Chemistry Unit 3 and 4
1/153
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
154 Terms
Absolute alcohol
common name for high purity ethanol and ethyl alcohol
absolute error
an expression of the uncertainty or inaccuracy of a measurement
absorbance
measure of the amount of light absorbed by a sample
acid
a chemical species that accepts electrons or donates protons or hydrogen ions
actinides
elements 90 (thorium) through to 103 (lawrencium)
activation energy
the minimum amount of energy needed for a chemical reaction to occur
actual yield
the quantity of product experimentally obtained from a chemical reaction
aliphatic amino acid
amino acid that has an aliphatic side chain
alkaline
an aqueous solution with a pH greater than 7.
alkene
a hydrocarbon containing a double carbon-carbon bond
allotrope
a form of an elemental substance
alloy
substance made by melting two or more elements, at least one of which must be a metal
alpha decay
spontaneous radioactive decay which produces an alpha particle or helium nucleus
amide
functional group containing a carbonyl group linked to a nitrogen atom.
amine
compound in which one or more hydrogen atom in ammonia is replaced by an organic functional group.
amino acid
an organic acid containing a carboxyl (-COOH) and amine (-NH2) functional group along with a side chain
amphiprotic
species that can both accept and donate a proton or hydrogen ion
anion
an ion with a negative electrical charge
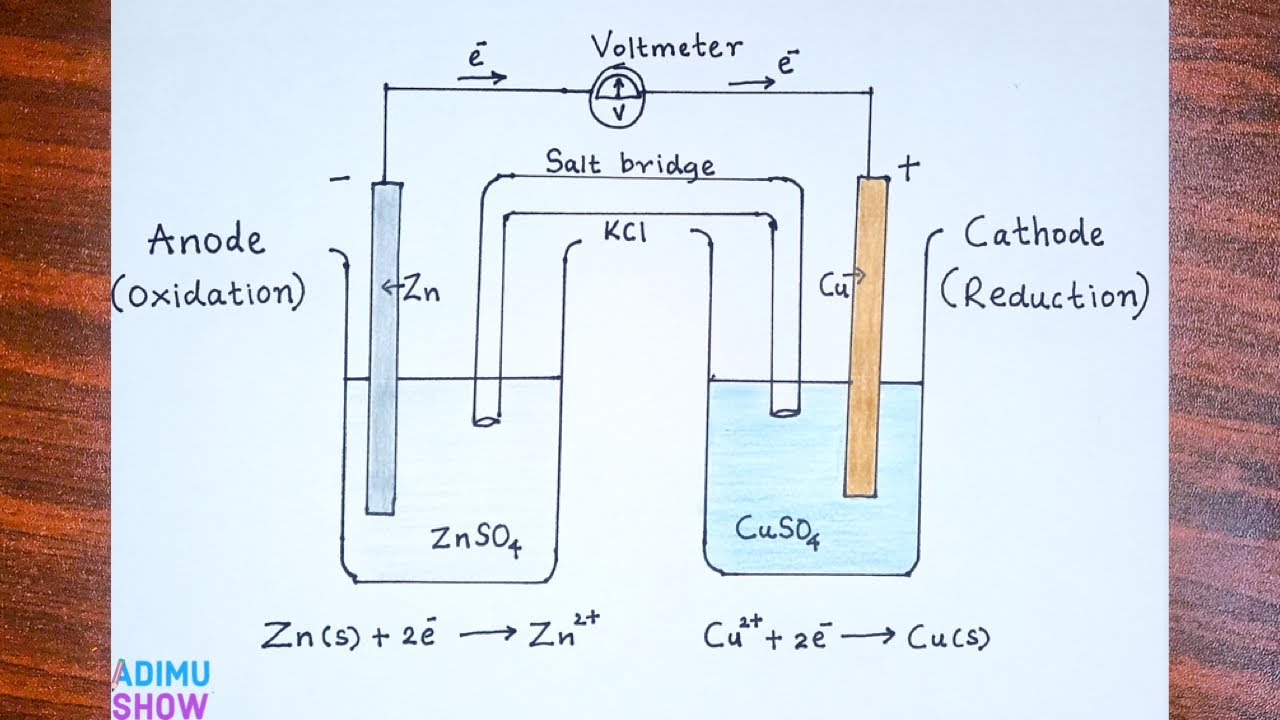
anode
electron where oxidation occurs; positive charged anode
aqueous
describes a system containing water
balanced equation
chemical equation in which the number and type of atoms and the electric charges are the same on both the reactant and product sides of the equation.
basic
alkaline or having a pH > 7
beta decay
type of radioactive decay that results in spontaneous emission of a beta particle
biochemistry
chemistry of living things
boiling point
temperature at which a liquid's vapor pressure is equal to the external gas pressure
bond
a chemical link formed between atoms in molecules and molecules and ions in crystals
Boyle’s law
ideal gas law that states the volume of a gas is inversely proportional to its absolute pressure, assuming constant temperature.
branched chain alkane
an alkane with alkyl groups bonded to the central carbon chain
calorimeter
instrument designed to measure the heat flow of a chemical reaction or physical change.
carbonate
an ion consisting of one carbon bonded to three oxygen atoms (CO32-) or a compound containing this ion
Carbonyl
functional group consisting of a carbon atom double bonded to oxygen, C=O
catalyst
substance that increases the chemical reaction rate by decreasing its activation energy
cathode
electrode where reduction occurs; usually the negative electrode
cation
ion with a positive electrical charge
Charles's law
ideal gas law that states the volume of an ideal gas is directly proportional to absolute temperature, assuming constant pressure.
chemical equilibrium
state of a chemical reaction where the concentration of the reactants and products remains stable over time.
chromatography
group of techniques used to separate mixture components by passing the mixture through a stationary phase.
combustion
chemical reaction between a fuel and oxidizer that yields energy (usually heat and light)
concentration
an expression of the quantity of a substance in a defined volume
Conductor
material that permits the flow of energy (e.g., electrical conductor, thermal conductor).
conjugate acid
HX, a compound differing from a base X by a proton
conjugate base
the species that gains a proton in an acid-base reaction
Covalent bond
chemical link between atoms or ions in which the electron pairs are more or less evenly shared between them.
Dalton’s Law
relation stating the total pressure of a gaseous mixture equals the sum of the partial pressure of the component gases.
daughter isotope
product formed after a radioisotope (the parent) undergoes radioactive decay
decomposition reaction
chemical reaction in which a single reactant yields two or more products
density
mass per unit volume
diffusion
movement of a fluid from a region of higher concentration to a lower concentration
dilute
solution containing a small amount of solute relative to the amount of solvent.
Dipole
a separation of electrical or magnetic charges
disaccharide
carbohydrate formed when two monosaccharides bond, removing a molecule of water from their structure.
double bond
chemical bond in which two electron pairs are shared between two atoms.
ductile
able to be stretched into a wire without breaking
efflorescence
process by which a hydrate loses water of hydration
elasticity
physical property of matter describing the ability to return to original shape after deformation
electrochemistry
scientific study of reactions and species formed at the interface between an electrolyte and a conductor, where electron transfer occurs.
electrode
the anode or cathode of an electrical cell
electrolysis
passage of direct current through an ion-conducting solution, producing a chemical change at the electrodes
electronegativity
roperty of an atom that reflects its ability to attract electrons in a chemical bond
electroplating
process of adding a metal coat to a material by using a reduction reaction
element
a substance that cannot be subdivided using chemical means; identified by the number of protons in its atoms
empirical formula
formula that shows the ratio of elements in a compound, but not necessarily their actual numbers in a molecule.
endothermic
process which absorbs thermal energy from its environment
enthalpy
thermodynamic property of a system that is the sum of the internal energy and the product of pressure and volume
entropy
measure of the disorder of a system
equilibrium constant
ratio of the equilibrium concentration of products raised to the power of their stoichiometric coefficients to the equilibrium concentration of the reactants raised to the power of their stoichiometric coefficients
equivalence point
point in a titration where the titrant completely neutralizes the analyte
exothermic
releasing energy to the environment in the form of heat; a type of exergonic process
Faraday constant
a physical constant equal to the electric charge of one mole of electrons, 96485.33 C/mol
fluorescence
luminescence released when an atom absorbs electromagnetic radiation and emits a photon when the electron falls to a lower energy state
force
a push or pull on a mass, with both magnitude and direction (vector).
frequency
number of times a point on a wave passes a reference point in one second
galvanic cell
electrochemical cell where reactions between dissimilar conductors occur through a salt bridge and electrolyte
gamma radiation
high energy ionizing photons, originating from the atomic nucleus
Gibbs free energy
a measure of the potential for reversible or maximum work done by a system at constant pressure and temperature
green chemistry
branch of chemistry concerned with lessening the environmental effect of chemicals, including development of new materials and processes
ground state
the lowest energy state of an atom, ion, molecule, or subatomic particle
half-life (t1/2)
time required to convert half of the reactant to a product or the time required for half of a radioactive isotope to decay into its daughter isotope
halogen
an element in Group VIIA of the periodic table (e.g., Br, Cl)
heat capacity
quantity of heat needed to raise the temperature of a sample by a specified amount
Henry’s Law
law that states the mass of a gas that will dissolve into solution is directly proportional to the partial pressure of the gas above the solution
Hess’s Law
law that states the energy change in an overall reaction equals the sum of the energy changes in its individual (partial) reactions
heterogeneous
consisting of dissimilar components
hydrocarbon
molecule consisting entirely of carbon and hydrogen atoms
hydrophobic
property of repelling water
hydroxyl group
functional group consisting of a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to an oxygen atom (-OH)
ideal gas constant
physical constant in the Ideal Gas Law, equal to the Boltzmann constant but with different units
indicator
substance that undergoes a visible change when its conditions change (e.g., a pH indicator)
inhibitor
substance that slows or prevents a chemical reaction
insoluble
unable to dissolve in a solvent
intermolecular force
the sum of all forces between neighboring molecules
ionic bond
chemical link between atoms caused by electrostatic force between oppositely charged ions
isolated system
thermodynamic system that can't exchange energy or matter outside of the system
IUPAC
International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, an authority on chemical standard
joule
SI unit of energy equal to the kinetic energy of a 1-kilogram mass moving at 1 meter per second
Kelvin temperature scale
an absolute temperature scale with 100 degrees between the freezing and boiling points of water (although values are given without degrees by convention)
kinetic energy
energy associated with motion
Law of Chemical Equilibrium
an expression of the relationship between the concentration of reactants and products of a chemical reaction mixture at equilibrium
limiting reactant
the reactant that determines how much product may result from a chemical reaction
macromolecule
molecule containing a very large number of atoms, usually more than 100