1. TRANSITION METALS ヾ(@⌒ー⌒@)ノ
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
d block elements
transition metals (only worry ab titanium to copper)
definition of transition metal
a metal that can form one or more stable ions with an incomplete d sub shell
d sub shell contains up to 10 electrons
transition metals must for atleats 1 ion that had between 1-9 electrons in the d subshell
scandium and zin
cannot form ions w between 1-9 electrons
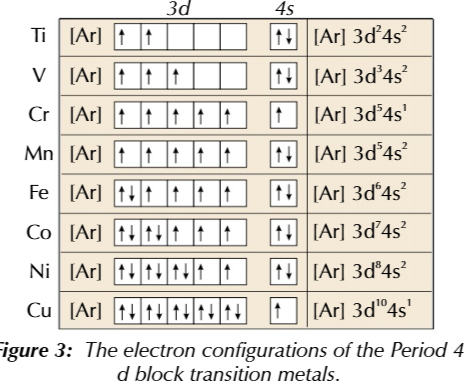
electron configuration rules
electrons full up the lowest energy subshells first
electrons fill orbitals singly before they start sharing
4s sub shell has lower energy that 3d subshell
so 4s subshell is filled up first singly then doubled up, with exceptions
chromium
4s subshell has 1 electron and 3d subshell has 5 electrons for stability
copper
4s subshell has 1 electron and 3d subshell has 10 electrons for stability
transition metal electron configuration

transition metal atoms form positive ions
4s electrons are removed first, then 3d electrons

writing the electron configuration of a transition metal ion
write down the electron configuration of the atom
work out how many electrons have been removed to give the ion’s charge
remove that number of electrons from the electron configuration taking them from the 4s orbital first then 3d orbital
scandium and zinc are not transition metals
their stable ions do not have incomplete d sub shells
scandium only forms Sc3+ which has an empty d orbital
scandium electron configuration [Ar]3d1 4s2, scandium ion electron configuration [Ar]
Zn only forms 1 stable ion Zn2+ which has a full d subshell
zinc electron configuration [Ar]3d10 4s2, zinc ion electron configuration [Ar]3d10
physical properties of transition metals
extremely high density
high melting and boiling points
chemical properties of transition metals
can form complex ions
form coloured ions
good catalysts
exist in variable oxidation states
TITANIUM
Ti2+ violet
Ti3+ purple
VANADIUM
V2+ violet
V3+ green
VO2+ (+4) blue
VO2+ (+5) yellow
CHROMIUM
Cr3+ green
Cr2O72- (+6) orange
MANGANESE
Mn2+ pale pink/colourless
MnO42- (+6) green
MnO4- (+7) purple
IRON
Fe2+ pale green
Fe3+ yellow/purple
COBOLT
Co2+ pink
NICKLE
Ni2+ green
COPPER
Cu2+ pale blue
incomplete d subshells cause special chemical properties of transition metals
