NSCI2101 Exam 2 Lec 1
1/83
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
corticospinal tract (pyramidal tract)
innervates spinal neurons → fine motor control
axons of the dorsal columns (dorsal funiculi) carry sensory information (light touch and vibration) from where?
from the body of the dorsal column nuclei in the medulla, where they synapse
where do axons in the dorsal column carry information to?
first they cross the midline as the sensory decussation and ascend to the thalamus as the medial lemniscus
spinal trigeminal tract
carries pain and touch information from the trigeminal nerve to the spinal trigeminal nucleus
spinal trigeminal nucleus
processes pain and touch information from the face and relays it to the thalamus (diencephalon)
inferior olive
innervates the cerebellum via inferior cerebellar peduncle
sulcus limitans
separates dorsal (sensory) spinal cord from ventral (motor) spinal cord, also exists in the brainstem
pontine nuclei
gets input from cerebral cortex and in turn, innervates the cerebellum. involved with motor control
interior/middle/superior cerebellar peduncles
routes for axons entering and exiting the cerebellum. these also hold the cerebellum onto the brainstem
superior colliculi
two bumps on the dorsal surface of the rostral midbrain that are involved with integrating visual input and motor input
inferior colliculi
two bumps on the dorsal surface of the caudal midbrain that process auditory input
cerebral peduncles
large fiber tracts originating in the cerebral cortex and projecting to the brain stem or spinal cord. corticospinal tract axons comprise part of these
decussation
an anatomical structure where axons cross the midline
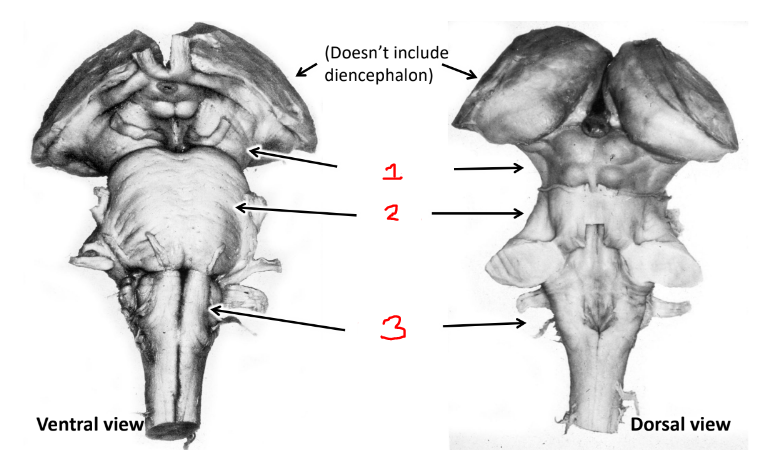
what is 1?
midbrain
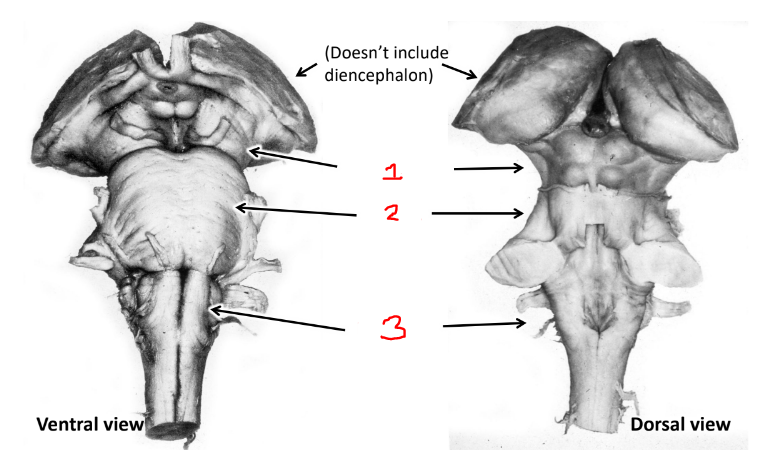
what is 2?
pons
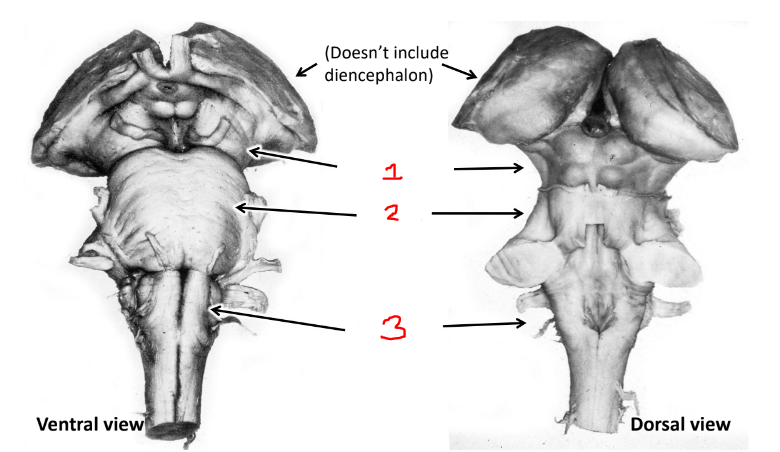
what is 3?
medulla
what is special about the brainstem?
it evolutionarily very old
it contains cranial nerve nuclei
contains tracts that run long distances
contains neurons innervating many different parts of the CNS
including the “reticular formation”
includes cells containing “monoamine” transmitters
what are some examples of monoamine transmitters?
serotonin
norepinephrine
dopamine
reticular formation
involved in sleep and many other functions
what happens to the brainstem as you go rostrally?
it gets bigger
changes shape
gets different lumps and bumps
why does the brainstem change shape?
structures (tracts or nuclei) get added
structures end
structures change size
fiber tracts move
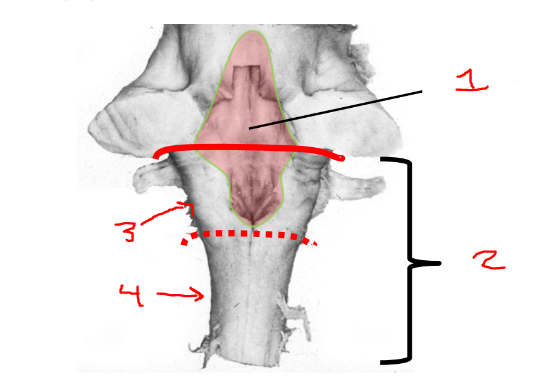
what is 1?
4th ventricle
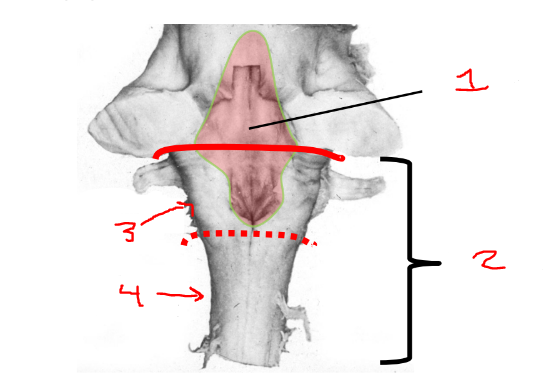
what is 2?
medulla
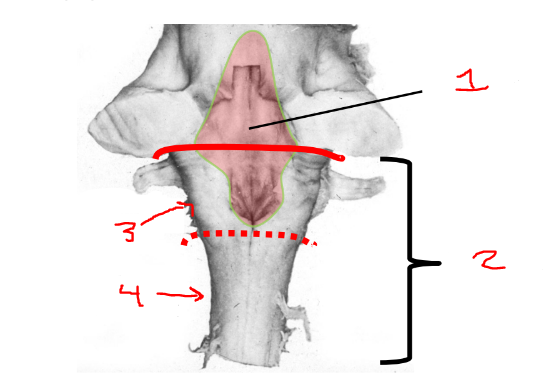
what is 3?
rostral medulla
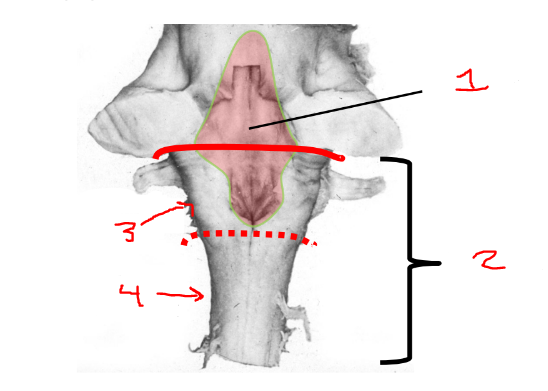
what is 4?
caudal medulla
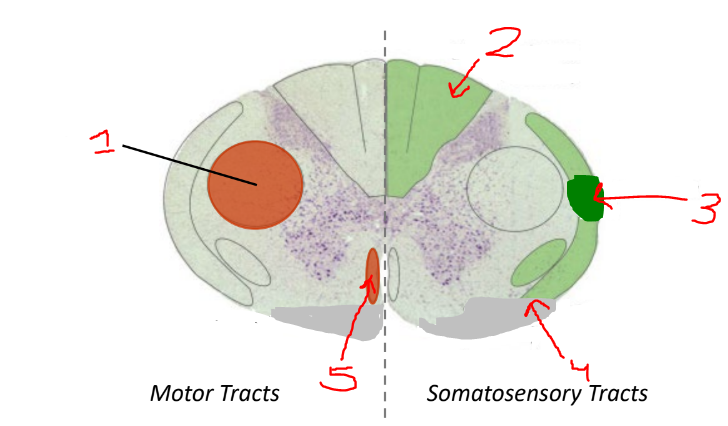
what is 1
lateral corticospinal tract
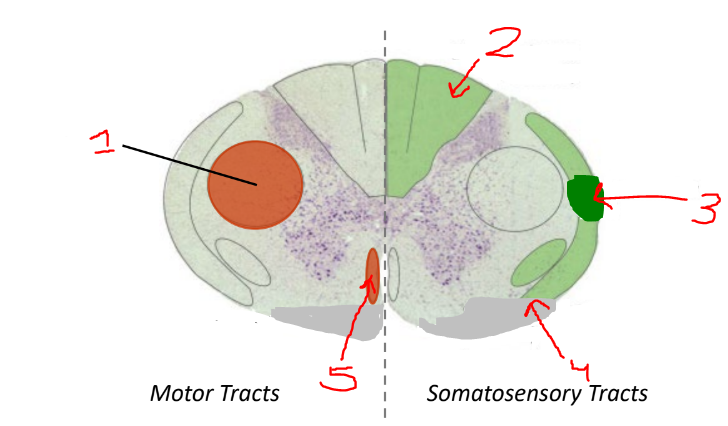
what is 2?
dorsal columns
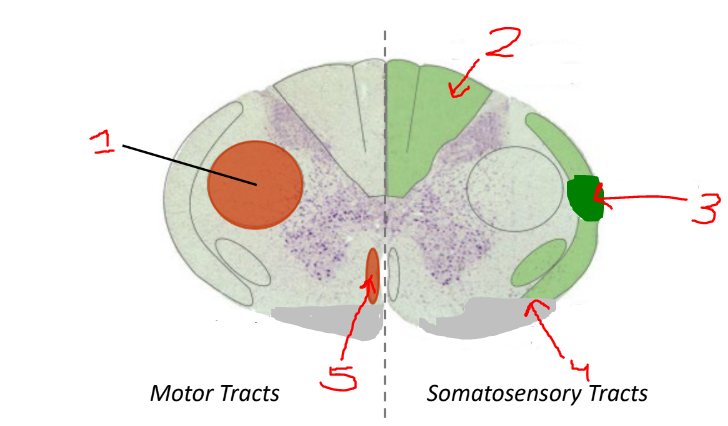
what is 3?
spinocerebellar tract
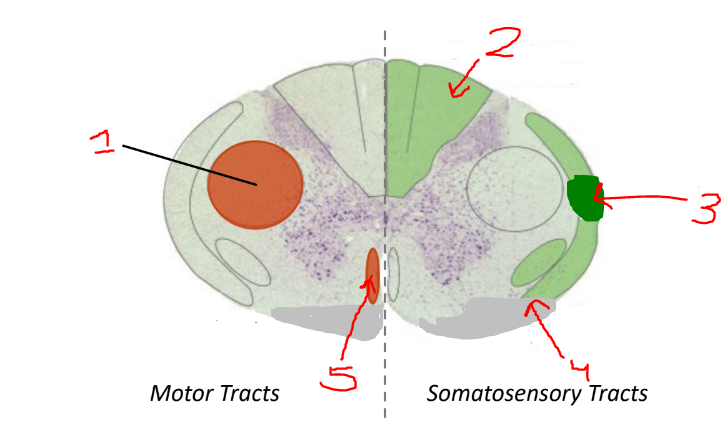
what is 4?
spinothalamic tract
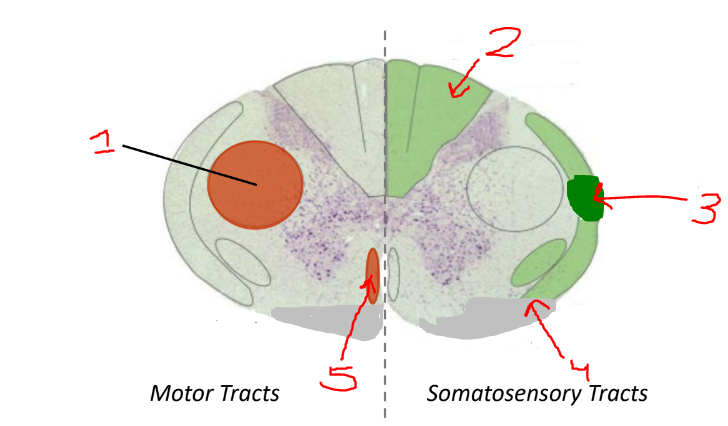
what is 5?
anterior corticospinal tract
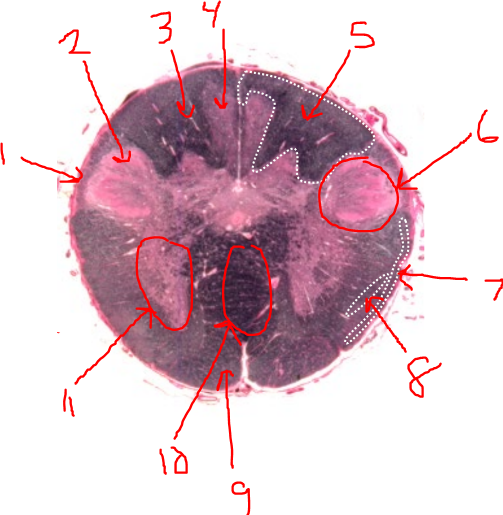
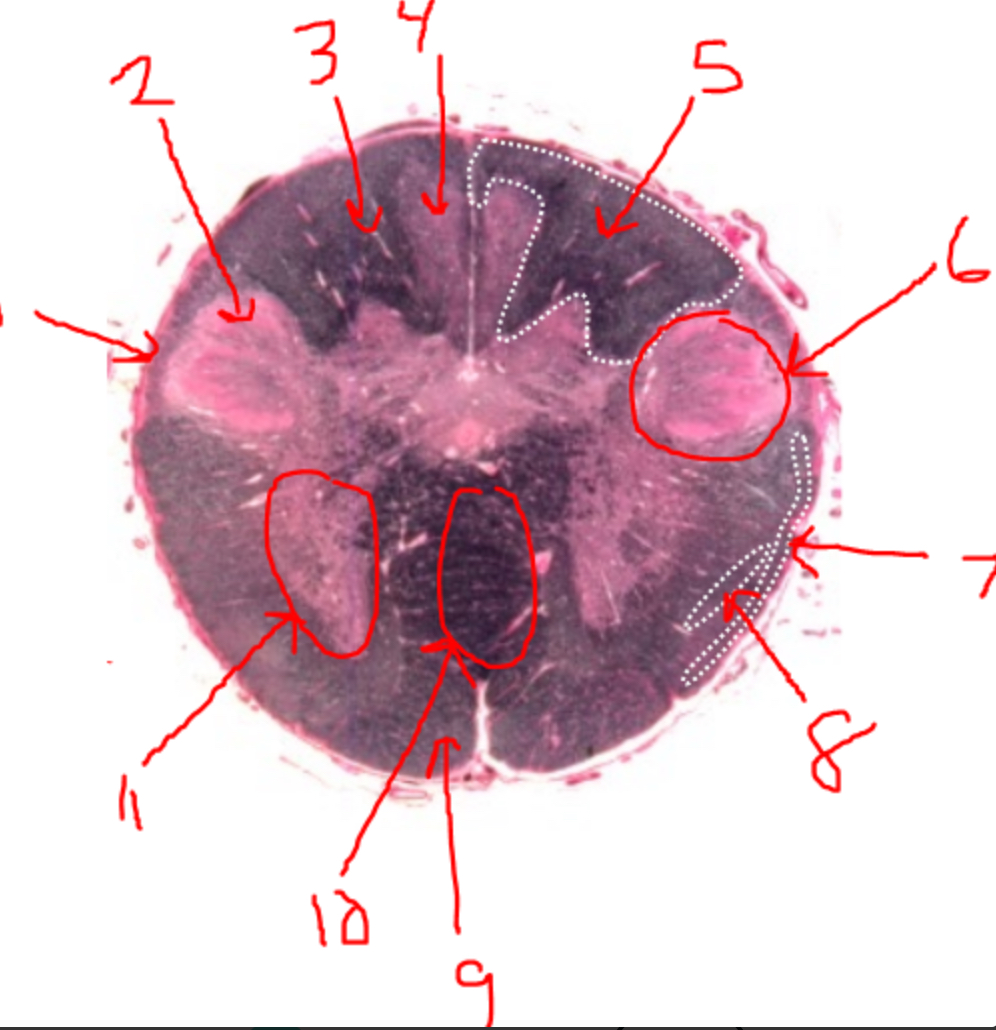
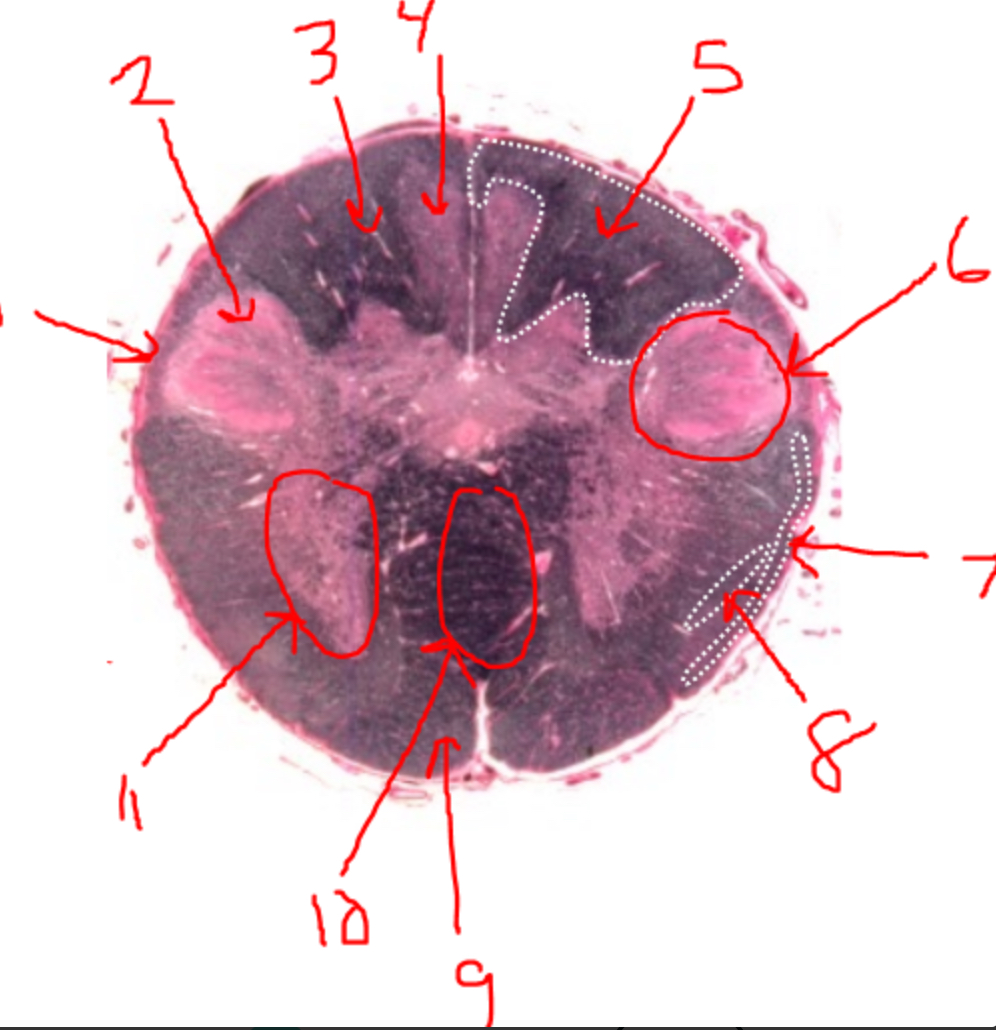
what is 1?
spinal trigeminal tract
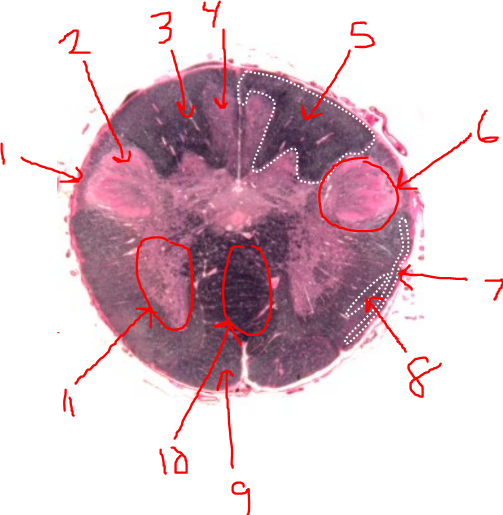
what is 2?
spinal trigeminal nucleus
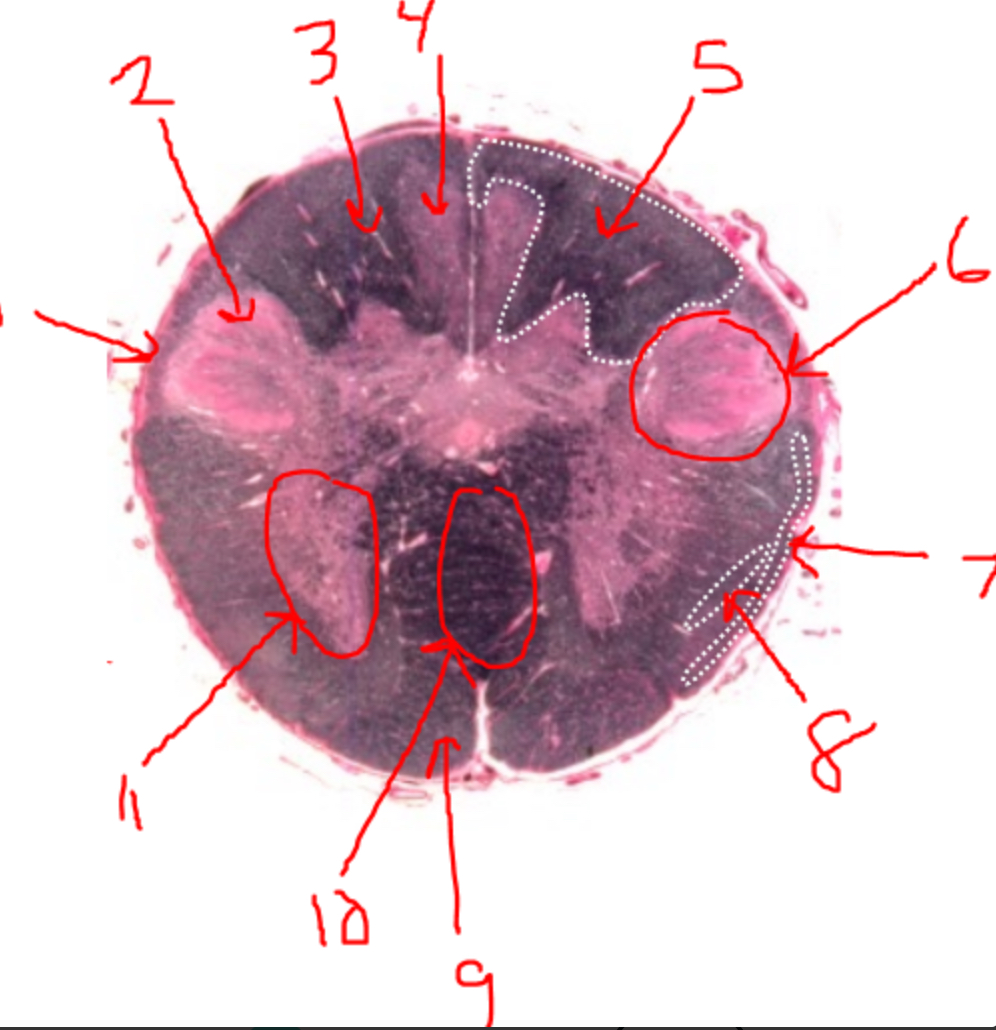
what is 3?
left dorsal funiculus
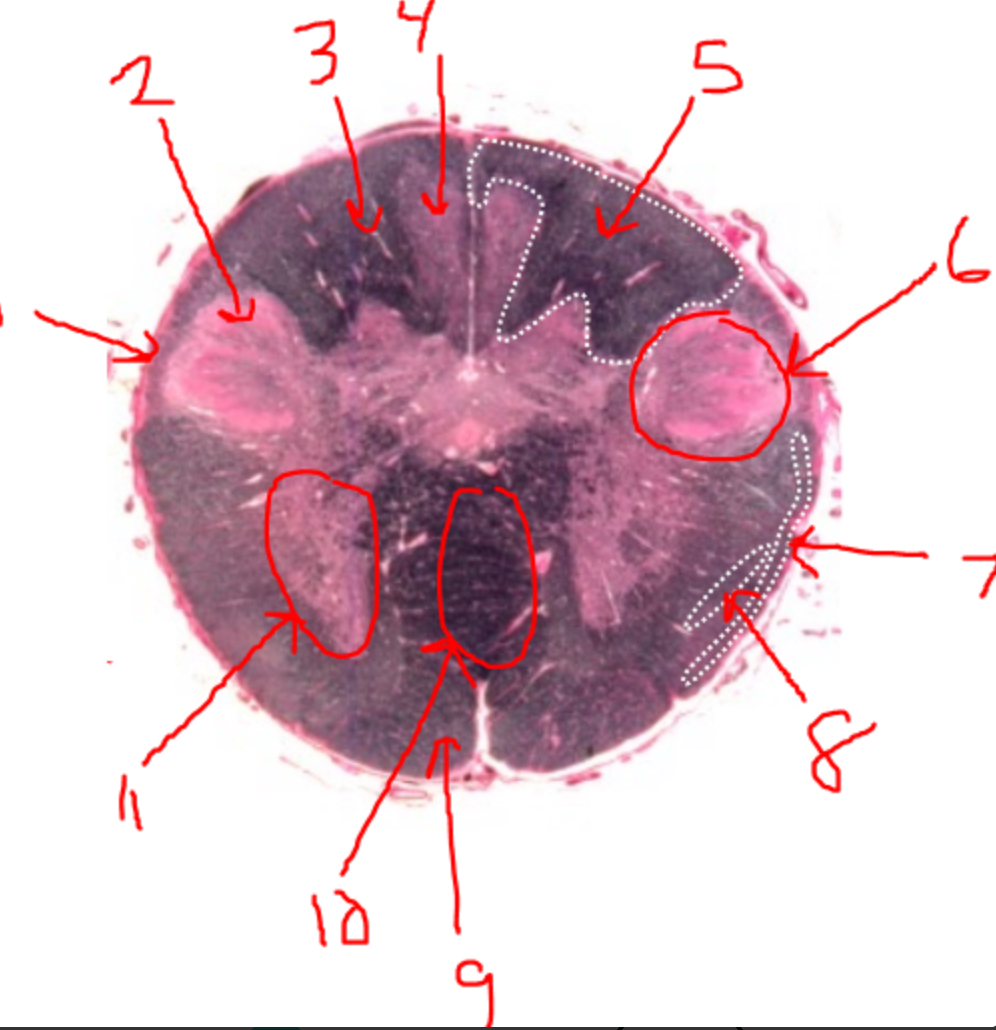
what is 4?
dorsal column nuclei
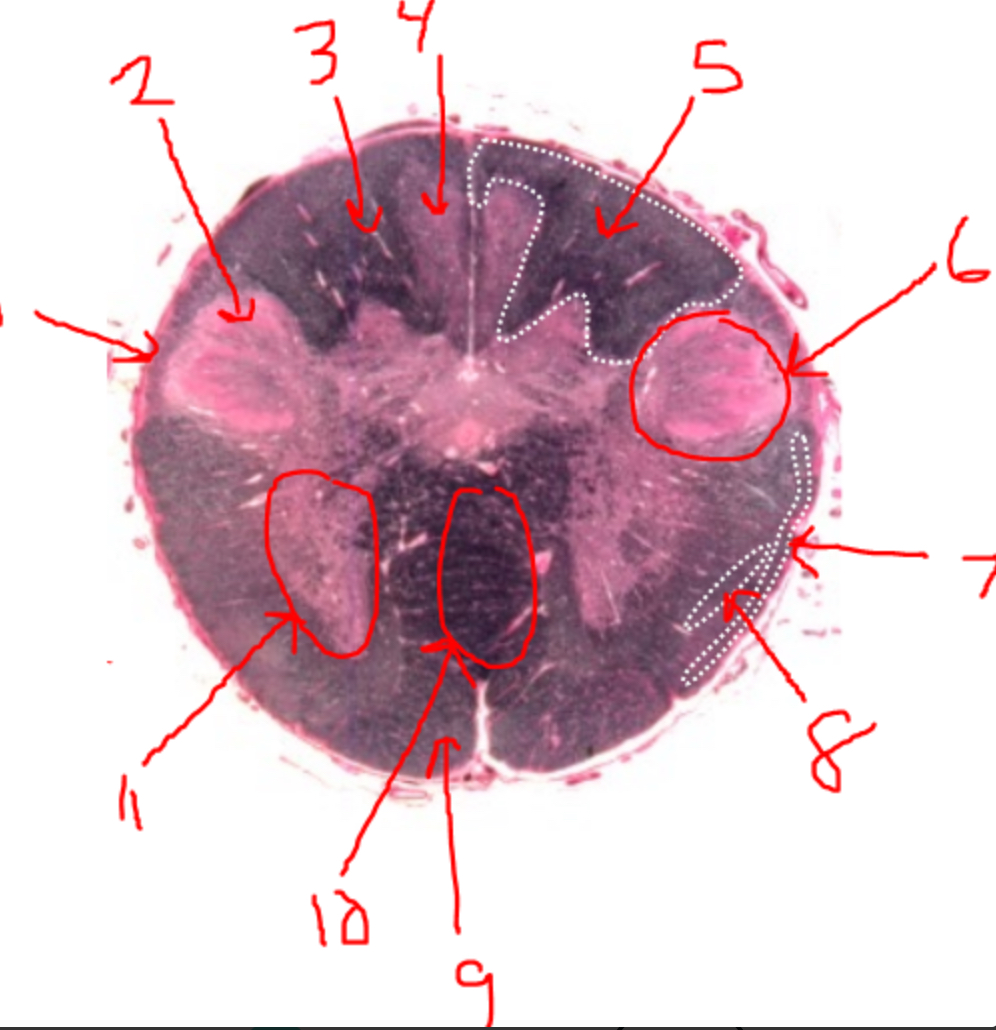
what is 5?
right dorsal funiculus
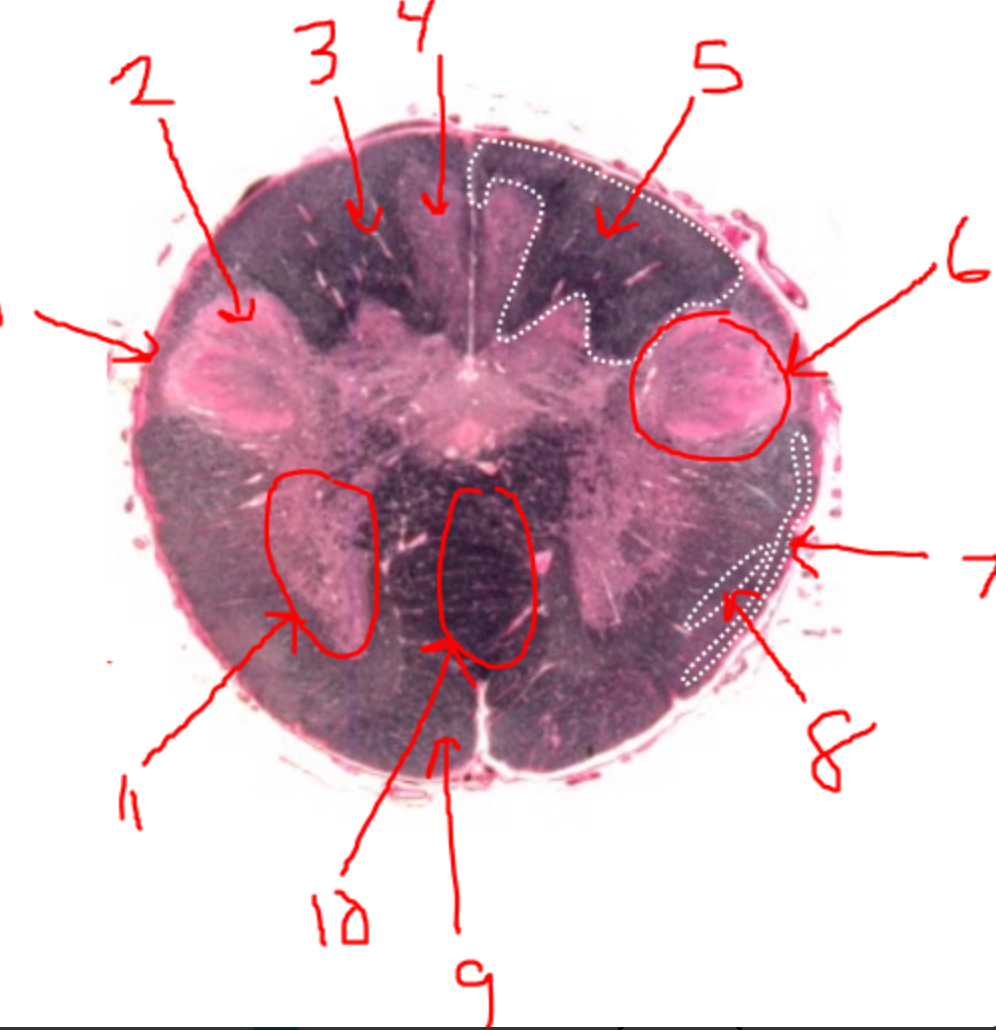
what is 6?
dorsal horn
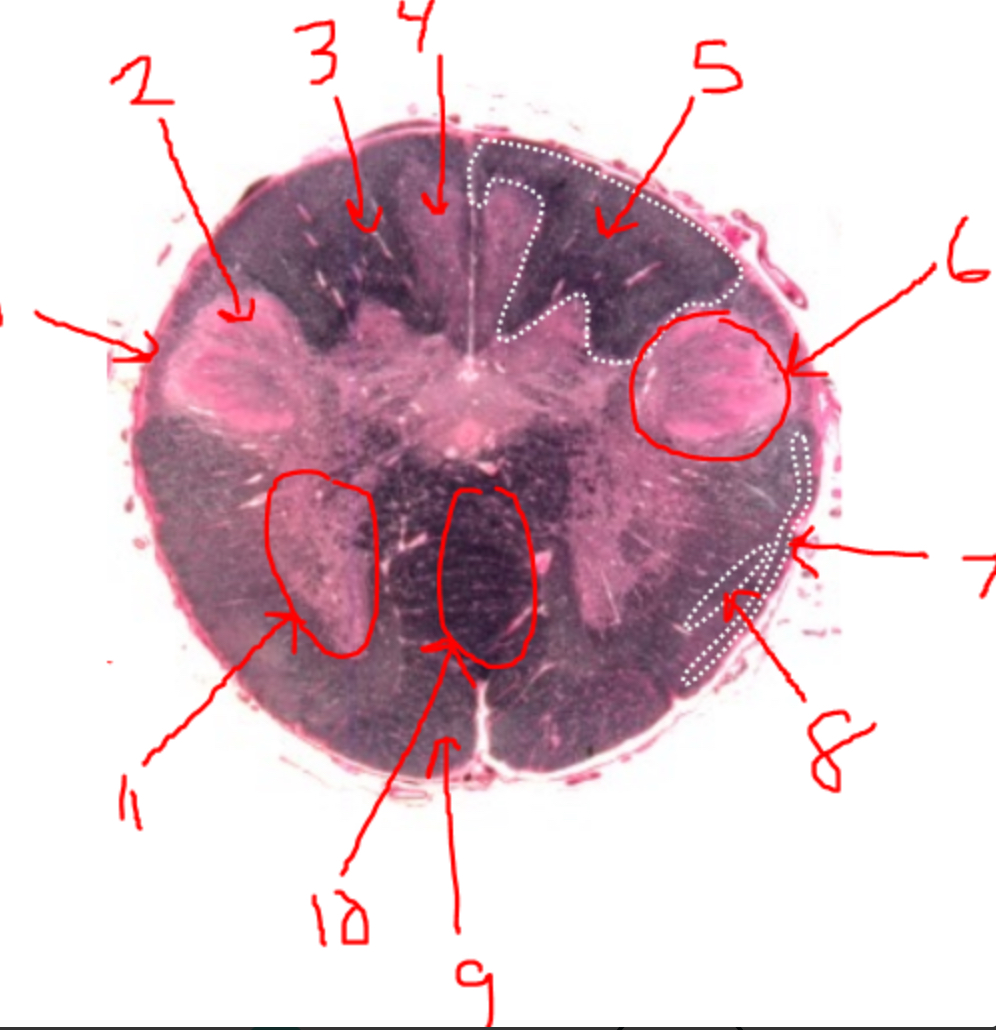
what is 7?
spinocerebellar tract
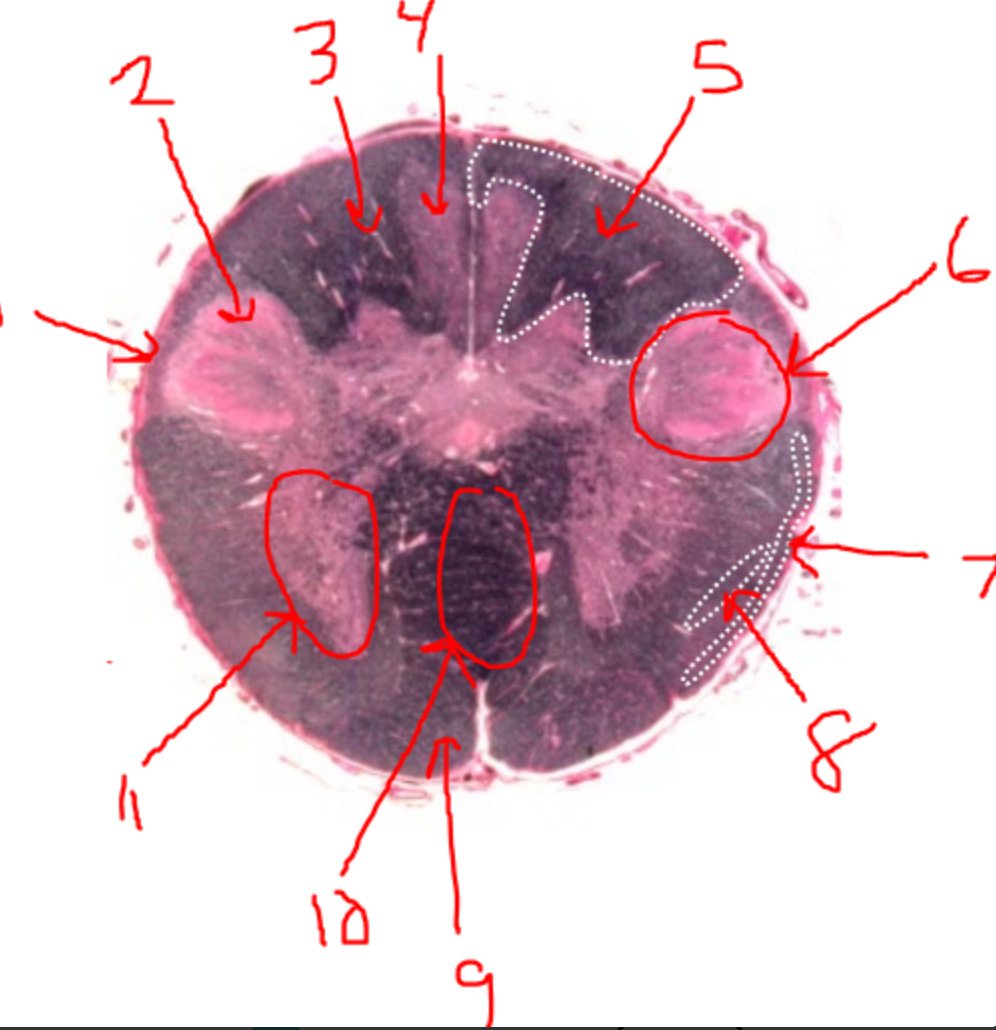
what is 8?
spinothalamic tract
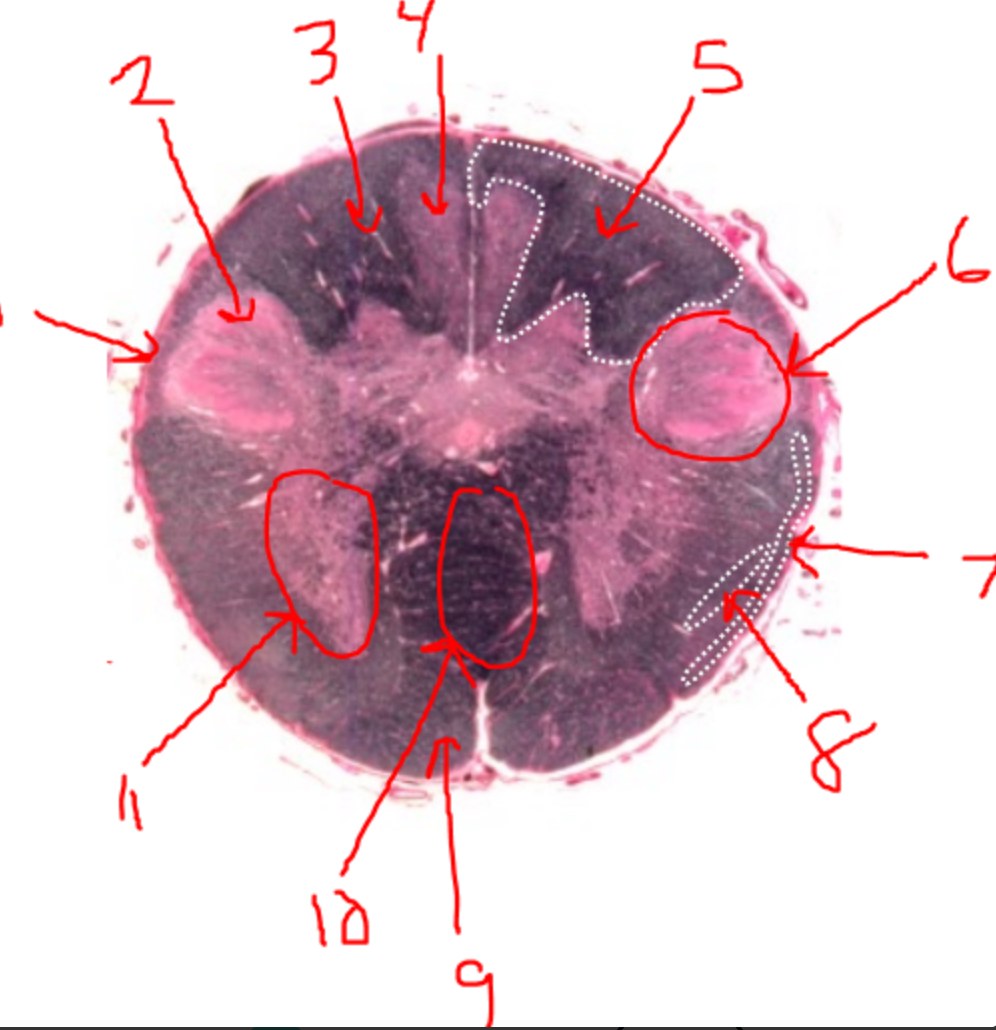
what is 9?
pyramidal tract(s)
what is 10?
pyramidal decussation
what is 11?
ventral horn
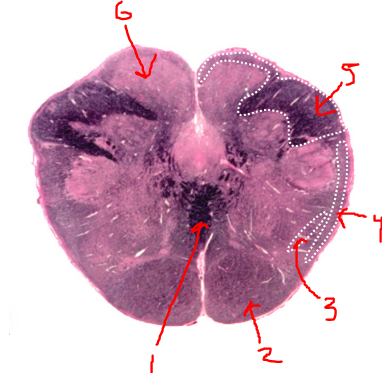
what is 1?
sensory decussation
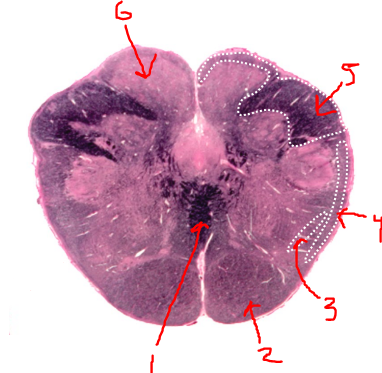
what is 2?
pyramidal tract
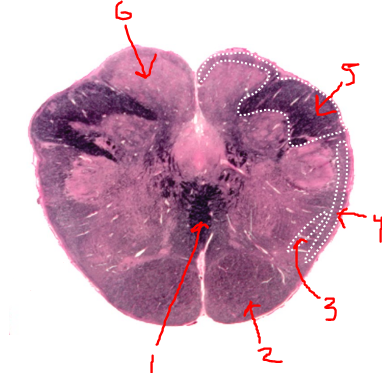
what is 3?
spinothalamic tract
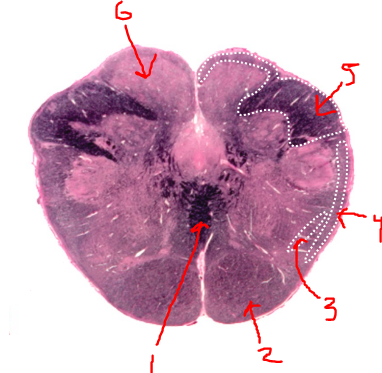
what is 4?
spinocerebellar tract
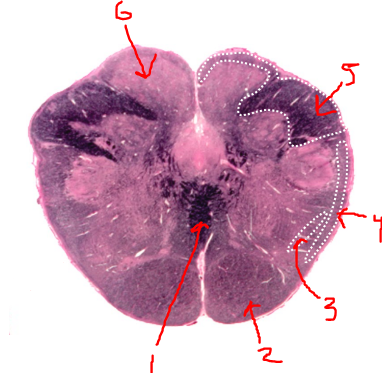
what is 5?
right dorsal funiculus
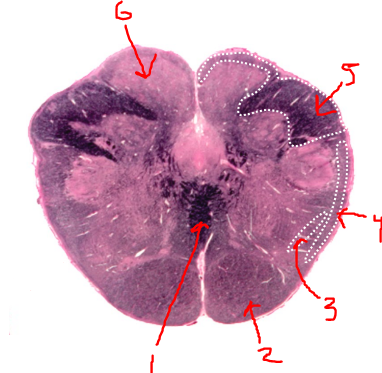
what is 6?
dorsal column nuclei
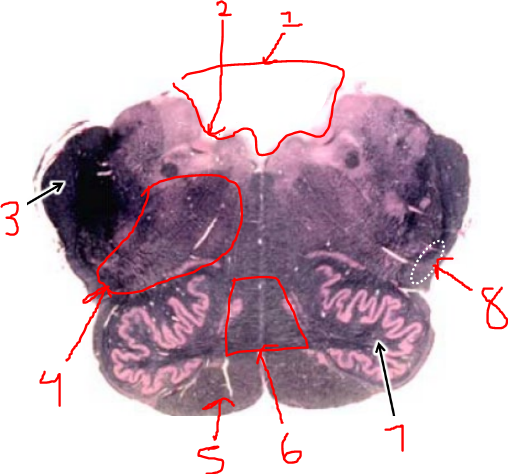
what is 1?
fourth ventricle
what is 2?
sulcus limitans
what is 3?
inferior cerebellar peduncle
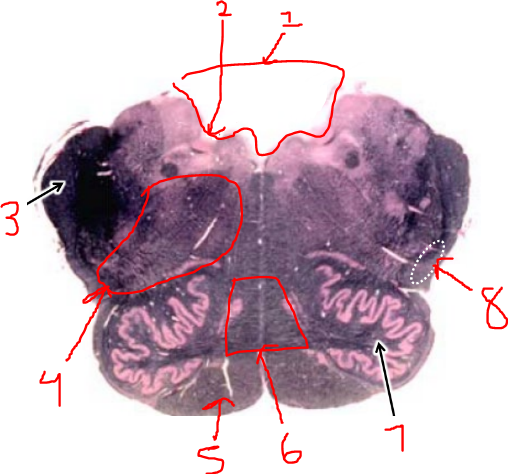
what is 4?
reticular formation
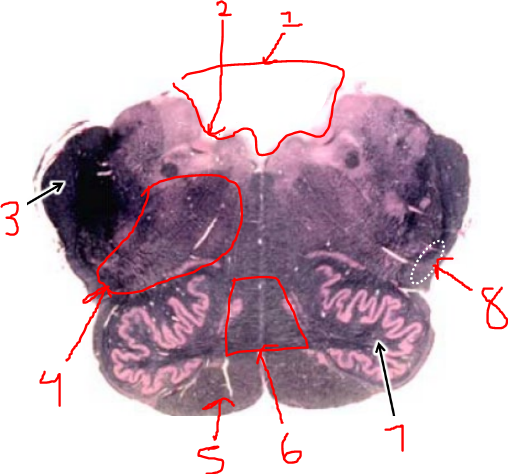
what is 5?
pyramidal tract
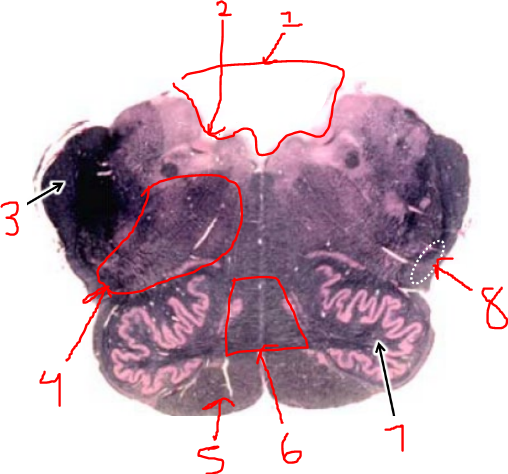
what is 6?
sensory decussation
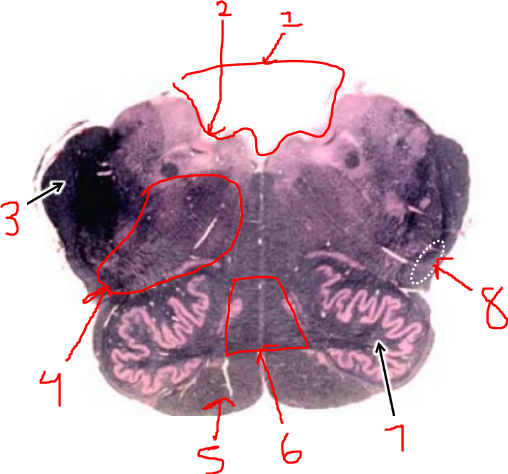
what is 7?
inferior olive
what is 8?
spinothalamic tract
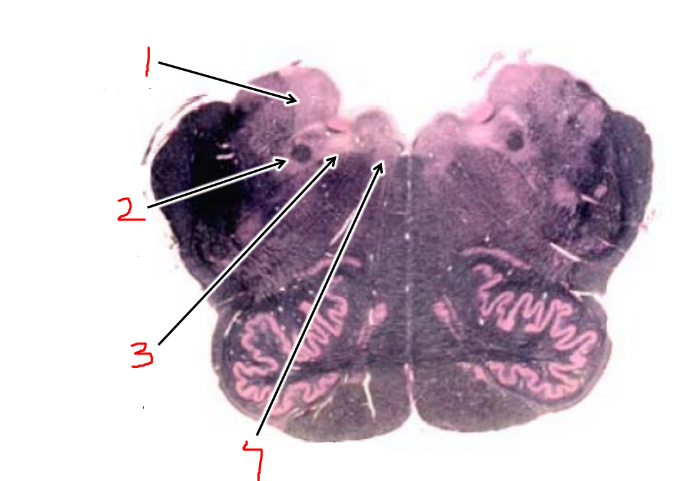
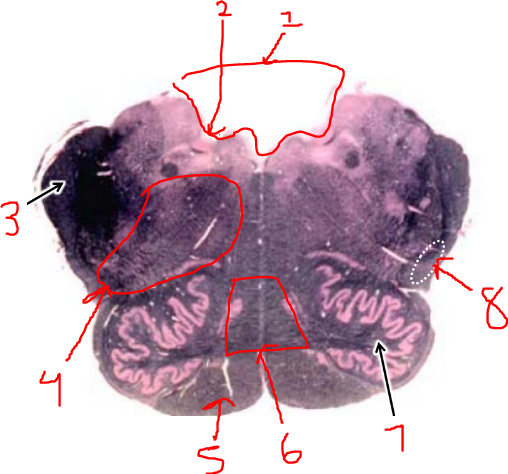
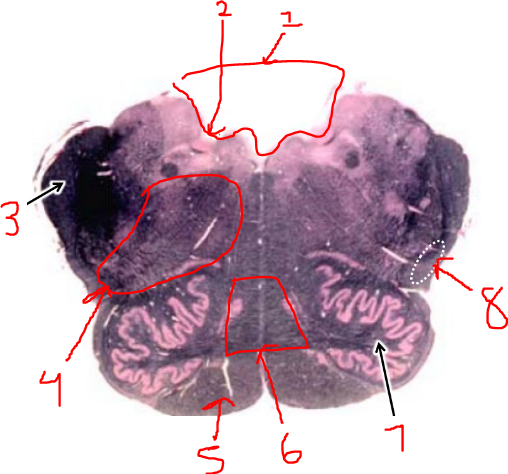
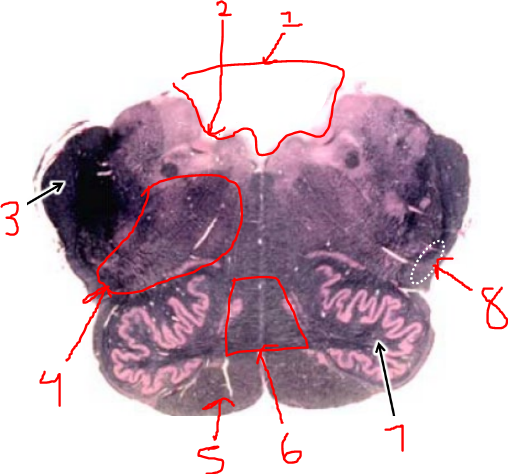
what is 1?
vestibular nuclei
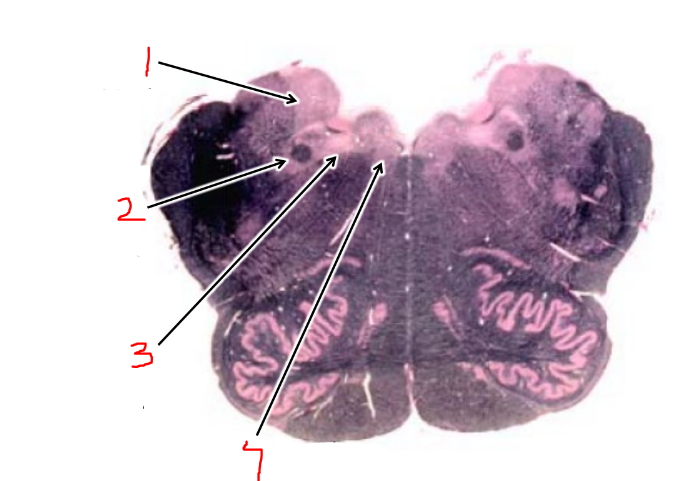
what is 2?
solitary tract and nucleus
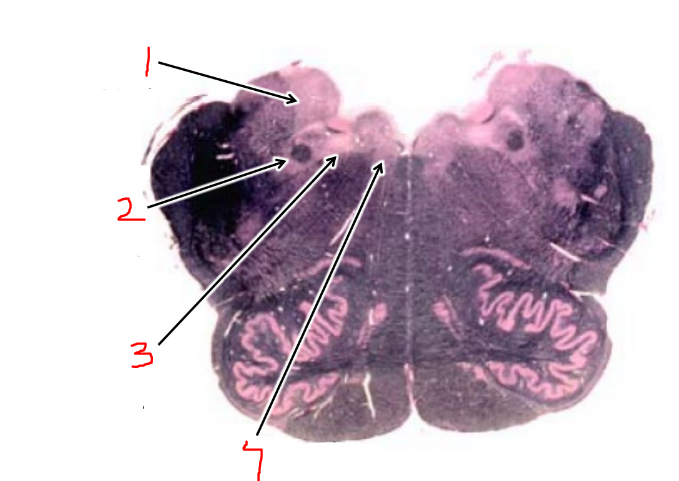
what is 3?
dorsal motor n. of vagus
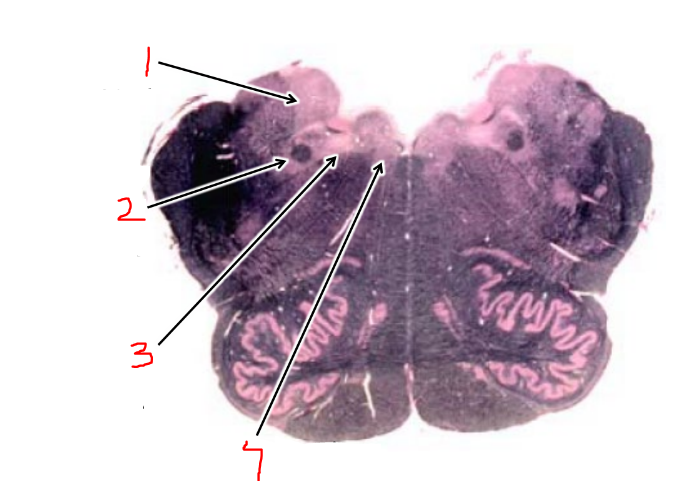
what is 4?
hypoglossal nucleus
what parts of the rostral medulla are for sensory functions?
vestibular nuclei
solitary tract and nucleus
what parts of the rostral medulla are for motor functions?
dorsal motor n. of vagus
hypoglossal nucleus
______ create the big bulge of the pons
pontine nuclei
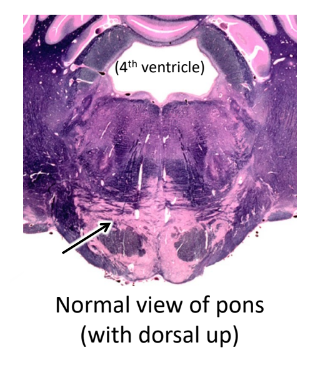
what is the arrow pointing at?
pontine nuclei
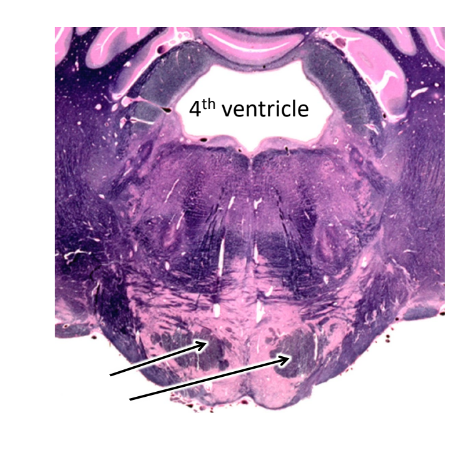
what are the arrows pointing at?
pyramidal tracts
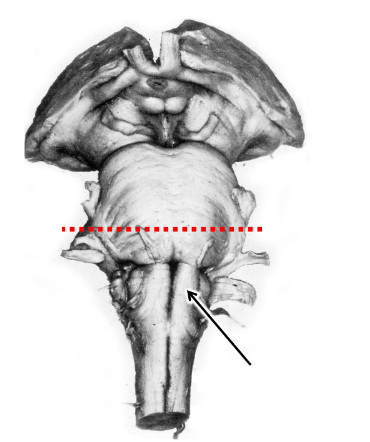
what is the arrow pointing at?
pyramidal tracts
Pyramidal fascicles
corticospinal fibers plus corticopontine fibers innervating pontine nuclei
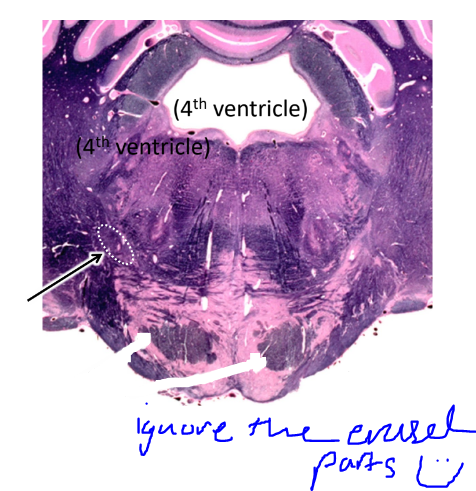
what is the arrow pointing at?
spinothalamic tract
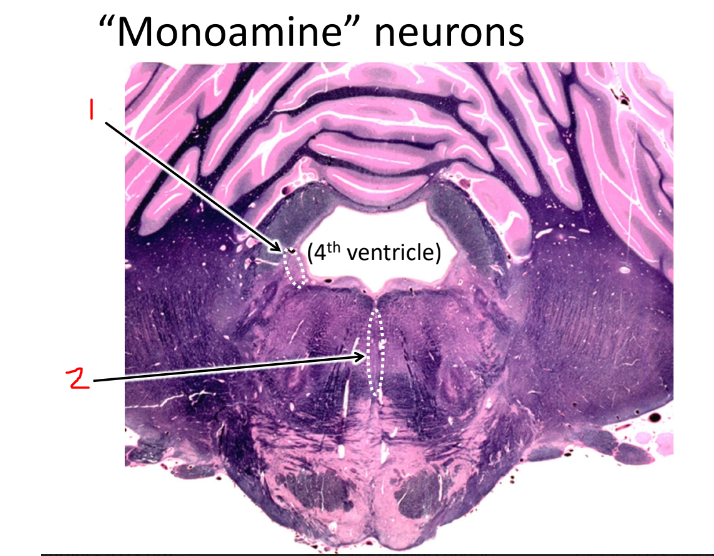
what is 1?
locus coeruleus that produces norepinephrine
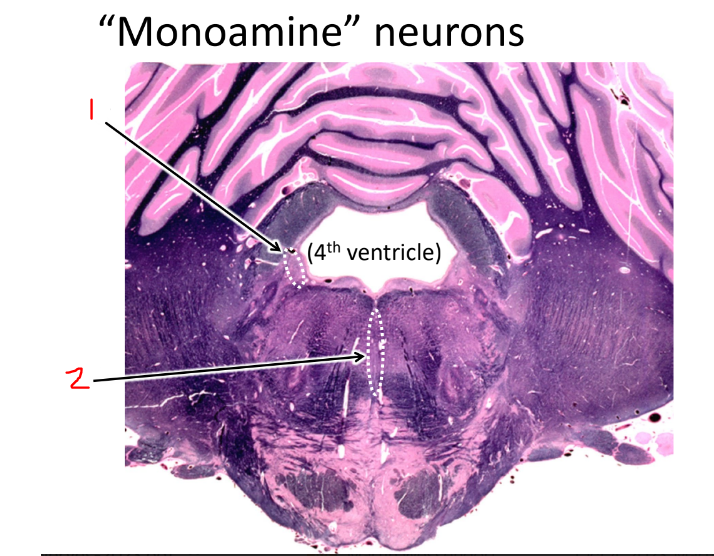
what is 2?
raphe nuclei that produces serotonin
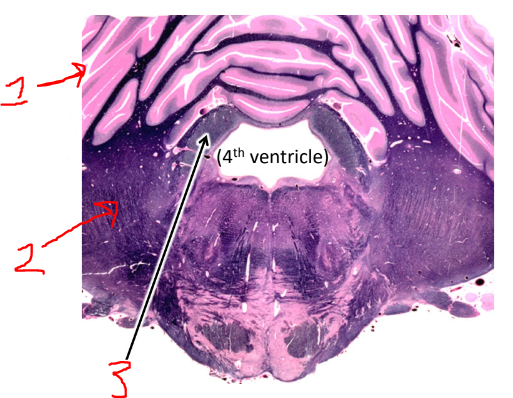
what is 1?
cerebellum
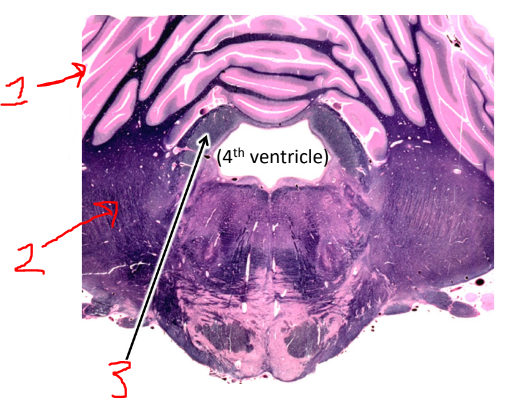
what is 2?
middle cerebellar peduncle
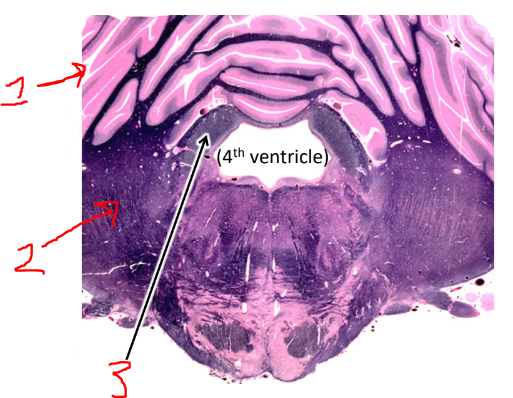
what is 3?
superior cerebellar peduncle
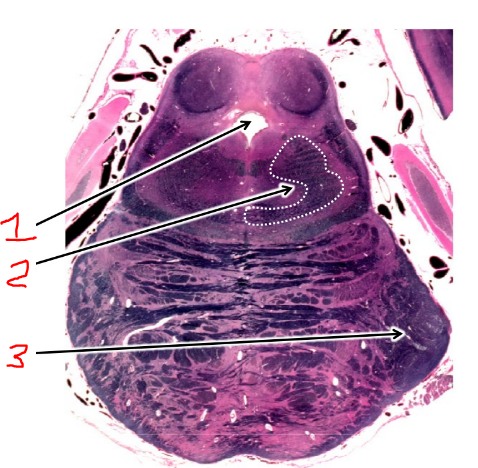
what is 1?
cerebral aqueduct
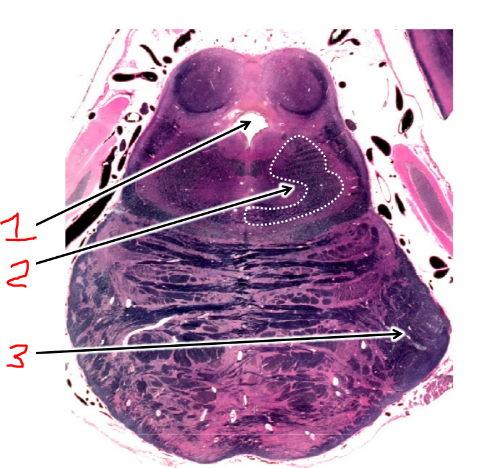
what is 2?
superior cerebellar peduncle
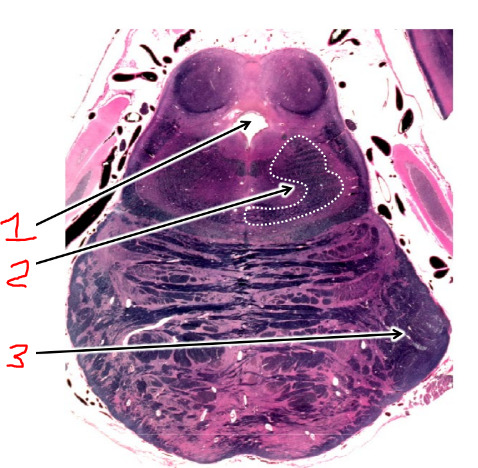
what is 3?
middle cerebellar peduncle
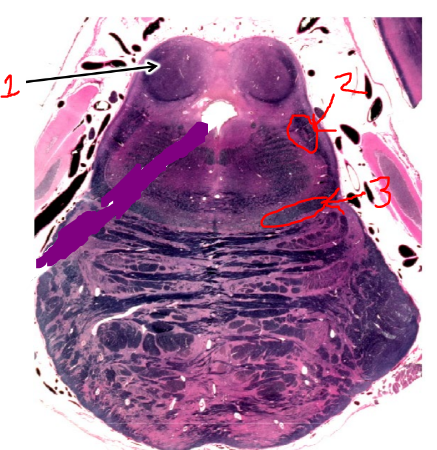
what is 1?
inferior colliculus
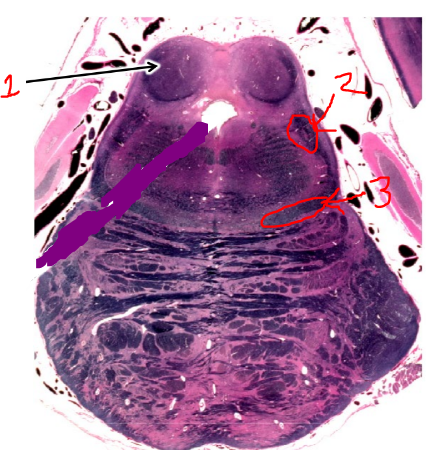
what is 2?
spinothalamic tract
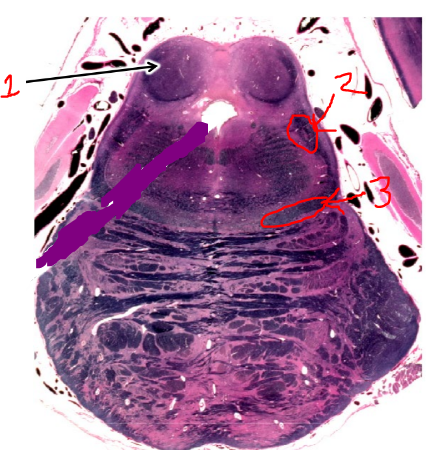
what is 3?
medial lemniscus
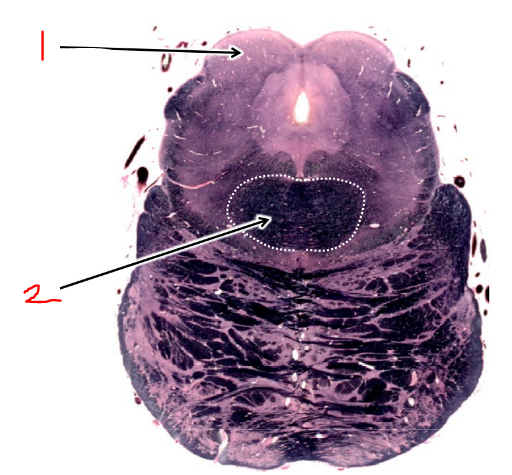
what is 1?
superior colliculus
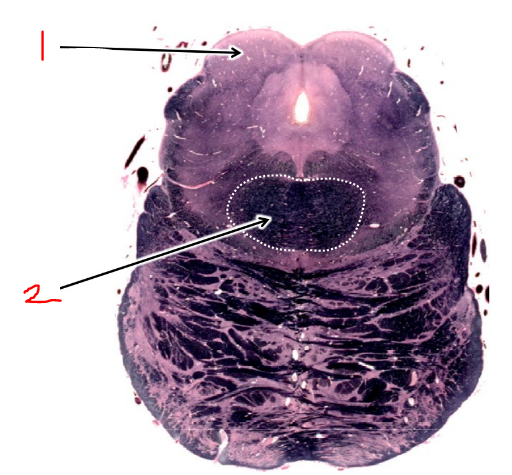
what is 2?
superior cerebellar peduncle
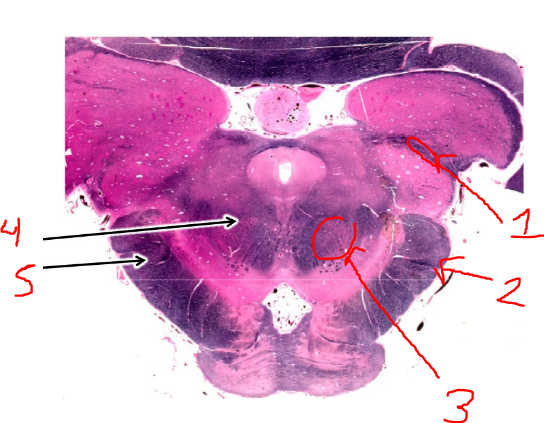
what is 1?
spinothalamic tract
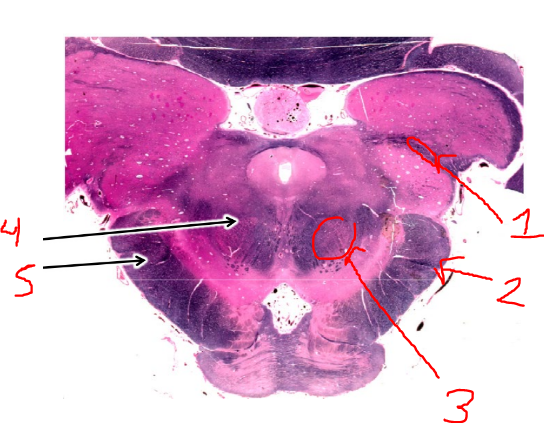
what is 2?
middle cerebellar peduncle
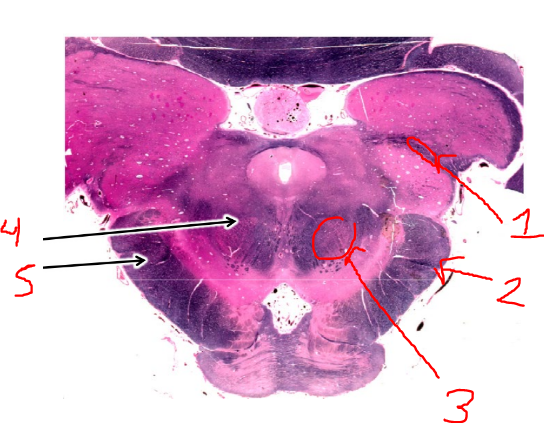
what is 3?
red nuclei
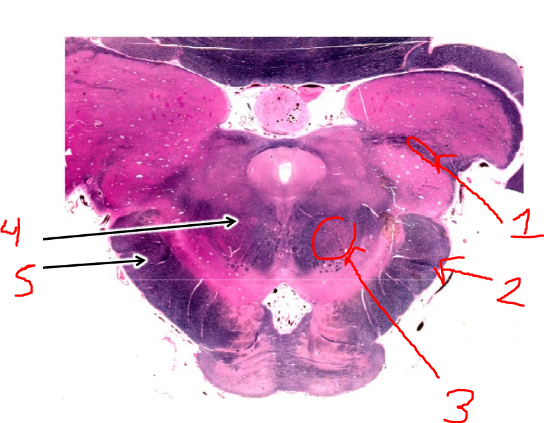
what is 4?
superior cerebellar peduncle