Bio Lab Midterm
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Physiology
Chemical processes that allow individual cells to function
Active transport
Those powered by cells energy containing molecules, ATP
Passive transport
Those powered by the molecular movement resulting from thermal heat energy
Diffusion
Where molecules or particles display net movement
Net movement
Molecules in an area of high concentration move to area where they are low in concentration until they reach equilibrium
Osmosis
The diffusion of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane
Solvent
Considered water
Solutes
Atoms or molecules
Semipermeable membrane
Means that some particles can freely move across the membrane while other particles cannot freely pass across it
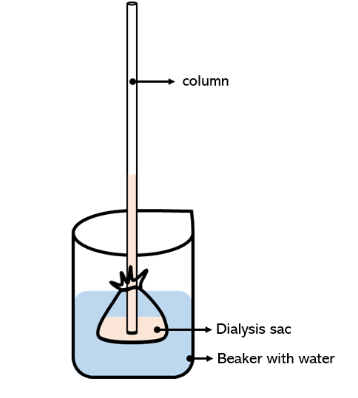
Osmometer
An instrument used to measure the osmotic pressure of a solution.
Hypertonic
A solution that has a higher concentration of solutes compared to another solution, leading to water moving out of cells placed in it.
Hypotonic
A solution that has a lower concentration of solutes compared to another solution, causing water to move into cells placed in it.
Isotonic
A solution that has an equal concentration of solutes compared to another solution, resulting in no net movement of water into or out of cells.
Metabolism
Refers to the set of all chemical reactions that occur within a living organism
Enzymes
Usually are proteins that act as catalysts, substances that speed up specific chemical reactions but are not used up in that reaction (most end in -ase)
Digestion
The enzymatic breakdown of a molecule into its smaller subunits
ATP
The main source of usable cellular energy
How is ATP made in an organism?
It is produced from glucose by aerobic cellular respiration (glucose + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + ~36 ATP)
How do organisms make ATP when there’s no oxygen present?
Via anaerobic cellular respiration
Fermentation
There are two types of fermentation, alcohol (glucose → ethanol + 2ATP) and lactic acid fermentation (glucose → lactic acid + 2ATP)
The disaccharide lactose is digested by lactase to make…
Glucose and galactose
Amylase digests starch to make…
Maltose
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single celled fungi well known to carry out…
Alcohol fermentation
Photosynthesis
The metabolic process used by autotrophic organisms to make glucose (6CO2 + 6H2O + sunlight → glucose + 6O2)
Where does photosynthesis occur?
Inside Chloroplasts
Where do the light reactions take place?
In the thylakoid membranes
Where does the Calvin benson cycle take place?
In the stroma
fermentation tube

calvin benson cycle
in prokaryotic autotrophs such as cyanobacteria, the chemicals needed for this cycle are free-floating in the cytoplasm, and the thylakoids are just infoldings of the plasma membrane
chlorophyll a
a green pigment necessary for photosynthesis to occur, and it is located in the thylakoid membranes
absorption spectrum
a graph showing which wavelengths of light a pigment will absorb and thus utilize for photosynthesis (a high peak indicates a high absorption at that wavelength)
chlorophyll a
every photosynthetic organism contains this pigment, it is called the primary pigment involved in photosynthesis because it starts the entire chain of chemical reactions that convert solar energy into chemical energy
antenna/accessory pigments
all other pigments, they gather other wavelengths of light and pass that energy on to chlorophyll a
chromatography
a technique used in analytical chemistry to separate chemicals dissolved in a solution based on how fast differently sized molecules migrate with a solvent front
cell cycle
refers to all the events and processes that occur as a cell matures, prepares for, and undergoes division
germ/stem/meristem cells
remain in the cell cycle, actively dividing and making more cells
dividing eukaryotic cells share the following cell cycle pattern…
interphase: where a cell grows, matures, functions, copies its DNA and prepares for division
nuclear division (mitosis): which separates copies of DNA depending on the type of cell needed by the organism
cytokinesis: where the whole cell divides into 2 or 4 cells, depending on the type of nuclear division
mitotic cell division
occurs when one parent cell divides into two daughter cells that are genetically identical to each other with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell
interphase is separated into how many subparts?
4; G0, G1, S, G2
meiotic cell division
only occurs in organisms when they are reproducing sexually
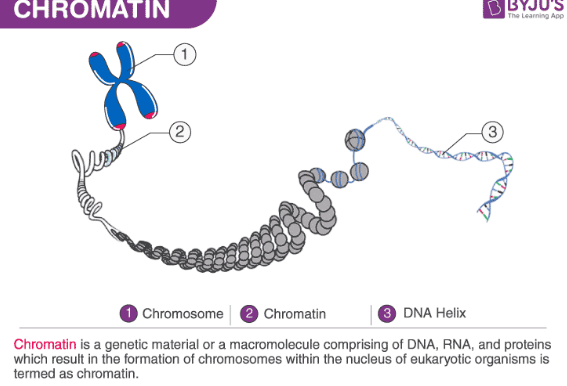
chromosome
a linear chunk of DNA
centromere
an area on the chromosome where microtubules can attach and sister chromatids are attached
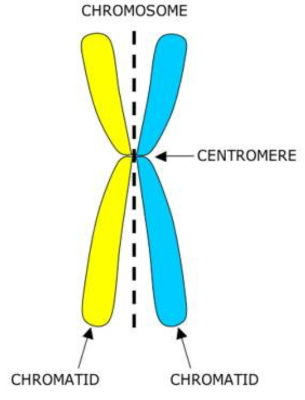
chromatid
is one half of a replicated chromosome
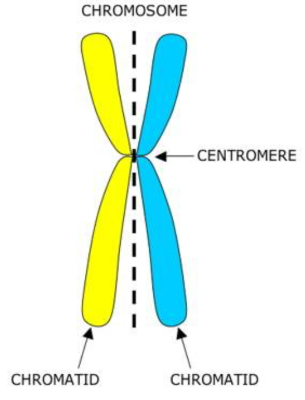
chromatin
mixture of DNA and proteins that form chromosomes (loose, not in a tight format like chromosomes)
prophase
the first stage of cell division, where chromosomes become visible as paired chromatids and the nuclear envelope dissappears
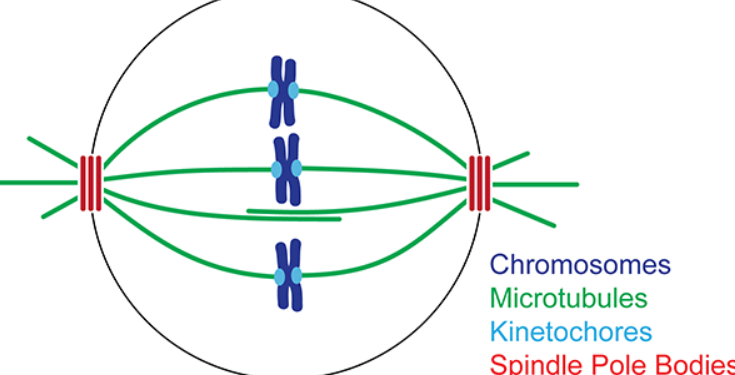
spindle pole (MTOC - microtubule organizing center)
center found in cells where microtubules emerge
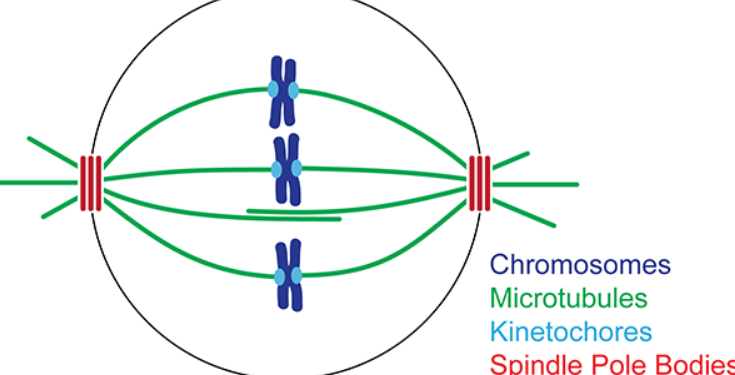
spindle fibers (spindle microtubules)
long protein ropes that come from the MTOC and connect at the centromere of the chromosome
asters (astrial microtubules)
a cellular structure shaped like a star, formed around each centromere during mitosis
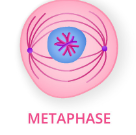
metaphase
second stage of cell division, chromosomes become attached to spindle fibers, in the middle of the cell, forming a metaphase plate
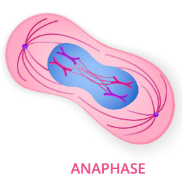
anaphase
centromeres divide and microtubules attached to kinetochores pull sister chromatids apart and to opposite poles
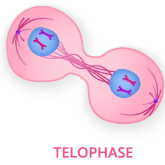
telophase
the unreplicated chromosomes, formerly sister chromatids, reach the poles. The nuclear envelope reforms, chromosomes begin to decondense
cytokinesis
separation of other cellular materials
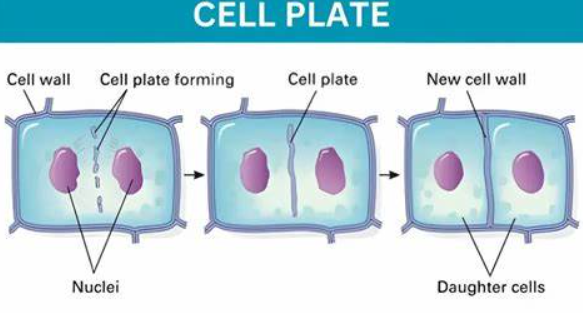
cell plate
a structure that forms when the cytoplasm of a plant cell divides
cleavage furrow
pinching off of a cell to make 2 sister cells
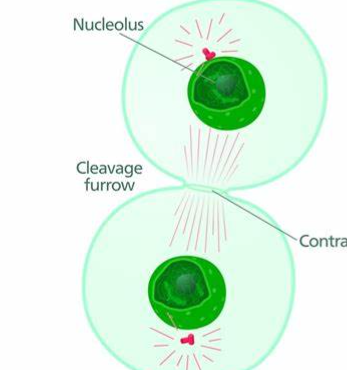
blastula
a particular stage in animal embryo development, where all cells of the embryo are actively undergoing mitotic cell division to produce many cells
the meristematic region of a plant (root and stem tips)
is where cells are continually dividing for elongation of roots and shoots
science
a way of thinking and a systematic method of investigating the world around us
general steps of the scientific method
make observations, and ask questions about those
do a literature search for relevant information and determine what is already known on the topic
develop hypotheses to answer the questions
design an experiment or observational study to test the hypotheses
carry out the experiment or study and gather data
summarize and analyze results (often mathematically/statistically)
make conclusions - compare observed results to what you expect for each hypothesis. Accept or reject each hypothesis
observations
interact with something and note what you see or experience. Observations should NOT include explanations
hypothesis
an educated guess. a testable, falfsifiable statement that potentially answers the research question
null hypothesis
state that there will be no difference or effect
alternative hypothesis
state that there will be a difference or an effect
prediction
what you expect to happen in your particular study if that hypothesis is supported
independent variable
is what is varied during the experiment
control
is the “normal” condition or absence of what you are sutdying
dependent variable
is what you measure, count or record; the kinds of data that a re gathered
constant
a factor or condition that is not changed throughout the experiment
sample size
the use of sufficent numbers of individuals or samples for each independent variable to ensure you obtain valid results for that variable
replicate
is each individual or sample being used to test the independent variable
experimental study
is the classic scientific experiment, often performed in the lab
some variables are controlled and some are manipulated
looks to see if the manipulation had some sort of effect or difference
cause and effect can be determined
observational study
is often employed when research is conducted in a natural setting
variables are not manipulated (no control or manipulated treatments)
comparisons are made among different scenarios (organisms, plots, sites)
cause and effect cannot be determined
bar vs. line graph
line graphs are best for chronological studies where data are collected on the same samples or individuals over a time fram or where the same samples or individuals are given different treatments at different times. bar graphs are best for showing categorical data (different kind of treatments on different individuals)