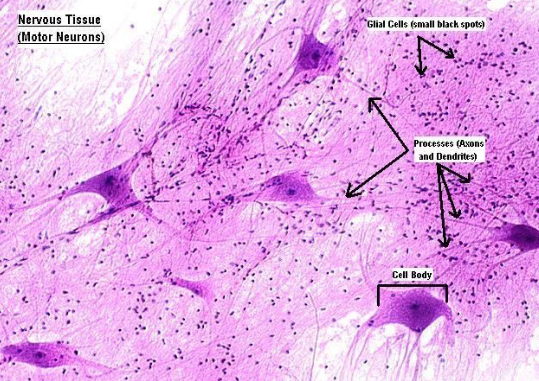
nervous tissues
recieve and interpret information from the external environment, and communicate information among the various body parts
muscle tissues
allow for an organism’s motility (skeletal muscle), as well as movement and function of organs (cardiac muscle tissue in the heart and smooth muscle in other organs such as the intestines and bladder)
connective tissue
have multiple functions including structural support via bone or cartillage tissues, energy storage via adipose tissue, and conneccting different tissues together such as dense connective tissues in tendons (that connect muscle and bone), and loose connective tissue that binds together everything else (nerves, vessels, membranes, skin, etc.) Blood is often considered a type of connective tissue, but some biologists consider it a separate tissue category, the vascular tissue, as mentioned above
organ
a distinct body part composed of several kinds of tissues all collectively working for a specific function or small range of functions
organ system
a group of organs working collectively for a particular function
simple squamous epithelium tissue
have a large surface area to volume ratio
help protect organs and the exterior of the organism
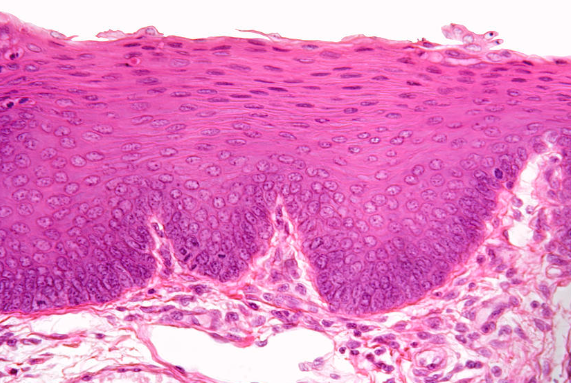
stratified squamous epithelium
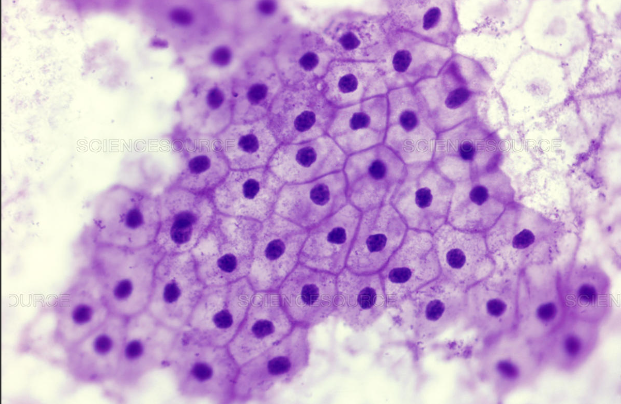
simple cuboidal epithelium
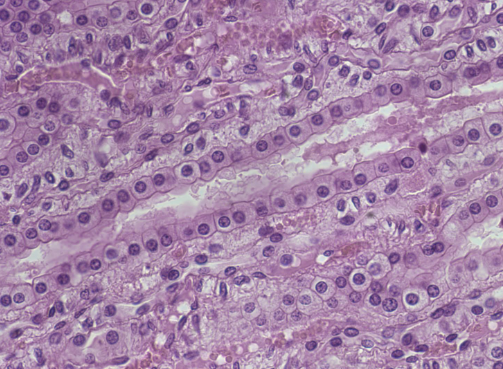
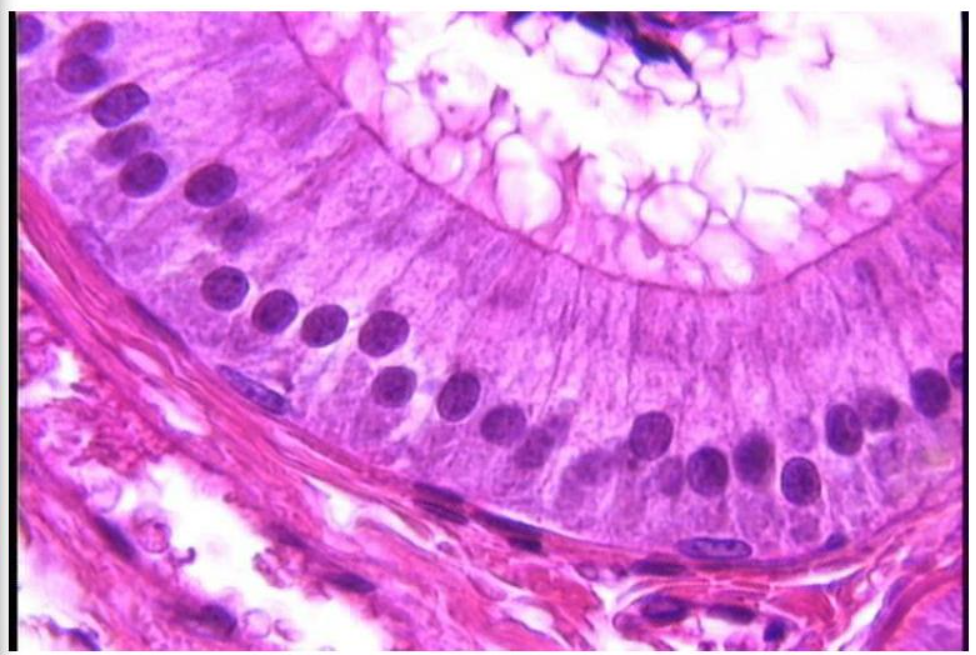
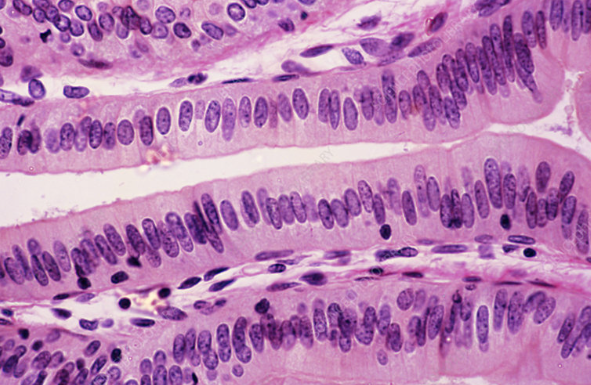
simple columnar epithelium
line organs (such as the stomach and intestines)
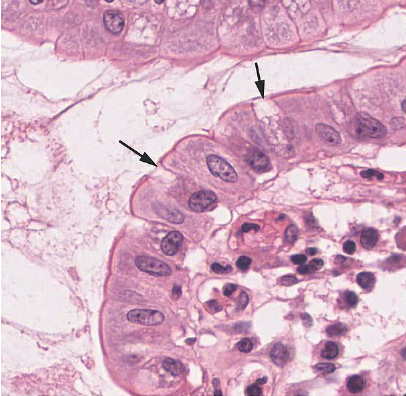
goblet cell
secrete mucus
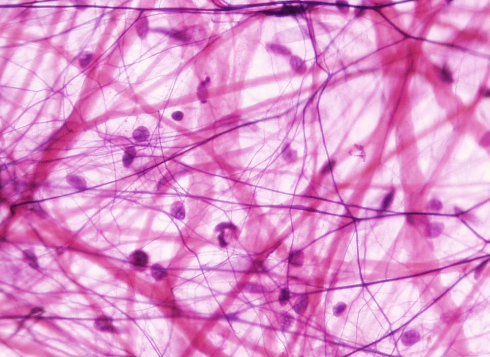
loose connective tissue
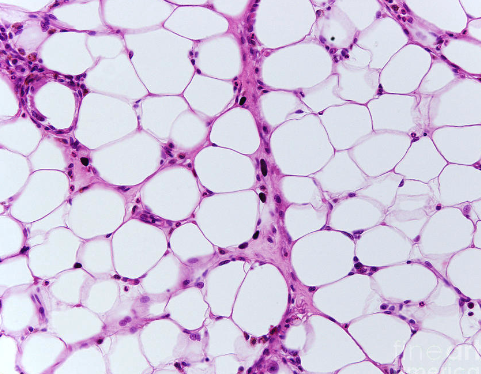
adipose tissue
found under your skin, between organs, and the inner cavities of bones
used to provide long term energy storage, and to act as a cushioin
triglycerides make up this cell
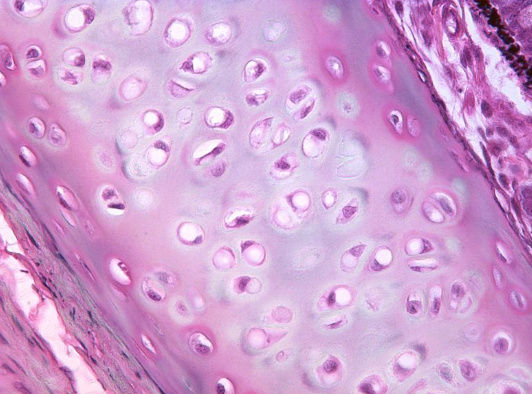
cartillage tissue
provide support in boney areas
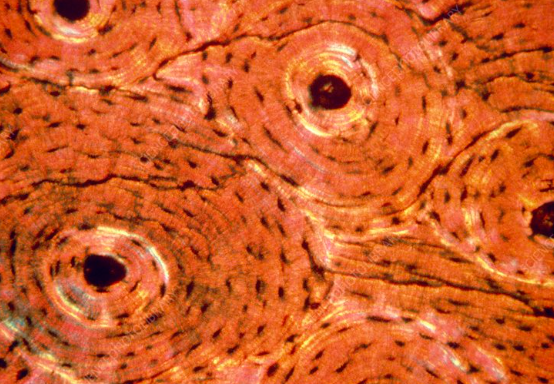
bone tissue
frog red blood cells

human red blood cells
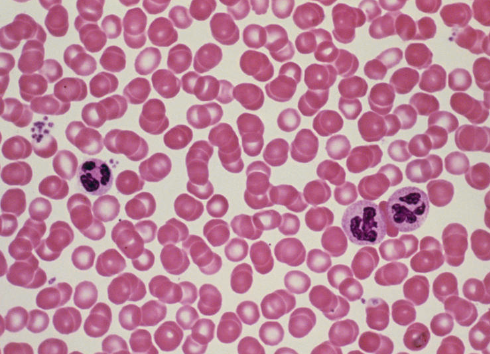
white blood cells
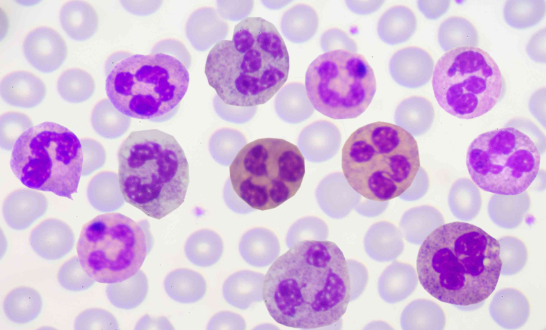
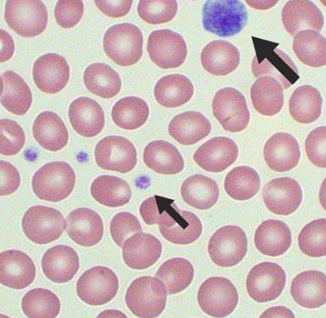
platelets
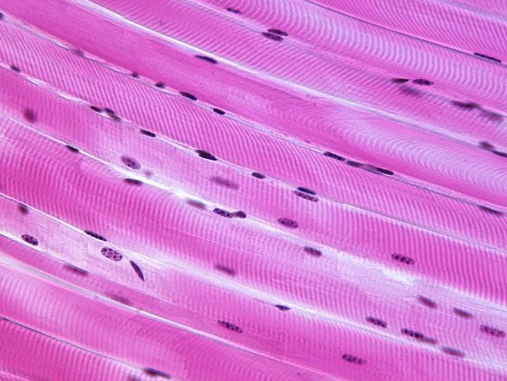
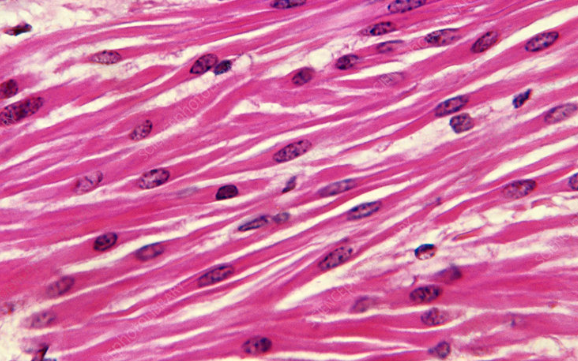
skeletal muscle tissue
found attached to bones
functions to help animals move
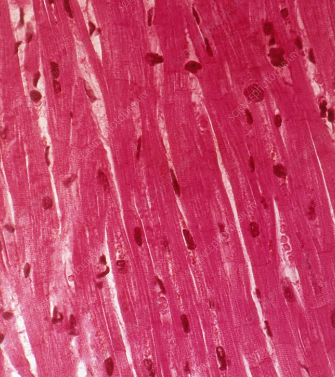
cardiac muscle tissue
found in the walls of the heart
helps the heart to contract and pump blood
smooth muscle tissue
found in the walls of organs
helps maintain blood pressure and blood flow
nervous tissue (motor neuron)
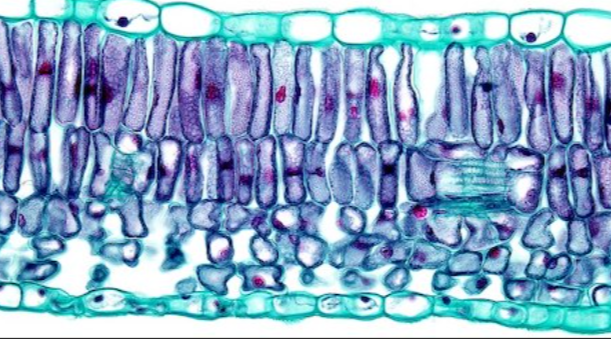
dermal tissue
lines all organs of the plant, and its exterior
ground tissue
support, protect, and metabolize
often called different names depending on the organ. for example, in a leaf they are collectively called the mesophyll, while in the center of a stem they are known as the pith, and in other places they are the cortex
vascular tissue
connects all various parts of the body by transporting materials
how many major tissue categories do plants have?
3: dermal, ground, and vascular
epidermal cells
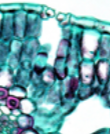
cuticle
a waxy layer made of cutin wax, exterior to the epidermal cells
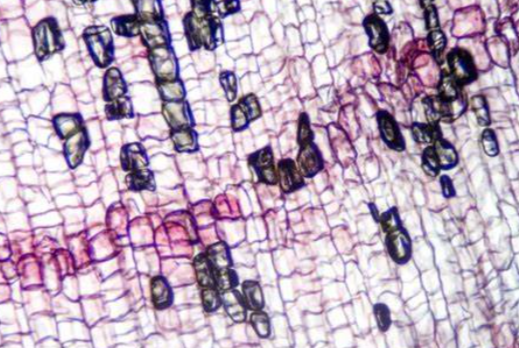
guard cells
surround an opening called the stoma and are only found on non-woody above-ground parts of plants
trichomes
these can be one or a few cells long, define as appendages or extensions of epidermal cells
prevent other animals from eating the plants, keep the plant warm, attract other organisms
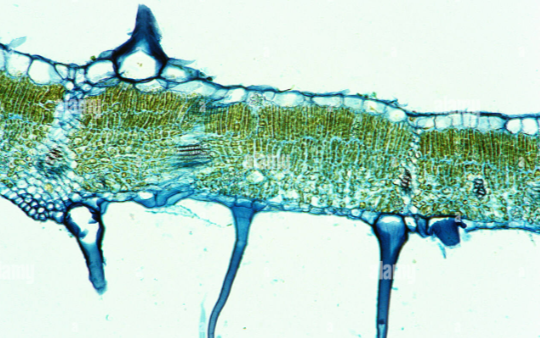
cork tissue
also called peridem
replaces the epidermis on older woody stems and roots. This tissue is several cell layers thick, consisting of __ cells. Contains a lot of suberin wax within their thick cell walls and usually are dead at maturity
act as a protective barrier and to prevent water loss
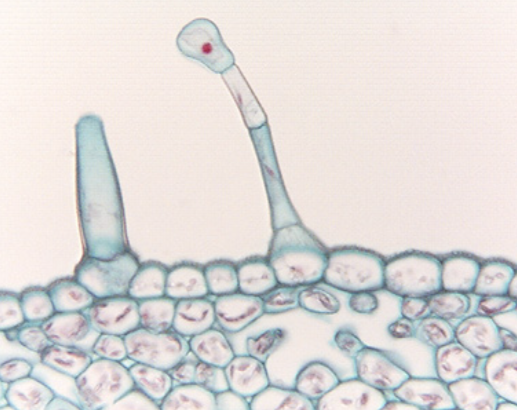
trichomes - glands
special kinds of trichomes for secreting substances such as nectar or toxins
trichomes - root hairs
are trichomes located on root tips, near the growing meristem region
allows the plant to absorb more water and nutrients
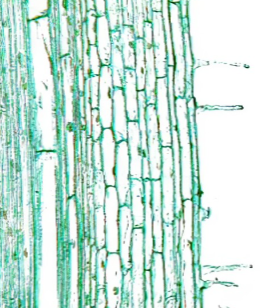
xylem
may contain two types of water transporting cells- tracheids and vessel elements. Both cell types have thickened cell walls that have distinctive structural features
transports water and minerals upward
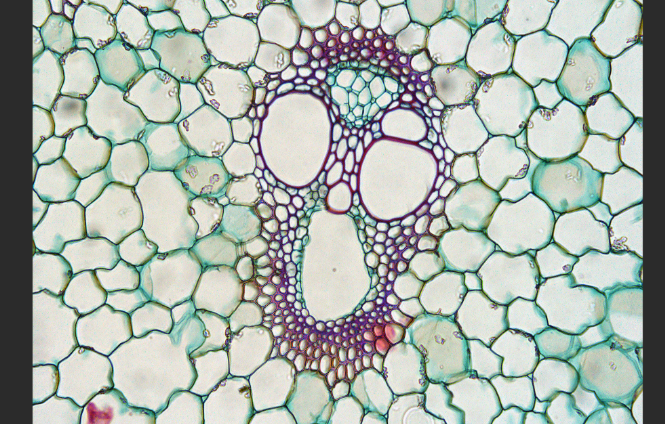
phloem
tissue of flowering plants contains sugar-conducting cells, sieve tube cells which lack a nucleus, paired with smaller nucleated companion cells that controll metabolic functions of sieve tube cells.
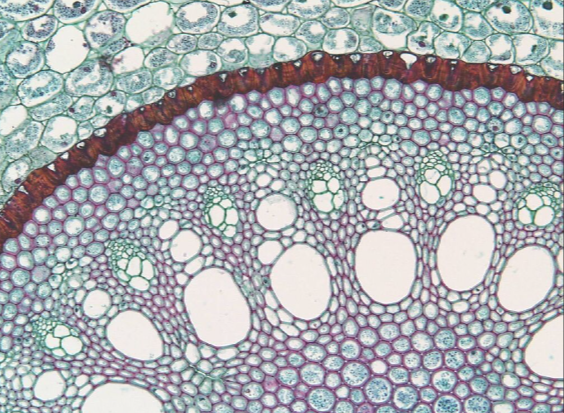
photosynthetic parenchyma
the most abundant and versatile in a plant, is composed of ____ cells. ___ cells are living, typically with a thin cell wall, and are able to divide and differentiate into other cell types.
has a wide variety of functions depending on its location
photosynthetic kind is composed of chloroplast that specifically carry out photosynthesis
with large air spaces in between the cells, this allows gases to flow through
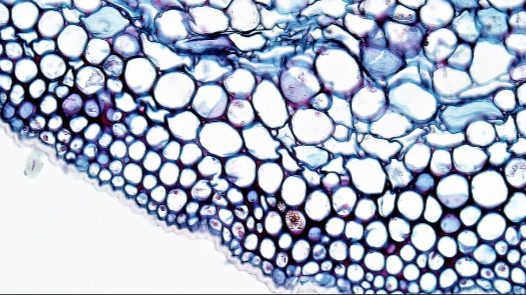
storage parenchyma
in stems and roots, this cell is responsible for cellular respiration and energy storage
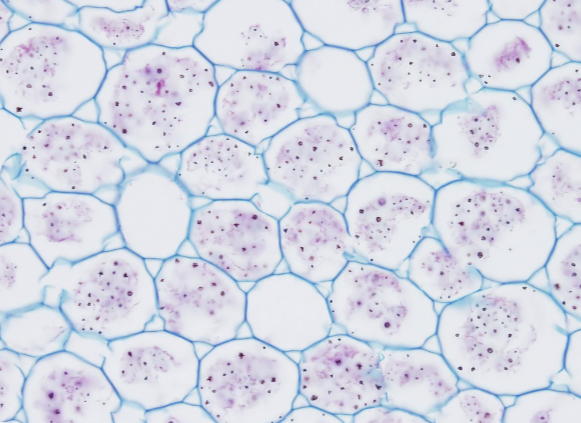
collenchyma
generally located in growing shoot areas (leaves, stems, fruits flowers). these cells have unevenly thickened cell walls and allow for flexible strength and support
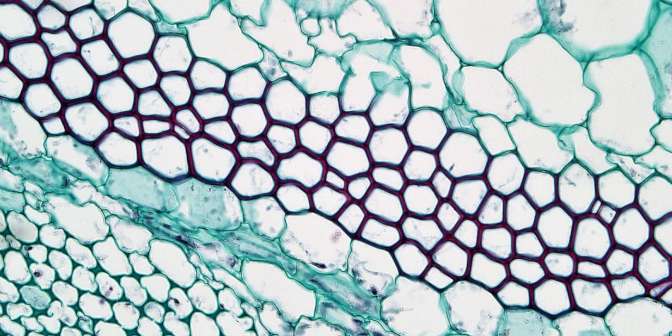
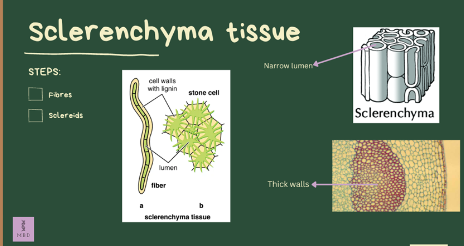
sclerenchyma
tissue that is composed of cells with very thick cell walls, so thick that often the cell dies. their function is to provide rigid protection and structural support
sclerenchyma - stone cells
small, irregularly shaped cells. These cells give pear fruits the gritty texture when you eat them, and in stone frutis like peach or cherry the sclereids form the hard “pit” that surrounds and protects the seeds
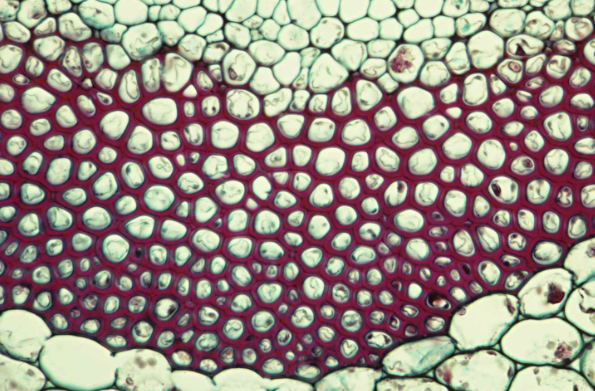
sclerenchyma - fibers
are long thin cells that form in thin sheets or in strands/bundles
located near the epidermis
these cells are used as another structural support