2.4 Price elasticity of supply
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
price elasticity of supply
is the responsiveness of a change in supply to a change in price. The formula for this is:

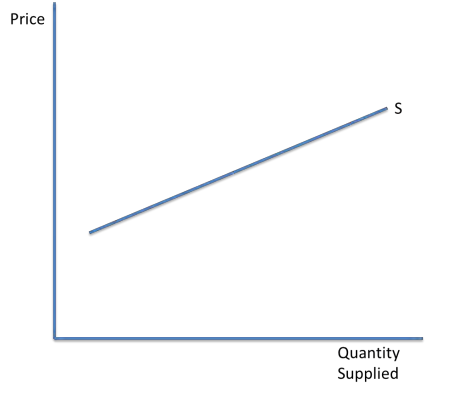
If supply is elastic
Firms can increase supply quickly at little cost. The numerical value for PES is >1
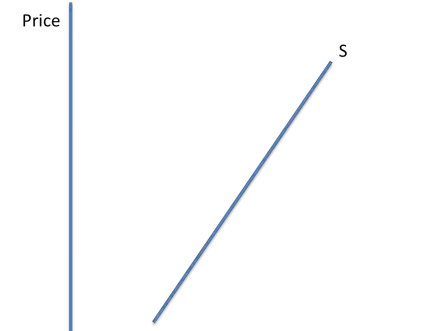
if supply is inelastic
an increase in supply will be expensive for firms and take a long time. PES is <1
Supply has PES = 0 supply is fixed, so if there is a change in demand, it cannot be met easily.

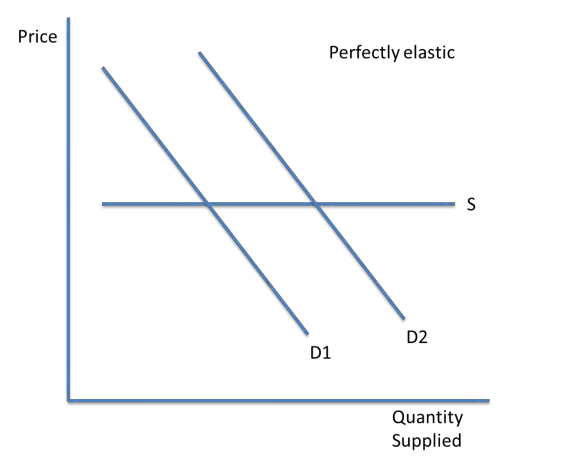
supply is perfectly elastic when PES = infinity. Any quantity demanded can be met without changing price
If the price of producing wheat increases by 15% and the quantity supplied decreased by 20%, the PES of wheat is : -20%/15% = -1.33
since the value is negative, the supply of wheat is relatively price inelastic.
factors influencing PES :
1) Time scale
2) Spare capacity
3) Level of stocks
4) How substitutable factors are
5) Barriers to entry to the market
Time Scale
In the short run, supply is more price inelastic, because producers cannot quickly increase supply. In the long run, supply becomes more price elastic.
spare capacity
if the firm is operating at full capacity, there is no space left to increase supply. If there are spare resources, for example in a recession there are lots of spare and unemployed resources, supply can be increased quickly.
Levels of stock
If goods can be stored, such as CDs, firms can stock them and increase market supply easily. If the goods are perishable, such as apples, firms cannot stock them for long so supply is more inelastic.
How substitutable factors are
If labour and capital are mobile, supply is more price elastic because resources can be allocated to where extra supply is needed. For example, if workers have transferable skills, they can be reallocated to produce a different good and increases the supply of it.
Barriers to entry to the market
Higher barriers to entry means supply is more price inelastic, because it is difficult for new firms to enter and supply the market