Physics Electricity
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Cell
Cell pushes current around circuit. Long side is positive.
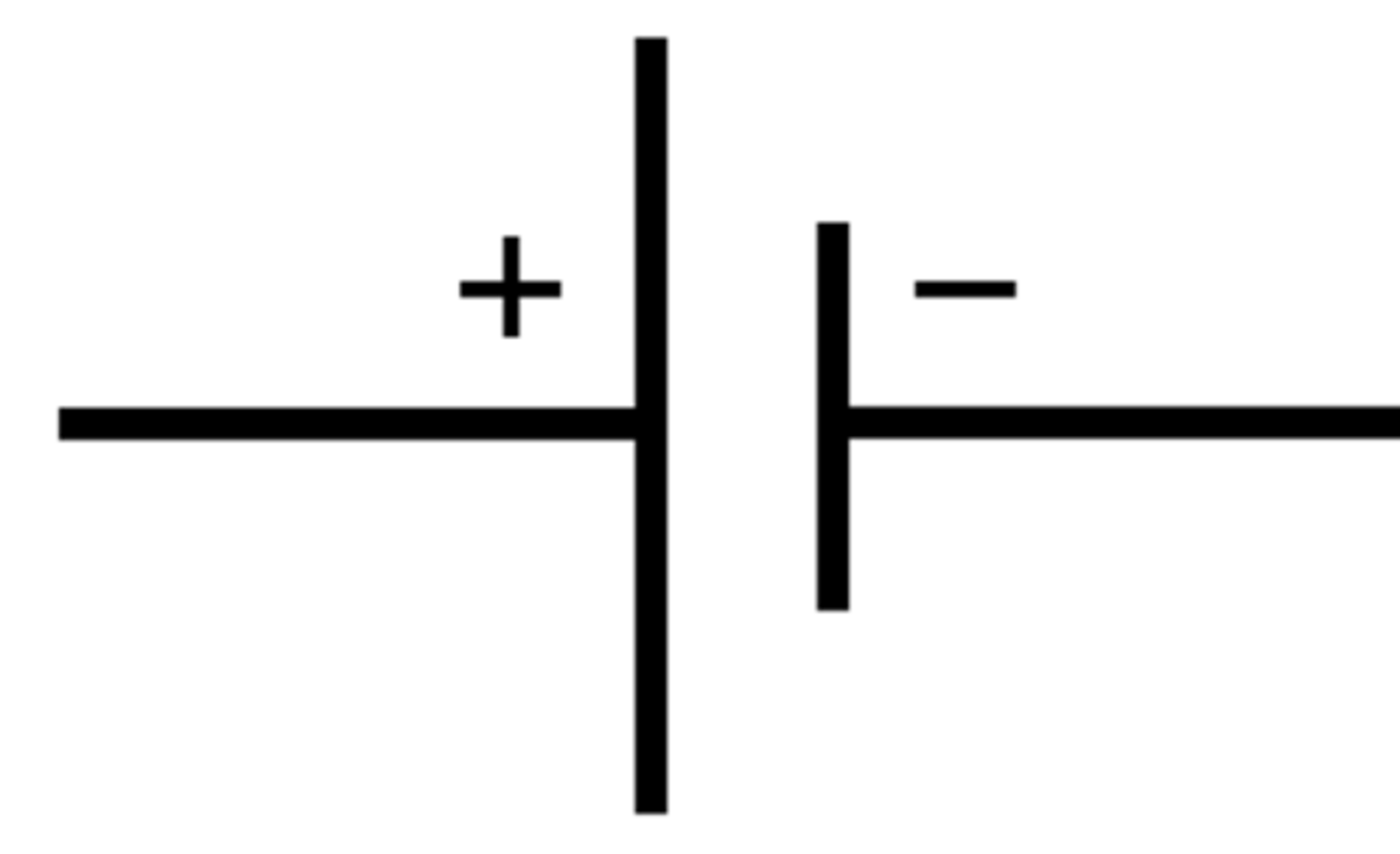
Battery
Two or more cells connected together is a battery.

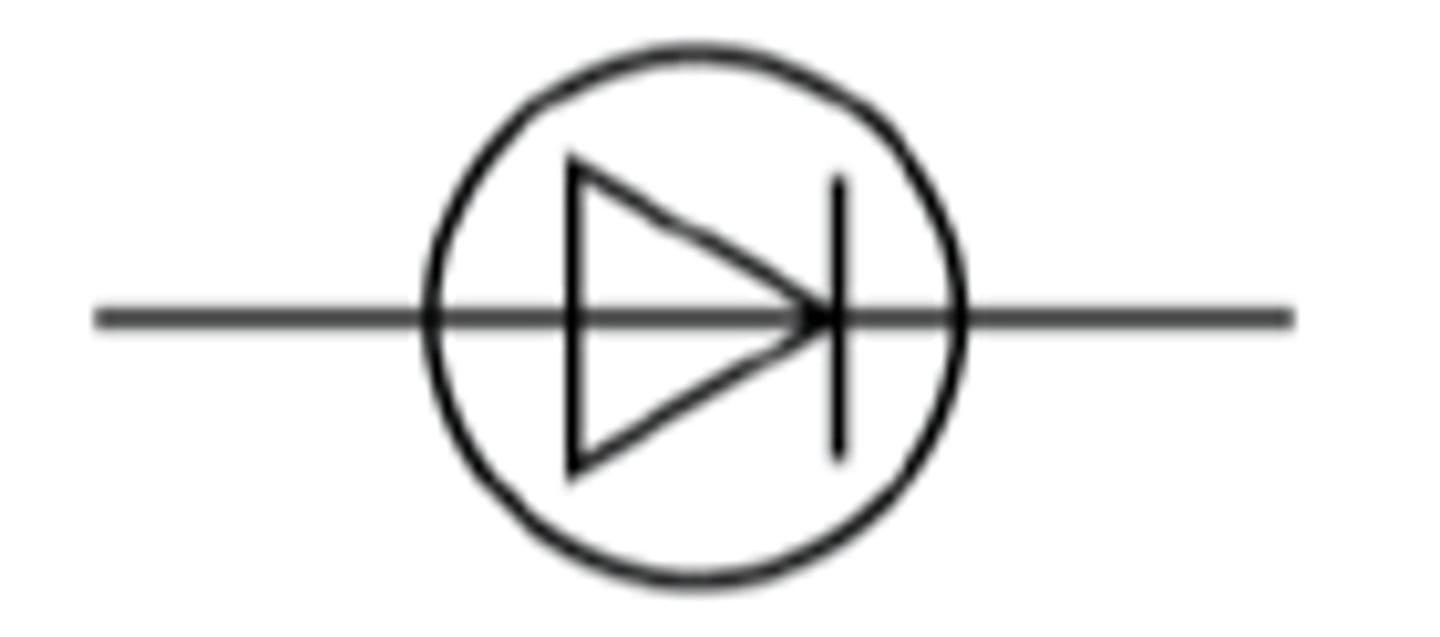
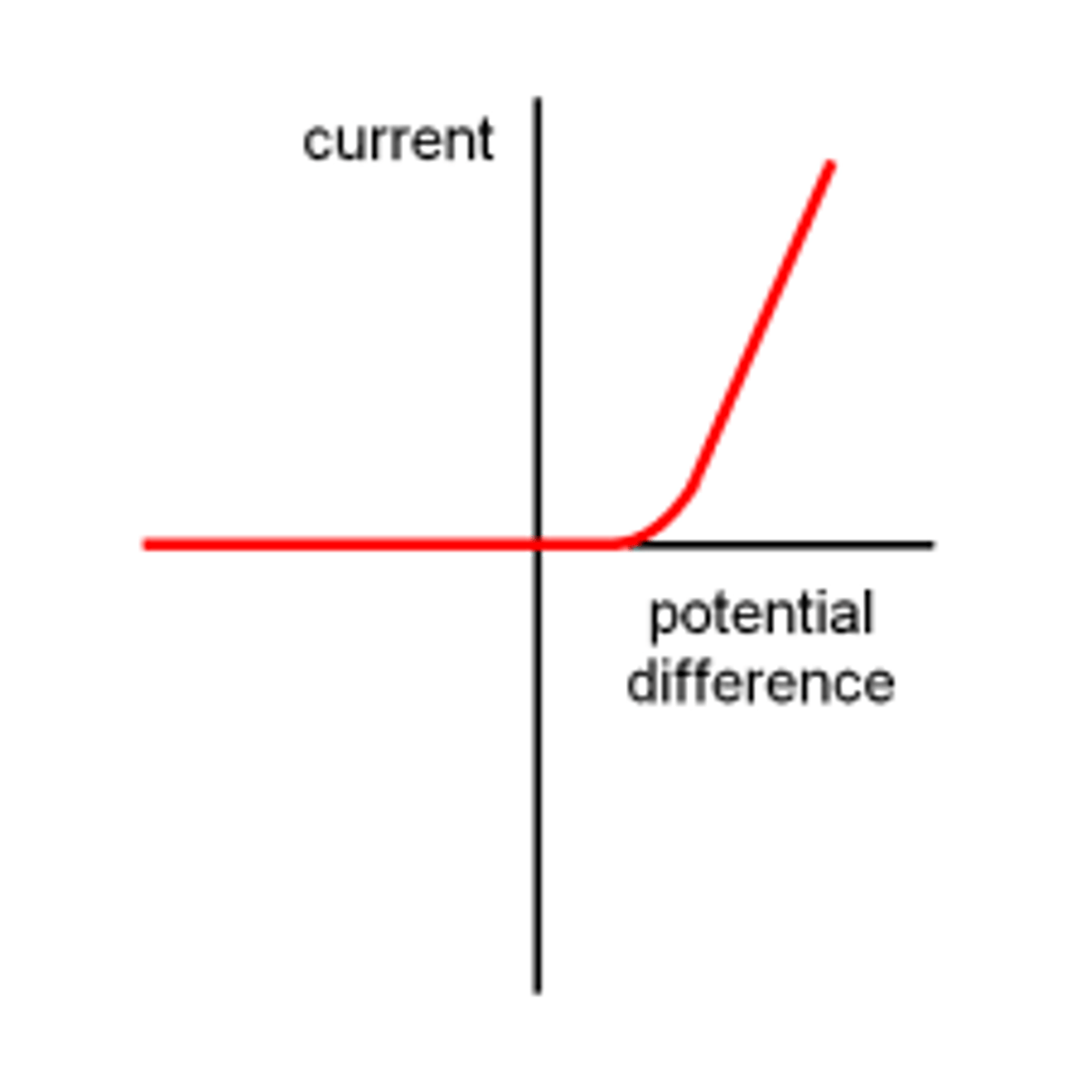
Diode
A device that permits current to flow through it in only one direction. (the way the arrow is pointing)
If the arrow in the diode is the same as the arrows on the circuit it is "forward biased". If the arrow faces the other way, it is "reverse biased". A forward biased diode lets current through.
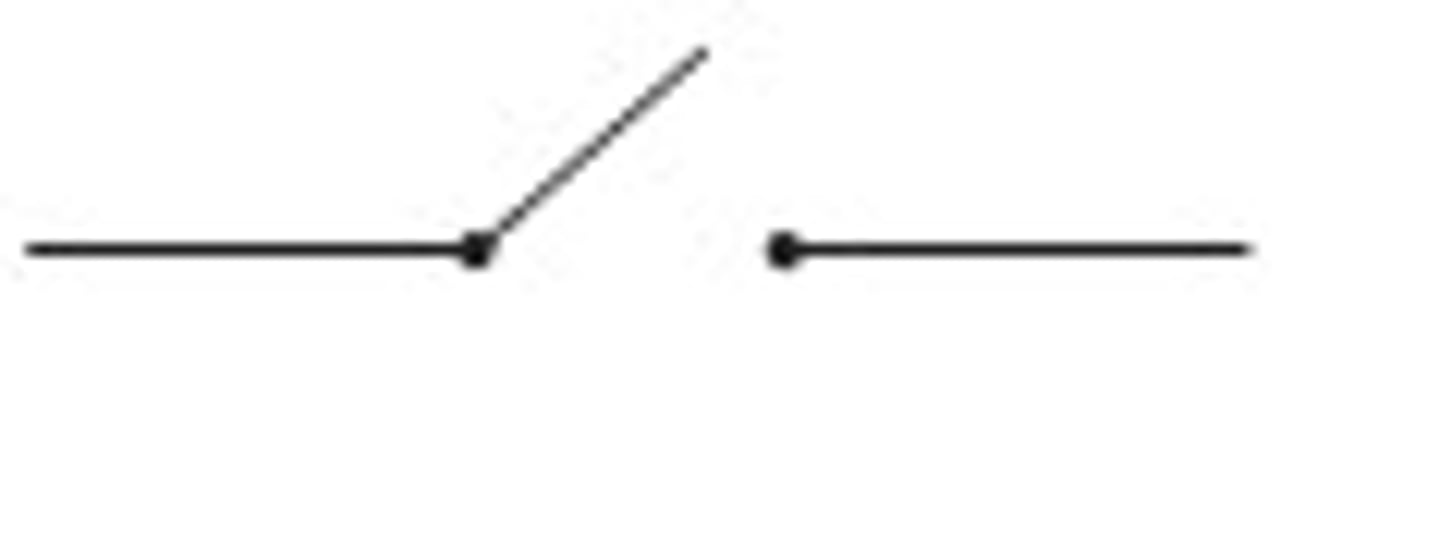
Switch
Can be open or closed
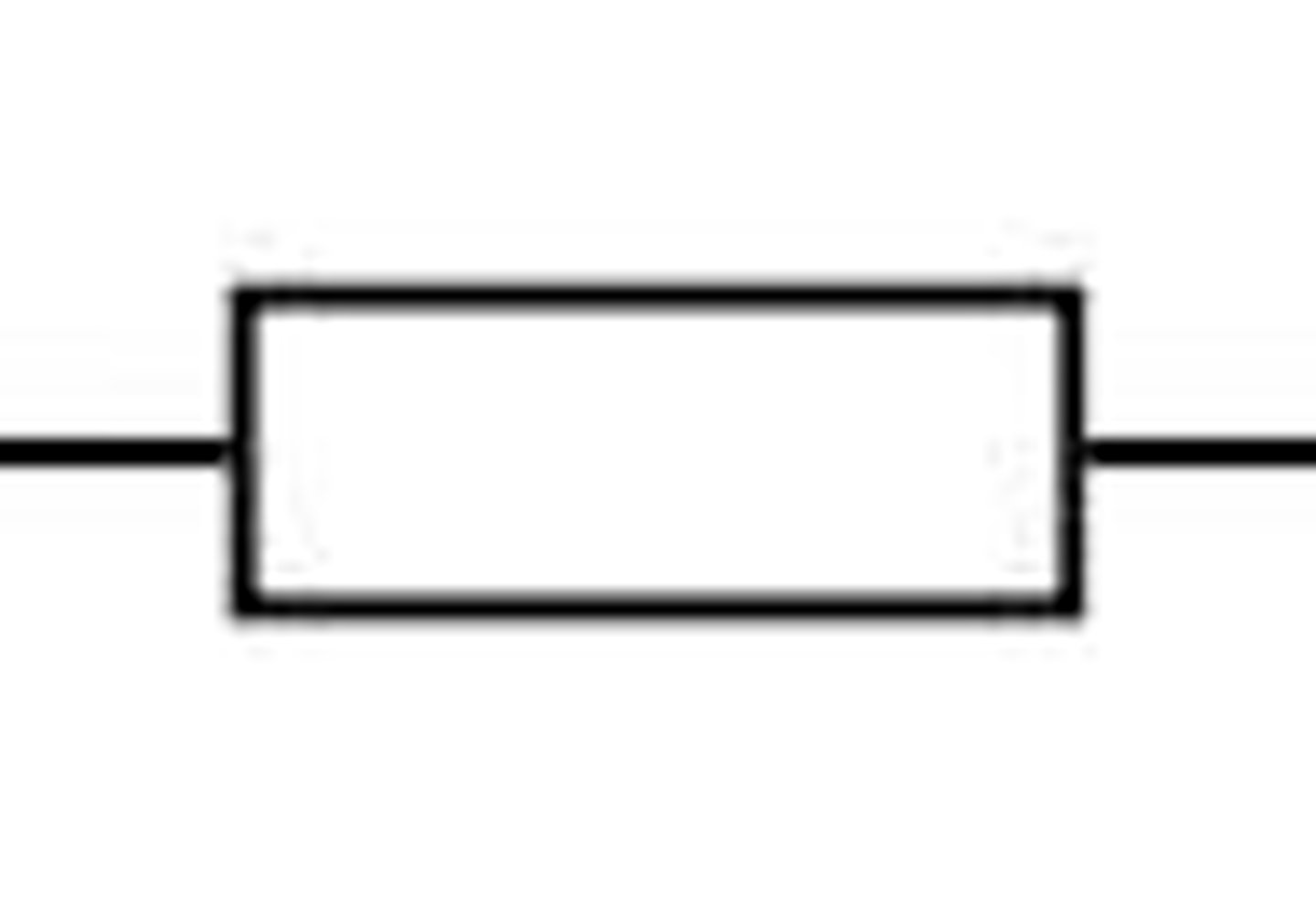
Resistor
Resistor is anything which can reduce the flow of current in a circuit.
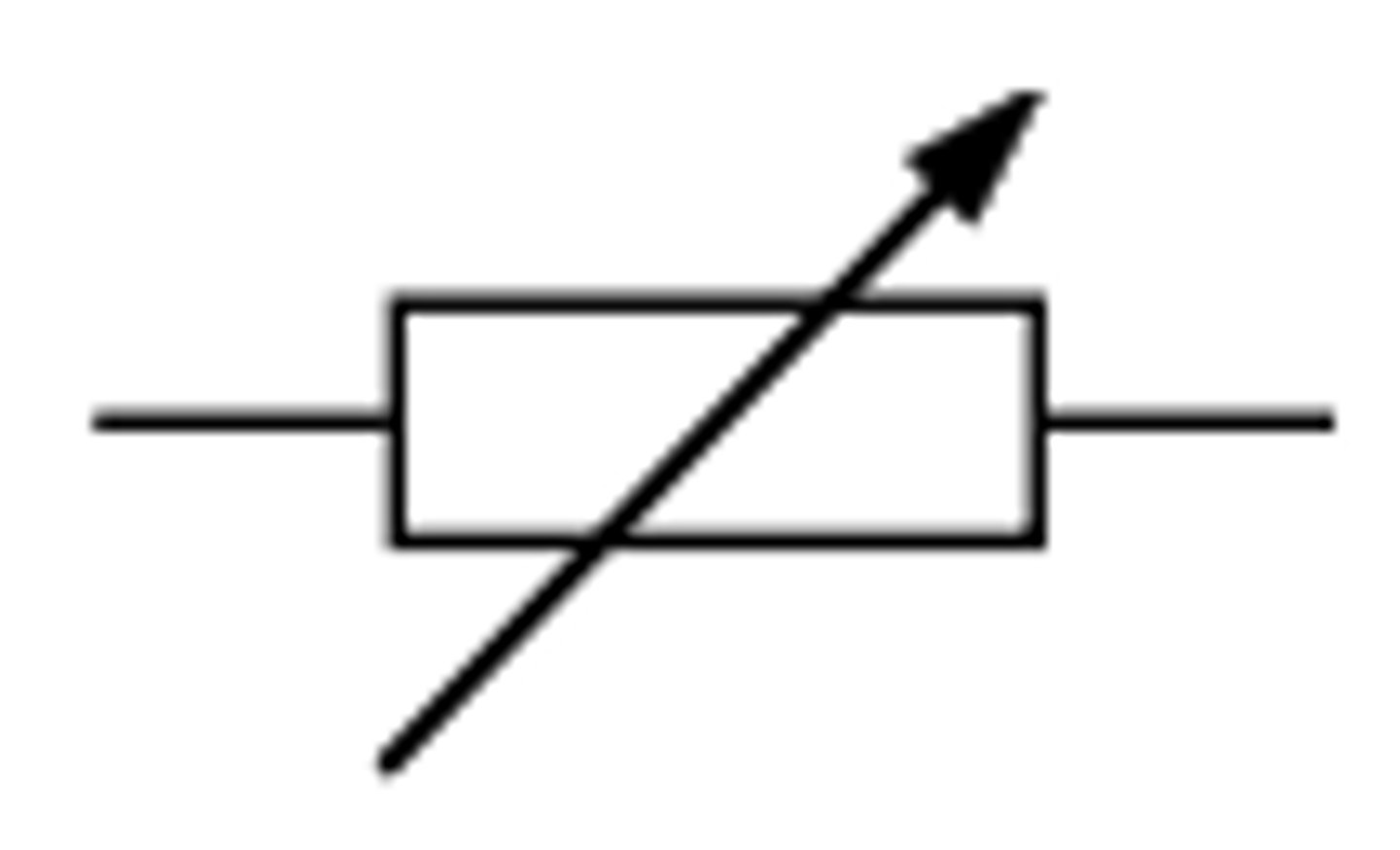
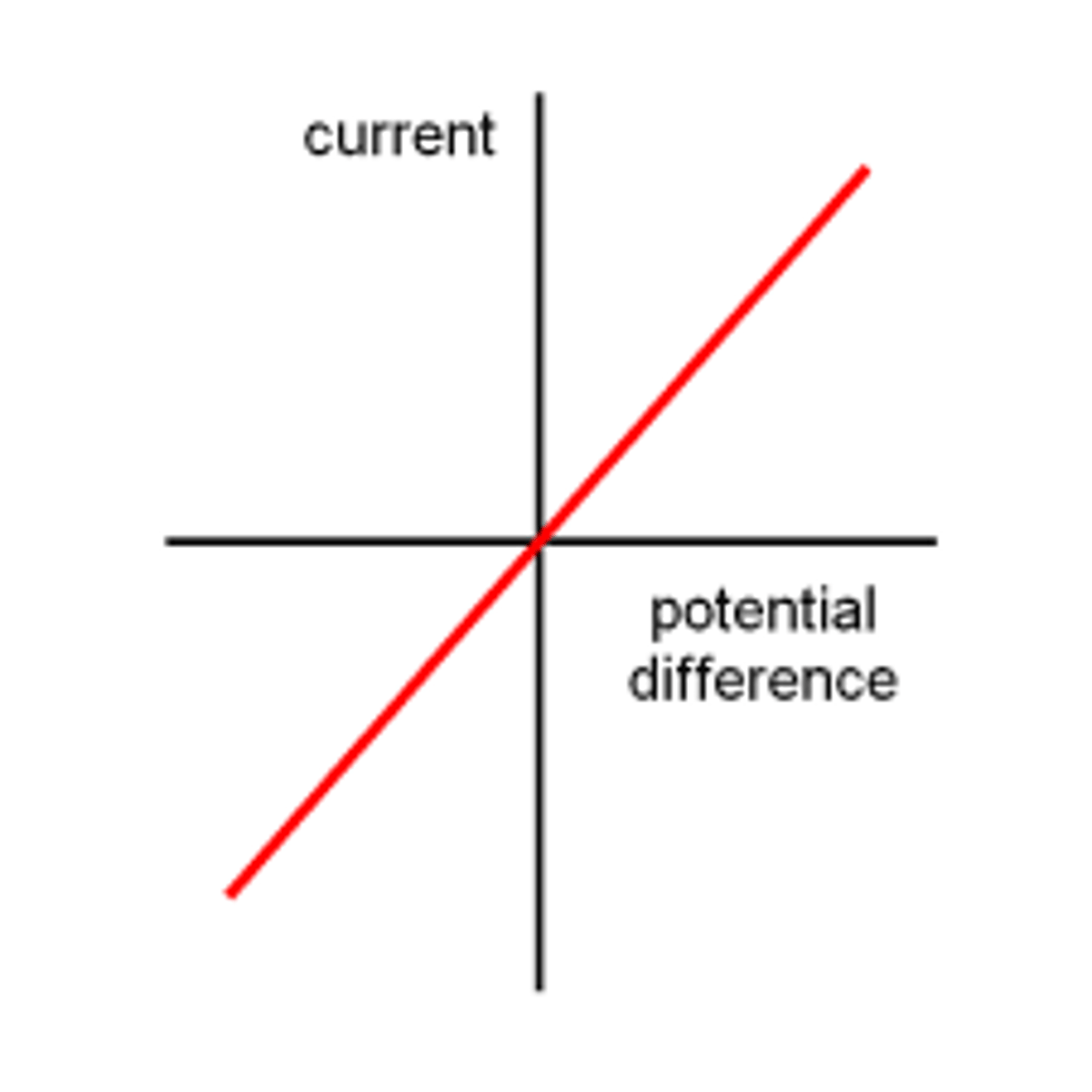
Variable resistor
You can change the resistance of a variable resistor.
As resistance of variable resistor is decreased, current through componenet increases.
Current and potential difference is directly proportional (linear).
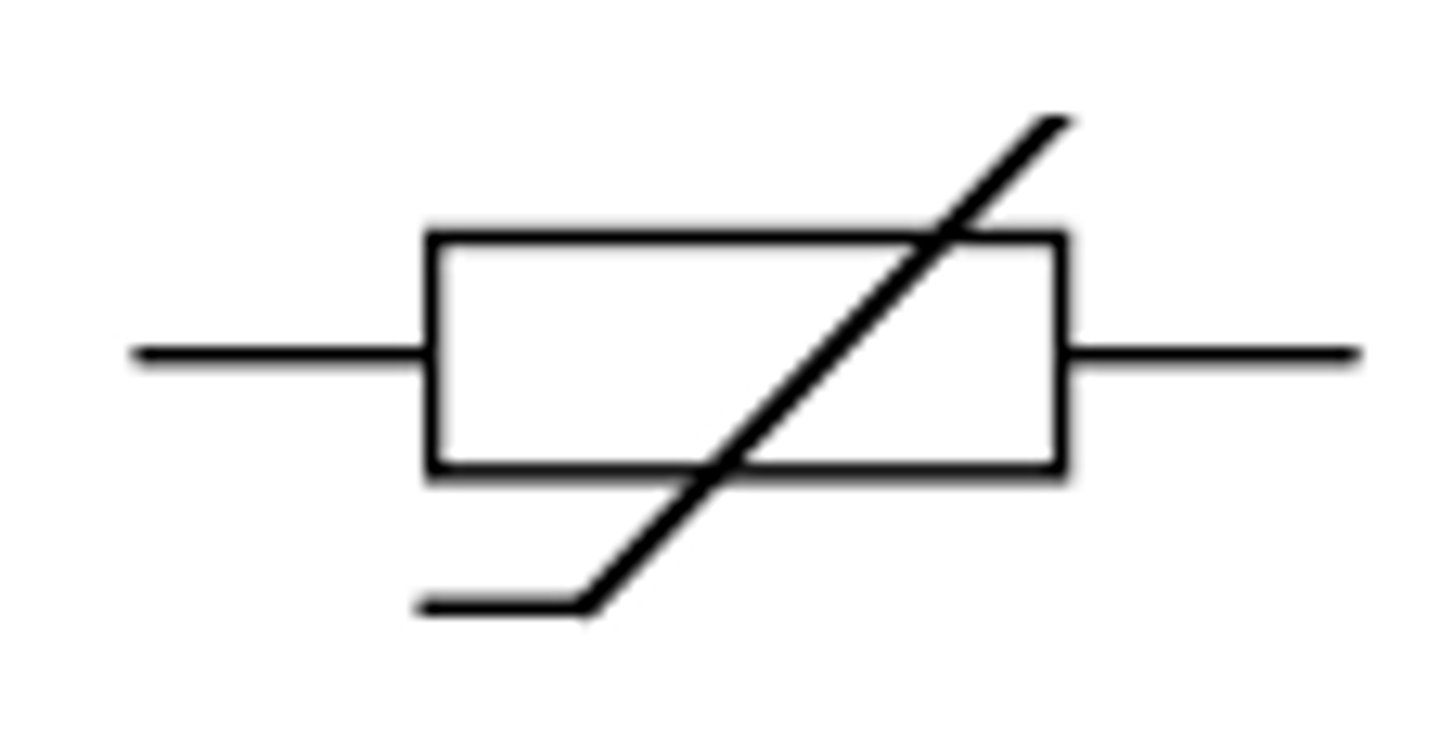
Thermistor
A type of resistor
The resistance of a thermistor changes with temperature.
Resistance decreases as temperature increases.
Graph is directly proportional (linear).
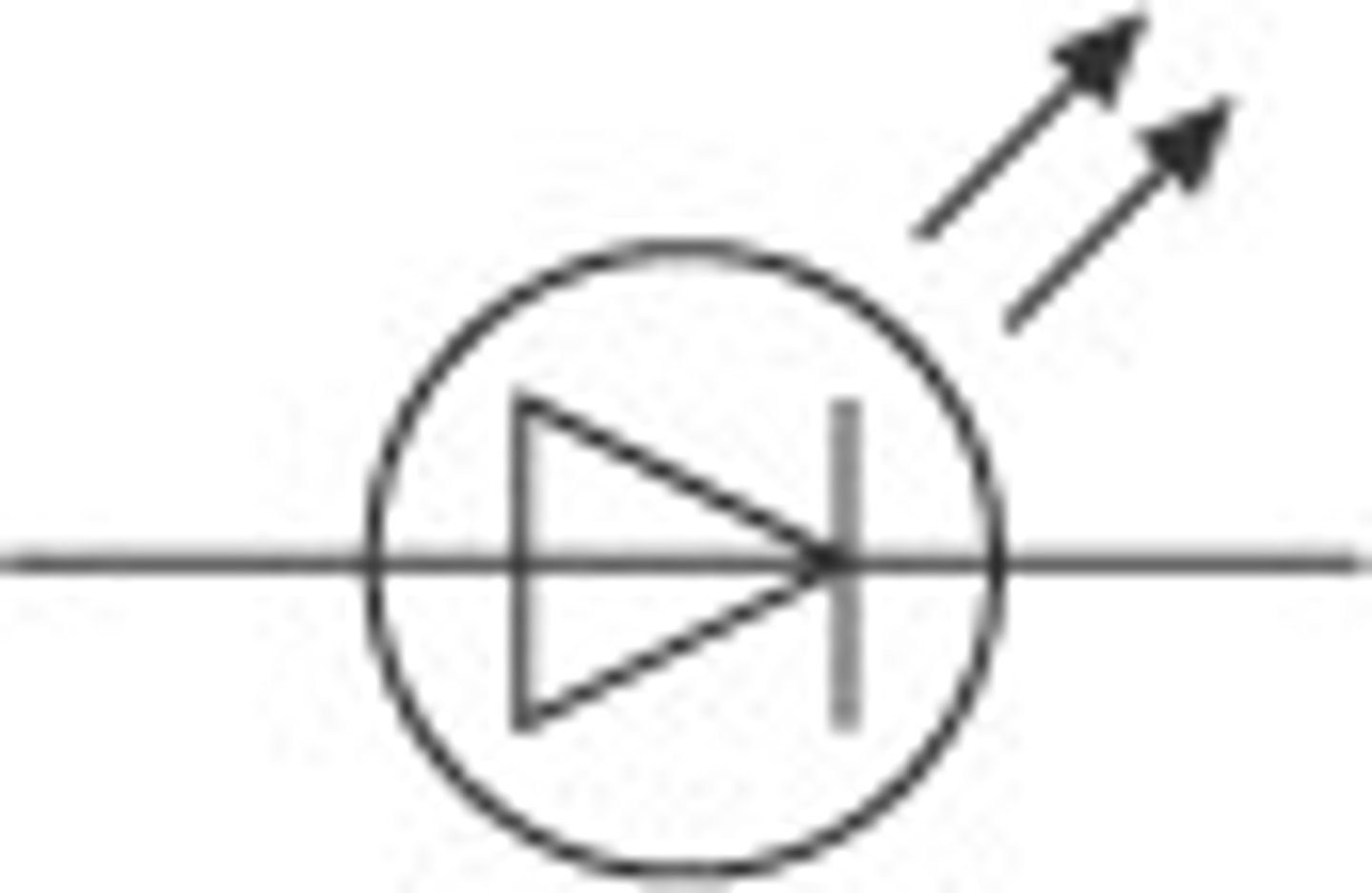
LED
Lamp
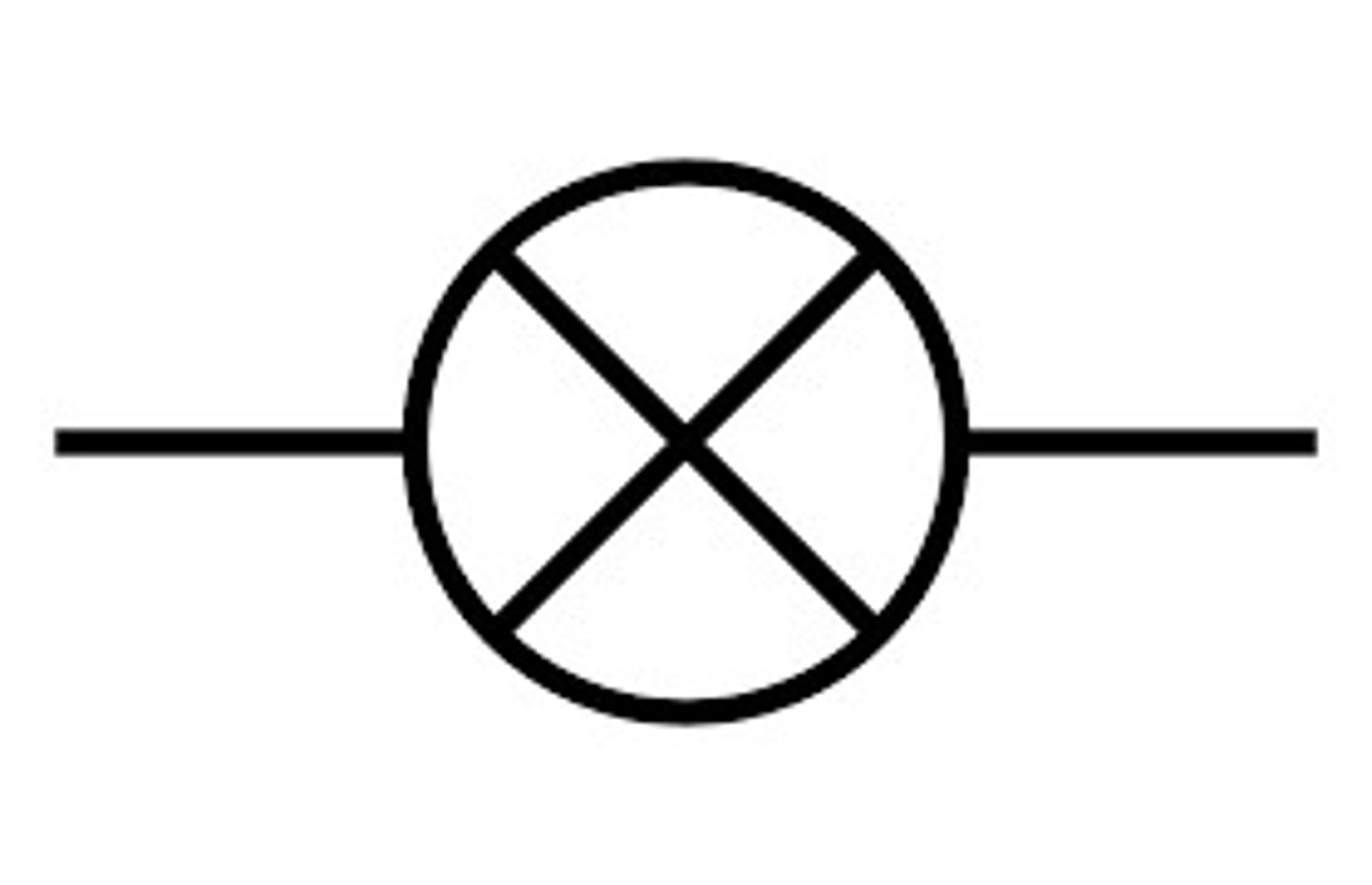
Fuse
Fuses set a maximum value for the current that can flow through a circuit.
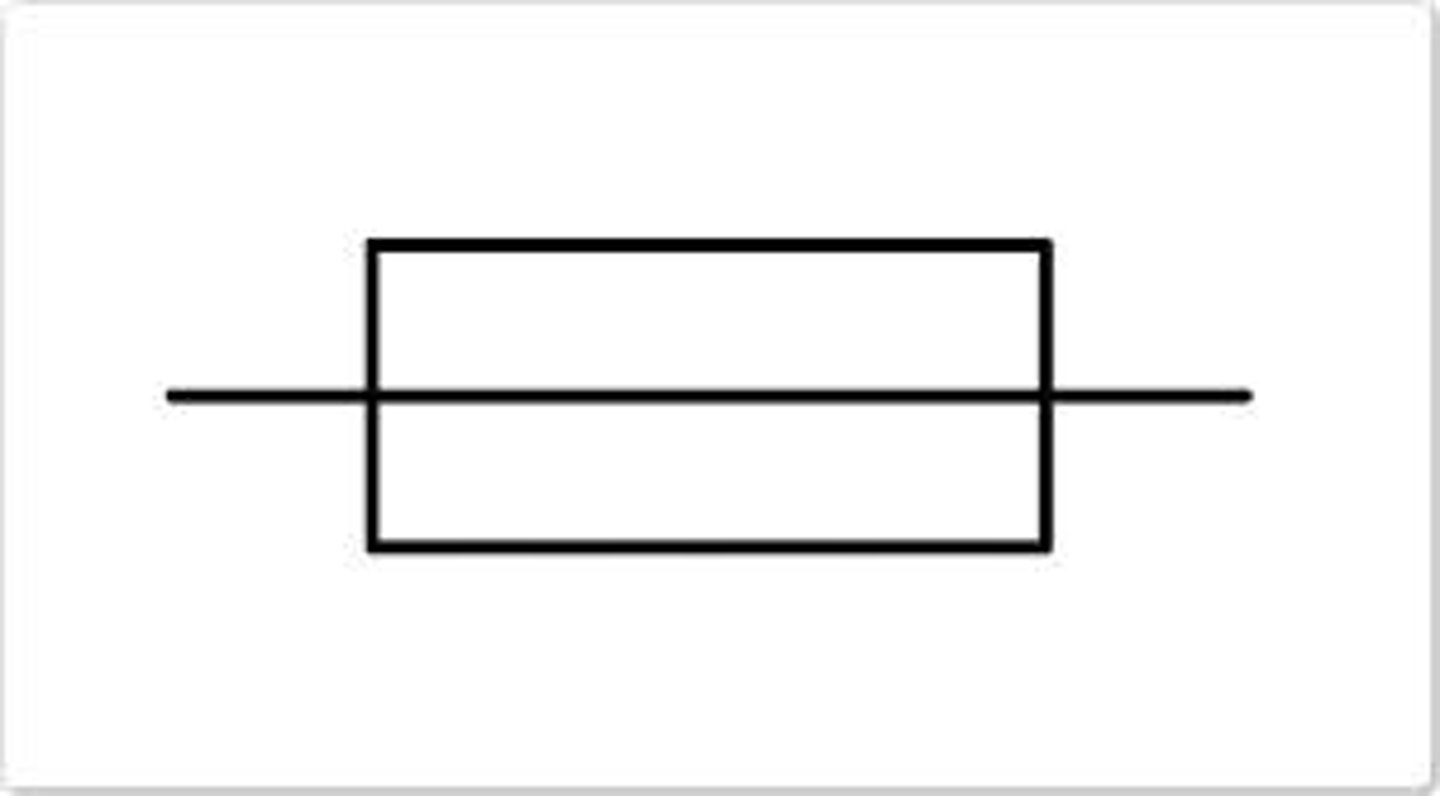
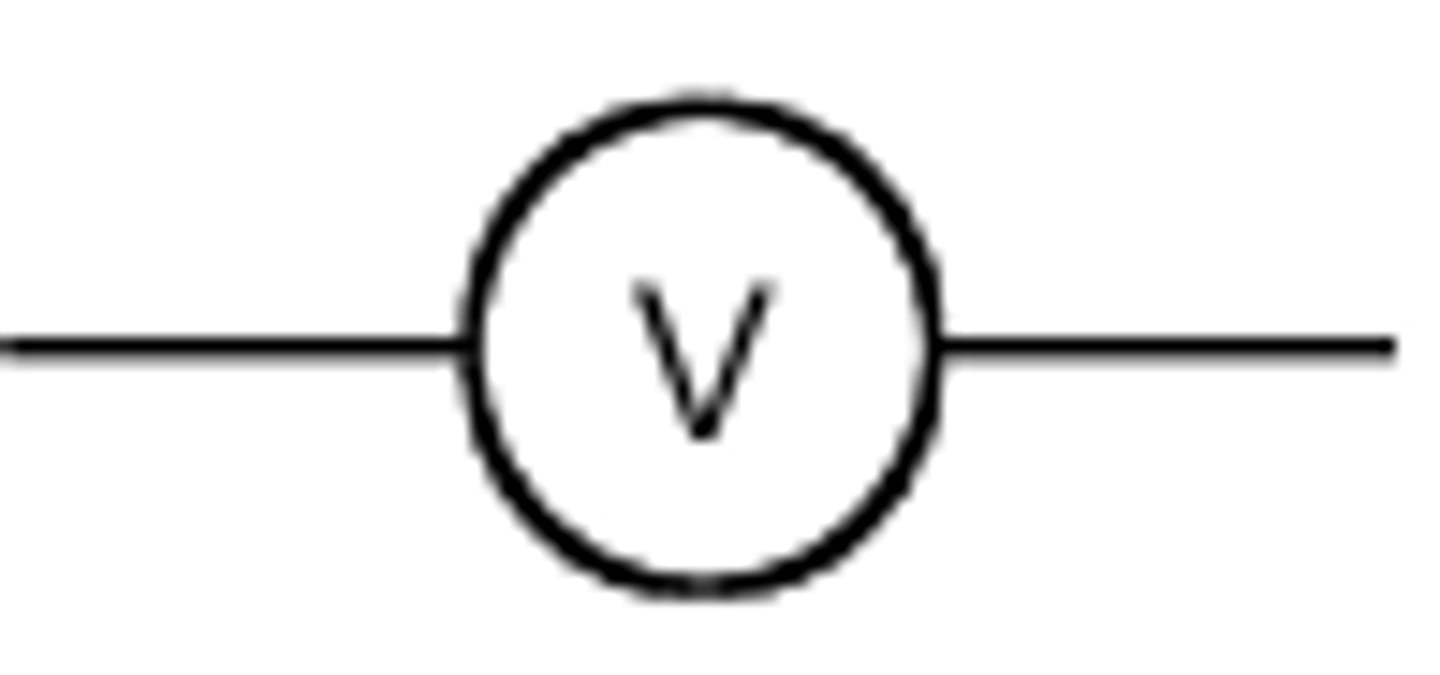
Voltmeter
Voltmeter measures potential difference between two points.
always connected in parallel
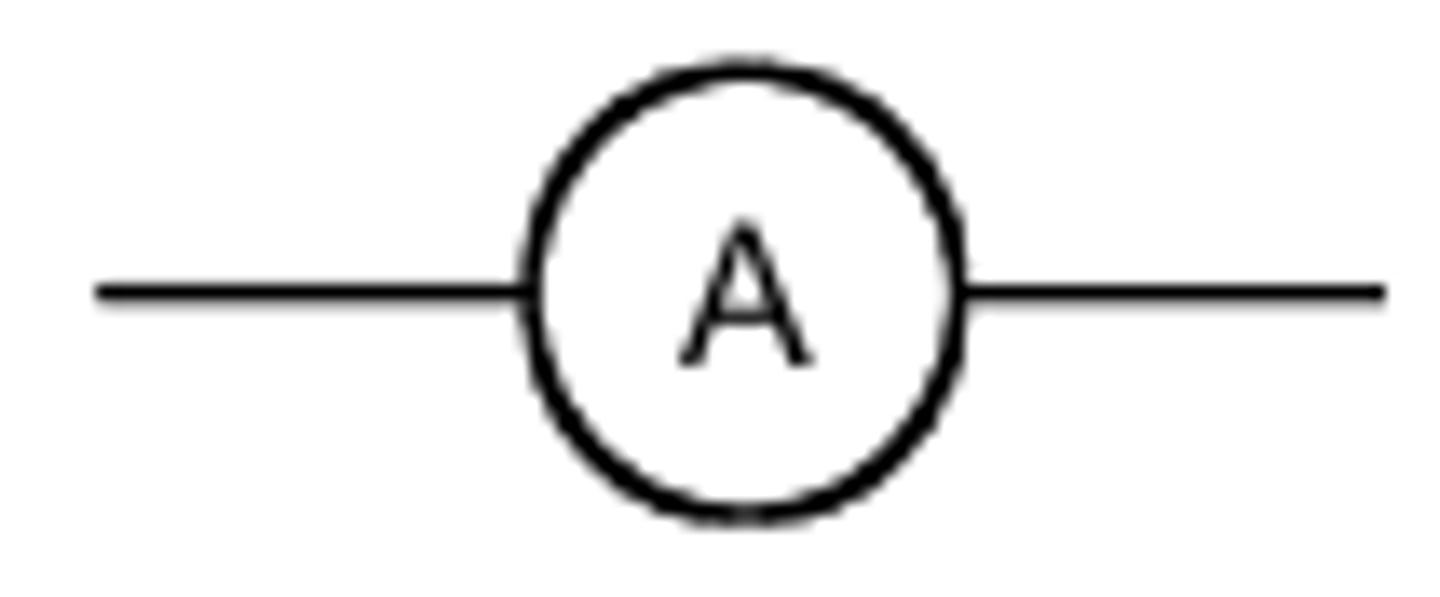
Ammeter
Ammeter measures current.
always connected in series
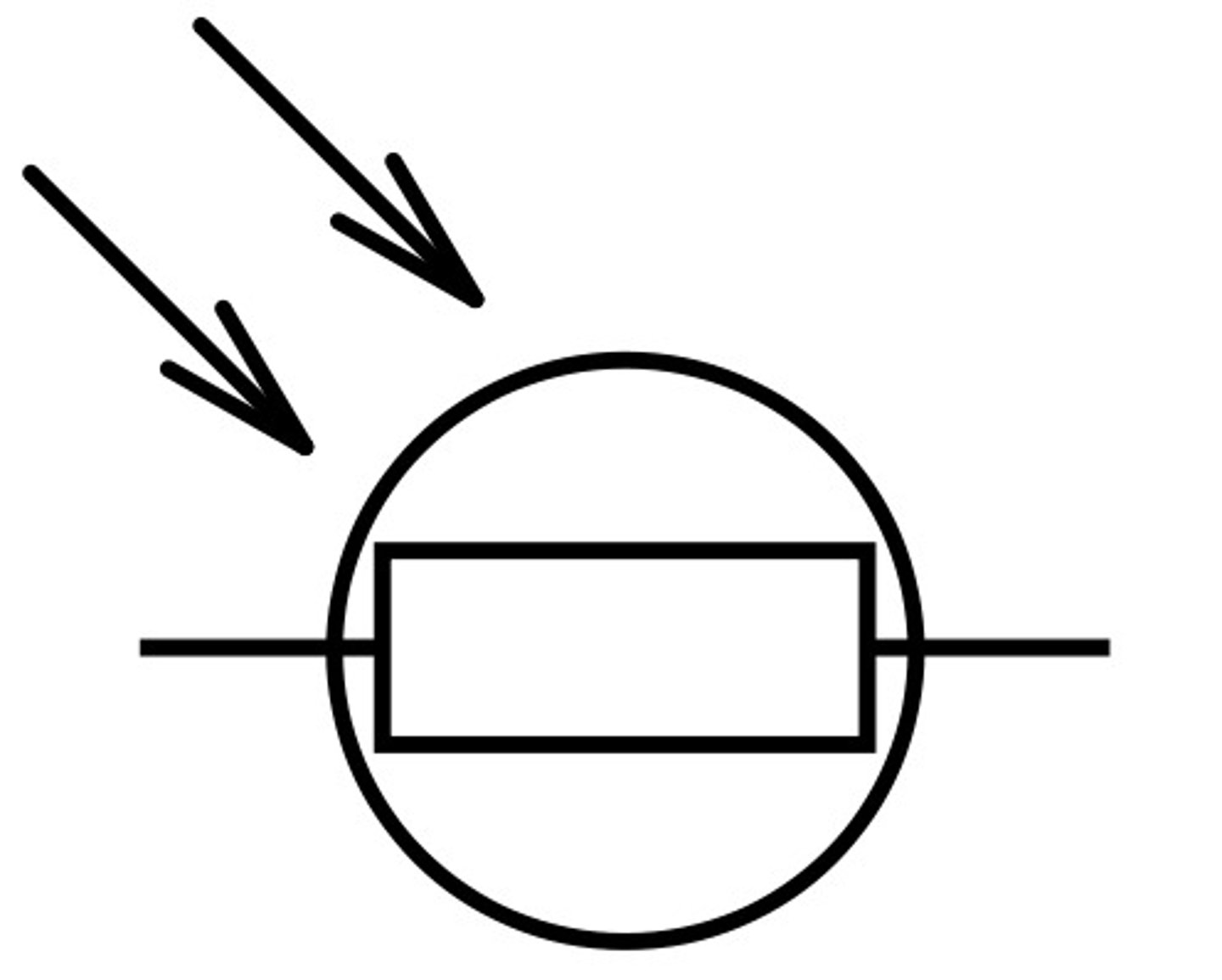
LDR
The resistance of the LDR (light dependent resistor) changes with brightness.
Resistance decreases as brightness increases.
Graph is directly proportional (linear)
Current
flow of charge. The amount of charge flowing past a given point every second.
Measured in amps (A)
symbol is I (capital i)
Equation linking charge and current
Q = I t
Q: charge coulombs (C), I: current amps (A), t = time (s)
Potential difference
When the charge leaves the cell, it has a maximum amount of EPE (electrical potential energy).
It gives its EPE to components as it goes around the circuit.
Equation linking current and resistance
V = I R
V: potential difference volts (v), I: current amps (A), R: resistance ohms (Ω)
current and resistance are inversely proportional
Ohm's law
the current through a component is directly proportional to the p.d. across it (provided that its temperature remains constant)
Current-voltage (I-V) characteristics for an ohmic resistor
Directly proportional, linear, through the origin
Variable resistor graph
non-ohmic
Diode graph
Series circuit
An electric circuit with a single path
Parallel circuit
A circuit that contains more than one path for current flow.
It has branches.
Current, potential difference and resistance in series circuits
current: the same everywhere
total p.d. of power supply shared between components
total resistance is sum of resistances of each component
Rtotal = R1 + R2
Current, potential difference and resistance in parallel circuits
current: total current equal to the sum of current in each branch
p.d. across each branch is equal
total resistance is less than the resistance of each resistor
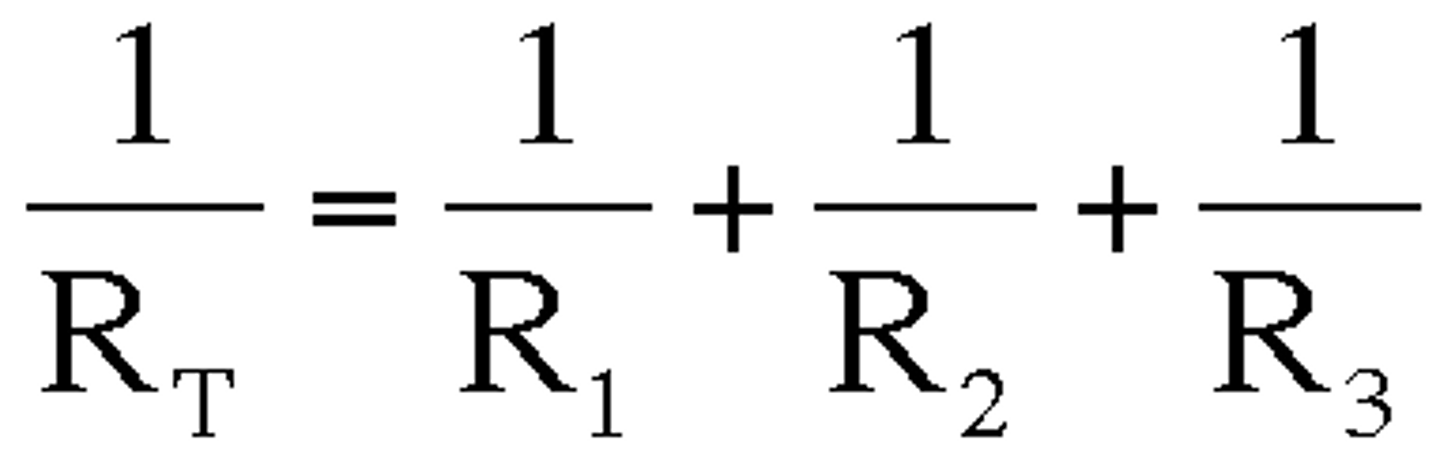
Direct current (d.c.)
Current which is supplied by cells and batteries.
Always flows in the same direction
graph of p.d. against time has a constant y value
Alternating current (a.c.)
Can come from a main socket
Changes direction constantly
graph of p.d. against time looks like a sine graph
Three core cable
Most plugs are attached to the mains using a three core cable.
This means there are three different wires within the order cable attached to each plug.
Each wire is colour coded.
Blue: neutral wire.
Green + yellow: earth wire.
Brown: live wire.
The wires are always in this order. Neutral, earth, live.
The plug also has a fuse.
Live wire
provides alternating potential (voltage) from power supply.
brown
Neutral wire
completes circuit (at or close to 0V).
blue
Earth wire
carries current if there is a fault. Provides a path with little resistance to the ground so current can go to the ground instead of through a person. eg. if a live wire was touching the metal casing of a washing machine, the current would flow through the earth wire to the ground.
green and yellow
Electric shocks
If you touch a live wire, even if the circuit isn't complete it is dangerous. The current will go through you to the ground which will complete the circuit.
Fuses
they are on the live wire
if the current exceeds a certain amount, the thin wire instead will melt and break the circuit.
Large current flows through fuse, maximum rating of fuse is exceeded, fuse 'blows', fuse reduces risk of electrical fires only
Circuit breakers
work much faster than fuses
When current exceeds a particular value, switch 'trips' (turns off)
Can help minimize risk of fire and electrocution
can be thermally activated, some compare amount of current entering and leaving an appliance and some are magnetically activated.
Double insulation
Electrical insulator - poor conductor of electricity.
Double insulation - two layers of insulation.
Eg a hairdryer. The plastic casing is one layer of insulation and the insulating wrap around the wires is the second layer of insulation.
Double insulated appliances do not need an earth wire.
Equation with power, volts and current
P = IV
P = power (Watts, W), I = current (amps, A), V = potential difference (volts, V)
Equation with power, current and resistance
equation for power dissipated
P = I^2 * R
Transformer
A transformer changes the voltage in an electric circuit.
Two types: step up and step down
Step-up transformers increase voltage. (decreases current)
Step-down transformers decrease voltage. (increases current)
By reducing the current, resistance is also reduced which means that lots of energy is saved rather than being dissipated.
Current and voltage are inversely proportional to each other.
Electricity is transmitted between pylons at a high voltage and low current.
Equation for electrical energy
E=V×I×t
where:
EEE is the energy dissipated,
VVV is the potential difference across the cable,
III is the current flowing through the cable,
ttt is the time for which the current flows.
The national grid
Power station --> step up transformer (increase voltage) --> pylon ---> step down transformer (decrease voltage) --> Homes
Insulators
Insulators do not allow charge to flow through them easily.
Conductors
Conductors allow charge to flow through them easily.
Charging by friction
Friction is a contact force that opposes motion.
Electrons are transferred.
Van de Graaff generator
A large charge will develop on the dome of a running Van de Graaff. Positive or negative will depend on the device.
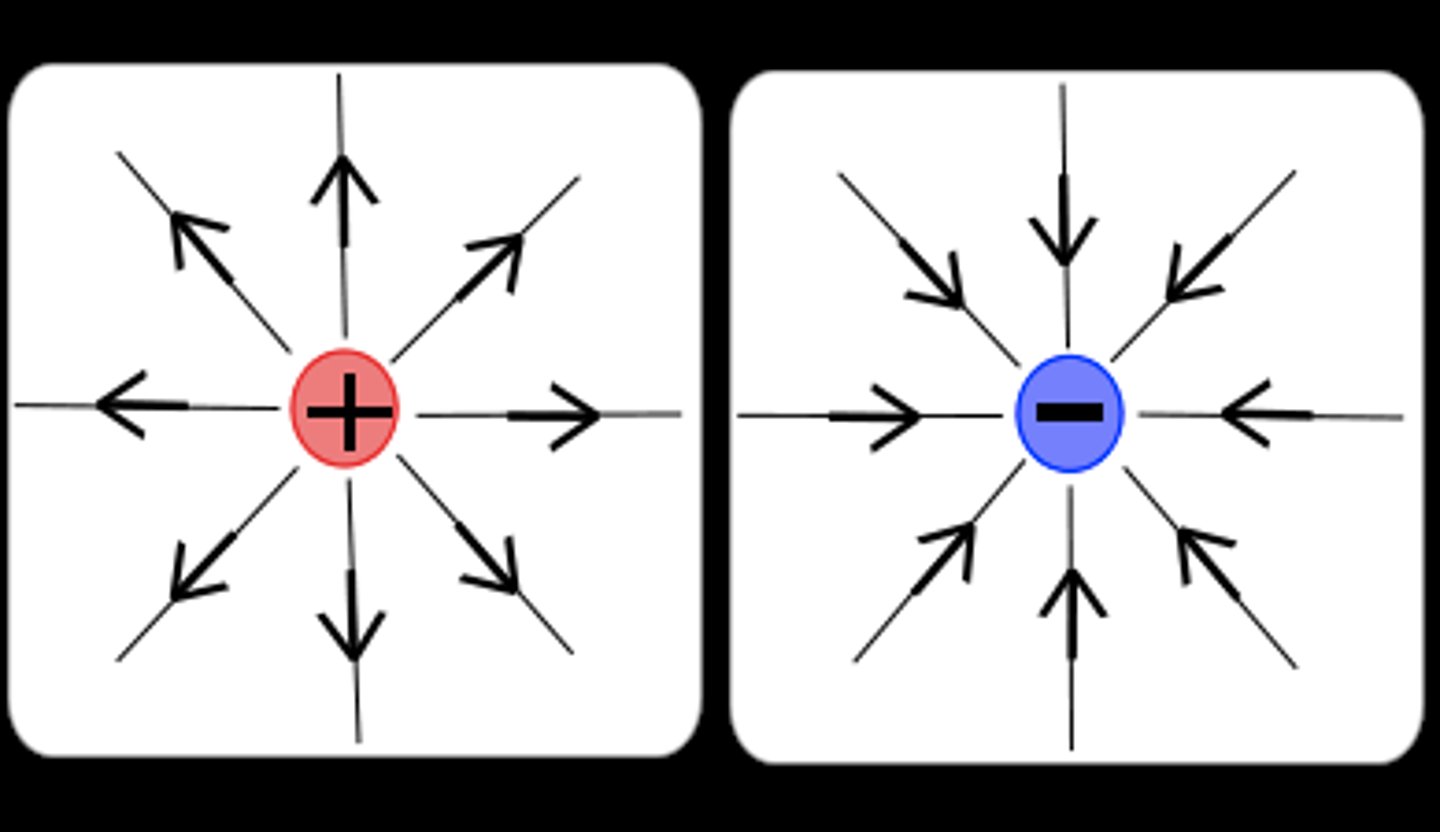
Electric field around a charged sphere
A positive charge placed around it will experience a force in the direction of the arrows.
Negative charges will always experience a force opposite to the direction in which the field lines are pointing.
The more closely spaced the field lines, the stronger the field and the larger the force that will be exerted on a given charge. Therefore, an electron that is closer to the sphere will feel a stronger force than a further away one.