Bio 1115- Chapter 14 (genetics and mendel)
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Genetics
The scientific study of heredity
Heredity
Passing of traits from parents to offspring
genes
DNA segments that serve as the key functional units in hereditary transmission.
alleles
Different forms of a gene
pure lines
produce identical offspring when self-pollinated
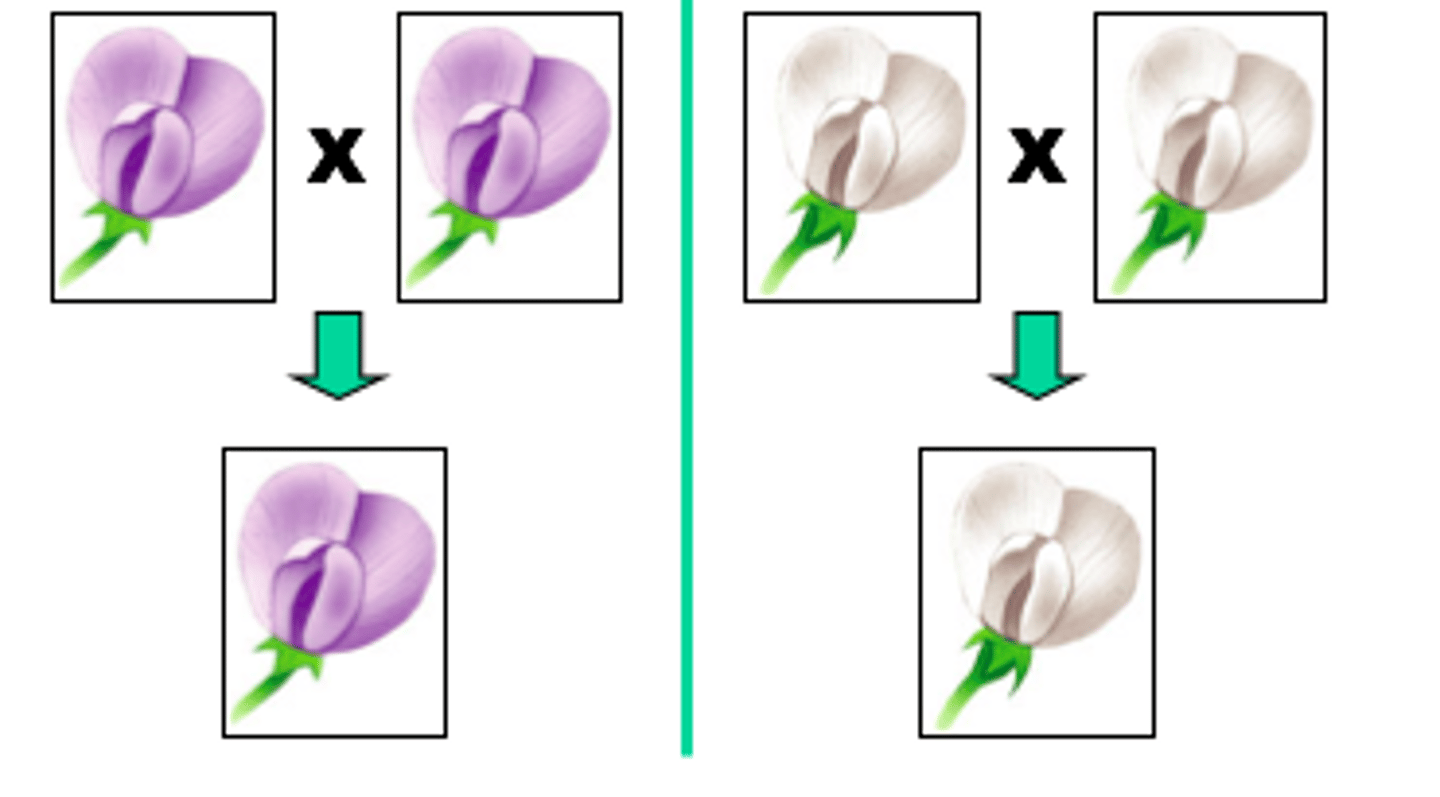
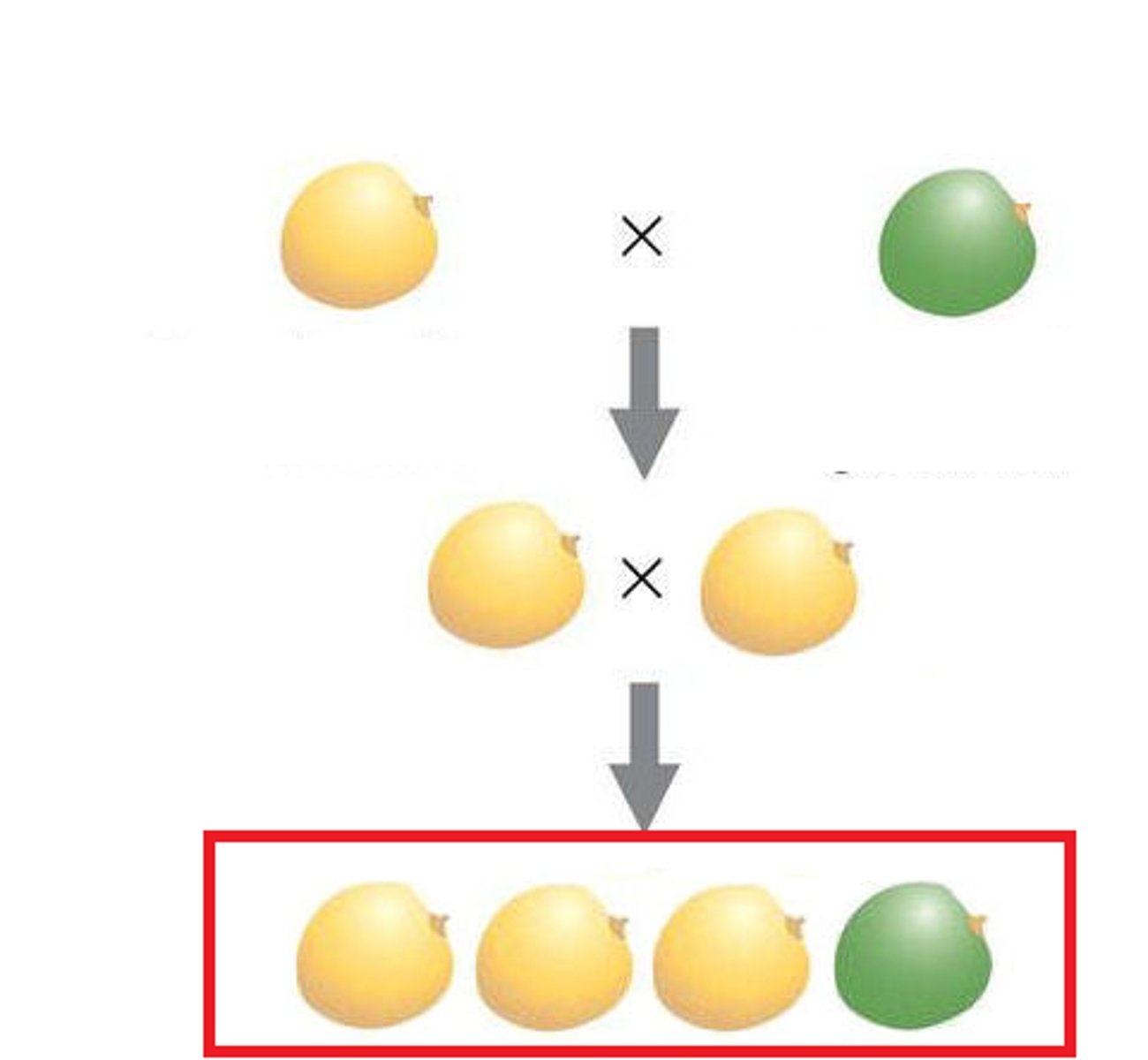
parental generation
the adults used in the first experimental cross of a breeding experiment
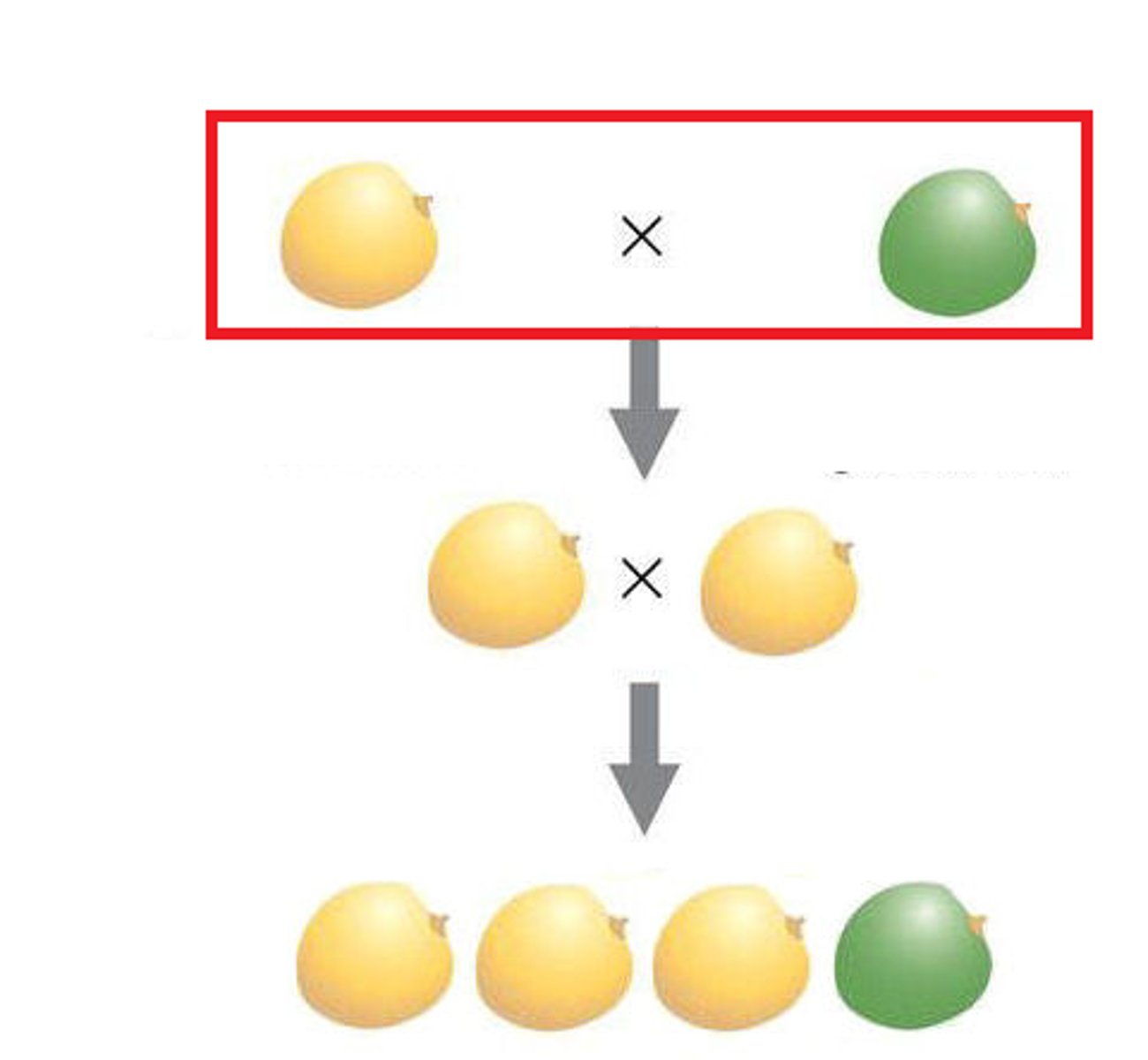
F1 generation
the first generation of offspring obtained from an experimental cross of two organisms
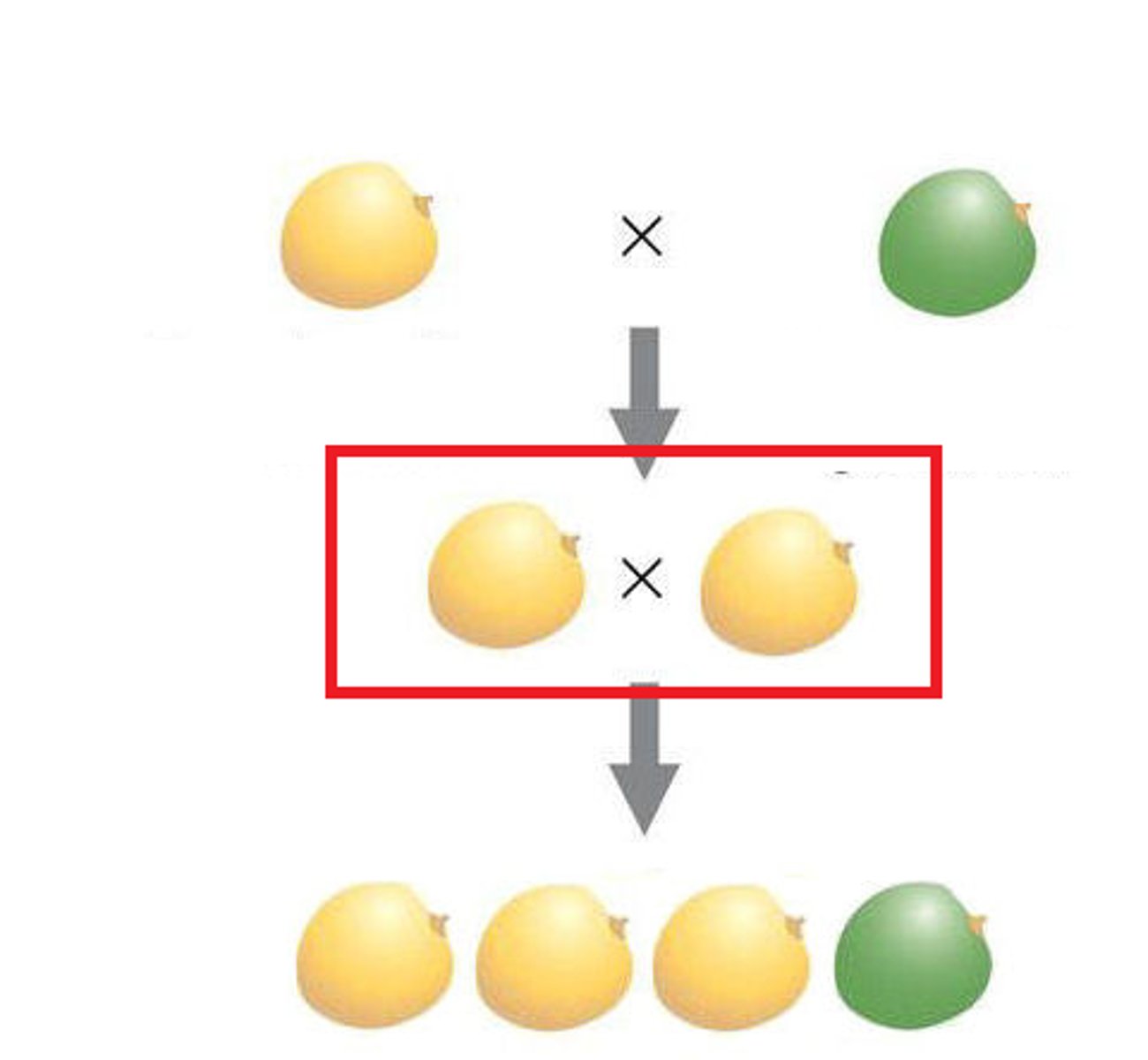
F2 generation
offspring of the F1 generation
genotype
genetic makeup of an organism
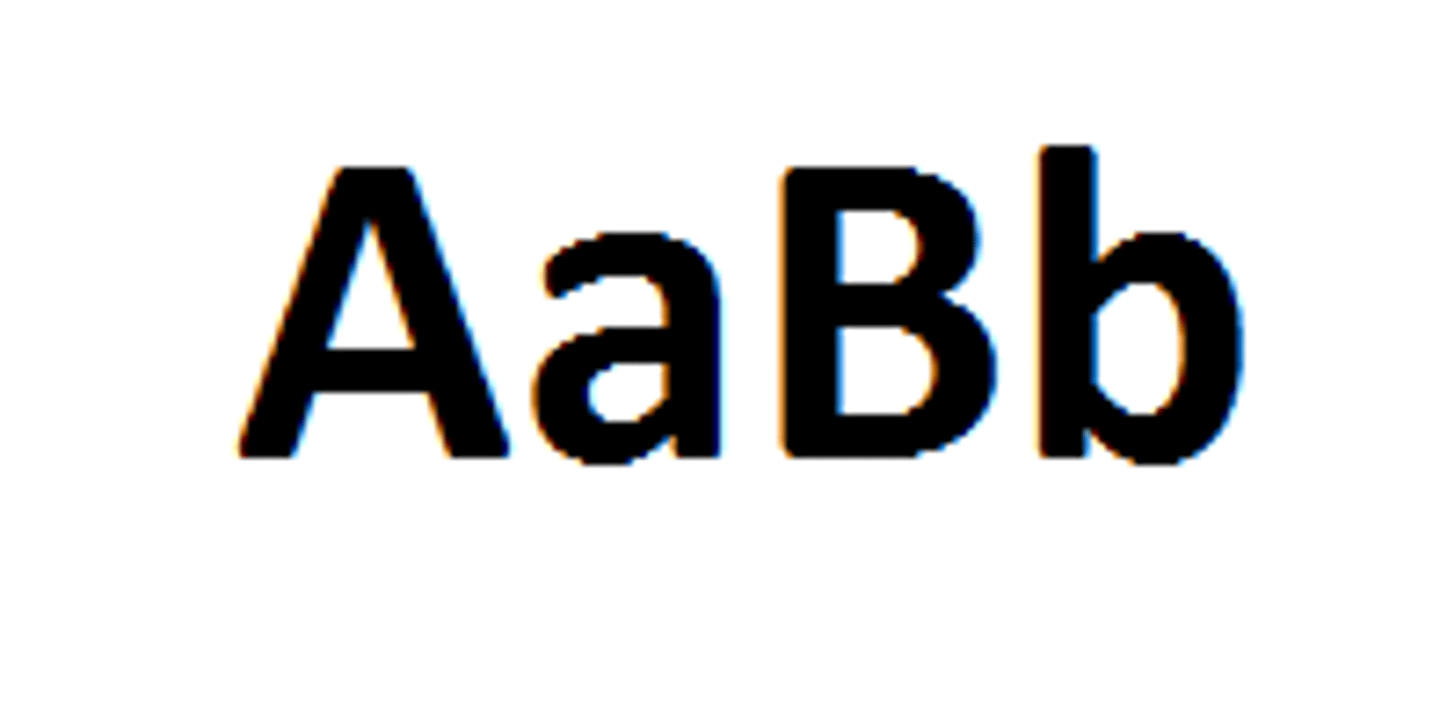
phenotype
An organism's physical appearance, or visible traits.
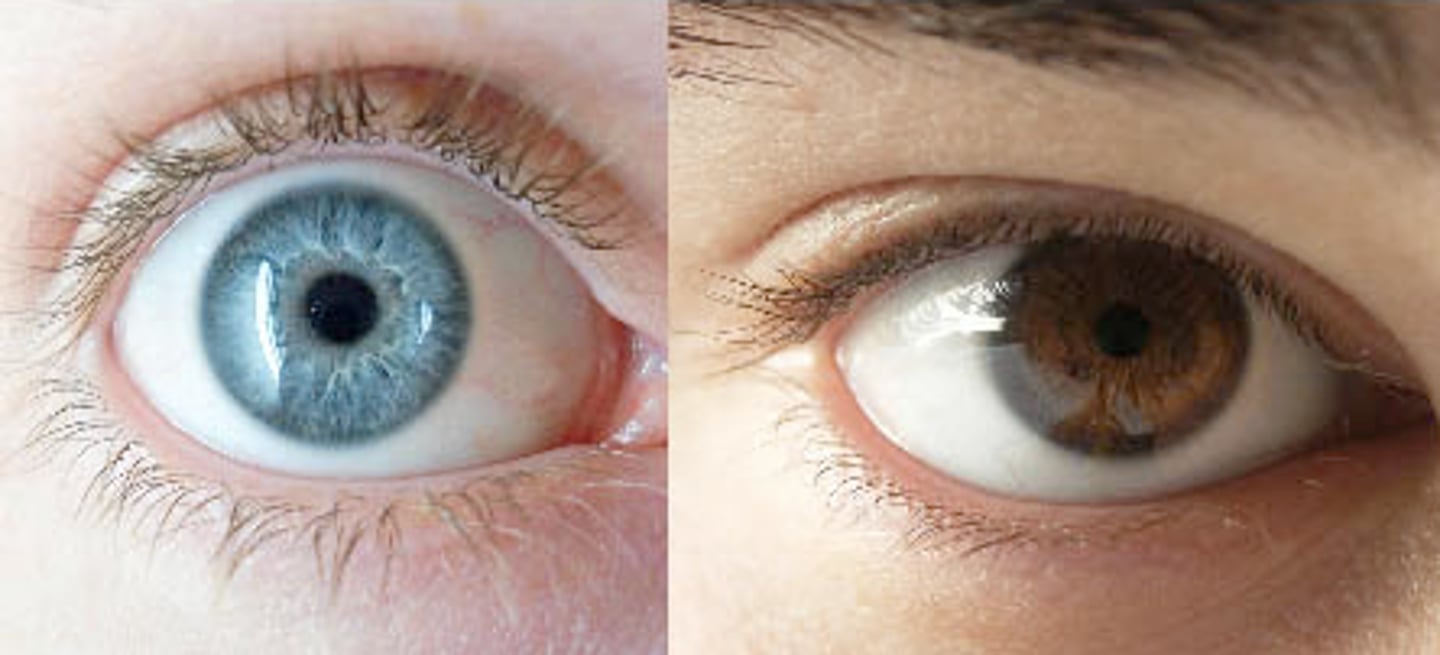
Heterozygous
An organism that has two different alleles for a trait
Homozygous
A cell or organism that has two of the same alleles for a particular trait (AA and aa)
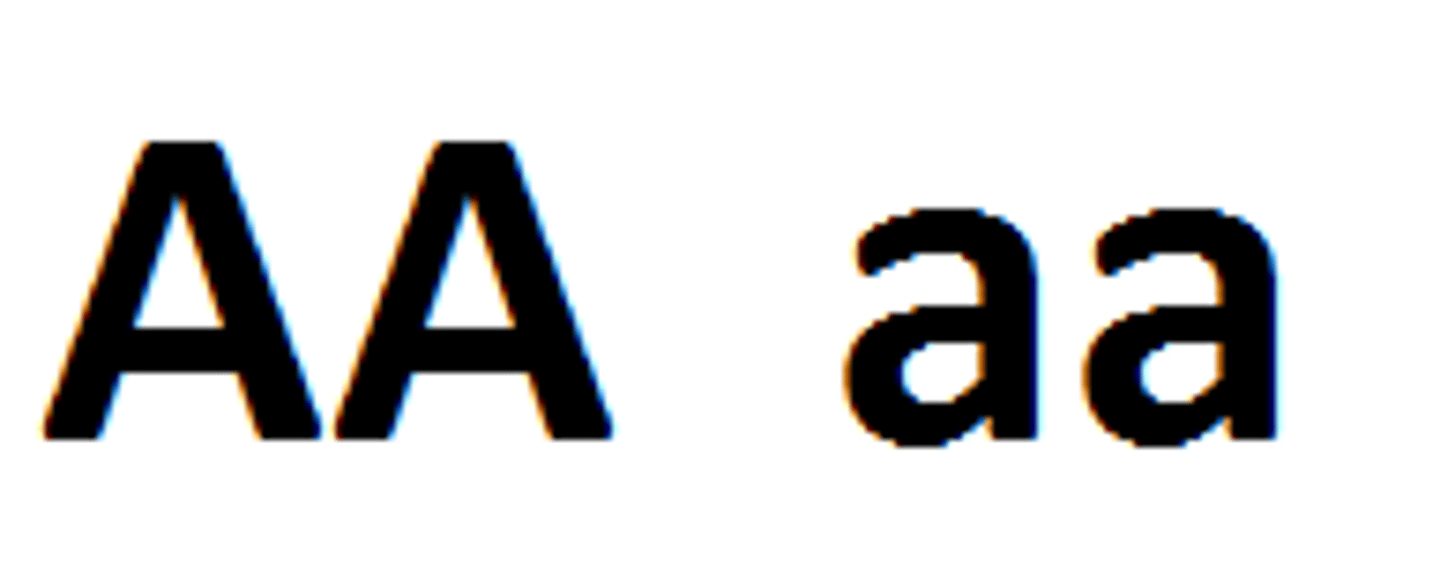
dominant allele
An allele whose trait always shows up in the organism when the allele is present.
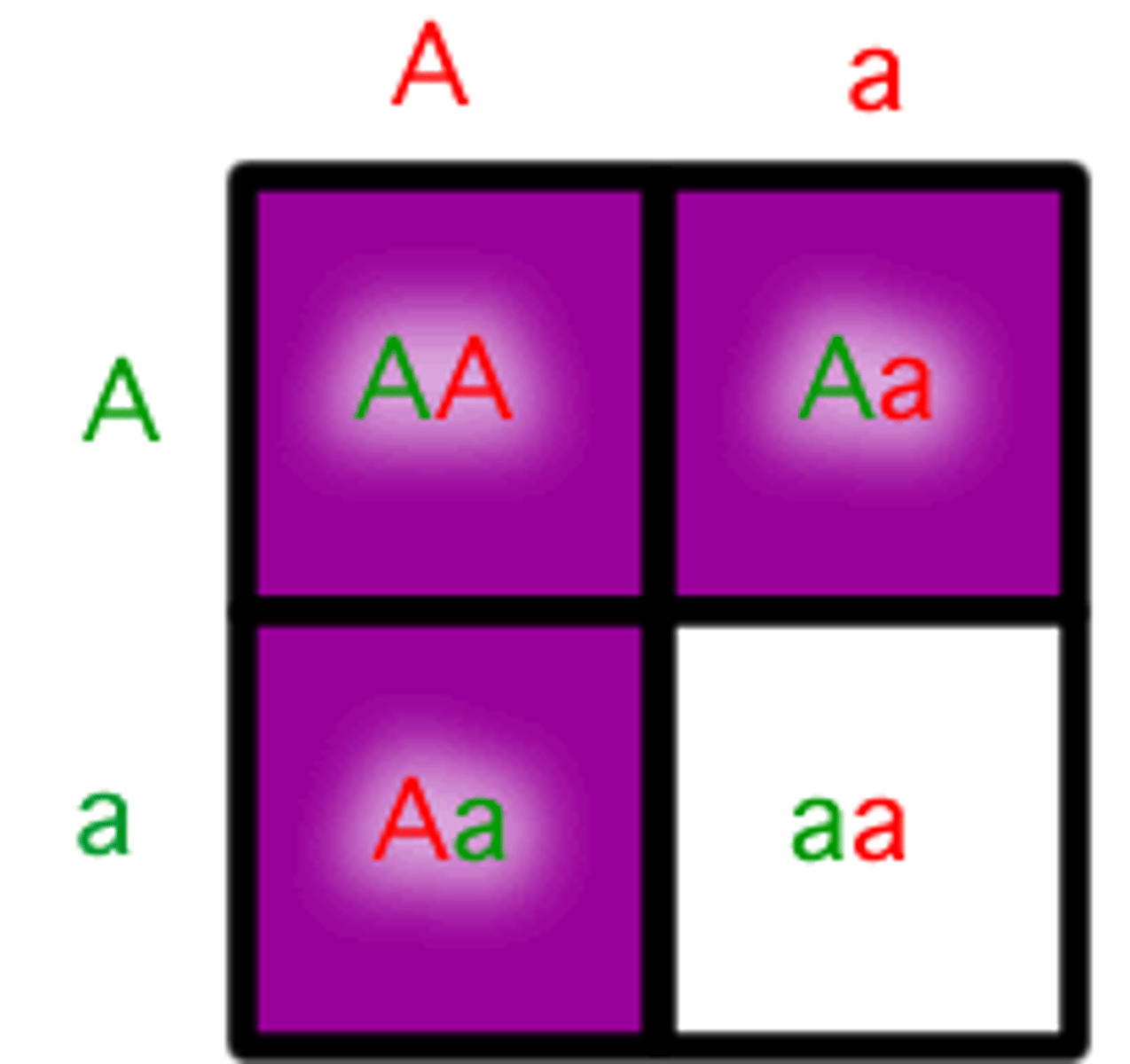
recessive allele
An allele that is masked when a dominant allele is present
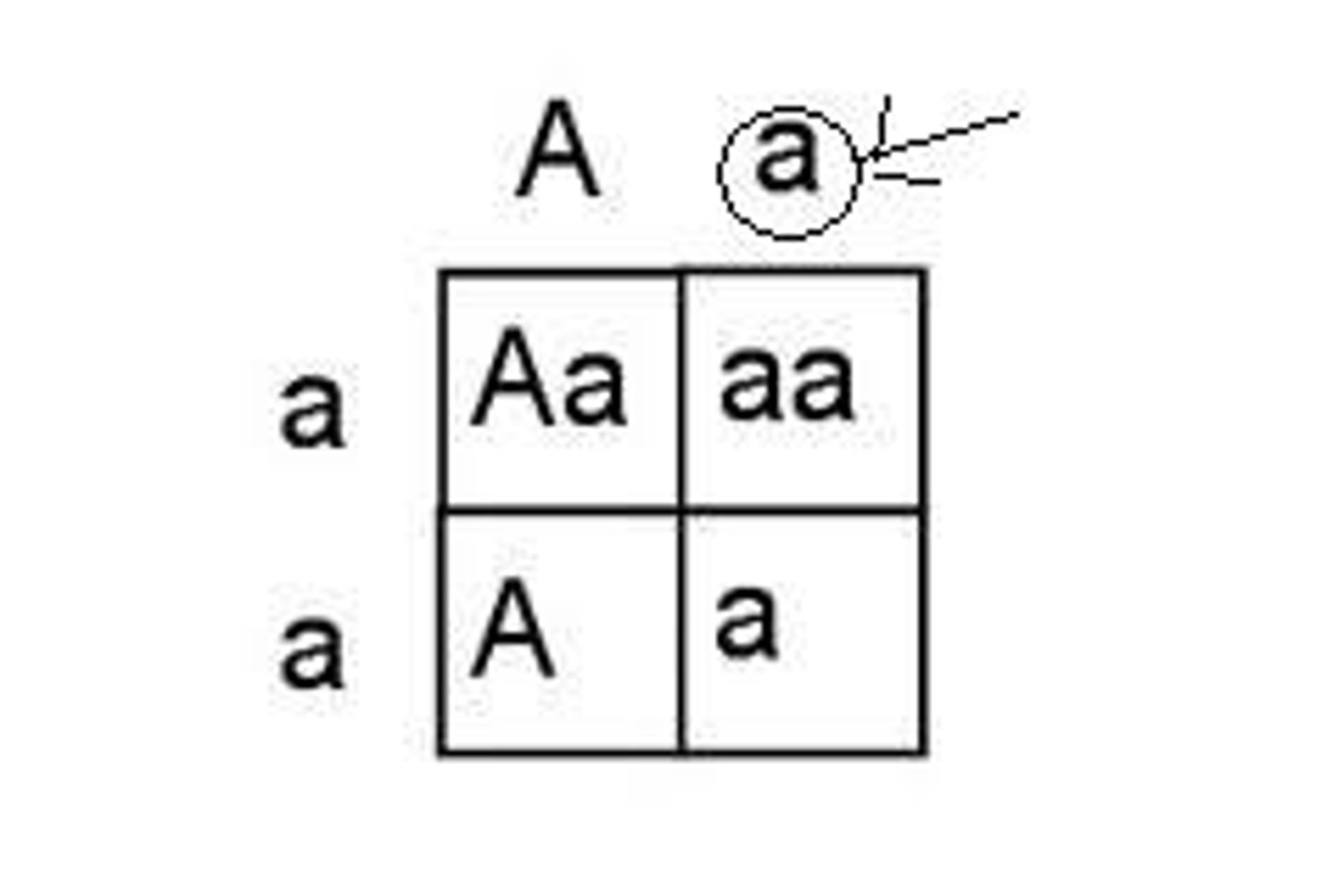
independent assortment and principles of segregation
two principles of inheritance
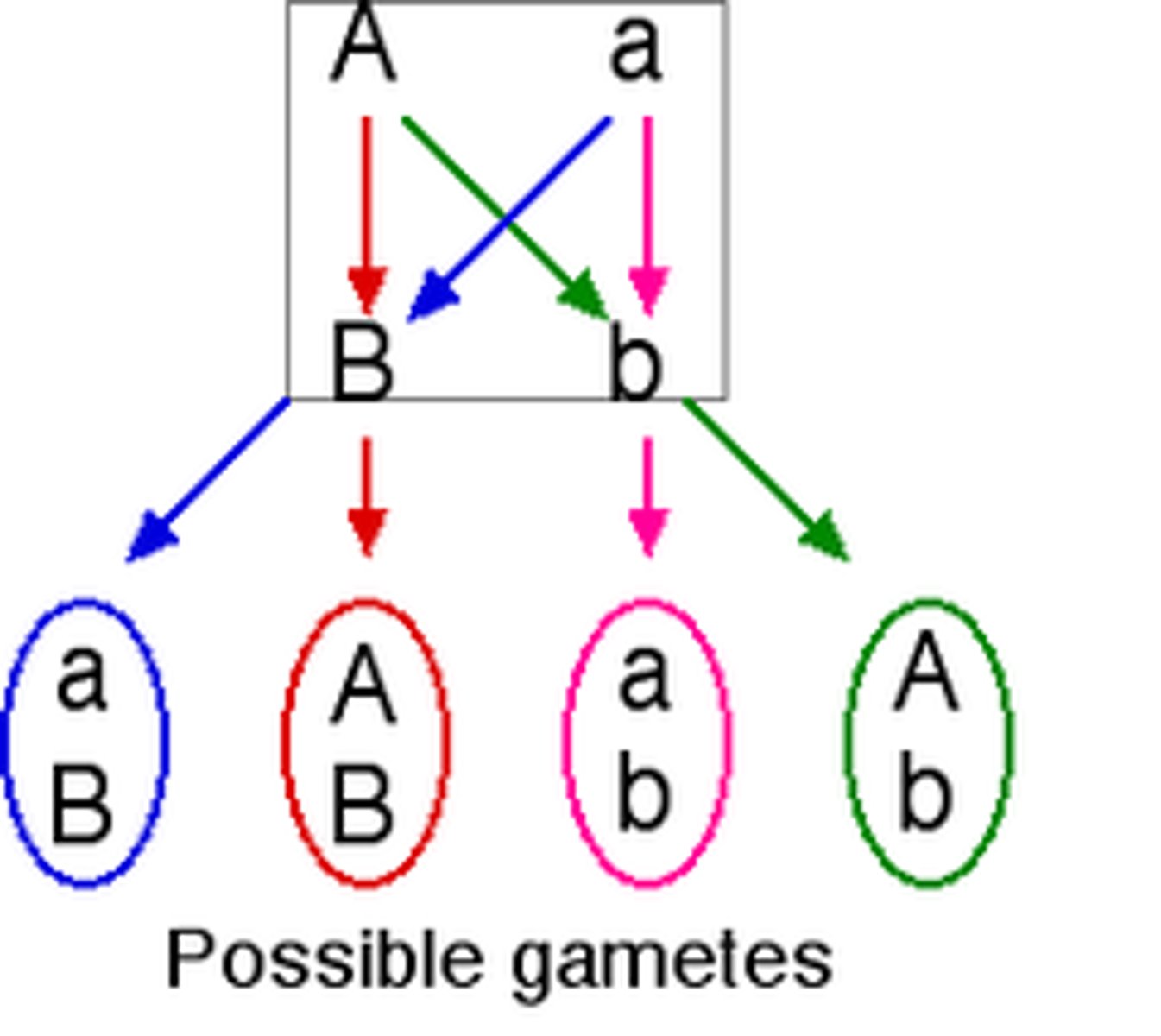
independent assortment
alleles of different genes are distributed independently of one another
principles of segregation
org. = two alleles for each gene but can only pass one
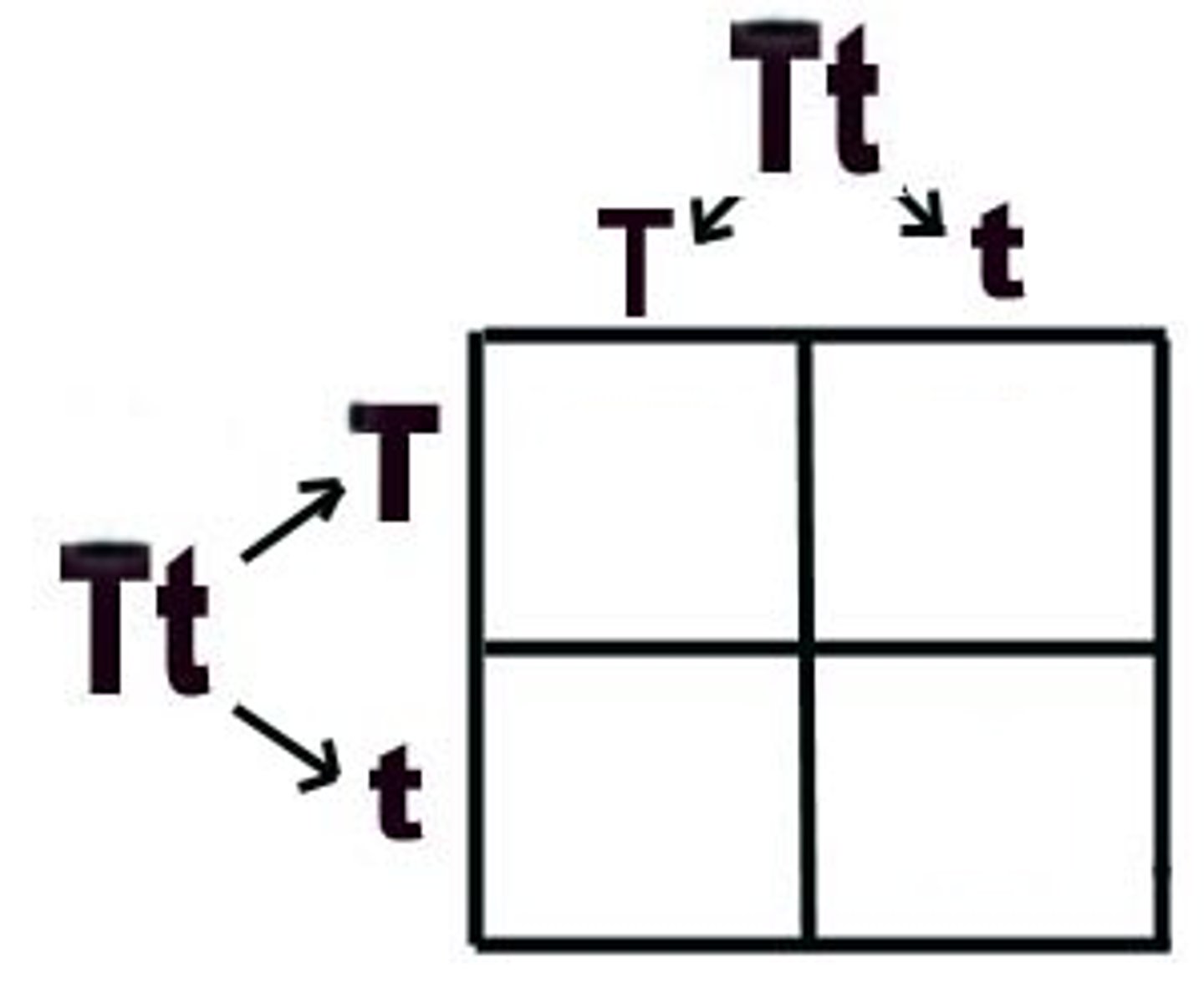
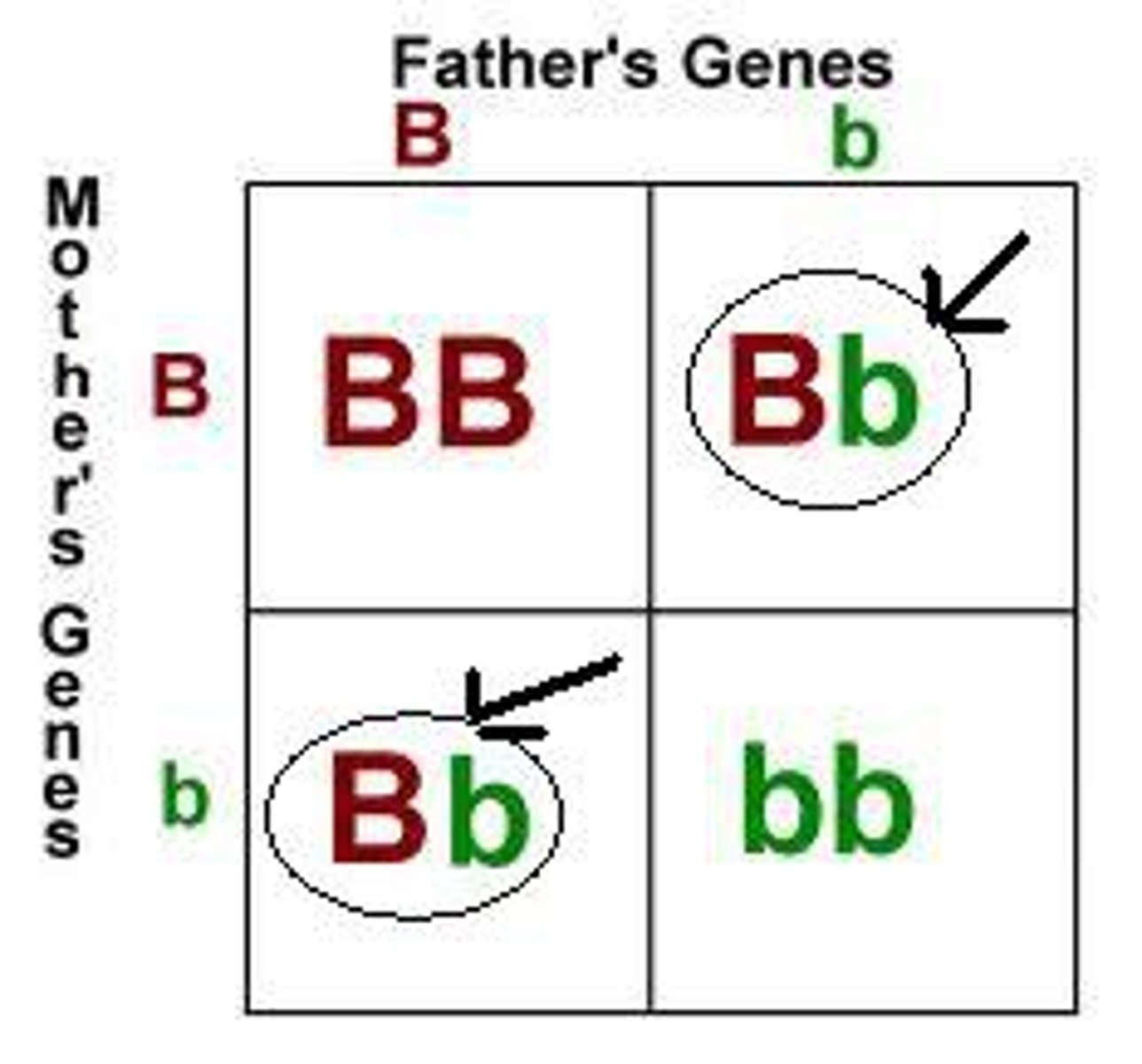
Punnett Square
segregation of alleles --> gametes and how they pair up during fertilisation
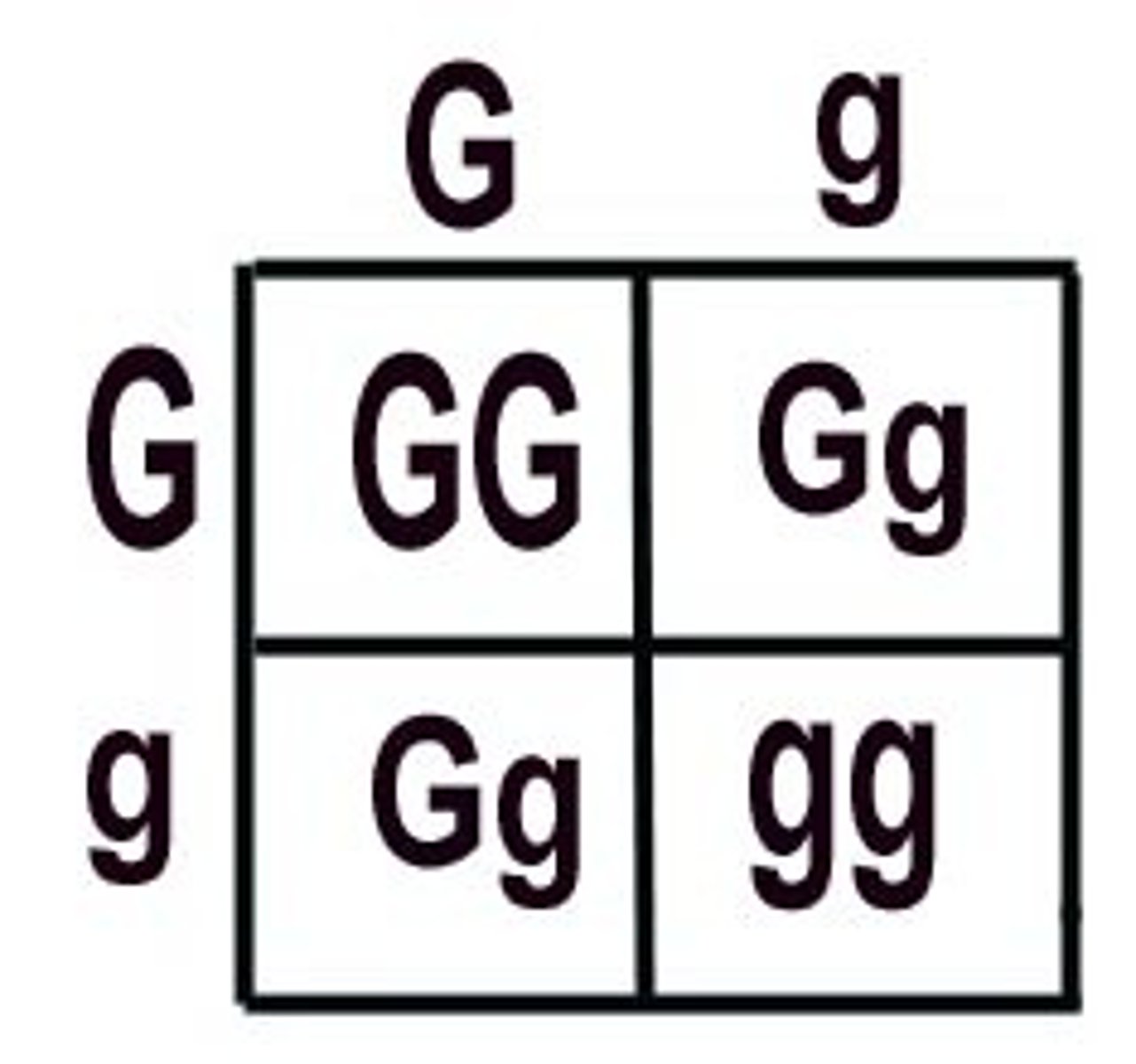
monohybrid cross
heterozygous mating --> single gene = same allele (self-fertilisation)
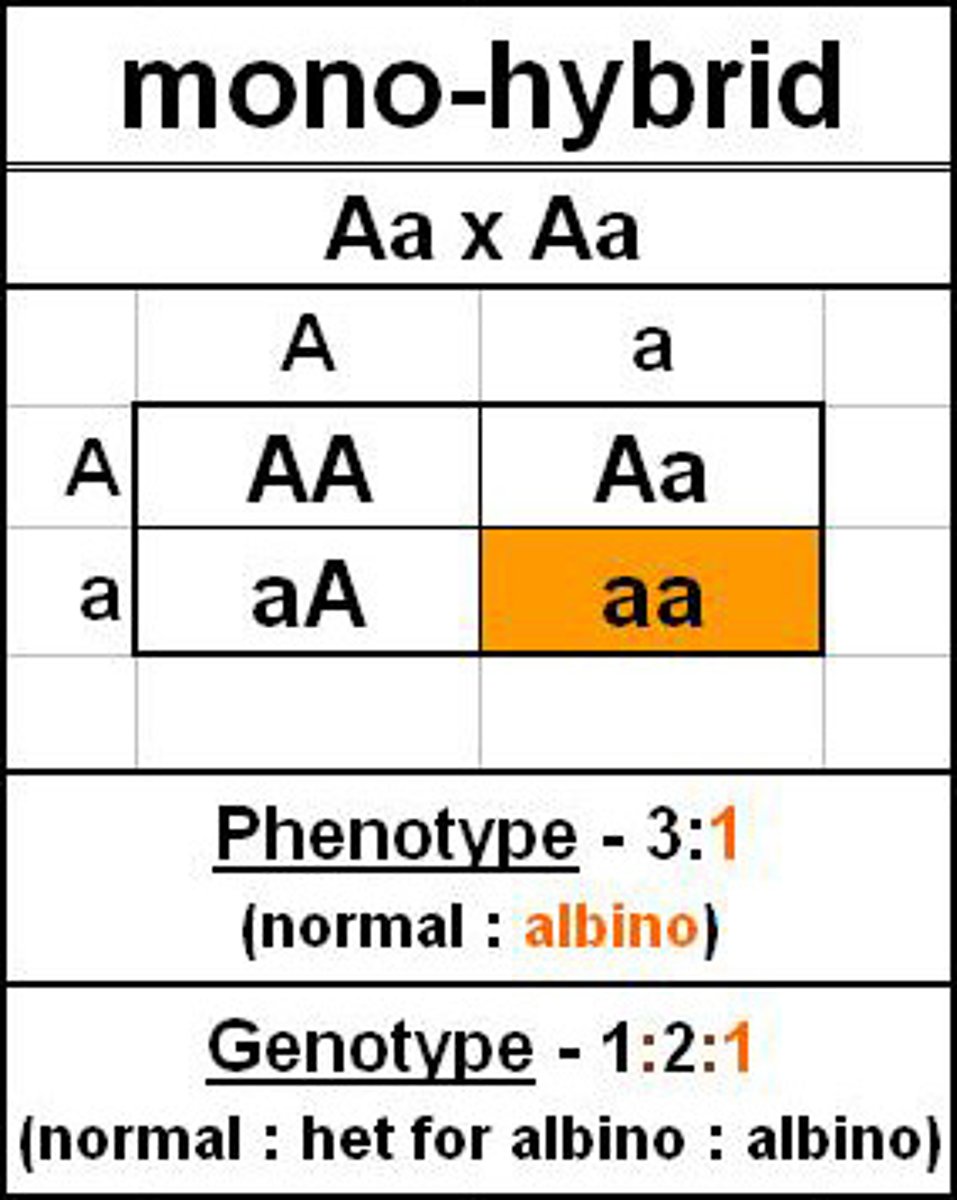
reciprocal crosses
A pair of matings in one of which a female of genotype A mates with a male of genotype B and in the other of which a female of genotype B mates with a male of genotype A.
3:1 ratio
monohybrid and reciprocal crosses pattern
dihybrid cross
two heterozygous (same genes) for two genes
--> alleles of diff. genes = segregated together or independently
bricks and mortar model
indi. = characteristics --> through out life --> collected physical sub. related characteristics --> because of reproductive organs
blueprint model
process of heredity = X directly transmit traits BUT INFO on traits
Gregor mendel hypothesis
1. blending hypothesis
2. inheritance of acquired characteristics hypothesis
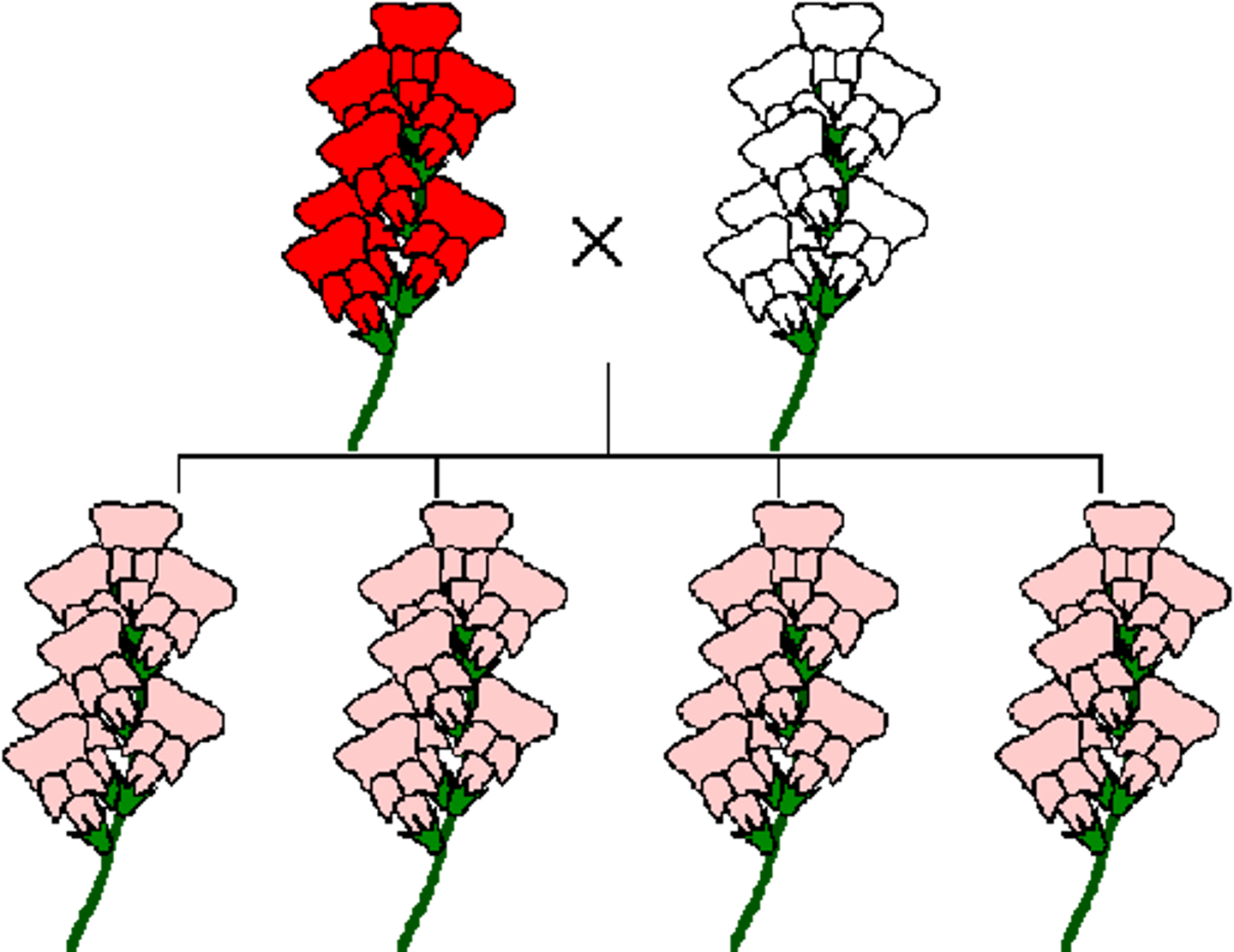
blending hypothesis
parental traits blend --> offspring = INTERMEDIATE traits
ex. blue and red = purple
- variation = lost over time
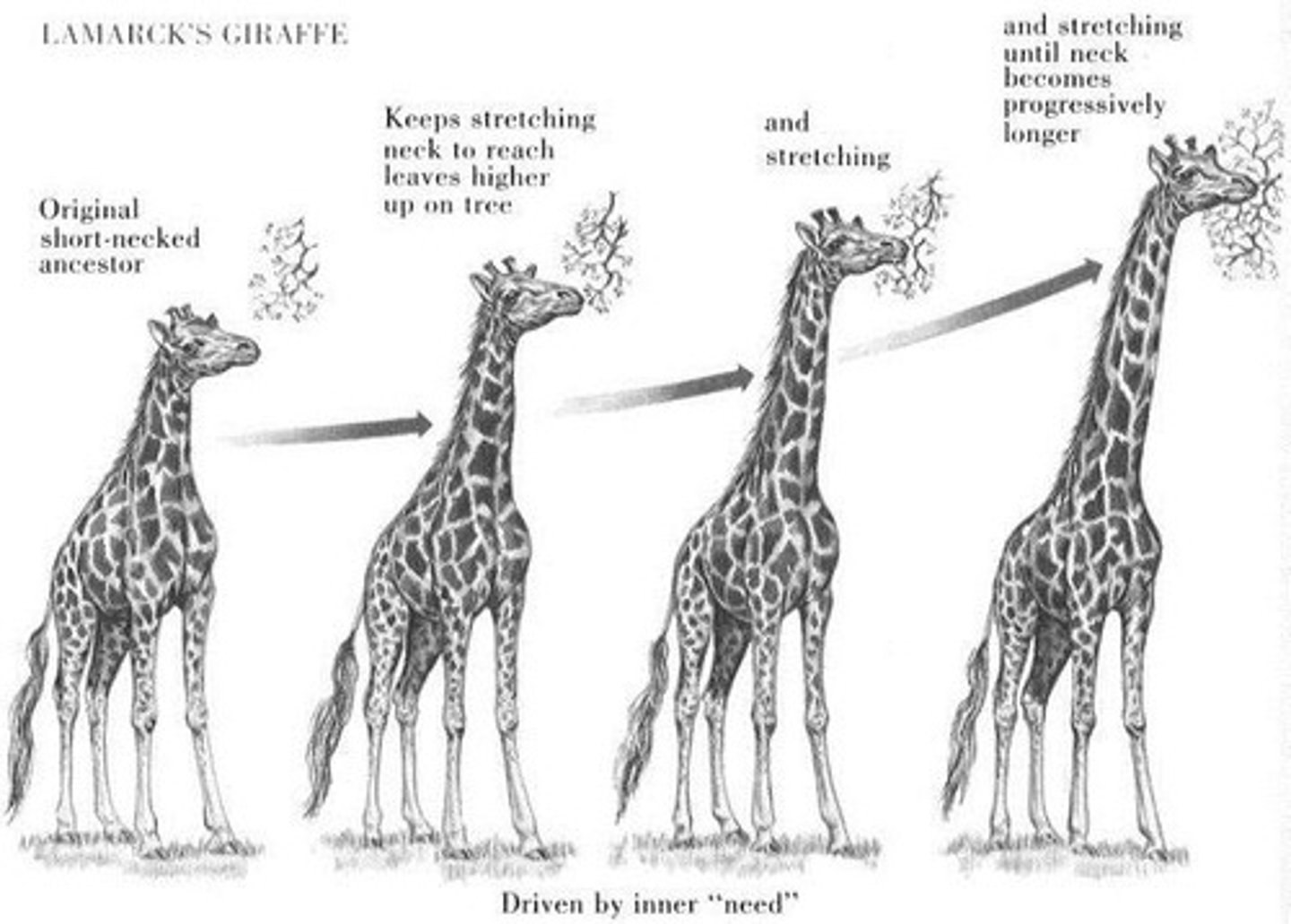
inheritance of acquired characteristics
indi. traits = MODIFIED over lifespan = passed --> offspring
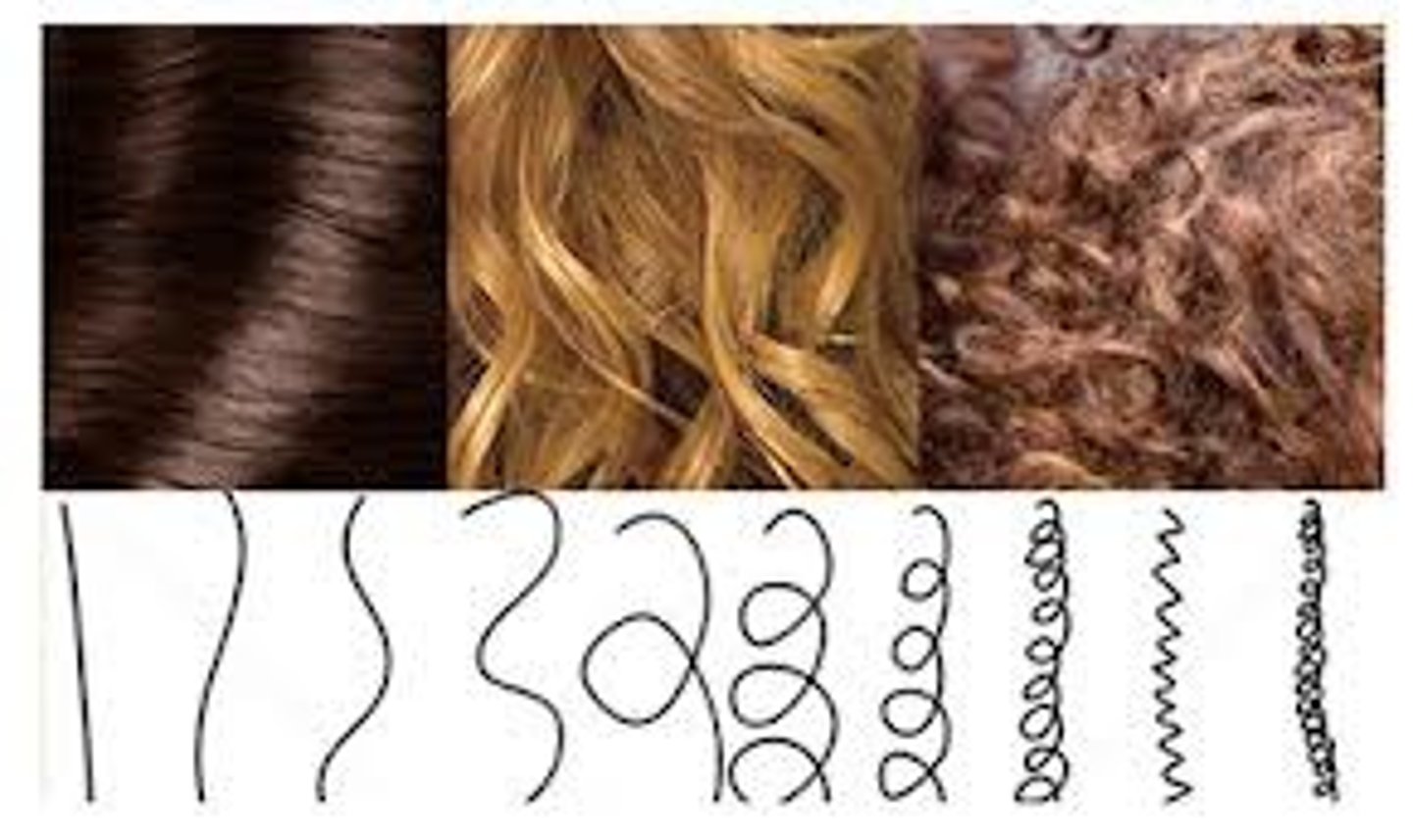
polymorphic trait
A trait that exists in two or more forms

cross-fertilisation/outcrossing
Gamates of two different individuals come together to form off springs
One flower pollen fertilizes a whole different flower
hypothesis of particulate inheritance
hereditary determinants DO NOT blend/change through use = discrete unchanged particles
independent assortment and meiosis
Independent assortment happens during meiosis, specifically in metaphase I
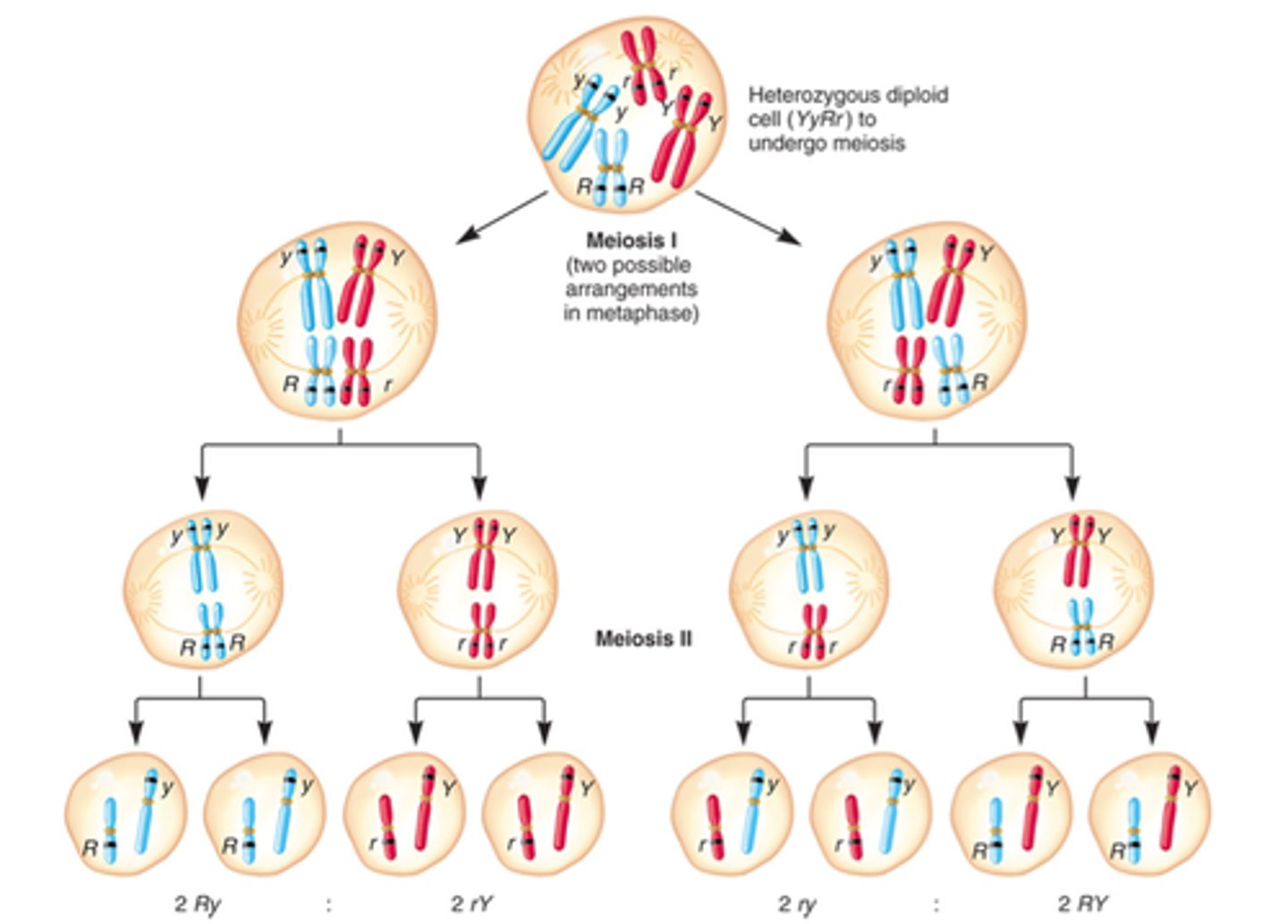
law of segregation and meiosis
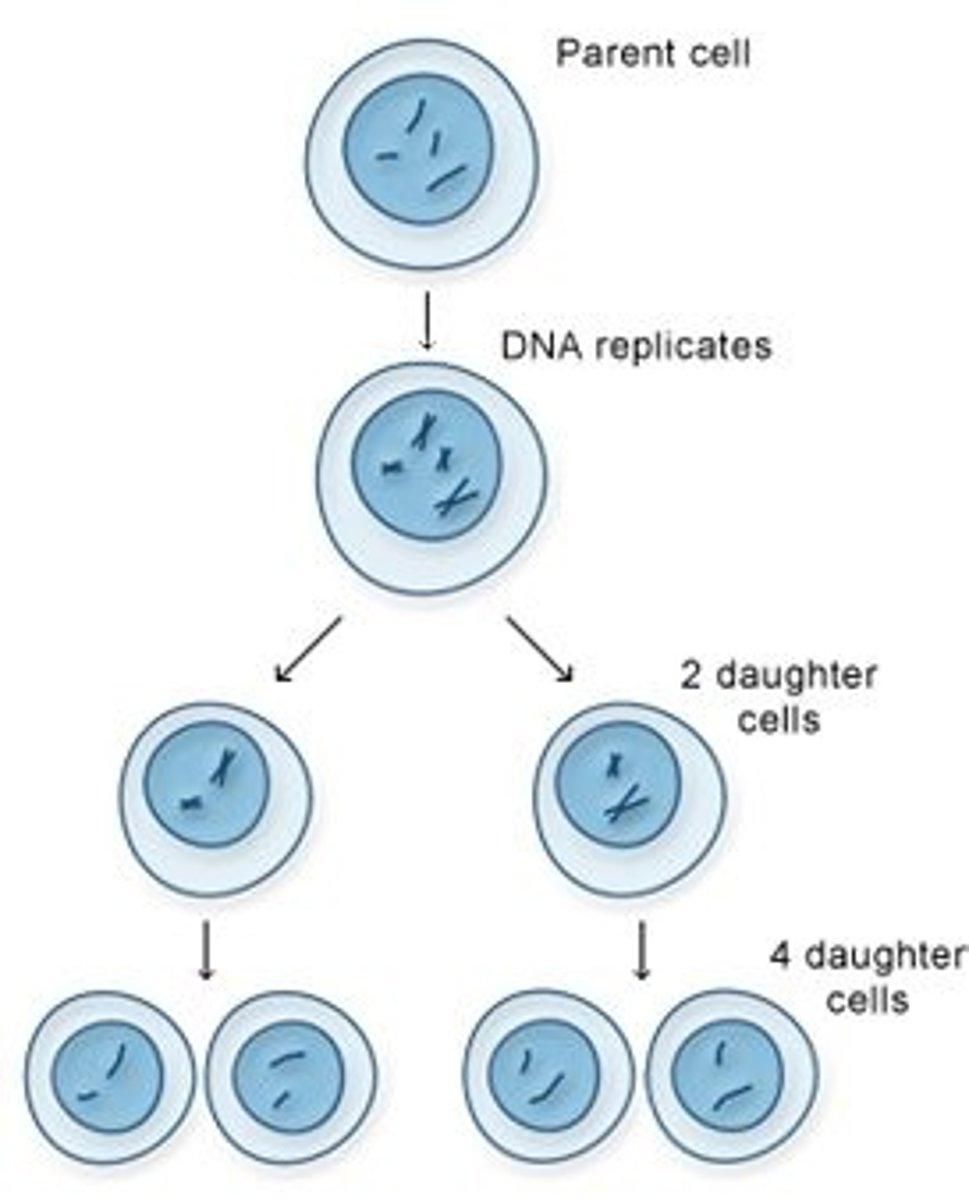
The Law of Segregation is directly connected to meiosis, specifically during anaphase I
multiplication rule
probability --> two or more INDEPENDENT events occur together = individual probabilities
addition rule
probability --> ANY two or more exclusive events occur = adding their probabilities