Lipids 3 - Dietary Digestion
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards on Dietary Digestion of Lipids
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Dietary Lipids
Found within foods containing vegetable oils or fats (animal and plant). Some spices and herbs are also good dietary sources.
inorganic food additives (like salt and sugar) lack this biomolecule
cooking may alter lipid characteristics but doesn’t eliminate it from food
Essential Fatty Acids
They are precursors to local hormones and essential for neural cell membranes. Deficiencies are rare.
these molecules are usually constinutents in dietary triacylglycerols in vegatable oils, nuts
Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Nuts/Fish
Plant-based omega-3 is ALA (alpha-linolenic acid). Fish-based omega-3s are EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid).
Lingual Lipase
Secreted by von Ebner’s glands in the tongue. It digests fats by breaking down triglycerides into diacylglycerols and free fatty acids.
Gastric Lipase
Cleaves triacylglycerols (TAGs) into diacylglycerols (DAGs) in the stomach, contributing to 10-30% of fat degradation.
Bile Salts
They non-enzymatically emulsify fats in the small intestine and destabilize bacterial membranes. They also aid in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K).
glycocholic acid is a major bile salt found in humans
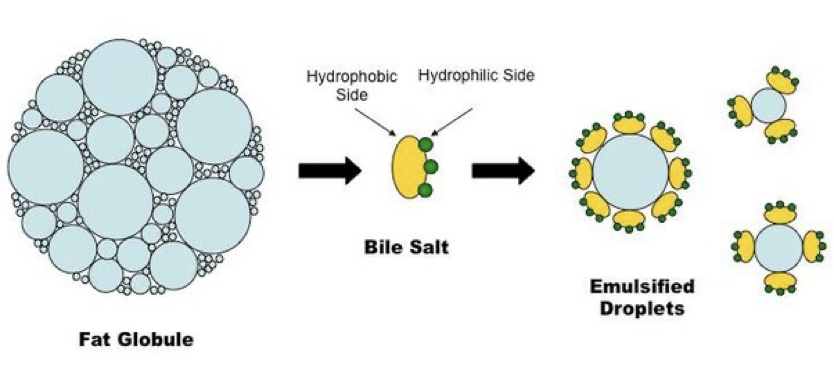
Pancreatic Lipase
Sequentially cleaves remaining TAGs and DAGs in the stomach, generating free fatty acids (FAs) and monoacylglycerol (MAG).
FA and MAG then moved across cells plasma membrane
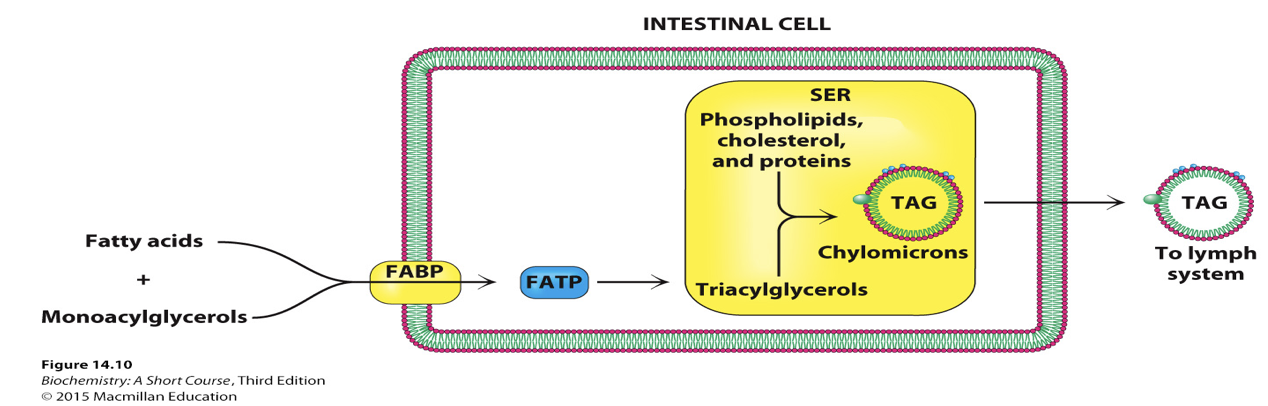
FABP
Fatty Acid Binding Protein, an embedded transporter that moves free fatty acids and MAG across the cell's plasma membrane.
FATP
Fatty Acid Transport Protein, a cytoplasmic protein that moves free fatty acids and MAG across the cell's plasma membrane.
Chylomicrons
Lipoprotein particles formed in enterocytes (intestinal cells) after TAGs are broken down into FA and MAGs that transport dietary fats to adipose tissue (for storage) or muscles (for energy).
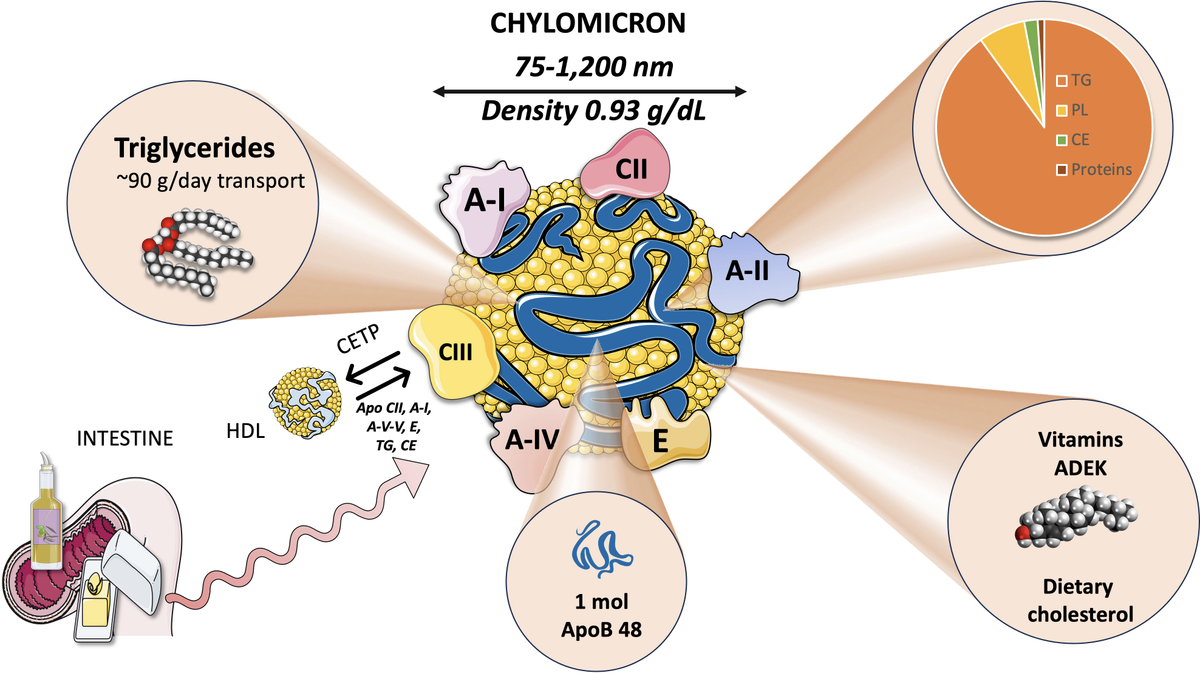
CCK, GLP-1 and GLP-2, insulin
Hormones that support the digestion, absorption, and repackaging of dietary fats into chylomicrons.
Omega-3 Fatty Acid
Alpha linolenic acid (18:3)
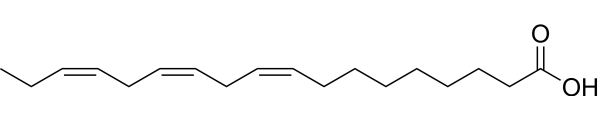
Omega-6 Fatty Acid
Linoleic acid (18:2)
Omega 6 in nuts/fish
Most nuts are much higher in omega-6 than omega-3
fish generally have much lower omega-6 than omega-3 (making them anit-inflammatory and beneficial for heart/brain health)
Farmed fish tend to have higher omega-6 than wild-caught due to their grain-based diets
Lingual Lipase activity
Most activity occurs when the enzyme is transported with food to the stomach where it is more active under acidic conditions
key enzyme in digesting milk fats in newborns
highly hydrophobic and readily enters fat globules
Hydrolysases
Enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of chemical bonds using water
Proteases (peptidases or proteinases)
Hydrolyze peptide bonds in proteins
Lipases
Hydrolyze ester bonds in lipids (triglycerides)
Hydrolase Family of enzymes
Both proteases and lipases belong to this- same catalytic triad
Vitamins A, D, and E
NOT precursors to coenzymes
Vitamin K
Essential for carboxylase activity
95% of FA
Percentage of FA absorbed by the small intestine
the rest is thought to provide nutrition to intestinal microbiota
TAGs in adipose tissue
Dietary fatty acids are stored here for later use
Metabolsim
Involves the beta-oxidation pathway and cellular respiration
Lipoprotein particles
contain fat-soluble vitamins and cholesterol and deliver dietary fat to adipose tissue (for storage) and other tissues in the body like muscles (for energy)