PD E3- Male GU
1/73
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
What age range of patients should you discuss testicular self exam & safe sexual practices as well as prostate & CRC screening, sexual function, & incontinence?
≥ 40
What is an ovoid, rubbery structure that produces testosterone & spermatozoa?
*network of tightly coiled seminiferous tubules that converge and anastomose into efferent tubules encapsulated by tunica albuginea
Testis
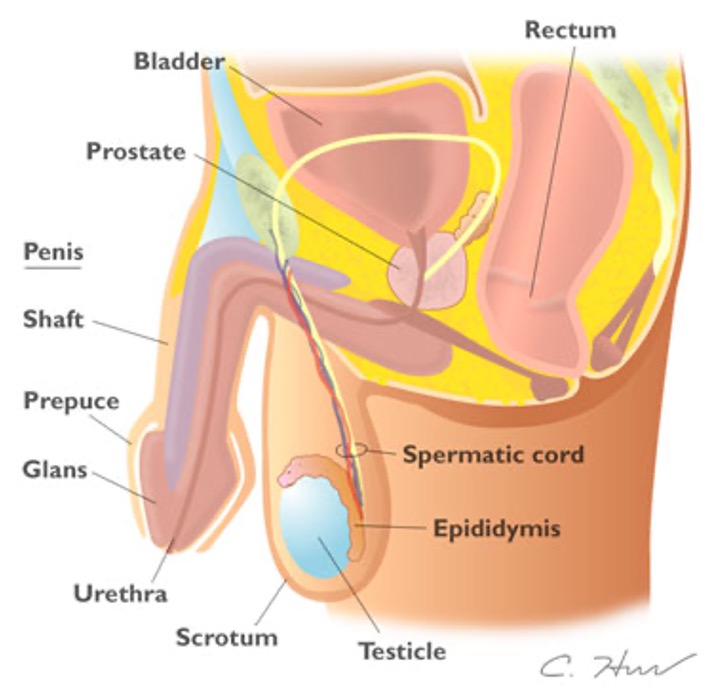
What is located on the posterolateral surface of each test and is a soft comma shape?
Epididymis
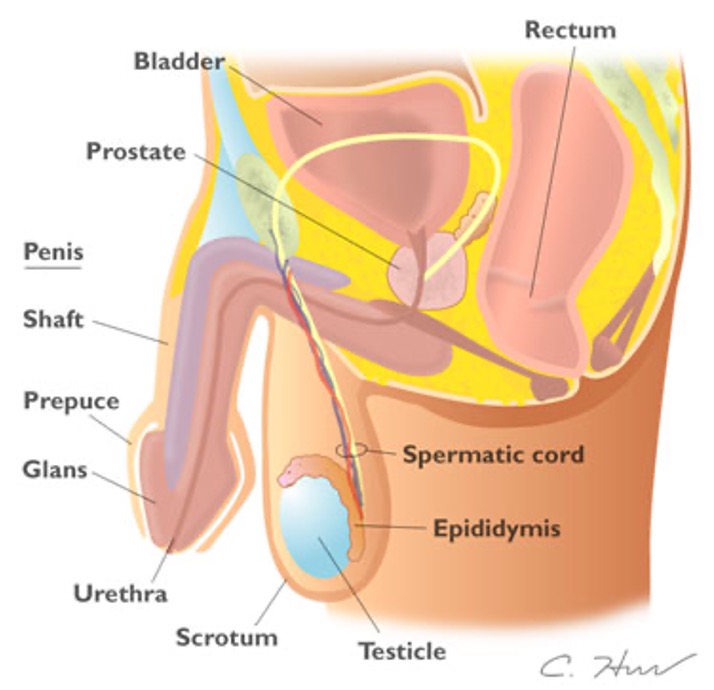
What begins at the tail of the epididymis, ascends the scrotal sac & passes through the internal inguinal ring into the abdomen and pelvis?
*joins seminal vesicle duct to form ejaculatory duct which passes into prostate gland
Vas deferens
What is a muscular pouch that contains the testes?
Scrotum
What structure is formed by vas deferent, testicular arteries, & veins?
Spermatic cord
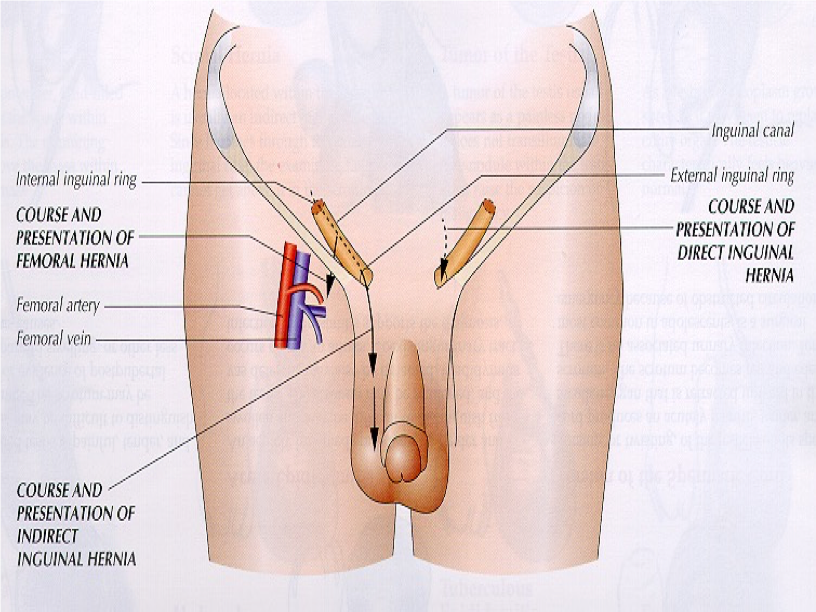
What structure?
lies above & approximately parallel to inguinal ligament & forms tunnel for vas deferens
exterior opening
Inguinal ring
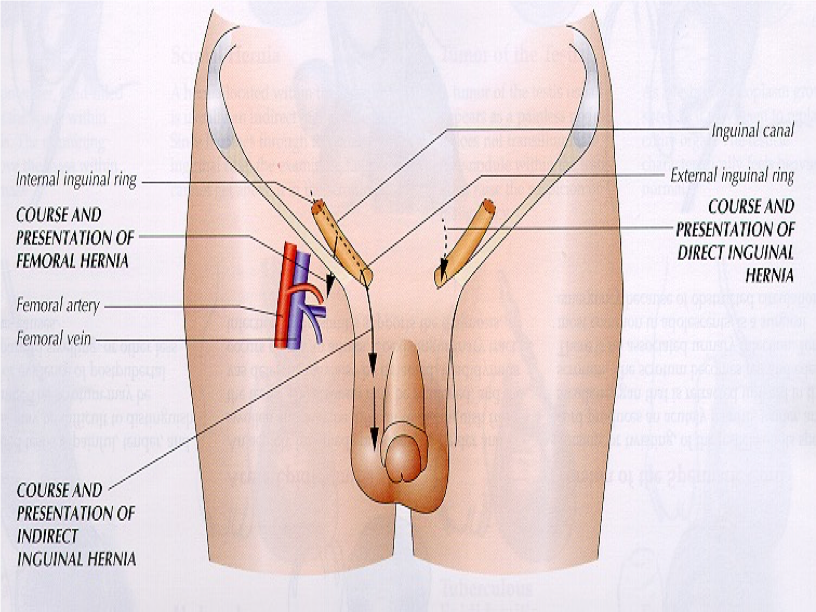
What structure?
lies below inguinal ligament
locate by placing R index finger from below on R femoral artery & middle finger will overlie femoral vein & ring finger will be on femoral canal where herniation may occur
Femoral canal
What are the borders of Hesselbach’s triangle?
Lateral (upper L to center): inferior epigastric vessels
Inferior (upper R to bottom L): Inguinal ligament
Medial (upper L to bottom L): rectus abdominis muscle
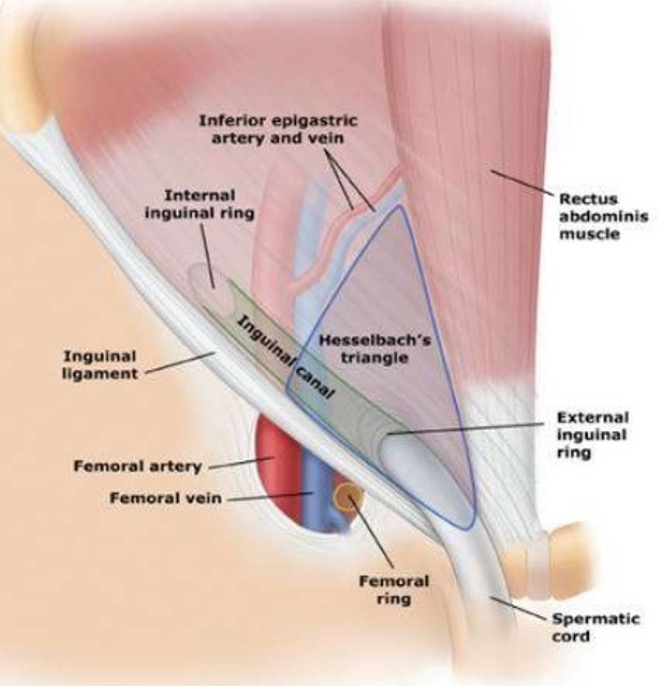
What is the region of potential weakness where a direct inguinal hernia can occur?
Hesselbach’s triangle
Direct or indirect inguinal hernia?
protrudes through both deep inguinal ring & superficial inguinal ring
can protrude into scrotum
due to incomplete closure of deep inguinal ring
possibly congenital
MC in males - infancy or old age
Indirect inguinal hernia
Direct or indirect inguinal hernia?
protrude through hesselbach triangle into inguinal canal
exit inguinal canal through superficial inguinal ring
lump in groin
caused by weakness in abdominal wall due to age
Direct inguinal herna
In what position should the patient be when you check for hernias or varicoceles?
Standing
What technique used to determine nature of a scrotal mass applies a light source to the side of scrotal enlargement?
Transillumination
What is cryptorchidism?
Undescended testes
What should you instruct the patient to do when inspecting inguinal / femoral area?
Cough or bear down
How do you elicit the cremasteric reflex?
*presence does NOT eliminate testicular torsion
Lightly stroke superior & medial thigh → utilizes sensory & motor nerve fibers of genitofemoral nerve (L1-L2)
What diagnosis?
Transillumination: no
Tenderness: none
Location: testes > 4cm inferior to pubic tubercle
Association: smooth with epididymis
Normal testes
What diagnosis?
Transillumination: no
Tenderness: none
Association: risk of testicular cancer
Cryptorchidism
What diagnosis?
Transillumination: yes
Tenderness: none
Location: anterior to testes
Association: fluid in tunica vaginalis
Hydrocele
What diagnosis?
Transillumination: yes
Tenderness: none
Location: head of epididymis posterior to testes
Association: benign
Spermatocele
What diagnosis?
Transillumination: no
Tenderness: none, unless infarction or torsion
Location: contiguous with testes anterior & posterior
Association: irregular nodule or mass
Neoplasm
What diagnosis?
Transillumination: no
Tenderness: none to mild
Location: posterior to tests - left side
Association: increase with valsalva, decrease with scrotal elevation; “bag of worms”
Varicocele
What diagnosis?
Transillumination: no
Tenderness: yes
Location: posterior to testes
Association: swelling or discrete nodule or mass
Epididymitis
What diagnosis?
Transillumination: no
Tenderness: yes
Location: swelling and mass tender around testes
Association: exquisite pain and tenderness, associated with testicular cancer
Torsion
What diagnosis?
Transillumination: no
Tenderness: no
Location: epididymitis anterior to testes
Association: normal variant
Anteverted epididymitis
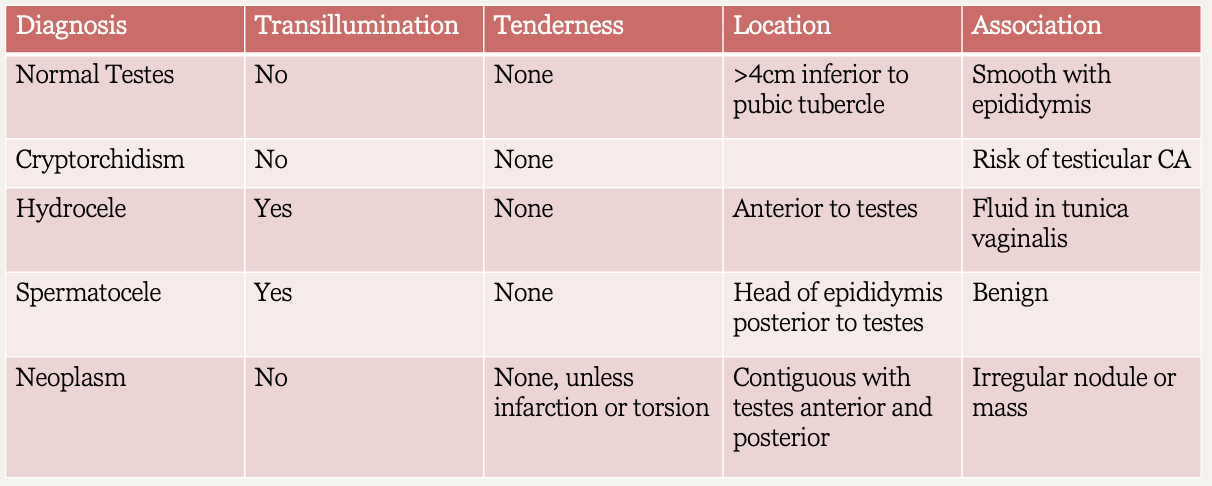
Scrotal diagnosis chart
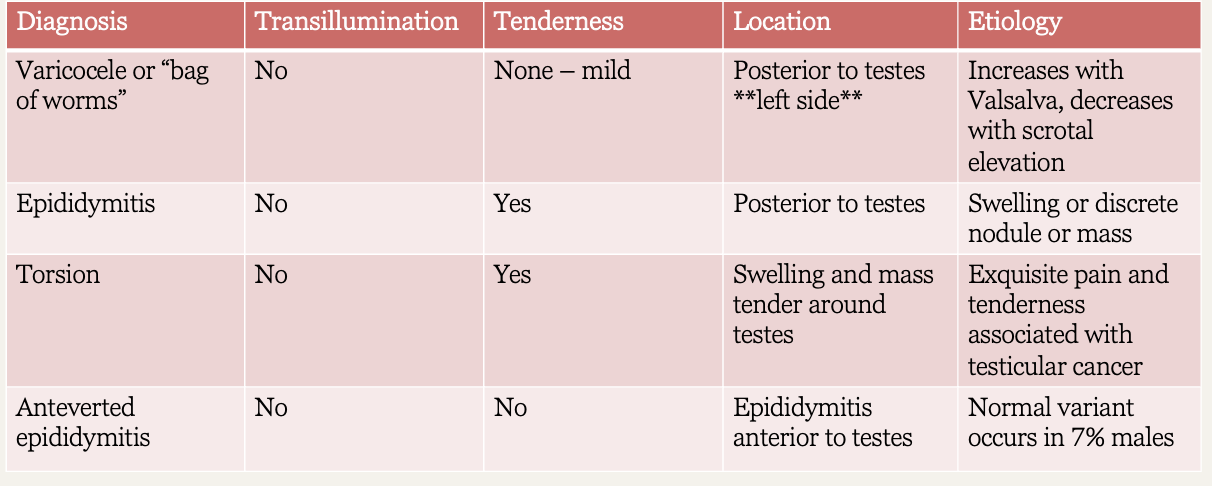
What emergent conditions might cause an acute scrotum?
Testicular torsion, fournier’s gangrene, epididymitis w/ abscess formation, strangulated inguinal hernia
What are hydroceles commonly associated with?
Indirect inguinal hernia
Most epididymides are _____
Posterior
What are RF for the development of Fournier’s gangrene?
Uncontrolled DM, high dose steroids, neutropenia
Where is an indirect inguinal hernia?
Out of hesselbachs triangle → enters inguinal canal lateral to inferior epigastric vessels & exits inferior to inguinal ligament
Where is a direct inguinal hernia?
Within hesselbach’s triangle → breaches posterior inguinal wall & passes medial to inferior epigastric vessels
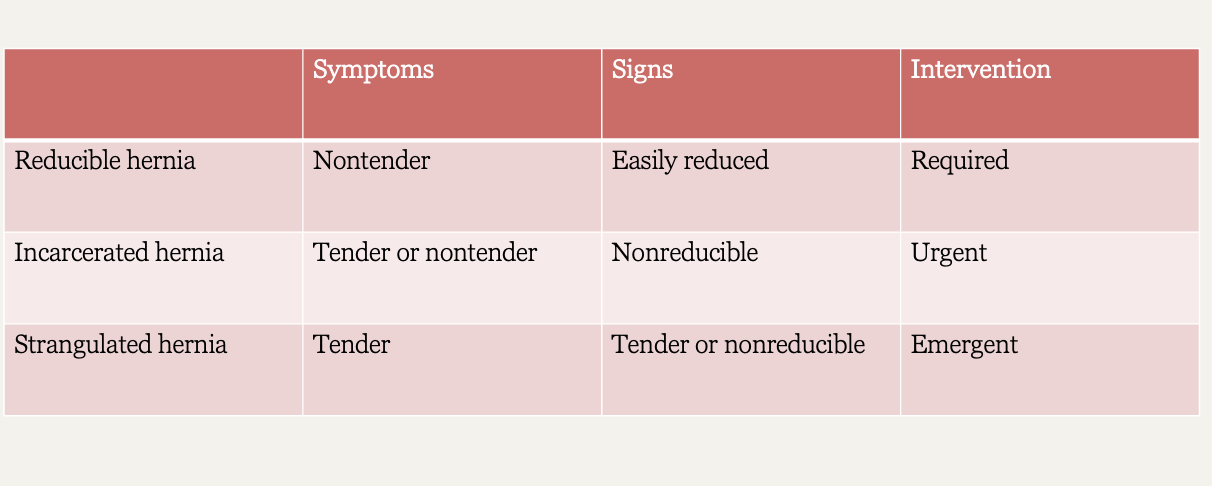
Hernia charts
What kind of hernia?
nontender
easily reduced
required intervention
Reducible hernia
What kind of hernia?
tender or nontender
non reducible
urgent intervention
Incarcerated hernia
What kind of hernia?
tender
non reducible
emergent intervention
Strangulated hernia
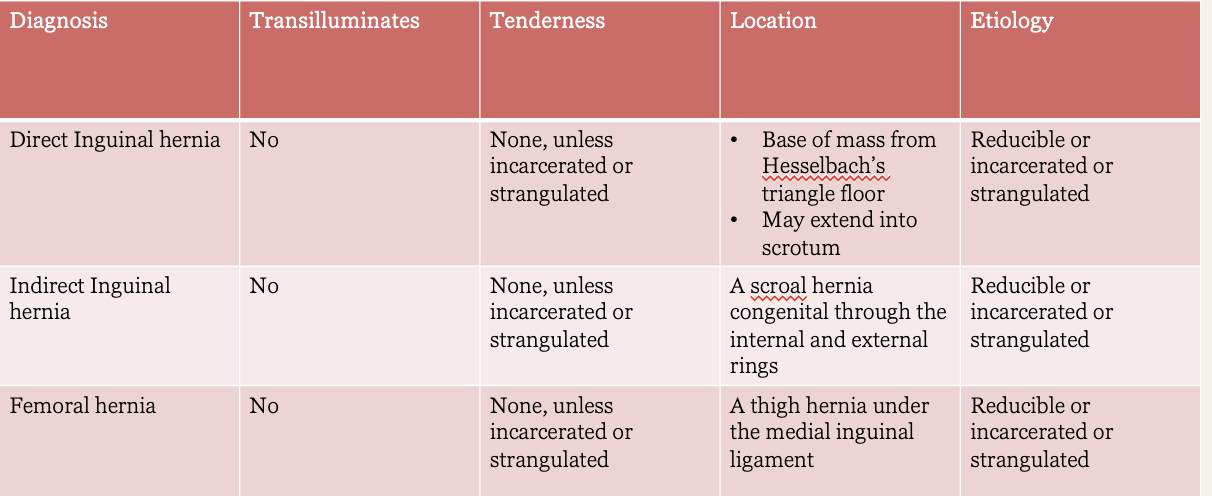
What kind of hernia?
Transillumination: no
Tenderness: none, unless incarcerated or strangulated
Location: base of mass from hesselbach’s triangle floor → may extend into scrotum
Etiology: reducible or incarcerated or strangulated
Direct inguinal hernia
What kind of hernia?
Transillumination: no
Tenderness: none, unless incarcerated or strangulated
Location:scrotal hernia; congenital; through the internal and external rings
Etiology: reducible or incarcerated or strangulated
Indirect inguinal hernia
What kind of hernia?
Transillumination: no
Tenderness: none, unless incarcerated or strangulated
Location: thigh hernia under the medial inguinal ligament
Etiology: reducible or incarcerated or strangulated
Femoral hernia
What is edematous foreskin that becomes trapped behind the head of the penis?
Paraphimosis
What is foreskin that is unable to be retracted from the head of the penis?
Phimosis
What condition?
inflammation of glans → redness, pain & swelling
urinary discharge, dysuria, dribbling of urine
causes: Candida albicans, reiter’s syndrome, or AI disorder
Balantitis
What is a hydrocele?
Nontender, fluid filled mass within the tunica vaginalis that transilluminates on exam
What is epididymitis?
Painful inflammation of epididymis
*exam may be easier for patient in supine
What is a spermatocele?
Painless, moveable cystic mass above the testes that transilluminates on exam
What are varicose veins of the spermatic cord that resemble a “bag of worms”?
Varicocele
What condition?
firm nodules w/in testicles
common bt ages 15-45
instruct pt on self exams → after warm shower, stand in front of mirror & observe any swelling in the scrotum & examine each testicle with both hands
Testicular cancer
What condition?
abrupt onset of testicular or scrotal pain
sometimes abdominal
MC during puberty - ages 12-18
cremasteric reflex absent in most
US & emergency surgery
Testicular torsion
What condition?
Necrotizing fasciitis of perineum and often involves scrotum
pain in abd wall & migrates to gluteal muscle, scrotum, & penis
emergency surgery necessary
Fournier’s gangreneI
Who is fournier’s gangrene MC in?
DM, indwelling catheters, urethral trauma or immunocompromised
What position?
supine with bent knees
used for DRE in patient with difficulty standing
Modified lithotomy
What position?
left lateral prone with right upper leg flexed
used for DRE in bedridden or weak patients
Sim’s position
What position for DRE allows for thorough inspection of anus and palpation of rectum?
Standing with hips flexed
How do you assess sphincter tone?
Ask patient to squeeze anal muscles around finger
How do you assess posterior and lateral walls of the rectum?
Rotate ringer through 180° by hyper pronating wrist
What is a normal finding in DRE?
Uniformly smooth & pliable
What might indicate an abscess (perirectal sepsis) on DRE?
Extreme tenderness
What is the course of enlargement of the prostate?
Small during childhood → inc 5-fold between puberty & 20 y/o → increasingly enlarges in 5th decade
How do you palpate the prostate during DRE?
Sweep finger anteriorly through rectal wall, identify the 2 lobes with longitudinal groove (median sulcus) between them, & note size, modularity, consistency, and tenderness
What prostate diagnosis?
2.5 cm from side to side
prominent median sulcus
consistency is rubbery and smooth
tenderness not usual
pt should feel urge to urinate when you palpate
Normal prostate
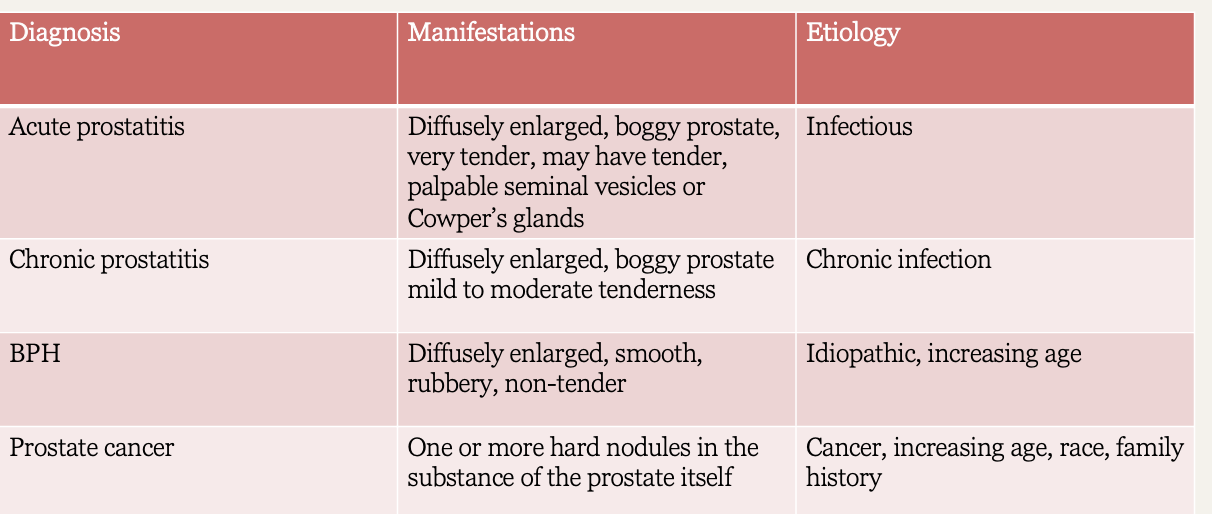
What prostate diagnosis?
enlargement of gland is symmetrical
marked protrusion into rectal lumen
smooth with no modularity
median sulcus may be indistinguishable
consistency is rubbery, boggy or slightly elastic
BPH
What prostate diagnosis?
asymmetric shape
hard consistency
discrete nodule may be palpable
median sulcus often obscured
Prostate cancer
What prostate diagnosis?
gland is swollen → diffusely enlarged, boggy prostate
firm consistency
very tender to touch
tender palpable seminal vesicles or cowpers glands
infectious etiology
Acute prostatitis
What prostate diagnosis?
gland is swollen → diffusely enlarged boggy prostate
mild to moderate tenderness
caused by trauma to prostate, as in bicycle riders
can be painless except for dull perineal pressure during urination or defecation
common cause of male infertility
Chronic prostatitis
Prostate diagnosis chart
What is a normal PSA?
≤ 4 ng/mL
What is an abnormal PSA?
> 4; doubles within a year
*can be elevated in benign conditions such as prostatitis, BPH
What PSA level is almost always due to cancer?
≥ 10
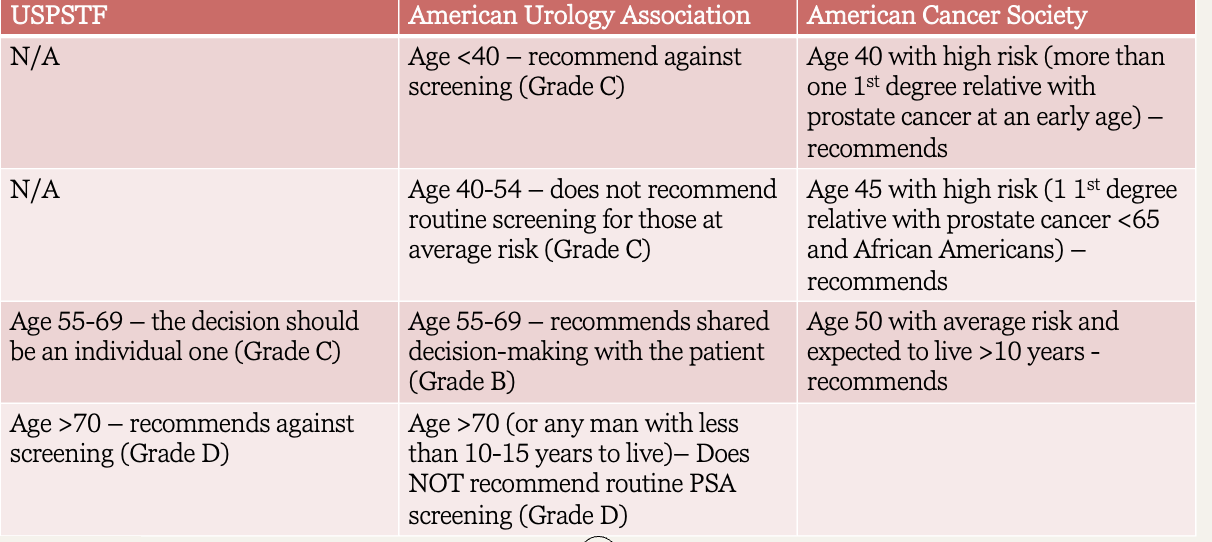
Prostate guidelines
What does a boggy prostate indicate?
Inflammation
What might the absence of a prostate indicate?
Past radiation or surgery for prostate cancer
What must also be assessed in any case of prostate enlargement?
Size of urinary bladder
What should be included in the exam of any man with suprapubic abdominal discomfort, distended abdomen, or both?
DRE / PSA